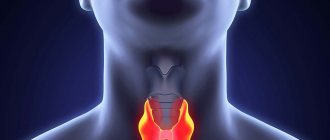
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is a pathological condition characterized by an increase in the size of the organ, accompanied by disturbances in its functions. There are diffuse and nodular hyperplasia.
Diffuse hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is a uniform, symmetrical enlargement of the organ. Over time, most of these conditions develop into a nodular form.
Single or widespread nodes cause uneven enlargement of the gland. Their appearance indicates the progression of the disease. Hyperplasia may not be accompanied by a visible increase in size or swelling in the neck area. However, even a slight enlargement of the gland can cause symptoms associated with compression of surrounding organs.
This condition affects approximately 740 million people on Earth. Its prevalence depends on the region of residence: 32% - eastern Mediterranean, 20% - Africa, 15% - Europe, Southeast Asia - 12%, western Pacific coast - 8%, America - 5%.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Chronic iodine deficiency plays the role of the etiological (primary cause) factor in the development of a disease such as diffuse nodular hyperplasia. But at the same time, there are a number of factors that provoke the appearance and progression of the disease. The main ones include:
- nutritional iodine deficiency;
- burdened hereditary history;
- radioactive exposure;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- chronic infections and frequent colds;
- hypercalcemia;
- long course of medications that interfere with the absorption of iodine; pituitary adenoma;
- nodular colloid goiter is a common cause of the development of nodular hypertrophy;
- pregnancy is a physiological cause of the development of hyperplasia;
- gender predisposition - women and older people suffer from this disease much more often.
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland during pregnancy is a compensatory reaction of the body to bearing a fetus. This is due to the fact that the thyroid gland in the developing child does not yet function, and, therefore, does not secrete the necessary amount of hormones for the development of organs and systems (in particular the nervous system). The mother's thyroid gland takes on the entire load. But we cannot exclude the development of a pathological process in the gland after the birth of the baby if the level of hormones has not returned to normal.
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland during pregnancy changes the degree of its activity depending on the gestational age. Thus, an increase in the size of the hormone-producing organ in the first trimester is considered a physiological norm. And its progressive growth in the II-III trimesters may indicate a worsening of the disease that existed even before the child was conceived.
Diffuse hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is increasingly common in children over 6 years of age. The main reasons for the development of this disease in children of different ages are a lack of iodine in the body, the lack of preventive work to prevent iodine deficiency, as well as unfavorable environmental conditions, including a persistent deficiency of iodine in water and soil in many regions.
In most cases, thyroid dysfunction in a child is accompanied by additional somatic diseases, as well as psycho-emotional disorders.
Toxic goiter and motherhood
Graves' disease rarely begins during pregnancy, but despite the traditional prohibition of taking medications in this state, some women are still forced to receive treatment. It is understandable that many of them are interested in the appropriateness of breastfeeding in this case. Young mothers should know: there is no danger to the health of their child, since only small amounts of the drug can pass into breast milk.
If pregnancy occurs while diffuse goiter is at a more severe stage, the woman may experience the following complications:
- Preeclampsia.
- Placental abruption.
- Miscarriage.
- Heart failure.
In this case, the baby's risk of developing health problems such as endocrine system diseases and low birth weight increases, and the birth itself may be premature; Stillbirths often occur.
Clinical picture (symptoms of thyroid hyperplasia)
The clinical symptoms of a phenomenon such as diffuse hyperplasia of the thyroid gland do not have a clear picture on the basis of which a diagnosis can be made without additional laboratory and instrumental methods of examining the patient. But there are a number of symptoms that are observed during this pathological process, and to which special attention should be paid. Among the main signs that distinguish thyroid hyperplasia from a broad group of thyroid diseases are:
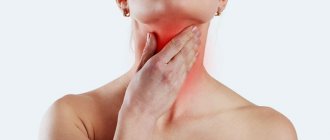
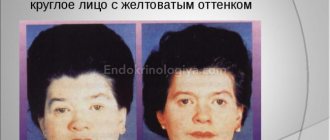
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, in advanced cases – a visual change in the cervical contours (see photo above);
- sensation of a foreign body (“coma”) in the throat;
- feeling of pressure in the neck;
- cough not caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract;
- the appearance of arrhythmias (including paroxysmal);
- feeling of heat (feeling of hot flashes);
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- tremor of the hands;
- dilation of pupils regardless of light exposure;
- increase in neck volume;
- frequent mood swings, sleep disturbances, increased anxiety;
- headaches, including migraine-like ones;
- sudden changes in weight not associated with changes in diet and nutrition;
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland in children also manifests itself in the form of a developmental delay from peers. Both the physical and mental health of the child are affected.
conclusions
After reading the article, you can draw the following conclusions:
- thyroid hyperthyroidism is an abnormal increase in the number of its cells, the cause of which lies in the inability of this organ to produce iron thyroid hormone in the required quantities;
- signs of the disease - compaction in the larynx, discomfort when swallowing;
- if you ignore diffuse focal hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland, this entails complications in the form of transition of the disease to new stages;
- you should not bring the matter to surgery, since the removal of such an important organ or part of it is irreparable harm to the patient;
- If a pregnant woman experiences all the symptoms described above, then she simply needs to contact an endocrinologist in order to protect her unborn child.
- First of all, people living in the Chernobyl zone, as well as those who have relatives with unhealthy neoplasms, should think about undergoing the examination.
- treatment and prevention - taking iodine-containing drugs and products of marine origin, reducing stress, maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Forms of the disease
The patient’s knowledge of what thyroid hyperplasia is should not be reduced only to a general concept of pathology. It is important to know what forms of the disease exist and how they differ from each other. There are 3 forms of the pathological process:
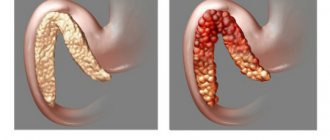
- diffuse – uniform growth of the entire thyroid gland is observed;
- nodular (focal) - gland tissue grows locally, within one lobe, forming nodes on the surface. The nodes have a fairly hard consistency and are easily palpated. Their formation is due to uneven growth of glandular tissue;
- diffuse-nodular - against the background of uniform growth of the entire organ, areas of compaction of a certain lobe are noted.
Depending on the localization of hyperplastic processes, we can distinguish:
- one-sided;
- bilateral hyperplasia.
The form and extent of the pathological process are one of the main parameters that determine how to treat the disease. The treatment regimen is strictly individual for each individual patient.
Why you should be hypervigilant
Even if you previously felt your neck on your own and did not find any signs of pathology on it, this does not always mean that you are healthy and there is no need to undergo an examination. It is better to waste one day of your life visiting an endocrinologist if you are not sick, than to later face problems that will certainly arise at a later stage. Endocrinologists note that late presentation of patients always leads to poor prognosis for their recovery. When a pathology is detected, they sometimes resort to a biopsy - removal of the affected area of tissue from the swollen thyroid gland for analysis and study of its structure. First of all, this is done in order to determine whether the tumor is malignant or not.
Degrees of hyperplasia
Currently, the following degrees of thyroid hyperplasia are distinguished depending on the severity and neglect of the pathological process:
- Grade 0 – there is a slight enlargement of the gland, diagnosed by chance;
- Grade 1 – has no clinical symptoms, most often it is an accidental finding during a routine or preventive ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland. A moderate enlargement of the thyroid gland on palpation can be noted;
- 2nd degree – the enlarged gland can be palpated, but does not cause discomfort to the patient;
- 3rd degree - the hypertrophied organ is noticeable from a distance, especially when turning the head to the side. The disease has pronounced clinical symptoms. The enlarged thyroid gland begins to compress nearby tissues and organs: trachea, esophagus;
- 4th degree – the neck is severely deformed. Often at this stage toxic or non-toxic goiter is diagnosed;
- Grade 5 – a significant enlargement of the glands, causing the patient discomfort not only when breathing and swallowing, but also in a state of complete rest. It is at this degree that foci of malignant neoplasms can be diagnosed.
Traditional methods
Many often turn to traditional medicine and, thus, consciously avoid traditional medicine, without realizing the full severity of their disease. It is worth emphasizing that in relation to this disease, the effectiveness of traditional methods does not receive scientific approval. Treatment of this pathology with some folk methods can even be dangerous.
For example, in no case is it recommended to self-prescribe large dosages of iodine, regardless of whether the medicine is of organic or inorganic origin. Since with this type of hyperplasia, focal formations have already formed in the tissues, against the background of which unjustified consumption of iodine can lead to thyrotoxicosis. Thus, many folk recipes often turn out to be ineffective or completely useless for this disease, so there is no way to delay professional treatment from an endocrinologist.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose thyroid hyperplasia only on the basis of a carefully collected medical history, examination, and the results of laboratory and instrumental studies . A modern diagnostic algorithm for searching for thyroid diseases includes:
- laboratory research methods: determination of the amount of iodine in excreted urine;
- determining the presence of autoantibodies to the thyroid gland by immunological analysis;
- blood test for hormones: TSH, T4;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid and parathyroid glands;
The first 2 laboratory methods are widely used in pediatric endocrinology.
When diagnosing thyroid pathologies in children, important attention is paid to the age of the child. The number of years, living conditions, the presence of chronic diseases are important parameters that a doctor should evaluate.
Why is the disease dangerous?
The progression of the disease is fraught with complications, some of which lead to death. The severity of the consequences is determined by the reasons for the growth of the thyroid gland. Common complications include:
- oligophrenia in children;
- delayed sexual development;
- functional thyroid insufficiency;
- intestinal obstruction;
- ischemic stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- tachycardia;
- gynecomastia in men (enlarged mammary glands);
- osteoporosis;
- muscle weakness;
- menstrual irregularities;
- anorexia, etc.
Compression of nerve endings by an enlarged organ leads to disruption of the innervation of the vocal cords and smooth muscles of the esophagus. Because of this, the swallowing reflex is disrupted and pain occurs. The growth of the thyroid gland during pregnancy is dangerous for heart defects and thyroid dysfunction in the unborn child.
Treatment of hyperplasia
When a doctor is faced with the question of how to treat thyroid hyperplasia, he must evaluate all the important parameters of the patient: gender, age, physiological characteristics, the presence of chronic diseases, the degree of neglect of the pathological process. Only then can an individual treatment plan for the patient be drawn up. For example, stage I thyroid hyperplasia is treated conservatively, while advanced stages are treated exclusively with surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment (drug treatment)
Conservative treatment of a disease such as diffuse hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is based on such treatment methods as:
- hormone replacement therapy with thyroid hormones ( Levothyroxine );
- use of iodine-containing drugs ( Potassium iodide, Iodomarin® 200 , etc. );
- prescription of thyreostatic drugs;
- irradiation with radioactive iodine.
Thyroid hyperplasia during pregnancy is treated exclusively with medication. Pharmacotherapy is aimed at normalizing the level of hormones in the body of the expectant mother. Treatment tactics are determined by a qualified specialist who monitors and manages the pregnancy of a particular patient. When choosing a group of medications and the dosage of the drug, the doctor is guided by the degree of activity of the pathological process, as well as possible risks for the mother and fetus.
As a rule, pregnant women are prescribed a course of iodine-containing medications and herbal medicine. Surgery is performed according to strict indications (grade 3-5 diffuse toxic goiter) and in the early stages, not exceeding 14 weeks of pregnancy.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated if the gland is very large and puts pressure on nearby organs, disrupting their function. The essence of surgical treatment is partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland. The scope of the operation is determined by the surgeon, assessing the type, degree of hyperplasia and degree of compression.
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland, which is treated surgically in childhood according to strict indications, after a course of conservative therapy should reduce the severity of clinical signs by eliminating the hypothyroid state. Surgical intervention on the organ in children is indicated only in the absence of the effectiveness of medication, suspicion of malignancy or excessive enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment with folk remedies for hyperplastic processes in the endocrine glands is additional in nature and is used as a secondary method of influence. Thus, thyroid hyperplasia, treatment of which with folk remedies is also popular among a large group of patients, is one of those pathologies for which alternative medicine is one of the additional components of combination therapy.
Patients who are faced with a condition such as thyroid hyperplasia, clearly understand what it is, and regularly visit their doctor, can turn to several popular recipes, including:
- red geranium tincture . To prepare, you need to fill a three-liter container with clean fresh red geranium leaves and pour in 500 ml of vodka. Cover tightly with a lid and place the vessel out of reach of sunlight for 3 weeks. After the specified time has passed, shake the jar well and let it brew for another 7 days. The resulting tincture should be carefully strained and taken 1 tbsp. spoon half an hour before meals 1 time per day. The course of treatment should not exceed 30 days;
- infusion of hellebore root . Pour 10 grams of dry crushed plant root into 500 ml of boiling water (it is advisable to use a thermos as a container). Leave to infuse for 8 hours. Strain the infusion through a fine sieve and take 1 teaspoon 25 minutes before meals for a week and a half, then increase the dosage to 2 teaspoons for the next week and a half. And after a month, take 4 teaspoons. The course of treatment is six months;
- iodine network . The simplest and most accessible way to influence the organ and replenish iodine deficiency. Using a cotton swab, previously soaked in iodine tincture, draw a grid in the area of the projection of the thyroid gland overnight. Perform the procedure every evening for 1.5-2 weeks.
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland during pregnancy and its treatment with traditional recipes are concepts that should be discussed with the woman’s attending physician. Many medicinal herbs can harm the expectant mother and baby at a certain gestational age.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is also required for patients suffering from compression of such important organs as the esophagus and trachea by the gland. Surgery is also required for those patients in whom atypical cells were found in the altered gland tissue during histological examination.
The second degree of the disease is characterized by a significant increase in nodal changes that can grow from three centimeters or more. In these cases, surgery to remove the nodes will not be the only step towards recovery, since they can grow again. In this regard, the further fight against relapse of the disease will consist in eliminating the pathogenic factors that provoke thyroid disease.
Often surgery is the only option to save the patient's life. This is explained by the fact that the advanced course of the disease can lead to the fact that a growing tumor in the gland can degenerate into a malignant manifestation.
Prevention
The basis of preventive measures aimed at preventing diseases such as thyroid hyperplasia in children and adults is a properly balanced diet rich in iodine. Particular attention is paid to seafood, nuts, dairy products, and beef. It is recommended to replace regular salt in your daily diet with iodized salt.
According to WHO, it is recommended to dose iodine preparations per day as follows:
- children - 100 mcg;
- pregnant and lactating women - 250 mcg;
- adults – 200 mcg.
An important role is given to a correct lifestyle, as well as maintaining the body’s defenses at a high level.
Products containing iodine
Few people know which foods contain iodine. So, this substance is present in the following products:
- in iodized salt. This is the most common and affordable of these products. You should take it not just as a medicine, in small doses, but completely replace regular salt in your diet with it. Fortunately, there are no special taste differences between iodized salt and regular salt; medicinal salt just costs a little more;
- in chicken eggs;
- in seafood such as mackerel, hake, and regular herring;
- already in less accessible seafood, such as squid and mussels, but they contain more iodine than fish;
- in edible seaweed.