Ultrasound diagnostics for suspected pancreatic dysfunction is the first and main method in detecting pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus and various diseases of the digestive system. Ultrasound is indicated for people who do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle or abuse bad habits.
The organ changes depending on the age of the person. At first it grows, then remains stable for a long time.
With age, certain changes may occur in the pancreas; it becomes smaller. Thus, for each age category there are certain norms, deviations from which indicate the development of a pathological process.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
Main indications for ultrasound of the pancreas
The content of the article
The pancreas is an organ related to the digestive system. This largest gland performs two important functions: it secretes pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes, plus it produces hormones that regulate carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism.
There are a number of factors that make it mandatory to undergo an ultrasound scan of the pancreas:
- Pain
: prolonged or periodic pain in the epigastric region (the area above the navel) or left hypochondrium, aching girdle pain, painful sensations when palpating the epigastric region. - Gastrointestinal disorders
: nausea, vomiting associated with hunger or food intake, diarrhea of unknown origin (origin), constipation, loose stools, increased abdominal volume, flatulence. - External manifestations
: yellow tint of the skin and mucous tissues, sudden sudden weight loss for no reason. - Deterioration of health
: high body temperature (rises during exacerbation) without colds and obvious infectious diseases. - Changes in tests, diagnostic indicators
: elevated sugar levels or diagnosed diabetes mellitus, deformation of the posterior wall of the stomach revealed on an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, distortion of its contours or duodenum, enlarged pancreas, fluid in the abdominal cavity. - Presumptive diagnoses
: suspicion of a benign or malignant neoplasm, complications of acute pancreatitis (necrosis, hematomas, abscesses, etc.). - Mandatory examination
: before and after surgery, abdominal trauma, pancreatitis (acute and chronic), disorders of the kidneys and gall bladder (these are dependent organs).
Recipes for folk remedies
For the treatment and prevention of pancreatic diseases, you can use folk recipes. They are harmless, and the ingredients are available in almost every home.
List of effective recipes:
- Oatmeal decoction. Helps cleanse the body of toxins and fixes loose stools. To prepare, you will need cereal and water in a 1:1 ratio. Leave for at least 10 hours. Then the infusion is boiled and filtered. Drink 110 ml once a day during the day. The full course of treatment is 10-11 days. Consume on an empty stomach.
- Propolis is a universal remedy for many diseases and strengthens the immune system well. It is enough to consume it 1-1 grams. before meals 1 time per day. Course until 11 days.
- Juice from fresh potatoes. Take 70-100 ml on an empty stomach, up to 1 time per day. The course is at least 10 days.
- You can make a compress from yogurt. It is advisable to do it at night. To do this, you need to soak a fabric (pleasant to the body) in yogurt. And tie it to the pancreas area. Tie polyethylene and a scarf on top. Course up to 1.1 months.
- You can make an infusion of garlic, parsley and lemon. The ingredients are taken in a 1:1:1 ratio. Just remove the seeds from the lemon, do not remove the peel. The ingredients are crushed and infused in the refrigerator. Take 10 ml per day (divided into 1 dose) before meals. Course up to 1 month.
Full recovery is possible when combined with drug treatment. Although folk remedies are harmless, you should consult a pediatrician before using them. He will adjust the course of treatment.
What pathologies does ultrasound detect?
Using this procedure, you can evaluate changes in the size and contours of the organ, the condition of the ducts, and also diagnose a number of dangerous pathologies:
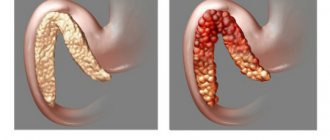
- acute, chronic pancreatitis;
- congenital pancreatic anomalies;
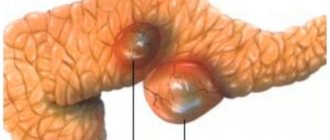
- cyst, malignant (cancer) and benign neoplasms;
- various inflammations, abscess (purulent inflammation);
- diabetes mellitus, tissue changes caused by diabetes mellitus, pancreatic lipomatosis.
Sizes of the gland before and after food loading
An additional examination method for pancreatitis is ultrasound with food load. Sonography is done twice: in the morning on an empty stomach and 2 hours after eating. Each time the transverse dimensions of the head, body and tail of the pancreas are measured. The increase in the sum of indicators after a physiological breakfast to the initial data is calculated. Based on it, conclusions are drawn about the condition of the organ. With enlarged pancreas:
- more than 16% is the norm,
- 6-15% - reactive pancreatitis,
- more or less than the initial data by 5% - chronic pancreatitis.
All conclusions are drawn based on a comparison of the obtained sizes with the data of normal indicators in a special table. The method allows you to prescribe adequate therapy when pathology is detected and control the process of tissue regeneration and restoration of pancreatic function.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the pancreas
In an emergency, ultrasound of the pancreas
carried out without prior preparation. Despite possible distorted results, an experienced specialist will be able to identify pathology that requires emergency medical care.
For a better diagnosis that gives accurate research results, preparation is necessary. It is necessary to begin preparatory activities 2 days before the procedure:
- following a light protein-free diet;
- do not eat food 10-12 hours in advance (on the eve of the morning procedure, a light dinner is enough);
- exclusion of products that cause gas formation (yeast and dairy products, fresh vegetables, fruits, beans, carbonated drinks, etc.);
- quitting smoking, alcohol, and chewing gum;
- a pause in taking medications and herbs (with the exception of mandatory therapy for chronic diseases: diabetes, hypertension, etc.);
- per day, patients prone to flatulence should take adsorbents (espumisan, activated carbon, etc.);
- on the eve of the procedure, cleanse the intestines (if necessary, use a laxative or enema).
Failure to follow the preparation rules reduces the information content of ultrasound by almost 70%. Also, examinations with a contrast agent and endoscopic manipulations performed on the eve of an ultrasound scan of the pancreas will contribute to distortion of the results.
How the research is carried out
Ultrasound of the pancreas is performed using two methods - classical and endoscopic. The first technique is the standard and is prescribed first. Endoscopic ultrasound is required to confirm a questionable diagnosis and in difficult cases.
Classic examination of the pancreas
The method of performing an ultrasound of the pancreas usually takes place through the abdominal wall using a special external sensor. The patient lies down in clothes (without shoes) on the couch with his back, exposing his stomach. The doctor applies a hypoallergenic ultrasound gel, which ensures maximum contact with the device, and then, slowly moving the probe from the central part of the abdomen to the left hypochondrium, examines the pancreas. During imaging, the patient must take a deep breath. The doctor will suggest holding your breath (inflating your stomach) so that the intestines move and nothing interferes with the examination of the pancreas.
To clarify questionable results, the doctor may ask the patient to change his body position (lie on his side or stomach, stand up) and conduct a repeat study. It is possible to obtain erroneous results due to the accumulation of gases in the intestines. To eliminate this problem, the patient needs to drink 2-3 glasses of water. The liquid will act as a “window” and allow you to examine the organs.
The procedure is absolutely painless, the patient does not experience any discomfort or discomfort. The duration is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Endoscopic ultrasound
In some cases, endoscopic ultrasound examination of the pancreas is used to examine inaccessible areas and reduce errors. This option is invasive and does not feel very pleasant. Visualization is performed using a thin flexible endoscope (device) with a video camera and an ultrasound sensor.
The probe is carefully inserted through the esophagus into the stomach and through it into the duodenum. To alleviate the patient’s nervous condition, 30-60 minutes before the procedure, he is given an intramuscular injection of a sedative. EndoUS is performed under anesthesia (local).
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine can be used as a preventive measure and used after the end of the main treatment to consolidate the result.
Popular infusions:
- The simplest thing is to drink a drink made from chicory, you can buy it at a pharmacy or in stores, or prepare it yourself. Two cups a day (morning and evening) are enough to normalize the functioning of the organ. Place no more than 11 grams per cup. powder (without additional ingredients). The course can last up to 1 month.
- Drink made from chamomile and immortelle. The ingredients are taken in a ratio of 1:1:10 (10 parts boiling water). Take 110 ml before meals up to 1 time per day. Duration no more than 1 week.
- You can use calendula tincture 90 drops (divided by 1 time) per day before meals. Treatment lasts no more than 1 month.
- Flax (seeds). They are taken in a ratio of 1:10 with water. Boil and leave for 10 minutes. Drink the resulting jelly all at once on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Dill. To prepare, you will need dill herb and milk in a ratio of 1:10. Cook over low heat for up to 11 minutes. Drink 10-10 ml every 60 minutes. The course is at least 10 days.
Tea helps more with recovery from illness. Decoctions and infusions alone will not cure you completely. Be sure to take a course of medication before taking them.
Normal indicators visible on ultrasound of the pancreas
The organ is normally located in the epigastric region. A healthy gland has the following signs:
| Form | Sausage-shaped, dumbbell-shaped, S-shaped or tadpole-shaped |
| Circuit | smooth, clear, visible limitation from surrounding tissues |
| Echogenicity (responsiveness of ultrasonic waves) | average |
| Echo structure (pattern visible in the image) | homogeneous (homogeneous), can be fine-grained or coarse-grained |
| Vascular pattern | no deformation |
| Wirsung duct | narrow, without extensions (diameter 1.5 – 2.5 mm) |
Dimensions of the pancreas in adults and children
The size of the pancreas within normal limits in children and adults differs, since the indicators are affected by the child’s growth:
| Indicators | In an adult | The child has |
| Head | min. 18 – 28 mm | 10 – 21 mm |
| Body | 8 – 18 mm | 6 – 13 mm |
| Tail | 22 – 29 mm | 10 – 24 mm |
Form
During an ultrasound examination, the shape and deviation from the norm are determined. If there are no problems, the organ will have an S shape. In some situations, it is possible to identify pathology that is expressed in a disturbed form. The organ can be ring-shaped, spiral, split, or additional in shape. The anomaly detected by ultrasound is an isolated pancreatic defect or part of a severe pathological process.
In most cases, ultrasound can reveal only indirect symptoms. We are talking about a narrowing or additional duct. In such a situation, the doctor may prescribe another study to exclude or confirm the deviation.
Pathological indicators: deviations from the norm visible on ultrasound
| Pathology, temporary changes, disease | Signs on ultrasound |
| Acute pancreatitis | The pancreas is larger than normal (or its individual parts are enlarged); blurry, uneven outline; heterogeneous structure (mainly hypoechoic); The duct of Wirsung is dilated; accumulation of fluid around an organ. |
| Chronic pancreatitis | uneven, blurred contour of the gland; heterogeneous, enhanced structure (hyperechoic); The Wirsung duct is dilated (more than 2 mm); stones are possible - round hyperechoic formations with an echogenic path behind. |
| Cyst or abscess | Echo-negative (black on images) formation with clear, smooth hyperechoic edges |
| Tumor | the part in which the tumor is located is enlarged; the structure is heterogeneous (hypoechoic, hyperechoic or mixed); dilated pancreatic and bile duct. |
| Diabetes mellitus or pancreatic lipomatosis | enhanced echogenic structure; fuzzy, blurry, uneven contour of the organ. |
| Duplication of the pancreas | 2 pancreatic ducts; the isoechoic structure appears uneven. |
| Annular pancreas | The segment surrounding the duodenum is enlarged |
| Metastases | one or more round, hypoechoic (not responsive to ultrasound waves) formations |
Contraindications
In general, ultrasound examination has no contraindications, but there are factors that make the procedure difficult or impractical.
Ultrasound of the pancreas is not performed if:
- allergic reaction to the gel;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- high degree of obesity - the organ is difficult to examine due to the thickness of the fat;
- damage to the skin of the abdominal cavity (wounds, infectious and inflammatory pathologies, fistulas, skin lesions due to systemic diseases).
Contraindications to endoscopic ultrasound:
- bleeding disorders;
- poor patency of hollow organs;
- some diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems (acute myocardial infarction, stroke, bronchial asthma, etc.);
- patient's state of shock;
- burns of the esophagus;
- acute circulatory disorders;
- acute perforated ulcer;
- nodular goiter in the 4th stage;
- upper cervical spine injury.
In each case, for certain pathologies, the doctor determines the possibility of performing an ultrasound on an individual basis.
Final diagnosis
It is important not to miss any ailment associated with pancreatic disease. The availability of ultrasound in this situation cannot be overestimated. The sooner changes in the organ are detected and appropriate measures are taken, the greater the chance of cure.
The diagnosis is made only by a doctor based on a combination of clinical manifestations, laboratory parameters and instrumental studies. In the future, dynamic monitoring of changes in the condition of the gland is needed.
The main contribution from the patient is not only strict adherence to treatment recommendations, but also maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, overeating, abuse of alcohol, sweets, fatty and fried foods.
Important for the health of the pancreas is maintaining immunity, protecting against stress, and eliminating household and professional intoxications.
Research alternatives, advantages of ultrasound over other techniques
There are several methods for examining the pancreas:
- radiological (x-ray, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, computed tomography);
- fiber optic diagnostic methods.
Ultrasound of the pancreas is the gold standard. It stands out compared to other methods because it does not expose the patient to radiation compared to X-rays, is more economical financially than CT (computed tomography), more accurate and much more informative compared to cholangiopancreatography, and is also simple, quick and absolutely painless procedure.
The study has no age restrictions and can be carried out even during pregnancy. The specialist does not limit himself to ultrasound and prescribes a comprehensive examination if he discovers a pathology that requires confirmation of the diagnosis.