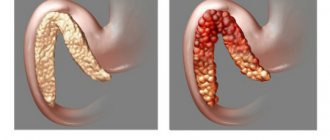
Inflammation of the pancreas is characterized by severe girdling pain, nausea, and vomiting, which does not bring relief. Mechanical jaundice is possible. The pancreas has two main functions - endocrine (in particular, insulin is formed in it) and exocrine
(it produces a number of enzymes necessary for digestion). The most common cause of insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function in adults is alcoholism, and in children - cystic fibrosis (a severe hereditary disease also accompanied by severe pulmonary infections). Cystic fibrosis should be suspected in all patients under 40 years of age with unexplained exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Causes of inflammation of the pancreas
The most common provoking factors leading to pancreatitis are alcohol abuse and gallstones. This disease can also develop as a result of injuries, infections and uncontrolled use of certain medications. Sometimes it happens that the reasons that led to inflammatory processes in the pancreas remain idiopathic (unexplained). In normal condition, the pancreas and its ducts do not give enzymes the opportunity to corrode the cells of the mucous membrane. But sometimes the outflow of enzymes into the small intestine fails, and digestive juices begin to have a destructive effect on the tissue of the gland itself.
Acute form of pancreatitis
Most often, an acute attack of pain is caused by blockage of the pancreatic ducts with gallstones or excessive alcohol intake. A sudden attack of pancreatitis can also be caused by prolonged drinking bouts.
Other reasons may also include:
- Injuries;
- Infections;
- Increased levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- Certain medications (steroids, antibiotics, drugs to treat hypertension).
Chronic form of pancreatitis
Experts believe that the development of chronic pancreatitis is caused by excessive consumption of fatty foods, smoking and alcohol abuse. It is not clear exactly how alcohol affects the functioning of the pancreas. Presumably, it may impede the release of digestive juices from the pancreas or greatly change their chemical composition, so they begin to cause an inflammatory process.
Drug therapy for pancreatitis
Pancreatin is an enzyme used for chronic pancreatitis.
In acute pancreatitis, first of all, you need to stop eating for several days. The body is supported through intravenous infusion of nutrient solutions: sodium bicarbonate, glucose, hemodez, administration of albumin, blood plasma. Only drinking plenty of alkaline water without gas is allowed.
In case of hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis, the most severe form of pancreatitis, loading doses of Trasylol, Gordox, and Contrical are used to suppress the activity of enzymes and reduce the rate of their synthesis. For the same purpose, intragastric hypothermia is used, cold is applied to the area of the gland projection. The use of antibiotics will help cope with the infection if complications arise. Auxiliary methods include laser irradiation and plasmaphoresis to remove toxins from the body. For edematous and chronic pancreatitis the following are used:
- antispasmodics (Eufillin, Drotaverine, Nitroglycerin)
- cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine)
- anticholinergics (Atropine, Pentoxyl, Scopolamine, Methyluracil)
- enzymes (Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal, Methionone)
- antibiotics to prevent infection (Carbennicillin, Kanamycin, Trichopolum, Tobramycin)
- antihistamines (Promethazine, Chloropyramine)
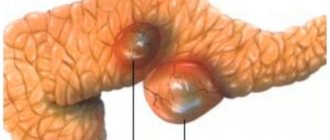
If diabetes mellitus is a complication of pancreatitis, treatment is carried out as prescribed by an endocrinologist. Complications of chronic pancreatitis can also include cysts and malignant tumors of the pancreas. Since they are hormonally active neoplasms, their appearance can be diagnosed in addition to ultrasound and MRI studies, also by the release of excessive amounts of hormones.
Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation
The most obvious symptom of inflammation of the pancreas is quite severe pain in the left hypochondrium or in the upper abdomen. Sometimes the pain radiates to the lower back and is girdling in nature. When you take a sitting position or bend slightly forward, the pain gradually subsides and becomes insignificant.
Symptoms also include:
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased sweating;
- State of shock;
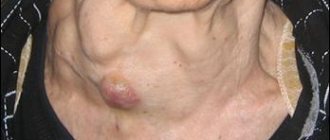
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin;
- Back pain, however, this symptom is sometimes provoked by diseases such as peptic ulcer, appendicitis, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction, diverticulosis.
How pancreatitis manifests itself: symptoms and signs
The main list of symptoms in the acute form:
- severe pain in the hypochondrium - taking into account the cause of the disease and accompanying pathologies, it can be girdling, right- or left-sided;
- reactions from the digestive tract - hiccups, belching with an unpleasant odor, nausea and repeated bouts of vomiting, constipation or diarrhea;
- general deterioration of the body - dehydration, dry mouth, weakness, increased or decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, increased sweating, high temperature;
- external manifestations are dull, sallow-colored skin, bluish or brownish spots in the lumbar region and supra-umbilical area, obstructive jaundice is possible.
Attention! The acute form requires urgent hospitalization followed by hospital treatment.
In the chronic form, the signs of pancreatitis are less pronounced:
- pain appears only after eating fried and fatty foods or alcohol; the rest of the time, mild discomfort may be observed in the hypochondrium area;
- reactions from the digestive system appear only in the dyspeptic form in the form of flatulence, diarrhea or constipation;
- external skin manifestations in the form of mild jaundice; with prolonged absence of treatment, weight loss, anemia, and type 2 diabetes are observed.
In the latent stage, the disease is asymptomatic; in the fibrous form, scar tissue can grow to form pseudotumor structures.
Important! Pancreatitis of the pancreas rarely manifests itself as an independent disease. Typically, the pathological process combines several digestive organs, involving the hepatobiliary system (liver, gallbladder and ducts), duodenum, and stomach. This fact requires diagnosing the entire human digestive system.
What happens when the pancreas becomes inflamed?
Acute pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can be mild or severe. The most common diagnosis is acute mild pancreatitis. This disease does not affect nearby organs and is cured quickly enough. When the correct therapy is prescribed, the symptoms of the disease disappear within a week after the start of treatment.
Therapy is carried out directly in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor who, depending on the individual characteristics of the human body, prescribes painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs and develops a system for taking them. As soon as the inflammation is eliminated, the patient will immediately recover.
But sometimes necrotic tissue of the pancreas or severe damage to its cells can occur. In this case, there is a danger of complete organ failure. In advanced cases, inflammatory processes in the pancreas can lead to death.
Chronic pancreatitis
Usually the disease becomes chronic after a series of attacks of acute pancreatitis and in the absence of adequate treatment. Experts say the most likely cause of chronic inflammation is constant abuse of alcoholic beverages.
This form of the disease occurs in different ways. Often chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by regular pain and associated complications. They include constantly recurring manifestations of all the symptoms of pancreatitis, blockage of blood vessels, small intestines, bile ducts, accumulation of air and fluid.
When most of the tissue of the pancreas dies, malnutrition occurs, since the organ ceases to produce the enzymes necessary for digestion, which help digest proteins and fats. The body cannot absorb fats, and they are simply excreted in the stool. It becomes thin, pale and foul-smelling due to the development of steatorrhea.
Damage to the cells responsible for the production of insulin (insulocytes) leads to the inability to absorb carbohydrates and sugar from food, which threatens the development of diabetes. Chronic inflammation of the pancreas increases the risk of developing cancer. It occurs in approximately 4 cases out of 100 in people with chronic pancreatitis.
Find out more: Pancreatitis - causes, symptoms, diet, as well as modern and traditional methods of treatment
Operation indications for performance
Surgeon intervention in acute pancreatitis is used in extreme cases, since surgery on this organ can lead to significant damage to the gland. When some tissue dies (pancreatic neurosis), an emergency operation is required to remove part of the gland. If the gland duct is blocked by stones, then in addition to the traditional method of removing them, it is possible to use laparoscopy as a less traumatic method of surgical intervention.
If you have to completely remove the pancreas, there must be good reasons for making such a decision, since this operation is very complex, with frequent complications and a high mortality rate. Enzymes of the gland, penetrating into the blood, cause lightning shock, once in neighboring organs, they contribute to their disintegration. After surgery to remove the gland, you will have to constantly make up for the lack of enzymes and hormones by taking medications.
Risk factors
The following factors significantly increase the risk of pancreatitis:
- Alcohol abuse. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body. The amount of alcohol that can lead to the destruction of pancreatic cells varies from person to person. On average, medical experts suggest that men should drink no more than two glasses of strong alcohol per day, and for women this norm should not exceed one glass;
- Gallstones. Gallstones can lead to blockage of the pancreatic duct, and as a result, the flow of digestive juices will be impaired;
- Increased levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- Deviation in the structure of the bile or pancreatic ducts, and congenital pathology, when the pancreas is divided and has two main channels.
It is important to know! You should seek medical help immediately if you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting for several hours, or minor pain for several days. It is not necessary that such symptoms indicate diseases of the pancreas, but a number of tests must be performed to exclude the diagnosis. You should not endure for a long time and wait for the symptoms to go away on their own. This is especially true for severe abdominal pain, since this condition can seriously threaten a person’s life.
Symptoms in children
Often this disease manifests itself in children. The difficulty is that children cannot clearly say in which area and how it hurts. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the overall picture of symptoms:
- Abdominal pain.
- Refusal to eat any food.
- Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees or more.
- Moodiness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Possible diarrhea.
To make an accurate diagnosis, children undergo an ultrasound and all the necessary tests.
Diagnosis of pancreatic inflammation
If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, the following medical specialists can take part in the diagnosis of this disease: therapist, surgeon, family doctor, gastroenterologist. A visual examination is carried out and a blood test is ordered, which may indicate the presence of blockage of the ducts or their infection. Then other studies are additionally prescribed, including ultrasound, which is the most common painless diagnostic procedure.
- Primary examination. To begin, the doctor conducts a visual examination and asks about symptoms. It also finds out all the diseases that preceded this health problem. If there is a suspicion of gallstone disease, the doctor pays attention to the yellowish tint of the skin and whites of the eyes, and conducts a digital examination of the abdomen. If there are attacks of nausea or vomiting, then it is necessary to find out their causes. To do this, you should describe your feelings at the doctor’s appointment as accurately as possible. It is necessary to accurately indicate the number of attacks and their duration. For a more thorough examination, detailed blood and urine tests, as well as x-rays, may be prescribed.
- Analyzes. To begin with, a study of the level of enzymes in the blood is prescribed. Based on the results of the data obtained, the doctor diagnoses the disease and decides to prescribe treatment for inflammation of the pancreas.
To get a clearer picture, two main blood tests are prescribed:
- Lipase level. An increase in its level in the blood may indicate an acute attack of pancreatitis;
- Amylase level. High amylase levels are a sign of inflammation.
Also, in addition to the above tests, the following may be additionally prescribed:
- Bilirubin test. Increased levels of this protein occur when the bile ducts are blocked;
- Complete blood test. If the pancreas is inflamed, then a large number of leukocytes will be present in the blood;
- Blood test for liver enzymes. In acute pancreatitis, which is caused by gallstones, there is an increase in the activity of alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase.
The following hardware techniques are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. With its help, you can find out how badly the duct is blocked and where the gallstones are located;
Localization of the inflammatory process
If the pancreas is inflamed, then the pain can be different: aching, cutting, stabbing, with a specific localization, for example, under the right rib, or without localization at all throughout the abdominal cavity, in the back or groin. The type of this pain directly depends on which part of the gland is inflamed: the body, head or tail. When the localization of pain is blurred, doctors often talk about a complete disease of the organ.
Aching pain in the middle part of the abdominal cavity indicates that the body of the pancreas is inflamed; if the pain is felt in the right side, the head of the gland is inflamed, and if in the left, the tail is inflamed. The presence of the last two cases is much worse, because a space-occupying formation (tumor) forms in these parts.
In the head of the pancreas
A general change in the size of the pancreas is much safer than enlarging any part of it. The head of the gland has a special shape and unique structure: in an adult it is located at the level of the first two vertebrae, and in a newborn baby it is slightly higher. In adulthood, the normal size of the head of the pancreas should reach up to 35 mm, and if it is smaller or larger in size, then this is considered a pathology.
A mass formation in the head of the pancreas is usually detected during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and is considered a dangerous disease. It can be benign or substandard, which requires immediate removal. This disease often occurs in people over 60 years of age. Even visually, an experienced doctor can detect the first signs of inflammation of the head of the gland: a change in skin color and yellow coloration of the whites of the eyes. Treatment of this form of the disease occurs in a hospital setting.
In the tail
The tail of the pancreas has an upwardly curved pear-shaped shape and comes close to the spleen. In an adult healthy person, the optimal width of the tail of the organ is 20-30 mm, and its length is about 15 cm. A severe pathology of the tail of the gland is its expansion or thickening, against the background of which obstruction of the splenic vein or subrenal form develops.
A tumor in the tail of the gland occurs rarely: about a quarter of all gastrointestinal diseases. But if it is diagnosed, then often the tumor is immediately malignant and almost impossible to treat, since it is discovered late, when it has already reached a significant size. When operating on a tumor in the tail of the pancreas, doctors often have to remove nearby organs.
Treatment of pancreatic inflammation
Most often, treatment is performed in a hospital setting. A sick person is prescribed painkillers, and a special drug regimen is developed to eliminate inflammation. With pancreatitis, air and fluid sometimes accumulate in the stomach, which can cause severe vomiting. To eliminate this symptom, a tube is inserted into the stomach through the nose, which removes fluid and air out.
The choice of therapy for pancreatitis will depend on the nature of the disease: acute attack or chronic course. Initial treatment for an acute attack of pancreatitis should be carried out in a hospital setting. The patient is prescribed intravenous infusions to replenish fluid loss and normalize blood pressure. NSAIDs are prescribed to eliminate inflammation. During this period, a strict diet is observed from three days to a week.
If there are gallstones that provoke attacks of inflammation of the pancreas, ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is prescribed to remove them from the bile duct. After eliminating the inflammatory processes, sometimes the gallbladder is removed surgically.
In the chronic course of the disease, when acute attacks of pancreatitis appear, similar treatment is prescribed. If it is necessary to dilate the pancreatic ducts, remove stones or cysts, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. After such a procedure, a person should be constantly monitored by the attending physician for about six months to avoid complications. At home, you should always adhere to an appropriate diet, avoid overeating and alcoholic beverages.
Medicines for the treatment of chronic inflammation of the pancreas
When treating chronic pancreatitis, painkillers, enzymes that improve food digestion, and, if necessary, insulin-containing medications are prescribed.
The main types of drugs for the treatment of pancreatitis:
- Painkillers. If the attacks of pain are tolerable, they can be relieved with ibuprofen or acetaminophen. For more intense and sharp pain, stronger painkillers are used as prescribed by the doctor;
- Insulin. If inflammation has led to the death of pancreatic cells responsible for the production of insulin, then the patient is prescribed insulin injections for life;
- Enzymes. In severe cases of inflammation in the pancreas, this organ may stop producing digestive enzymes, which are vital for the digestion and proper absorption of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. In this case, the patient is prescribed enzymes. Entering the body, they help food to be fully absorbed.
Using enzymes to treat chronic pancreatitis may cause side effects. For example, pain in the anus or mouth. Most enzymes are made from pork protein, so they should not be taken if you have a pork allergy.
Enzymes should be taken with caution and under the direct supervision of a physician in childhood, as large amounts of them can lead to intestinal obstruction.
Find out more: Medicines used in the treatment of pancreas
When is surgery necessary?
The pancreas is a very delicate organ that can be easily damaged during surgery; doctors prefer not to prescribe interventions whenever possible. However, sometimes surgery is simply necessary, since the risk of complications due to dead pancreatic tissue is much higher than the risk of complications from surgical treatment.
If pancreatitis is caused by the presence of gallstones, then usually choose from two types of operations:
- Laparoscopy;
- Open surgery on the gallbladder.
In the presence of gallstones, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is used. It is also used if it is necessary to widen or drain the narrow pancreatic duct.
Various methods are used to eliminate dead pancreatic tissue:
- Laparoscopic necrectomy, which is performed for limited necrosis of pancreatic tissue. Such an operation is important for preserving the patient’s life, although after it the volume of enzymes and hormones secreted by the organ decreases;
- Open necrectomy. Indicated for widespread necrotic processes in the tissues of the pancreas. Excision of necrotic cells is carried out, followed by removal of inflammatory exudate, drainage of retroperitoneal tissue and lavage of purulent cavities.
Pancreatic necrectomy is an organ-sparing operation that involves removing all dead tissue.
What to do if complications of the inflammatory process begin?
Attacks of pancreatitis do not go away without a trace and are often accompanied by complications. These include:
- Necrotization of pancreatic tissue;
- Infection;
- Cyst.
Sometimes surgery is required to remove gallstones or resection of the damaged part of the pancreas. If the disorders are critical, the patient will most likely have to take insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. And for normal digestion of proteins and fats, medications containing digestive enzymes are prescribed.
If the inflammation of the pancreas is chronic, then the sick person requires a constant diet that completely excludes the consumption of alcoholic beverages, including low-alcohol ones. It is also necessary to constantly take painkillers. The patient needs to develop a nutritional system together with the attending physician. Changing your eating habits is quite difficult, especially for people with a weak will, but with the right approach, good planning and the support of your family, it all becomes possible.
Complications of chronic pancreatitis include:
- Accumulation of excess fluid around the pancreas;
- Blockage of blood vessels;
- Constant attacks of pain;
- Stenosis of the bile ducts and small intestine;
- Risk of pancreatic cancer.
Treatment if the patient's condition worsens
The consequence of long-term chronic inflammation of the pancreas is a decrease in the amount of digestive enzymes it secretes. Therefore, the body cannot fully digest fats. Reduced enzyme synthesis leads to steatorrhea. This is the discharge of liquid, oily feces.
Since proteins and fats are not absorbed from food, a person begins to lose weight. This problem is solved with the help of medicines containing enzymes. If pancreatitis has led to the cessation of secretion of the hormone insulin by the pancreas, then the sick person is prescribed appropriate injections.
During treatment, if an infectious inflammatory process develops, the patient is prescribed antibiotics or the necrotic affected pancreatic tissue is surgically removed. However, doctors are trying to treat this organ without resorting to surgery, since the pancreas is very delicate and vulnerable.
Find out more: The most effective recipes for restoring the pancreas!
How to treat
When pancreatitis is detected, the patient should be treated as soon as possible. The longer the pancreas is left without help, the more likely it is to develop severe complications such as purulent abscesses, pancreatic necrosis, diabetes mellitus or malignant tumors.
Medicines to relieve pain during an attack
The most difficult problem during an attack accompanied by painful symptoms is how to relieve the pain. According to clinical recommendations, it is allowed to take over-the-counter painkillers from the following groups:
- antispasmodics based on drotaverine;
- analgesics (metamizole sodium);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on nimesulide, ibuprofen.
In practice, these drugs are not always effective for relieving pancreatic pain and you have to look for something else to relieve the pain. Often there is a need to take opioid non-narcotic analgesics (for example, Tramadol), which are sold only with a doctor's prescription.
Complex treatment
Sometimes relief of a pain attack occurs as a result of the use of non-drug measures. Hunger for 1-3 days, cold on the gland area and complete rest help not only get rid of pain, but also eliminate dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, heartburn, bloating).
The best effect during exacerbation is provided by complex treatment, including diet and drug therapy.
The use of medications for pancreatitis helps to suppress the inflammatory process, eliminate painful symptoms, and quickly restore digestive function.
- For frequent, debilitating vomiting, antiemetic tablets with the active ingredients metoclopramide or ondansetron are effective.
- To reduce the secretion of the digestive glands - drugs omeprazole, pantoprazole, famotidine.
- To reduce the acidity of gastric juice - magnesium hydroxide in combinations.
The most important factors in the complex treatment of acute pancreatitis remain strict adherence to the diet (on the first day - hunger + warm drinks) and complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages.
Omeprazole capsules
What to do outside periods of exacerbation
The dynamics of destruction of the pancreas depends on the frequency of exacerbations: the more often this organ suffers from acute attacks, the more likely the rapid progression of inflammation and the development of severe complications. Therefore, the main task of doctors and the patient himself is to prolong the period of remission and reduce the frequency of exacerbations. The task is easily accomplished for disciplined, sensible patients who are ready to give up unhealthy eating and other destructive habits.
Radical changes in the diet, a healthy, balanced diet, excluding fatty, smoked, sour, salty and spicy foods, limiting sweets, sufficient drinking regime - all this will help you return to your usual activities and forget about exacerbation of pancreatitis for a long time.
Do herbs and other folk remedies help?
Herbs and other folk remedies should be treated with a certain amount of caution and consult a doctor before using them. It is necessary to understand that medicinal herbs for pain relief at home are not enough. And some plants have effects that are undesirable in the treatment of pancreatitis. For example, choleretic, laxative, tonic.
In order not to cause even more harm to the pancreas, it is recommended to take light, unsaturated drinks – teas – rather than strong decoctions or infusions. As a basis, take plants that have a calming, enveloping, vitaminizing effect.
It is useful to drink teas from rosehip, mint, lemon balm, chamomile, thyme, brewed at the rate of 1 teaspoon of herb per glass of boiling water. Herbal teas for pancreatitis are indispensable on the first day of an exacerbation, when the patient is allowed only warm drinks. However, herbal teas are not able to relieve pain during an attack with acute symptoms at home.
Prevention of pancreatic inflammation
It is impossible to guarantee pancreatic inflammation, like any other disease.
However, you can reduce risk factors and thereby minimize the likelihood of new attacks:
- Since most often attacks of pancreatitis occur against the background of alcohol abuse, if you have such a disease, alcohol should be completely eliminated from your life. Even a small amount of it can provoke an attack of pain or complications. Large doses of alcohol can be life-threatening for a person with pancreatitis;
- Since chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by attacks of pain, painkillers are prescribed, as well as digestive enzymes;
- The intake of fatty, fried, smoked, spicy foods is limited, as they irritate the pancreas and cause pain;
- If pancreatitis is provoked by gallstones, then you should monitor your diet and lead a healthy, active lifestyle;
- Smoking also provokes the development of pancreatic diseases, so you should think about quitting this bad habit;
- You need to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meats, baked goods made from wholemeal flour, and porridge cooked in water.
Only a timely visit to a doctor in the presence of the first symptoms of pancreatitis, compliance with all his recommendations for the treatment and prevention of the disease, will help maintain the normal functions of such an irreplaceable digestive organ as the pancreas.
Nutrition and diet
Regardless of the form of the disease, to treat inflammation of the pancreas it is necessary to follow a strict diet. If the disease worsens, you should not eat any food in the first two days. Only rosehip decoction, still mineral water or weak and unsweetened tea are allowed. It is imperative to exclude from the diet during exacerbation of the disease:
- alcohol;
- spices, seasonings;
- fatty, fried;
- sausages, smoked meats;
- pickles, canned food;
- confectionery, chocolate, sour juices.
What products can
If inflammation of the pancreas is chronic, then doctors allow the following products:
- Dairy products: non-acidic cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir.
- Low-fat fish: pike, bream, pike perch.
- Meat products in the form of puree, cutlets, soufflé from rabbit, veal, beef, turkey or chicken.
- Boiled grated vegetables.
- Rusks or dry wheat bread.
- Steamed egg omelet.
- Cereal, chicken, noodle or vegetable soups.
- Oils: refined sunflower, olive, butter.
- Pasta, grated cereals.
- Sweet jellies, jelly, compotes.
- Baked pears, apples.
- Wheat bran decoction, weak tea, rosehip decoction, still mineral water.
Menu
If the pancreas is inflamed, you can use the sample diet described below. The menu is designed for 1 person for 2 days:
The first day
- Breakfast 1: mashed potatoes 100 g, 2 crackers, mineral water.
- Breakfast 2: steamed omelette of 2 eggs, 2 steam cutlets, 1 wheat cracker, low-fat milk 200 ml.
- Lunch: chicken soup 200 ml, boiled fish 100 g, boiled zucchini 100 g, 1 cracker, steamed raisins 30 g, tomato juice 200 ml.
- Afternoon snack: fruit jelly 200 ml, still mineral water.
- Dinner: oatmeal 150 g, 1 steam cutlet, carrot puree 100 g, 1 cracker, tea with milk 200 ml.
Second day
- Breakfast 1: boiled beef 100 g, oatmeal 150 g, 1 cracker, mineral water.
- Breakfast 2: applesauce 100 g, curd pudding 100 g, 1 cracker, 200 ml tea.
- Lunch: vegetable soup 250 ml, 2 steamed fish cutlets, pumpkin porridge 100 g, cottage cheese 100 g, 1 cracker, tea.
- Afternoon snack: carrot puree 150 g, meatballs 100 g, applesauce 100 g, yogurt 100 g.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes 150 g, meatloaf 150 g, curd pudding 100 g, 1 cracker, fruit jelly 100 ml, tea.
After a heavy feast or due to alcohol abuse, did you experience a sharp pain under the ribs, radiating to the back? Does just looking at fatty foods make you vomit? You should immediately seek medical help - there is a high probability that this is acute pancreatitis, and here delay is like death!
Causes of pain in the pancreatic area
Pain in the pancreas can be caused by diseases such as:
- pancreatitis (acute and chronic);
- pancreatic necrosis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- cancer of pancreatic tissue;
- organ cysts;
- gland abscess.
The most common is pancreatitis, which is characterized by “self-destruction” of the gland by its own activated enzymes. This can occur when the outflow of pancreatic juice and the reverse reflux of bile are disrupted. The main causes of pancreatitis are alcoholism, smoking, cholelithiasis, anatomical features and poor nutrition. Heredity plays an important role.
Pancreatitis is more common in middle-aged men
You can learn more about the functions of the pancreatic gland and the causes of its diseases from the video at the end of the article.
Pathologies of other organs located nearby can lead to pain in the pancreas area. It can be:
- osteochondrosis,
- intercostal neuralgia,
- gastritis and gastroduodenitis,
- left-sided pyelonephritis,
- cholecystitis,
- left-sided lower lobe pneumonia,
- angina pectoris
- myocardial infarction,
- cholelithiasis (hepatic colic),
- intervertebral hernias,
- herpes zoster,
- hepatitis, etc.
With all of these diseases, the patient may think that his pancreas hurts, because the location of the pain is very similar. Therefore, many diseases often mimic pancreatitis and vice versa. But still, there are some features of symptoms that are useful for everyone to know.
The nature of pain in pancreatic diseases
First you need to figure out where the pancreas hurts. The projection of the organ is on the left hypochondrium, and the gland itself is located behind the stomach. It consists of a head, body and tail, and the localization of pain depends on which part is damaged. If the head is affected, the pain is more in the left hypochondrium, the body – in the epigastric zone or “under the stomach”. If the tail is inflamed, it hurts in the area of the right hypochondrium. But since the most common disease of the organ is pancreatitis, the entire gland is often affected.
The patient is bothered by a rather acute, sometimes burning pain, mainly in the left hypochondrium and epigastrium, sometimes throughout the entire upper abdomen. The pain typically spreads to the left lumbar region, so the pain is said to be girdling in nature. When pressing at the point of the left costovertebral angle, the pain intensifies (Mayo-Robson symptom). For many, the onset of pain is associated with recent consumption of alcohol, fatty foods or spicy foods.
Important: if you experience pain with the symptoms described above, immediately seek help from a doctor.
Treatment of severe cases of pancreatitis
How to treat complex, advanced cases of pancreatitis if conservative therapy methods have exhausted themselves? Surgical intervention for diseases of the pancreas is performed in extreme cases, because it is very easy to damage this organ during various manipulations.
There are 2 types of operations in medical practice:
Direct indications for open surgery on the pancreas are the spread of dead organ tissue, stones in its ducts, etc. During surgery, the source of danger is removed and the peritoneum is drained.
Modern minimally invasive methods using laparoscopy can remove stones from the pancreatic ducts and limited areas of organ necrosis. The operation is performed using special equipment through small punctures of the abdominal cavity, under constant computer monitoring.
Complications of inflammation of the pancreas, the symptoms of which were discussed above, are:
- extensive organ necrosis;
- cysts;
- tumor malignant or benign formations, etc.
To eliminate such negative consequences of pancreatitis, surgical intervention is required.
Diet for pancreatitis
Diet for pancreatitis is a serious method to improve the patient’s well-being. Proper therapeutic nutrition allows you to better control the disease, slow its progression, and reduce the need for drug therapy. Diet for pancreatitis should be balanced, rich in vitamins and minerals, low in fat (no more than 10 grams per main meal). Food should be taken in small portions, but often.
Acute pancreatitis requires a short period of absolute diet. Any food can cause complications. In severe cases, the patient needs a special probe, which looks like a long thin tube and is inserted into the duodenum through the nose and esophagus. Fasting under medical supervision can also be useful during exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
What can you eat if you have pancreatitis:
- dietary meats (chicken breasts, fish, veal, rabbit) that do not contain a lot of fat;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- juices;
- liquid, with the exception of caffeine-containing drinks.
Cooking methods: cooking in boiling water and steaming.
Causes of pancreatitis
The disease can occur equally in both men and women. The current opinion that pancreatitis is a purely male disease is associated with the main cause of its occurrence. The starting point for the development of pancreatitis in 98% of cases is the abuse of alcoholic beverages of any strength over a long period. Experts have calculated the average statistical norm for alcohol consumption. For men, it is no more than 100 g of strong drinks per day, and for women, taking into account physiological characteristics, it is 2 times less. Any excess of this norm entails a violation of the functionality of the organ.
Other common causes of inflammation of the pancreas include:
- genetic predisposition;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of fatty, spicy and fried foods;
- smoking;
- prolonged stressful situations;
- some types of potent drugs (NSAIDs, Furosemide);
- cholelithiasis;
- allergic reactions;
- Crohn's disease;
- cystic fibrosis;
- liver pathologies;
- diseases of the duodenum;
- peritoneal injuries;
- surgical interventions;
- parasitic infestations, etc.
Sometimes inflammation of the gland occurs for unexplained (idiopathic) reasons.
Now we need to determine what signs of inflammation of the pancreas appear in adults.
Help yourself - use folk experience
A decoction of wormwood promotes the production of bile and normalizes the functioning of the gland.
The use of traditional medicine can complement the treatment of pancreatic inflammation in remission. The therapeutic effect is achieved slowly, but very gently and without side effects, therefore, when using folk remedies, you need to be patient. You can try various tinctures, decoctions, and herbal preparations to make you feel better:
- Oatmeal jelly. Wash, dry and grind oat grains sprouted in a warm place. Stir oatmeal with cool water, then pour boiling water, heat to a continuous boil (1-2 minutes). Leave for 20-30 minutes, drink only freshly prepared, do not store or reheat.
- Mix burdock roots, elecampane, chamomile and calendula flowers, St. John's wort, sage, wormwood, dried grass, string, horsetail, take one tablespoon of this collection, pour boiling water, leave, strain. Take 100-150 ml only for chronic forms of the disease half an hour before meals.
- A decoction of wormwood (boil 1 tablespoon of dried wormwood for 5 minutes, leave for 25-30 minutes) will help produce bile and normalize the functioning of the gland. Take 1-2 tbsp before meals. spoons.
- For the same purposes, an infusion of burdock, dandelion and licorice root is used. One tbsp. Pour boiling water over a spoonful of this mixture, leave for 30-40 minutes, strain, drink 100 ml hot before meals.
- For pain relief during exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease, an infusion of Japanese Sophora can be used. 1-2 tablespoons of the herb are poured into a thermos with 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 3-4 hours, drink warm before meals. Treatment with Sophora cannot last more than 10 days; after a 1-1.5 month break, the course can be repeated.
- For 2-3 weeks, you can use a collection of chamomile and immortelle flowers to relieve inflammation. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, infuse, and drink in 3 doses.
- For a similar purpose, you can take a mixture of lemon juice, boiled in water for 5 minutes, and a raw chicken egg from poultry. This mixture should be drunk on an empty stomach, after which you should not eat for 3 hours. Dosage cycle: once during the first, third, sixth, twelfth, and twenty-fourth days from the start of use. After six months, the course can be repeated.
Whether or not to use these recipes is a personal matter for everyone. The main thing is to supplement, and not replace, these medications with the treatment prescribed by your doctor, and adhere to your diet.
First aid at home for acute pain in the pancreas
First aid for acute pain in the pancreas is provided according to the following scheme:
- The patient is helped to take a comfortable lying position and is provided with complete rest.
- To relieve spasms, place a heating pad with cold water on the area where it hurts.
- If, 20 minutes after applying cold, the pancreas does not stop hurting, then before the ambulance arrives, the patient is given 1-2 tablets of No-shpa with a minimum amount of water.
When the pancreas hurts, and there is no opportunity to get medical help, the only medicine that can be used at home is No-shpa (Drotaverine). The drug can be taken to relieve acute pain for no more than 2 days in a row.
Useful video
If the pancreas hurts, this may indicate a disease. To understand why pathologies of this organ are dangerous, you should know its main functions. Gland cells synthesize enzymes that are secreted into the duodenum in the form of digestive juice and promote the digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
An even more important function is the endocrine one. In special islets of pancreatic tissue, the hormones insulin and glucagon are formed, which regulate carbohydrate metabolism. Often the first signs of pancreatic pathologies go unnoticed, and lack of treatment can lead to irreversible changes in this important organ.