Thyrotoxicosis
Hepatitis
Diabetes
4169 06 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Glucose (in blood) (Glucose): indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
What is glucose, its main functions
Glucose is a simple carbohydrate, due to which each cell receives the energy necessary for life. After entering the gastrointestinal tract, it is absorbed and sent into the bloodstream, through which it is further transported to all organs and tissues.
But not all glucose ingested from food is converted into energy. A small part of it is stored in most organs, but the largest amount is deposited in the liver in the form of glycogen. If necessary, it is able to break down again into glucose and replenish the lack of energy.
Like the liver, plants are also capable of storing glucose in the form of starch. That is why, after eating certain foods of plant origin, glucose in the blood of diabetics rises.
Glucose performs a number of functions in the body. The main ones include:
- maintaining the body’s performance at the proper level;
- energy substrate of the cell;
- fast saturation;
- maintaining metabolic processes;
- regenerative ability relative to muscle tissue;
- detoxification for poisoning.
Any deviation of blood sugar from the norm leads to disruption of the above mentioned functions.
Signs of high sugar levels
When a healthy person’s blood sugar rises, he feels unpleasant symptoms; as a result of the development of diabetes mellitus, clinical symptoms intensify, and other diseases may occur against the background of the disease. If you do not consult a doctor at the first signs of a metabolic disorder, you may miss the onset of the disease; in this case, it will be impossible to cure diabetes mellitus, since with this disease you can only maintain a normal state.
Important! The main sign of high blood sugar is a feeling of thirst. The patient is constantly thirsty, his kidneys work more actively to filter out excess sugar, while they take moisture from tissues and cells, so a feeling of thirst arises.
Other signs of high sugar levels:
- increased urge to go to the toilet, increased fluid output, which is due to more active kidney function;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- itching of the skin;
- itching of the mucous membranes, most pronounced in the intimate organs;
- dizziness;
- general weakness of the body, increased fatigue.
Symptoms of high blood sugar are not always obvious. Sometimes the disease can progress indirectly; such a latent course of pathology is much more dangerous than the variant with a pronounced clinical picture. For patients, the discovery of diabetes mellitus comes as a complete surprise; by this time, significant disturbances in the functioning of organs may be observed in the body.
Diabetes mellitus must be constantly maintained and regularly undergo blood tests for glucose concentration or use a home glucometer. In the absence of constant treatment, patients' vision deteriorates; in advanced cases, the process of retinal detachment can provoke complete blindness. High blood sugar levels are one of the main causes of heart attacks and strokes, kidney failure, and gangrene of the extremities. Constant monitoring of glucose concentration is the main measure in the treatment of the disease.
If symptoms are detected, you should not resort to self-medication; self-therapy without an accurate diagnosis, knowledge of individual factors, and the presence of concomitant diseases can significantly worsen the patient’s general condition. Treatment of diabetes mellitus is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Principle of blood glucose regulation
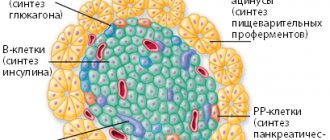
Glucose is the main supplier of energy for every cell in the body; it supports all metabolic mechanisms. To keep blood sugar levels within normal limits, beta cells of the pancreas produce a hormone - insulin, which can reduce glucose and accelerate the process of glycogen formation.
Insulin is responsible for the amount of glucose stored. As a result of disruption of the pancreas, insulin failure occurs, therefore, blood sugar rises above normal.
General information
In the body, all metabolic processes occur in close connection. When they are violated, various diseases and pathological conditions develop, including increased blood
glucose Nowadays people consume very large amounts of sugar, as well as easily digestible carbohydrates. There is even evidence that their consumption has increased 20 times over the last century. In addition, people's health has recently been negatively affected by the environment and the presence of large amounts of unnatural food in the diet. As a result, metabolic processes are disrupted in both children and adults. Lipid metabolism is disrupted, and the load on the pancreas, which produces the hormone insulin, .
Already in childhood, negative eating habits are developed - children consume sweet soda, fast food, chips, sweets, etc. As a result, too much fatty food contributes to the accumulation of fat in the body. The result is that symptoms of diabetes can appear even in teenagers, whereas previously diabetes was considered a disease of older people. Nowadays, people experience signs of increased blood sugar very often, and the number of cases of diabetes in developed countries is now increasing every year.
Glycemia is the level of glucose in a person’s blood. To understand the essence of this concept, it is important to know what glucose is and what the glucose levels should be.
Glucose - what it is for the body depends on how much of it a person consumes. Glucose is a monosaccharide , a substance that is a kind of fuel for the human body, a very important nutrient for the central nervous system. However, its excess causes harm to the body.
Normal values in venous blood
Table of normal indicators by age.
| Age | Glucose norm, mmol/l |
| Newborns (1 day of life) | 2,22-3,33 |
| Newborns (from 2 to 28 days) | 2,78-4,44 |
| Children | 3,33-5,55 |
| Adults under 60 years old | 4,11-5,89 |
| Adults from 60 to 90 years old | 4,56-6,38 |
The normal blood sugar level for people over 90 years of age is 4.16-6.72 mmol/l
What to do if sugar rises only in the morning on an empty stomach
To keep your morning fasting sugar at a stable level, the main thing is to have a proper dinner in the evening. You may also need to take diabetes pills at night, and in severe cases, inject insulin. You can ensure that your fasting sugar is normal every morning, that is, not higher than 5.5 mmol/l, like in healthy people. This is a realistic and achievable goal even for severe type 1 diabetes, and even more so for type 2 diabetes, which is a milder disease.
In many patients, blood sugar rises only in the morning on an empty stomach, and remains normal throughout the day and in the evening before bed. If this is your situation, don't consider yourself an exception. The reason is the dawn phenomenon, which is very common.
The diagnosis of prediabetes or diabetes depends on the highest values your glucose levels reach. See blood sugar standards. And the diagnosis is made based on the results of an analysis of glycated hemoglobin.
Treatment
Treatment of high blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach:
- Refuse late dinners, do not eat anything after 18-19 hours.
- Taking metformin (preferably extended-release tablets Glucophage Long) at night with a gradual increase in dose from 500 to 2000 mg.
- If early dinners and the drug Glucophage do not help enough, you also need to take long-term insulin in the evening before bed. Start with a low dose and try to increase it based on the results of previous injections.
- Unfortunately, long-acting insulin injections at night may not last until the morning. And if you inject too much, hypoglycemia will occur during sleep. It causes nightmares and even worse consequences. This is a common and serious problem. To solve this, try switching to Tresiba extended-release insulin, which lasts longer than others.
- In severe cases of diabetes, it may turn out that even an injection of Tresiba at night will not work. In this case, you will have to wake up to the alarm every time in the middle of the night, take an additional injection of insulin and fall asleep again. This is what Dr. Bernstein does. Thanks to this, he is alive and in good shape at 86 years old. If he had been lazy, complications from diabetes would have killed him long ago.
- Please note that fasting sugar in the morning is affected by the insulin you inject at night and other measures taken in the evening. The insulin you take in the morning after waking up has nothing to do with your morning fasting sugar. It will take effect later.
First of all, you need to get used to having dinner early. Eat in the evening at least 4 hours before bedtime, preferably 5 hours before bedtime. You can eat only permitted low-carbohydrate foods, with the complete exclusion of prohibited ones. If you do not follow a low-carb diet, then it is impossible to achieve normal sugar levels. No pills or insulin will help.
Read more about the products:
- Bee honey - buckwheat, white acacia, instead of sugar
- Porridge - buckwheat, rice, millet, barley and others
- Oil - butter, olive, flaxseed, coconut
- Nuts - walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, cashews, pistachios and others
- Fruits and berries
Ideally, you will have dinner around 6 pm and go to bed at 10-11 pm. As a last resort, have dinner before 7 pm, but certainly not later. How to develop this habit? Set a reminder in your phone every day at 5:30 or 6 p.m., saying it’s time for dinner, and let all your work wait. If you have dinner late, your fasting blood sugar the next morning will be high, and no pills taken at night, or even insulin injections, will help.
Today, the newest and best long-acting insulin for injections at night is Tresiba. So even he cannot overcome the negative impact of late dinners. Not to mention other types of insulin and, especially, tablets. Getting into the habit of eating dinner early is absolutely essential. This not only normalizes your blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach, but also provides other benefits. You will sleep better, get better sleep and wake up well rested in the morning.
Diabetes tablets to take at night
We've sorted out the nutrition, now let's move on to the pills. What diabetes medications help lower blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach? There is only one option here. This is metformin, and not regular, but in extended-release tablets. This is the drug Glucophage Long and its analogues.
Why do you need extended-release metformin to lower fasting sugar? The tablets are taken at night before bedtime. Regular metformin tablets last 4-6 hours, that is, their effect does not last until the morning. You don't want to wake up to an alarm in the middle of the night to take your medication, do you? But the medicine needs to act in the morning, that is, from about 3-4 o’clock to 8-9 o’clock in the morning. Because during these hours the so-called dawn phenomenon appears. It has to be extinguished with pills, or even insulin. Only extended-release metformin can cope with this task, but not regular tablets.
Metformin helps:
- patients with type 2 diabetes,
- people suffering from type 1 diabetes who are overweight.
If you are slim, thin, and athletic, you will most likely have little or no benefit from taking this medication. You need to immediately move on to insulin injections at night, which are described below. However, most diabetics who have high blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach also have excess weight and fat deposits in the body. It is beneficial for them to take metformin.
At night before going to bed, you need to take metformin, not regular, but extended-release. It will work in the body in the early hours, helping to normalize fasting sugar. Metformin is an active substance that is sold in medications under different brand names. Try imported Glucophage Long or Metfogamma. There are many more Russian-made drugs. It is better to use them secondarily. Try to take imported medicines, not Indian ones. Make sure that the instructions indicate that metformin tablets are slow-release, that is, long-acting.
How to take them? People often complain about the side effects of metformin, namely diarrhea and nausea. To prevent this from happening, you should not take the full daily dose from the first day, but start with a minimum dose, one tablet a day. Then, over the course of one to two weeks, gradually increase your dose to the maximum possible. This needs to be done gradually so that the intestines have time to get used to it.
You will have 500 or 850 mg tablets. Take them as late as possible before bed. If you have dinner early, as you should, then do not take the pills with dinner, but postpone it until later, when you are already falling asleep. Start with one tablet at night. If there is no diarrhea, then after 3 days you can try two tablets. And so on until the maximum possible dose or until your fasting sugar in the morning is stably below 5.5 mmol/l.
Let us repeat that metformin does not help diabetics with a thin, slender, athletic build. It is contraindicated for people whose diabetes has already seriously damaged their kidneys. It is useful to study the article “Tests for kidneys in diabetes” and, if necessary, take the recommended tests in the laboratory.
Long-acting insulin injections at night
For many diabetics, eating an early dinner and taking metformin at night is enough to lower their fasting sugar to normal. However, in severe diabetes, this may not be enough, and you will have to take the next step - insulin.
Many patients with type 2 diabetes desperately resist, categorically do not want to be treated with insulin, despite the fact that their sugar is high on an empty stomach or after meals, and diet and medications do not help enough. The choice here is simple. Either take insulin, or you will have to get acquainted with the complications of diabetes.
Below we describe in detail how to use insulin to reduce sugar in the morning on an empty stomach to normal, that is, to the levels of healthy people, not higher than 5.5 mmol/l. Please note that your morning fasting glucose levels are affected by the insulin you take at night and other measures you take in the evening, such as eating an early dinner and taking metformin. They need to be used all together.
The insulin you inject in the morning after waking up has nothing to do with your morning fasting sugar. It will take effect later.
People often ask, how much insulin should I inject if I wake up and find that my fasting sugar is high in the morning? In this situation, it is already too late to drink Borjomi. You had high blood sugar for several hours while you were sleeping, starting around 3-4 am. He's already done damage.
You will now inject your daily insulin. Perhaps the dose needs to be increased to bring down the elevated sugar, or it will return to normal after 9 o’clock in the morning, when the effect of the dawn phenomenon ceases. However, you had to think about sugar in the morning on an empty stomach in the evening. And tonight you can take steps to ensure that your fasting sugar levels are normal tomorrow morning.
What kind of insulin should you inject to reduce sugar in the morning on an empty stomach? And how to choose the dose? You need to inject long-acting insulin, that is, long-acting, at night before bed. Currently, the best of these drugs is Tresiba. It is the newest, lasts longer than others, but is also very expensive. If they give it to you for free or you can easily afford to buy it, then use it.
If for financial reasons you cannot inject Tresiba, then try Levemir, Lantus or Toujeo. The injection should be given as late as possible before bedtime. Just like taking metformin. And for the same reason - so that the effect of the injection would last until the morning.
How to choose a dose? On the one hand, if you inject too little insulin, your fasting blood sugar in the morning will not drop enough or not at all. On the other hand, if you take a large dose, you will have low blood sugar in the middle of the night while sleeping. Its symptoms are nightmares, moaning, grinding teeth in sleep, sweating, trembling, uncontrollable hunger, and so on.
Theoretically, a diabetic may not wake up at all if he injects himself with too much insulin. Of course, this is unlikely, but too large doses should not be taken at night. You need to select them carefully. That is, the dose of insulin should be large enough to keep sugar normal in the morning on an empty stomach, but not too large so as not to cause low sugar in the middle of the night. How to determine this dose, read the article about long-acting insulin. Or watch the video.
Unfortunately, it often happens that the maximum possible dose of insulin at night is not enough to keep blood sugar normal in the morning on an empty stomach. That is, the glucometer shows above 5.5 mmol/l, although the diabetic eats dinner early, takes metformin and is treated with insulin.
What to do in such a situation? First of all, try to switch to Tresiba. It really works better than other types of long-acting insulin. It is highly likely that switching to Tresiba will solve the problem. However, in severe type 1 diabetes with severe dawn phenomenon, even this may not be enough.
Treatment measures for severe diabetes
Patients with severe diabetes who try to maintain normal sugar levels in the morning on an empty stomach have to:
- Set an alarm in the evening for the middle of the night.
- Wake up at night with an alarm and give an extra injection of insulin.
- After that, try to fall asleep again and sleep until the morning.
This is what Dr. Bernstein does. He has lived with type 1 diabetes since he was 12 years old, since 1946. Now 86, he is in great shape, still works with patients and does tricks in the gym almost like a professional acrobat. If he had been lazy about injecting himself with insulin in the middle of the night, the complications of diabetes would have killed him long ago.
When Tresiba insulin came out, Dr. Bernstein switched to it from Levemir, but still continues to give himself an extra injection in the middle of the night so that his fasting sugar in the morning is always below 5.5 mmol/L. He takes a dose of insulin in the evening, so that at night he can only stick a needle into the skin and immediately fall asleep again. He often says that an additional injection at night is a difficult measure, but he had no other way to avoid becoming disabled and live to his age.
If you regularly have high blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach, you should not ignore this problem. Failure to take care of it can lead to the development of diabetes complications within months or years. What are these complications? Kidneys may suddenly fail, vision may decline to the point of blindness, and legs may begin to go numb and rot. Or you'll just have a heart attack.
Tests to determine glucose concentration
To determine blood glucose levels, the following diagnostic methods are available:
Blood on sugar (glucose)
The analysis requires whole blood from a finger prick. Usually the study is carried out on an empty stomach, with the exception of a glucose tolerance test. Most often, glucose levels are determined using the glucose oxidase method. Also, glucometers can sometimes be used for express diagnostics in emergency conditions.
The blood sugar levels are the same for women and men. Glycemic values should not exceed 3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l (in capillary blood).
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
This analysis does not require special preparation and can most accurately indicate fluctuations in blood glucose levels over the past three months. More often, this type of examination is prescribed to monitor the dynamics of diabetes mellitus or identify a predisposition to the disease (prediabetes).
The norm of glycated hemoglobin is from 4% to 6% .
More detailed information about the analysis for HbA1c at the link: https://sdiabetom.ru/laboratornye-analizy/glikirovannyj-gemoglobin.html
Blood chemistry
Using this study, the concentration of glucose in venous blood plasma is determined. Blood is drawn on an empty stomach. Often patients do not know this nuance, which leads to diagnostic errors. Patients are allowed to drink plain water. It is also recommended to reduce the risk of stressful situations and delay playing sports before taking the test.
The blood sugar level from a vein (in plasma) will differ by 10-11%, reference values should be in the range of 4.0-6.1 mmol/l.
Blood fructosamine
Fructosamine is a substance formed as a result of the interaction of blood proteins and glucose.
Based on its concentration, one can judge the intensity of the breakdown of carbohydrates over the last three weeks. Blood is taken for fructosamine analysis from a vein on an empty stomach. Reference values (normal) – 205-285 µmol/l
Glucose tolerance test (GTT)
In common parlance, “sugar with a load” is used to diagnose prediabetes (impaired carbohydrate tolerance). Another test is prescribed for pregnant women to diagnose gestational diabetes. Its essence lies in the fact that the patient's blood is drawn two, and sometimes three times.
The first sample is taken on an empty stomach, then 75-100 grams of dry glucose are stirred in the patient’s water (depending on the patient’s body weight), and after 2 hours the test is taken again.
Normally, the sugar concentration after exercise should not exceed 7.8 mmol/l. Otherwise, the doctor will refer the patient for re-examination or an HbA1c test.
Sometimes endocrinologists say that it is correct to carry out GTT not 2 hours after a glucose load, but every 30 minutes for 2 hours.
C-peptide
The substance that results from the breakdown of proinsulin is called c-peptide. Proinsulin is a precursor to insulin. It breaks down into 2 components - insulin and C-peptide in a ratio of 5:1.
The amount of C-peptide can indirectly judge the condition of the pancreas. The study is prescribed for the differential diagnosis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes or suspected insulinoma.
The norm of c-peptide is 0.9-7.10 ng/ml
Hyperglycemia (high sugar): causes, symptoms and treatment
Hyperglycemia can develop due to:
- decreased insulin production;
- increased binding or destruction of the hormone;
- insensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin.
More often it is a sign of diabetes mellitus (if these diseases are present, treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist), less often of other endocrine diseases, and very rarely of pancreatitis.
Clinically, hyperglycemia manifests itself:
- thirst;
- increasing weakness;
- dry mouth;
- frequent urination (the main causes of frequent urination are described here);
- changes in appetite (first increased and then decreased);
- loss of body weight;
- skin itching.
At the beginning, hyperglycemia is not detected on examination. With a long course, weight loss, the smell of acetone from the breath, peeling, dryness and reduced elasticity of the skin, traces of scratching on it, redness of the face, pustular rash are detected. The severity of the manifestations depends on the level of glucose in the blood - the higher it is, the brighter the signs. Various drugs are used to lower glucose. Thus, for patients with insufficient insulin secretion (type 1 diabetes), additional administration of the hormone from outside is indicated.
Doctor's advice
People who are accustomed to drinking sweet tea or coffee are recommended to use a sweetener, for example, Sukrazit. There is a special line of products for diabetics that can be found in any grocery store. Instead of glucose, they contain fructose. Use in small quantities is acceptable. Due to the fructose content, people with diabetes can sometimes eat a spoonful of honey, but not more than once a week.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
For type 2 diabetes mellitus, diet therapy and a sufficient level of physical activity have a good effect. If they are ineffective and blood sugar remains elevated (the tables indicate the norm for women and men before and after 60 years), doctors prescribe glucose-lowering drugs to patients.
How often should a healthy person and a diabetic check their sugar?
The frequency of testing depends on your general health or predisposition to diabetes. Individuals with diabetes I often need to test their glucose up to five times a day, while diabetes II requires testing only once a day and sometimes once every two days.
For healthy people, it is necessary to undergo this type of examination once a year, and for people over 40 years old, due to concomitant pathologies and for the purpose of prevention, it is advisable to do this once every six months.
3 tests for diabetes. Sugar - under control!
Literature
- R.B. Bazarbekova, A.K. Dosanova. Fundamentals of clinical diabetology. Patient education. Almaty, 2011.
- D. Gardner, M.I. Shobek Basic and clinical endocrinology. Book 2/Trans. from English – M: “Binom”, 2013.
- Melnichenko G.A. // Practical endocrinology. – M: Medicine, 2010.
- P. A. Bakumov, M. V. Levkina // Perioperative management of patients with diabetes mellitus. Medicinal Bulletin. No. 6 (46) 2012 Volume 6.
- Neymark M.I. Perioperative period in endocrine surgery. – M: Medicine, 2003.
Symptoms of changes in glucose levels
Glucose can either rise sharply when there is insufficient amount of insulin administered or when there is an error in the diet (this condition is called hyperglycemia), or fall when there is an overdose of insulin or glucose-lowering drugs (hypoglycemia). Therefore, it is so important to choose a good specialist who will explain all the nuances of your treatment.
Let's consider each state separately.
Hypoglycemia
The state of hypoglycemia develops when the blood sugar concentration is less than 3.3 mmol/l. Glucose is a supplier of energy for the body; brain cells react especially acutely to a lack of glucose, hence one can guess the symptoms of such a pathological condition.
There are plenty of reasons to lower your sugar levels, but the most common are:
- insulin overdose;
- doing strenuous sports;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and psychotropic substances;
- lack of one of the main meals.
The clinical picture of hypoglycemia develops quite quickly. If the patient experiences the following symptoms, he should immediately inform his relative or any passerby:
- sudden dizziness;
- severe headache;
- cold clammy sweat;
- unmotivated weakness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- confusion;
- strong feeling of hunger.
It is worth noting that patients with diabetes get used to this condition over time and do not always soberly assess their overall well-being. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically measure blood glucose levels using a glucometer.
It is also recommended that all diabetics carry something sweet with them in order to temporarily relieve the lack of glucose and prevent the development of an acute emergency coma.
Hyperglycemia
The diagnostic criterion according to the latest WHO (World Health Organization) recommendations is considered to be a sugar level reaching 7.8 mmol/l or higher on an empty stomach and 11 mmol/l 2 hours after eating.
If this condition is not stopped, over time the body adapts to the excess sugar, and the symptoms are muffled. Due to hyperglycemia, various complications of diabetes mellitus develop.
A large amount of glucose in the bloodstream can lead to the development of an emergency condition - hyperglycemic coma. To prevent the development of this condition, you need to be aware of factors that can increase blood sugar. These include:
- incorrectly reduced insulin dosage;
- inattentive use of the drug with missing one of the doses;
- eating carbohydrate foods in large quantities;
- stressful situations;
- cold or any infection;
- systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages.
To understand when to call an ambulance, you need to know the signs of developing or ongoing hyperglycemia. The main ones:
- increased feeling of thirst;
- frequent urination;
- severe pain in the temples;
- increased fatigue;
- taste of sour apples in the mouth;
- visual impairment.
Hyperglycemic coma often ends in death; it is for this reason that it is important to be careful in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Decoding the result
Increased glucose levels (hyperglycemia)
Observed in the following diseases and conditions:
- Diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy).
- Physiological hyperglycemia, causes: moderate physical activity, strong emotions, stress, smoking, adrenaline release after injection.
- Active infectious process.
- Trauma, recent surgery.
- Endocrine system diseases:
- a) pheochromocytoma - a tumor of the adrenal glands that produces adrenaline and is characterized primarily by a persistent increase in blood pressure; b) thyrotoxicosis – a pathological condition in which the thyroid gland begins to produce too many hormones (thyroxine and/or triiodothyronine); c) acromegaly is a disease associated with a violation of the synthetic activity of the pituitary gland (a gland located in the brain). It is characterized by excess production of growth hormone, leading to changes in facial features, enlargement of the hands and feet. d) gigantism - a pathology, also associated with the pituitary gland, is hereditary in nature, the first manifestations occur in early adolescence; e) Itsenko-Cushing syndrome is a condition in which the adrenal glands produce excessive amounts of cortisol. Characterized by a violation of carbohydrate metabolism; f) somatostatinoma - a tumor of hormonally active cells of the pancreas or cells located in the wall of the duodenum, secreting somatostatin; g) polycystic ovary syndrome - a symptom complex accompanied by the formation of cysts in the ovaries, menstrual irregularities, excess body weight, and infertility.
- Diseases of the pancreas (acute and chronic pancreatitis, pancreatitis with mumps, cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, pancreatic neoplasms).
- Chronic liver and kidney diseases.
- Cerebral hemorrhage, myocardial infarction.
- Taking thiazide diuretics, beta blockers, caffeine, oral contraceptives, glucocorticoids (a full list is presented in the section “What may affect the results”).
Low glucose levels (hypoglycemia)
- Patients with diabetes may experience low glucose levels in the following situations:
- a) insulin overdose; b) overdose of drugs that lower blood glucose levels; c) increased physical activity; d) skipping meals; d) drinking alcohol.
- Severe liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, carcinoma, hemochromatosis).
- Tumor diseases: pancreatic cancer, adrenal cancer, stomach cancer, fibrosarcoma.
- Reactive hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood glucose levels decrease 1-3 hours after eating.
- Dietary disorders (prolonged fasting, malabsorption syndrome - impaired absorption of nutrients due to intestinal diseases).
- Taking large doses of alcohol.
- Intense physical activity.
- Feverish conditions.
- Taking a number of medications:
- a) beta blockers (atenolol, propranolol, etc.) – used in the treatment of coronary heart disease, hypertension; b) flecainide and quinidine (drugs for arrhythmia); c) indomethacin (painkiller); d) insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs; e) some antibiotics, antifungal drugs; e) aspirin; g) a number of antiepileptic, anti-anxiety drugs (pregabalin); h) monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of tumor or autoimmune diseases.
How to prevent the development of emergency conditions?
The best way to treat diabetes emergencies is to prevent them from developing. If you notice symptoms of an increase or decrease in blood sugar, then your body is no longer able to cope with this problem on its own, and all reserve abilities have already been exhausted. The simplest preventive measures for complications include the following:
- Monitor glucose levels using a glucometer. Buying a glucometer and the necessary test strips will not be difficult, but will save you from unpleasant consequences.
- Take hypoglycemic medications or insulin regularly. If the patient has poor memory, works a lot, or is simply distracted, the doctor may advise him to keep a personal diary, where he will put a check mark next to the appointment he took. Or you can set a reminder notification on your phone.
- Avoid skipping meals. In every family, having lunch or dinner together more often becomes a good habit. If the patient is forced to eat at work, it is necessary to prepare a container with ready-made food in advance.
- Balanced diet. People with diabetes should be more careful about what they eat, especially foods rich in carbohydrates.
- Healthy lifestyle. We are talking about playing sports, refusing to take strong alcoholic drinks and drugs. This also includes getting a healthy eight hours of sleep and minimizing stressful situations.
Diabetes mellitus can cause various complications, such as diabetic foot, and reduce quality of life. That is why it is so important for every patient to monitor their lifestyle, go to preventive appointments with their attending physician and follow all his recommendations on time.
Support the author. Share with your friends:
What may affect the results
Eating food, alcohol, certain medications, fatigue, or stress can affect your blood glucose levels.
Medicines that may cause increased blood glucose levels.
- Corticosteroid hormones (another name is glucocorticoids). They are intended to treat diseases caused by inflammation: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, allergies. Systemic (tablet form, intravenous or intramuscular) steroids include hydrocortisone and prednisolone. However, topical steroids in creams and ointments or inhaled steroids (used to treat asthma) do not significantly affect glucose levels.
- Medications for anxiety, attention deficit disorder, depression and other mental health problems.
- Oral contraceptives (birth control pills).
- Some medications to normalize high blood pressure.
- Statins, used to lower cholesterol levels.
- Adrenaline (can be used for severe allergic reactions).
- High doses of non-inhaled asthma medications (given intravenously for severe attacks).
- Isotretinoin (used to treat acne and other dermatological conditions).
- Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressant (prescribed after organ transplantation).
- Some antiviral medications prescribed to patients with HIV and hepatitis C.
- Pseudoephedrine (a decongestant found in some cold and flu medications).
- Cough syrups (many contain sugar).
- Niacin (vitamin B3).
In addition to medications for the treatment of diabetes, the following medications and dietary supplements can reduce glucose levels:
- Aspirin.
- Aloe.
- Magnesium salicylate.
- Quinine.
To get the most reliable result, it is recommended to refrain from taking these medications until the test is taken, having agreed upon the timing of drug withdrawal with your doctor.
Female sex hormones also affect glucose levels, so a few days before your period, your glucose levels may be higher than on other days.
You can take a blood glucose test at the nearest INVITRO medical office.
A list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory research is presented in the “Addresses” section. Interpretation of study results contains information for the attending physician and is not a diagnosis. The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: medical history, results of other examinations, etc.
About the conditions of preparation for the study
To obtain objective results of a basic analysis on the eve of blood sampling, the patient must:
- stop using medications;
- do not eat sweet foods for dinner and do not drink alcoholic beverages;
- limit sports and other physical activities.
The main condition is to adhere to a fasting regime for 8–12 hours. On the day of the test, it is not recommended to perform oral hygiene and use chewing gum.
Sugar measurement
Blood plasma or serum obtained through defibrination is examined. Reliable information about the state of glycemia can be obtained from the results of the analysis of a biofluid taken on an empty stomach from a vein or finger. The difference between the indicators of venous and capillary blood is 12% and is taken into account when assessing the final data.
Blood is drawn using a sterile disposable instrument.
Measuring glucose levels after meals (postprandial glycemia) is carried out as part of the diagnosis of insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, prediabetic conditions, and in pregnant women with suspected GDM. Diabetics control sugar after meals on their own.
Important! Any food entering the body changes the composition of the blood. Products are broken down into simple components, and the released glucose is absorbed through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream. Therefore, after eating, the glycemic index always increases.
The unit of glucose measurement in the Russian Federation is millimoles per liter. You can measure how many mmol is in your blood yourself using a portable glucometer or a multifunctional smart bracelet. Laboratory techniques for determining glycemia are more complex and accurate.
Blood sampling for sugar is carried out in any clinic upon the direction of a doctor or in a paid clinical diagnostic center at the request of the patient. A healthy person and a diabetic patient have different blood glucose levels. For diabetics, separate standards are provided, according to which the stage of compensation of the disease is assessed.
The stage of diabetes mellitus is defined as:
- Initial or compressed stage. Hyperglycemia can be corrected with glucose-lowering medications. Blood sugar values are close to normal.
- Subcompensation. It is characterized by moderate severity of the disease with the development of complications. It is not always possible to maintain normal glucose levels.
- Decompensation. The final stage of the disease with persistent hyperglycemia and concomitant vascular diseases.
In the decompensated stage, there is a risk of developing a diabetic coma.