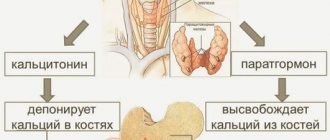
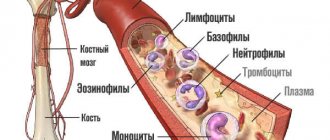
The formed elements of blood perform the basic functions of liquid connective tissue. In general, there are three main types of these structures.
- Leukocytes. They perform the task of protecting the body. These are immune cells, they work as protectors.
- Platelets. Red records. The main function is to create a plug that covers the wound surfaces. To prevent the development of massive, life-threatening bleeding. There are other tasks as well. But they are secondary.
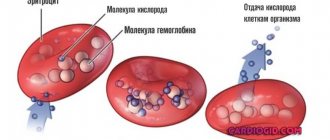
- Red blood cells. Red bodies. Within the framework of the topic under consideration, they play a special role. They act as transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Responsible for normal cellular respiration and removal of processed products.
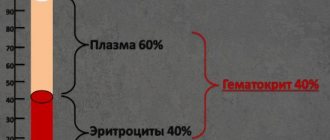
Hematocrit is an indicator that is calculated as the ratio of the number of red blood cells to the total mass of plasma.
Sometimes other shaped cells are used for calculations, but no large deviation in levels is observed. Since over 90% of the structures are red bodies.
If the hematocrit is elevated, this means that the number of red blood cells has increased relative to the plasma volume. The condition is not normal and usually accompanies various pathological processes. Which ones exactly?
Normal indicators
Normal hematocrit values will differ slightly depending on the age category and gender of the person.
Thus, the level of red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets per volume of the main human biological fluid is:
- for men – from 40 to 48%;
- for women – within 36-46%;
- in a newborn baby – no more than 60%;
- in children under 13 years of age – varies from 38-40%.
If the values are increased by at least 0.55%, then patients are diagnosed with “high hematocrit.”
Children's tests - what to prepare for
Newborns often exhibit hyperprolactinemia, indicating an increase in protein in the blood plasma. It is caused by feeding the child milk from a goat or cow (situation: the mother is not able to breastfeed) with a high protein content. To increase the tendency for blood to thicken, you should buy milk with less protein.
Danger - a child with a lower number of red blood cells than normal experiences oxygen starvation.
Over the age of 3 years, there is a decrease in mental abilities, fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin color and rapid heartbeat. Among the diseases in children, there are all the diseases characteristic of this group, however, unpleasant conditions are also caused by trivial vitamin deficiency.
Helminthic infection, which is more typical for children and adolescents than for adults, can be eliminated by taking anthelmintic drugs, after a course of which the tests return to normal.
Etiology
As already mentioned, an increase in hematocrit is most often a consequence of the onset of development or progression of a disease.
The most common causes of this disease:
- Severe dehydration (dehydration) occurs against the background of the fact that a person in one situation or another ingests a small amount of liquid, which affects the functioning of internal organs and systems. This problem can be caused by excessive vomiting, persistent diarrhea and prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Chronic hypoxia is a lack of oxygen in organs and tissues. Most often, such a pathology is detected in diabetes mellitus and in those individuals who have been smoking for many years.
- Erythremia.
- Neoplasms of the kidneys.
- Polycystic adrenal gland.
- Any type of anemia.
- Peritonitis.
- Internal hemorrhages.
- Poisoning with toxic substances or drugs, in particular hormonal and glucocorticoids.
- Chronic heart diseases.
- Emphysema.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Chronic bronchitis.
- COPD
- Hypoventilation syndrome.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
- Apnea.
- Oncological neoplasms.
- Ischemic kidney disease and other ailments of this organ.
- Extensive burns.
- Internal wounds.
The above factors influence the increase in hematocrit levels in both adults and children. However, it is worth noting that a slight increase of 10-12% in infants under one year of age is quite normal.
However, there are several possible negative reasons for the increase in this indicator:
- previous transfusion of biological material;
- transfer of placental blood to the baby after birth;
- chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
In addition, physiological sources of this condition are:
- the period of bearing a child, especially during pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester;
- changes in air composition;
- long-term influence of stressful situations;
- specific working conditions - the main risk group consists of people forced to work at height.
Normal values for hematocrit
Folk remedies
In addition to drug treatment, traditional medicine is quite effective in correcting hematocrit.
To normalize the ratio of formed elements to total blood volume in case of anemia, you should take:
- various fruit cocktails and mixtures of: currant, peach, apple, pomegranate;
- tomato juice;
- fresh carrot salad: 100 g of product with 2 tbsp. l. sour cream 20-30% fat for 1 month;
- apples with pork fat, egg yolks, sugar and chocolate: grate 5-6 apples (Antonovka variety) in 400 g of pork fat and put in the oven (no more than 80°C) for 1.5-2 hours, then add 12 chicken egg yolks , separated in advance and mixed with grated dark chocolate (400g). Take orally, 4 times a day, after meals, with warm milk.
With elevated hematocrit values, you can take an infusion of yarrow, meadowsweet and budra (50% of the total collection), adding celery leaves, parsley and immortelle.
Two tablespoons of the resulting herbal mixture are poured into a thermos (2 liters) and poured with boiling water. Let it brew for 2 hours. For treatment, the dose should be divided into 4 servings (500 ml each) and taken throughout the day. The resulting infusion restores kidney function and relieves inflammation in the body.
For erythrocytosis (increased number of red blood cells in the blood), taking an infusion of garlic (200g) and honey (300g) will be effective. The ingredients are thoroughly crushed and mixed, after which they are allowed to brew for 3 weeks. Take 1 tbsp. 3 rubles/day, for 30 min. before meals.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy is aimed at eliminating from the diet: alcoholic beverages, fatty, dried and fried foods.
If the hematocrit decreases, add foods rich in iron and protein to the diet:
- seaweed;
- beef liver;
- parsley;
- beans;
- sea fish and caviar;
- cranberries, apples, peaches.
With elevated levels, foods rich in vitamins are indicated to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract:
- dairy products (sour cream, cottage cheese, butter);
- grated vegetables and fruits.
Compliance with dietary table No. 11 (consumption of boiled and steamed food). This limitation is associated with the loss of salts by the body, as well as a violation of the water-salt balance.
Symptoms
If the hematocrit is increased, then this will not go unnoticed by a person. The clinical picture directly depends on the etiology that provoked this deviation.
In some cases, the problem may not manifest itself with any external signs, and besides a slight malaise, the person will not feel anything else.
The main symptoms of high hct in a blood test include:
- attacks of dizziness, which can range from mild to severe;
- respiratory dysfunction - patients complain that they have difficulty breathing;
- numbness of the upper and lower extremities;
- constant nausea that does not lead to vomiting;
- weakness and fatigue;
- partial loss of orientation in space;
- misunderstanding of what is happening.
Similar symptoms develop in both adults and children. The only difference may be the degree of severity of external manifestations.
Increase factors in women
Growth is possible for several other specific reasons.
Menstrual cycle
Especially in the initial stage. When the hormonal background is not yet stable. The disorder develops spontaneously and disappears just as quickly.
We can say that the deviation is physiological and does not require special drug correction or other intervention.
In some cases - pregnancy in the initial phase
In the later stages of gestation, the opposite is true. And that's okay. As for the first trimester, there are options.
As with the menstrual cycle, no special measures are needed. Everything will recover on its own. Provided that the patient is relatively healthy and does not have the disorders described earlier.
Climax
Menopause is a hormonal imbalance caused by age. Hematocrit increases in women after 50 years of age due to the natural decline of reproductive function. Accompanied by pressure surges and changes in the blood picture.
If necessary, medications are prescribed to correct hormonal levels. Estrogens, taken orally.
Diagnostics
The basis of the diagnostic process, against the background of which it will be discovered that the hematocrit is higher than normal, is a general clinical study of blood.
The analysis consists of several stages:
- collection of biological material;
- placing it in a sterile flask;
- going to the centrifuge;
- the procedure for separating liquid into its component parts - for this, the blood must be in a centrifuge for 1.5 hours.
Then a laboratory study and interpretation of the results by a hematologist takes place, after which all information is transferred to the attending physician who referred the patient for examination.
To determine the cause of a deviation from the norm in a larger direction, the clinician must:
- study medical history to look for chronic ailments;
- collect and analyze a life history - to establish the fact of the influence of harmless sources;
- conduct a thorough physical examination of the patient and evaluate his appearance;
- interview the patient in detail - to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, which can also indicate an underlying disease.
Additional laboratory and instrumental examinations are selected individually for each person.
Valid values
As stated above, the hematocrit norm (designation - NST) will differ slightly according to the following factors:
- according to the age;
- by gender.
The following table shows the valid values:
| Age | Indicators |
| Newborns | From 42 to 60% |
| 1 month | From 31 to 54% |
| 2 months | From 28 to 42% |
| 3-6 months | From 29 to 41% |
| Six months-2 years | From 27.5 to 41% |
| From 3 to 6 years | From 31 to 40.5% |
| From 7 to 12 years | From 32.5 to 41.5% |
| From 13 to 16 years old | Girls – from 33 to 43.5% Guys – from 34.5 to 47.5% |
| Among women | From 18 to 45 years old – 39-50% Over 45 years old – 35-46% |
| In men | From 18 to 45 years old – 35-45% Over 45 years old – 40-50% |
The norm of hematocrit in the blood of women during pregnancy is 33-40%. The most minimal numbers are observed starting from the 33rd week of intrauterine development of the fetus and persist immediately until labor.
Treatment
Successful therapy and normalization of the described indicator consist of eliminating the cause.
In some situations, specific measures are not required, but only:
- quit bad habits;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- regularly ventilate the premises;
- drink enough fluids;
- stop taking uncontrolled medications;
- rationalize your lifestyle.
Other ways to lower your hematocrit include:
- taking medications aimed at thinning the blood;
- bloodletting no more than 500 milliliters per day;
- replacement of biological fluid with solutions that reduce its viscosity.
Clinicians most often prescribe:
- "Interferon";
- "Hydroxycarbamide";
- "Anagrelide";
- "Busulfan";
- radioactive phosphorus.
The drug Busulfan
In addition, do not forget about the special diet that is recommended for people suffering from this disease. It is recommended to enrich the menu with products that can thin the blood.
Regardless of why the hematocrit in the blood is increased, you must eat:
- greenery;
- fermented milk products;
- sunflower, corn, olive and other vegetable oils;
- sunflower and pumpkin seeds;
- nuts;
- tomatoes and carrots;
- offal;
- fatty fish.
It is worth noting that eliminating the underlying disease can be either conservative or surgical.
How to lower hematocrit in the blood?
If an overestimated parameter appears due to an unbalanced diet, you should change your usual diet. Approximate requirements for drawing up a complete therapeutic diet are reflected in this table:
| Types of food | Recommended Products | Prohibited or strictly restricted products |
| Fruits and berries | That's it, a special place is given to citruses and sour berries | Bananas, careful use of currants, lingonberries, viburnum, blackberries and mangoes |
| Vegetables and greens | Yellow, orange and red fruits (especially carrots, pumpkins, zucchini and tomatoes) | Green plants (broccoli, cabbage, spinach, zucchini, arugula) |
| Fermented milk and dairy foods | Low-fat sour cream and cottage cheese, Varenets, fermented baked milk, kefir | Powdered and whole milk, sour cream with a high percentage of fat content, butter, cream and cheese |
| Cereals, legumes | Barley, barley, millet, oats in the form of oatmeal, brown rice, corn | All legumes and buckwheat |
| Meat and fish | Fatty varieties of sea fish (mackerel, salmon, trout, tuna) and lean meat (turkey) | Lard, ham, liver, goose, duck, lamb, pork and beef |
| Mushrooms | — | All |
| Seafood | Everything, including seaweed | Black and red caviar |
| Sweets and baked goods | Honey, rye bran bread | — |
| Convenience foods and fast food | — | All |
| Preservation and smoked meats | — | All |
| Spices | Cinnamon, ginger | — |
| Beverages | Pure water, juices without added sugar, herbal teas based on sage, licorice, sweet clover and hawthorn | Soda, coffee, alcohol, black and green tea, pomegranate juice |
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe medications that reduce hematocrit and normalize blood viscosity. Often among them appear:
- anticoagulants (Heparin-Agrikhin 1000, Warfarex, Clexane, Sinkumar);
- antiplatelet agents (Curantil, Ticlopidine);
- NSAIDs (Aspirin).
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to special medical procedures such as erythrocytopheresis. In addition to the above, it is worth noting that the positive result will be more noticeable if you start doing physical exercise every day (even walking will do) and get rid of dangerous bad habits - alcoholism and smoking.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the development of a pathology such as increased hematocrit in the blood, only a few simple rules should be followed.
Prevention includes:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- drinking at least 2 liters of fluid per day;
- avoiding the influence of stressful situations;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the clinician;
- early detection and complete elimination of any of the above pathological causes;
- regular preventive laboratory and instrumental examinations in a medical institution.
The prognosis for an upward deviation of hematocrit from the norm is favorable in the vast majority of situations, but only if you seek qualified help in a timely manner. Otherwise, the risk of worsening the course of the underlying pathology and developing complications is high.
Why is it dangerous?
What does it mean if the hematocrit is increased? How dangerous is this?
- The cause of an increased hematocrit may indicate a serious disease (for example, erythremia or kidney cancer).
- Hematocrit is a synonym for blood viscosity. The higher the viscosity, the slower the blood flows through the vessels, the higher the risk of stasis and blood clots. And thrombosis in small and medium-sized vessels means strokes, heart attacks, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism. These are the most serious complications that most often lead to sudden death.
Can it give symptoms?
Changes in blood viscosity often occur unnoticed by the patient. Small deviations in the hematocrit number cannot be suspected by external signs. They appear with significant changes in value, provoked by an increase in the number of blood cells and an increase in circulatory disorders. You can suspect a high hematocrit (and with it an increase in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells) by:
- unpleasant sensations in the extremities (numbness of the fingers, itching, feeling of “crawling goosebumps”);
- headaches;
- chronic fatigue;
- changes in skin color (takes on a bluish tint, red dots appear);
- dizziness, disorientation;
- rapid breathing, shortness of breath.
Patients often complain of feeling overwhelmed, disturbances in the thought process, poor understanding of what is happening, and inability to concentrate.
Recommendations
- First of all, you need to control your water and salt balance . To do this, you need to maintain a drinking regime and limit the consumption of coffee, alcohol, melons, watermelons, lingonberries, kefir, and cottage cheese.
- It is recommended to promptly seek medical help to prescribe an examination and appropriate therapy.
- It is not recommended to take coffee and alcohol, as they are diuretics.
- It is necessary to stop smoking and start doing moderate physical activity.