Kholin is an essential nutrient needed for optimal health.
It plays a key role in maintaining brain function, heart health, and liver function. This substance is also extremely important during pregnancy.
Cases of true choline deficiency are quite rare. However, many residents of Western countries often receive insufficient amounts of this nutrient (below the recommended intake). ()
To get more choline into your diet, add more choline-rich foods to your diet, such as salmon, eggs, broccoli and cauliflower.
Record-breaking foods for choline content
The human liver is capable of independently synthesizing choline in the form of phosphatidylcholine. Natural choline is not enough for the body. To meet your vitamin needs, you should take foods that contain choline.
The leader in choline content are egg yolks of any animal. For example, 1 piece of chicken yolk contains 172 mg of choline (34% of the daily value). There is also quite a lot of choline in liver (and other offal), chicken breast, and fish. Beans are the leading plant products.
Egg Yolk Powder: 2403 mg Raw: 820 mg
Beef kidneys513 mg
Liver Beef: 426 mg Chicken: 326 mg Turkey: 220 mg
Eggs Chicken: 293 mg Goose: 263 mg Quail: 263 mg Duck: 263 mg
Shrimp135 mg
Chicken breast117 mg
Soy116 mg
Fish Pink salmon: 113 mg Salmon: 112 mg Sockeye salmon: 112 mg Coho salmon: 109 mg Herring: 104 mg Mackerel: 101 mg
Beans97 mg
Lentil96 mg
| + 16 more popular foods rich in choline (mg) | |||
| Peas | 95 | Cashew | 61 |
| Chicken | 91 | Pumpkin seeds | 63 |
| Beef | 86 | Sunflower seeds | 55 |
| Flaxseeds | 78 | Buckwheat | 54 |
| Pork | 76 | Almond | 52 |
| Sardines | 75 | Hazelnut | 46 |
| Pistachios | 72 | Oats | 40 |
| Peanut | 65 | Corn | 29 |
View the entire table of herbal products 290+ ➤
View the entire table of animal products 100+ ➤
Food sources
Rich sources of choline include: ()
- Beef liver - 68 g contains 290 mg of choline
- Chicken liver – 68 g contains 222 mg
- Eggs - 1 egg contains 113 mg
- Fresh cod – 85 g contains 248 mg
- Salmon -110 g contains 62.7 mg
- Cauliflower - half a glass contains 24.2 mg
- Broccoli - half a glass contains 31.3 mg
- Soybean oil - 1 tablespoon contains 47.3 mg
One hard-boiled egg contains up to 25% of the daily requirement of choline, and one serving of beef or liver (85 grams) provides the daily requirement for a woman and almost completely for a man. (, )
Daily intake of choline for women, men and children
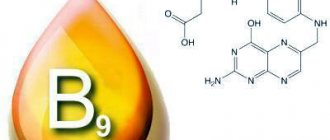
The norm for choline (vitamin B4) is 550 mg for men, and 425 mg for women over 18 years of age.
*Recommendations are given in milligrams (mg/day). The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has issued general recommendations for EU countries. The National Academy of Medicine (NAM) has made recommendations that apply in the United States, Australia, and New Zealand.
| Categories of people | EFSA standard (EU), mg | NAM standard (USA), mg | Upper limit, mg |
| 0-6 months | Not installed | 125 | Not installed |
| 7-12 months | 160 | 150 | Not installed |
| 1-3 years | 140 | 200 | 1000 |
| 4-6 years | 170 | 250 | 1000 |
| 7-8 years | 250 | 250 | 1000 |
| 9-10 years | 250 | 375 | 1000 |
| 11-13 years old | 340 | 375 | 2000 |
| Men | |||
| 14 years | 340 | 550 | 3000 |
| 15-18 years old | 400 | 550 | 3000 |
| 19+ years | 400 | 550 | 3500 |
| Women | |||
| 14 years | 340 | 400 | 3000 |
| 15-18 years old | 400 | 400 | 3000 |
| 19+ years | 400 | 425 | 3500 |
| Pregnancy | 480 | 450 | 3500 |
| Lactation | 520 | 550 | 3500 |
Source: en.wikipedia.org []
Summarize
- Choline is an essential nutrient needed for optimal health.
- It may play a key role in healthy brain function, heart health, liver health, and a healthy pregnancy.
- Although actual deficiency is rare, many people do not get enough of this nutrient.
- To increase your intake, consider eating more choline-rich animal and plant foods such as organ meats, fish, eggs, broccoli and cauliflower.
Tags: Choline
- Related Posts
- Quercetin: what it is, properties, products, dosage, side effects
- 9 most important eye vitamins for improving vision: list
- 4 Potential Side Effects of Excess Folic Acid
« Previous entry
Why do we need choline?
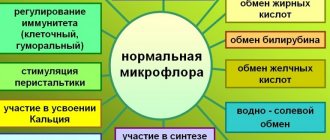
Choline ensures normal metabolism, optimal functioning of the intestines and other internal organs. Without vitamin B4, complete transmission of nerve impulses is impossible.
In addition, choline takes part in a number of important physiological processes:
- Renewal of the cellular structure of tissues after toxic injuries from both toxic substances and pharmaceuticals and drugs.
- Control of metabolism, fat excretion, reduction of cholesterol parameters.
- Prevents the destruction of nerve fiber cells.
- Activates the regeneration of the liver structure.
- Suppresses the formation of intraorgan stones.
- Reduces fatty acid levels.
- Participates in the production of methionine.
- Has a beneficial effect on myocardial function.
- Strengthens pancreatic cells responsible for producing insulin.
- Stimulates reproductive function.
- It has a beneficial effect on the condition of patients with diabetes.
[Video] Medical consultant of NPTsRIZ, geneticist, Ph.D. Irina Yuryevna Saburova talks about the mechanisms of action of choline:
Physicochemical characteristics
Chemical formula of the substance: C5H14NOX, or [ (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OH ] X−.
The structural formula of choline is presented below:
Although choline chloride is used for medical purposes, its structural formula is:
Another name for vitamin B4 is trimethylethanolamine. It is a colorless substance with a strong odor. It is highly soluble in water, therefore it is classified as a water-soluble compound. Vitamin B4 destruction occurs at temperatures above 180C. Reacts with many acids to form salts.
This video explains the properties of choline better:
What diseases does choline deficiency lead to?
Insufficient concentration of vitamin B4 in the body provokes the development of hepatosteatosis (non-alcoholic liver damage) and damage to muscle fibers []. Medical observation of a group of 57 adults showed that a decrease in choline in consumed foods led to the development of negative liver symptoms in 77% of men, 44% of premenopausal women and 80% of menopausal women [].
A study of postmenopausal women led to the conclusion that choline deficiency leads to damage to muscle tissue and the liver. These symptoms were recorded in 73% of study participants. The negative manifestations disappeared after the diet was adjusted [].
The intake of choline into the body of a pregnant woman is extremely important for the full formation of the child’s neural tube. Observations suggest that following a diet high in choline during the period of conception prevents the formation of neural tube defects in the fetus []. If during pregnancy a woman’s body lacks vitamin B4, the likelihood of developing preeclampsia, premature birth of the baby, and the baby becoming underweight increases [].
Of course, most people don't count the choline content of the foods they eat. The body of a healthy person has enough of its own vitamin and what it receives with food. For this reason, choline deficiency is extremely rare.
At-risk groups
Choline deficiency is most often detected in certain categories of patients:
- Pregnant women.
Observations by obstetricians and gynecologists indicate that at least 90-95% of all pregnant women receive less choline than they need []. A reduced concentration of choline is observed in the body of women during pregnancy and lactation when they do not receive additional folic acid. A lack of vitamin B4 in the blood is observed against the background of low levels of vitamin B12.
- Persons with genetic characteristics
. Changes in the structure of genes responsible for the metabolism of choline, methionine and folic acid negatively affect the synthesis and absorption of the vitamin [10-11].
- Patients receiving parenteral nutrition.
The use of total parenteral nutrition over a long period of time causes a decrease in the level of choline in the blood in children and adult patients. In children, these indicators are at least 5.7 nmol/ml, in adults - 5 nmol/ml. Deviations from the norm can cause obesity and liver dysfunction [12-13].
- Athletes involved in endurance sports.
Long-term endurance exercise, such as long-distance running, reduces choline concentrations [].
- Alcoholism
. Persons who drink alcohol frequently and in significant quantities suffer from choline deficiency. Signs of vitamin deficiency appear intensely with an inadequate diet [].
- Postmenopausal women.
Estrogens support normal choline production. A decrease in hormone levels causes the likelihood of a drop in the concentration of a vitamin compound [].
Impact on Heart Health
High choline intake is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. ()
Folates and choline help the body convert the amino acid homocysteine into methionine.
Thus, insufficient intake of folate or choline can lead to the accumulation of homocysteine in the blood.
Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood are associated with a greater risk of heart disease and stroke. ()
However, the evidence for this hypothesis is mixed.
Although choline may lower homocysteine levels, the relationship between choline intake and heart disease risk is not clear. (, , , , , )
Conclusion:
Choline helps reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering homocysteine levels. However, the evidence for this hypothesis is mixed.
The benefits of choline for various diseases
Improving memory and cognitive functions of the brain.
Large-scale observations prove that providing the body with choline stimulates brain functions, improves mental processes and information analysis [17-18]. Subjects aged 50 to 85 years received 1000 mg of choline per day. This had a positive effect on long-term and short-term memory[].
Another study lasted 6 months. Patients diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease received phosphatidylcholine. Improvements in memory processes were recorded in this group []. Notably, this effect was not observed in healthy participants or patients with dementia.
Stimulating brain development in the fetus.
Most of the studies showing the positive effects of choline on brain development have been conducted on animals []. However, even small observations of people make it possible to formulate similar conclusions.
A laboratory experiment involving 1,210 pregnant women found that choline supplementation in the second trimester of pregnancy was associated with higher memory scores after 7 years []. It is noteworthy that at the age of up to 3 years, the activation of mental performance in children is not associated with choline [].
In another study, 750 mg of choline per day was given to 99 pregnant women. The vitamin was offered to them from 18 weeks to 3 months of pregnancy. No significant improvements in brain and mnemonic processes were found in expectant mothers [].
Stable psyche
. The positive effect of choline in the treatment of mental disorders has been recorded. Medical observation proves that low concentrations of choline in the blood cause the development of anxiety, but do not affect the appearance of depressive conditions []. The level of choline acts as an indicator, a differential sign in the diagnosis of certain mental mood disorders. In the treatment of bipolar disorder, the administration of choline relieves manic symptoms in patients [].
Reduces the risk of cancer.
Scientific experiments prove that women who consume sufficient amounts of foods with choline suffer from breast cancer much less frequently [27-28]. Observations of 1508 study participants showed that the introduction of a high amount of choline into the diet helped reduce the incidence of breast cancer by 24% [].
However, the effect of choline on cancer development should be continued. For example, eggs contain large amounts of choline and cholesterol, which are detected by histological analysis of prostate cancer cells. From 1994 to 2008, a large-scale study was conducted involving 27,607 men who consumed more than two eggs per week. In 2011, observational results were published that showed an 81% increase in the risk of prostate cancer, compared with men who consumed less than ½ egg per week.
A follow-up study of 47,896 men demonstrated that excessive levels of choline in the blood caused a 70% higher chance of developing prostate cancer.
Reducing the risk of neural tube defect in the fetus
. A sufficient intake of choline into the body of a pregnant woman reduces the likelihood of neural tube defects in the child. Observations of women taking vitamin B4 in high doses before conception showed that in their children, disturbances in the formation of the neural tube appear 51% less often []. Observations of pregnant women whose diets contain few choline foods indicate that they are twice as likely to have children with neural tube defects [].
The combined intake of choline and folic acid prevents the development of neurological abnormalities and dementia in a child. Based on the results of numerous observations, the American Academy of Pediatrics in 1985 recommended the addition of vitamin B4 to infant formula. For 100 calories of artificial nutrition there should be 7 mg of choline.
Buying phosphatidylcholine: rules of choice
Which choline dietary supplement is better to buy - from soybean or sunflower oil? The first bioregulator is obtained by processing the feedstock at low temperatures. The drug preserves vitamins A and E, complex lipids and isoflavones, which are similar in structure to estrogens - the hormones of the female body.
Advice. Expectant mothers during pregnancy should pay special attention to the content of phytoestrogens. The substance improves the functionality of the reproductive system, but in large quantities it can adversely affect the development of the fetus.
Sunflower phosphatidylcholine is extracted from the oil of the plant. The product is healthier than soy and does not cause allergies or negative reactions in the body. Suitable for children.
Judging by the reviews, many buyers try to take sunflower dietary supplements, fearing the use of genetically modified soybeans in supplements.
PS sunflower, 100 mg, capsules from Healthy Origins
Very high quality phosphatidylcholine, an excellent and inexpensive analogue of Essentiale. Buyers note an improvement in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the disappearance of discomfort in the right side after the first course of treatment.
Moreover, there are reviews claiming that this choline compound eliminated age spots and acne on the body. For many, their skin condition has improved, the oiliness in the T-zone has gone away, and their complexion has evened out.
You can buy Healthy Origins phosphatidylcholine on iHerb for RUB 1,917. with discount.
Phosphatidylcholine, 420 mg, capsules from Source Naturals
The best soy bioregulator. It does not contain GMOs, as is directly stated in the instructions, it is highly effective and completely safe. The product contains 3 times more choline than regular phosphatidylcholine.
Consumers note the excellent cleansing effect of the capsules, talk about the disappearance of the smell of sweat and improved liver function. The feasts held the day before pass without a trace, without causing pain or heaviness in the stomach. Hepatitis patients report normalization of AllAT and AsSAT levels.
Price for 180 capsules – 1798 rub. with discount.
Symptoms of Choline Overdose
- The appearance of a “fishy” odor from the body.
- Vomit.
- Excessive sweating.
- Hypersalivation.
Against the background of excess amounts of choline, the liver experiences a toxic effect. The body activates the production of TMAO, which causes cardiovascular disorders.
Pharmacological action[edit | edit code]
While having the same effects as acetylcholine, choline is much less active. Even 10 g of choline when taken orally does not have a clear effect. Physiological functions. Choline performs several functions in the body. It is an important component of phospholipids, promotes the mobilization of fatty acids in the liver (lipotropic effect), serves as a donor of methyl groups and is necessary for the formation of the mediator acetylcholine (Chapter 6) and platelet activating factor (Chapter 26).
Phospholipid component[edit | edit code]
Choline is part of the main phospholipid - lecithin, plasmalogens (present in large quantities in mitochondria) and sphingomyelins (which the brain is especially rich in). Thus, choline serves as an essential structural component of many biological membranes and plasma lipoproteins.
Lipotropic action[edit | edit code]
As already mentioned, the important role of choline as a dietary component was first noticed in connection with its ability to reduce fat content in the liver of dogs with experimental diabetes mellitus. Substances that stimulate the removal of excess fat from the liver are called lipotropic. These include choline, inositol, methionine, vitamin B 12 and folic acid. Some of them apparently serve as donors of methyl groups in the synthesis of choline. As a result, the formation of lipid components of plasma lipoproteins occurs and the transport of fat from the liver is accelerated. A methyl group donor, choline can serve as a donor of (methyl)methyl groups necessary for the synthesis of other compounds. First, betaine is formed from choline, which is a direct donor of the methyl group. The methyl group can then be transferred to homocysteine, resulting in the formation of methionine. The role of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and folic acid in the metabolism of single-carbon compounds is discussed in Chap. 54.
Formation of acetylcholine[edit | edit code]
Acetylcholine is synthesized from choline and acetyl-CoA by choline acetyltransferase and broken down by AChE (Chapter 6). In the endothelium of the brain capillaries there is a system of facilitated diffusion of choline in both directions, and the amount of choline entering the central nervous system depends on its concentration in the plasma. When choline chloride is administered to rats, not only the concentration of choline in the plasma increases, but also the concentrations of choline and acetylcholine in the brain. These data may help in the treatment of diseases in which acetylcholine synthesis is reduced (see below). Synthesis of platelet activating factor. This factor is formed from choline-containing membrane phospholipids, in which at position 1 of the glycerol residue there is an alkyl ester instead of a fatty acid ester. Hormone-sensitive phospholipase A2 acts on the phospholipid, forming 1-O-alkyllisophosphatidylcholine. Under the action of a specific acetyl transferase, which catalyzes the transfer of the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to position 2 of this intermediate product, platelet activating factor is formed. It plays an important role in inflammatory reactions and other processes (Chapter 26). Deficiency symptoms. Choline deficiency in animals is accompanied by fatty degeneration and cirrhosis of the liver, an increased risk of hepatic cell cancer, hemorrhagic kidney damage and impaired coordination of movements. Fortunately, none of these manifestations of choline deficiency have been observed in humans.
Indications for use
Choline preparations are prescribed for a number of conditions:
- Traumatic brain injuries, disorders of consciousness, coma.
- Acute cerebrovascular accidents. Condition after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Psychoorganic diseases associated with degenerative and involutional processes. Insufficiency of cerebral vessels, expressed in the form of memory impairment, disorders of consciousness, disorientation, attention disorder, motivation.
- Disorders of behavior and emotional state - irritability, emotional instability, loss of motivation, interests, senile pseudomelancholy, dementia.
Historical background[edit | edit code]
Source:
Clinical Pharmacology by Goodman and Gilman, Volume 4
.
Editor
: Professor A.G.
Gilman Ed.
: Practice, 2006.
In 1932, Best et al. found fatty liver degeneration in insulin-treated dogs with their pancreas removed, which could be prevented by adding lecithin (from raw egg yolk) or bovine pancreas to the food. The substance responsible for this effect turned out to be choline. These data gave impetus to widespread study of the role of lipotropic substances, especially choline, in animal nutrition. The functions of choline in the body are associated not only with lipid metabolism, but also with other important processes.
Instructions for use of vitamin B4
Low choline levels negatively affect phospholipid production. In this condition, the release of fatty acids into the blood plasma is impaired. Taking these features into account, the likelihood of thrombosis increases. For liver diseases, 200-300 mg of choline per day is prescribed. This dosage is enough to stimulate the renewal of liver cells and prevent fatty degeneration of its tissues.
When treating traumatic brain injuries, 1000 mg of choline preparations are prescribed parenterally - intravenously, intramuscularly. The therapeutic course lasts from 10 to 20 days. It is acceptable to administer injections 1-4 times a day, depending on the clinical symptoms and condition of the patient. At the end of the main course of treatment, maintenance therapy is prescribed for a period of 4 to 6 months.
Patients with dementia are prescribed choline at a dose of 400 mg three times a day. The treatment program lasts 3-6 months.
Pregnant women are advised to take choline preparations in a dosage of 1000 to 3000 mg per day. This will ensure the normal formation of the child’s central nervous system and his harmonious physical development. The woman is advised to avoid nervous stress. Choline suppresses the activity of the stress hormone cortisol. This serves as additional protection for mother and child from negative conditions.
Phosphatidylcholine: the first enemy of atherosclerosis
Not only our health and longevity, but also the condition of our skin, as well as the presence of fat deposits on the sides, abdomen and thighs, depend on the ratio of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol in the body. What kind of substance is this that can rejuvenate and restore a slim figure?
Attention. Non-specialists often use the terms “lecithin” and “phosphatidylcholine” as synonyms, which is not entirely correct. Lecithin is the general name for a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids and essential phospholipids, and phosphatidylcholine is only one of them, although the most common.
Phosphatidylcholines contain fatty acid residues and choline, prevent the occurrence of atherosclerosis, protect liver tissue from degeneration, stimulate memory, normalize blood glucose levels, relieve stress and improve skin condition.
The biological role of phosphatidylcholine is determined by its participation in ensuring the vital functions of the entire organism. The substance performs the following functions:
- acts as a source of choline;
- preserves cell structure;
- improves neuronal transmission;
- plays the role of membrane transport;
- nourishes the nervous system;
- activates brain function.
This beneficial choline compound is used in medicine and cosmetology to treat skin diseases and get rid of the first signs of aging.
No less interesting is the use of phosphatidylcholine as a lipolytic for mesotherapy. The substance is injected into areas of fat deposits along with deoxycholate and quickly removes extra centimeters. Using phospholipid injections, you can eliminate ptosis of the upper eyelid and remove a double chin.
As for the methods for obtaining phosphatidylcholine, the best bioregulator is obtained from vegetable oils - soybean or sunflower. This substance is absorbed faster and more completely, normalizes the digestion process and gastrointestinal motility.
Animal sources of choline do not have these properties. Phospholipid is obtained from the brain and spinal cord of mammals or the connective tissue of sturgeon fish. The disadvantage of the substance is the presence of a large amount of cholesterol.
Which choline supplement should you choose?
Lecithin. Available in the form of a dietary supplement. Contains 10–20% phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylcholine is produced in the form of powder or tablets, in which choline is approximately 13% of the total volume of the drug []. Other vitamin supplements contain choline in the form of chloride, CDP-choline, alpha-GPC and betaine.
Names of drugs and their costs
| Drug name | Volume | Cost in rubles |
| Cholitilin (capsules) | 400 mg | 28 capsules – 890 RUR |
| Gleatser (solution in ampoules of 4 ml) | In 1 ml - 250 mg | 5 ampoules - 520 RUR |
| Choline alfoscerate (solution in ampoules of 4 ml) | In 1 ml - 250 mg | 5 ampoules - 400 RUR |
| Noocholine (solution in ampoules of 4 ml) | In 1 ml - 250 mg | 3 ampoules – 330 RUR |
| Cerepro (capsules) | 400 mg | 14 capsules - 690 RUR |
| Cereton (in capsules or ampoules) | Per capsule - 400 mg in 1 ml - 250 mg | 14 capsules – 590 RUR 5 ampoules - 450 RUR |
| Gliatilin (capsules or ampoules) | Per capsule - 400 mg in 1 ml - 250 mg | 14 capsules – 820 RUR 3 ampoules - 630 RUR |
Should you take supplements?
If you can't get enough choline from food sources, you may want to look into supplementation. Supplements are an option, but should not be relied upon as a replacement for choline-rich food sources. There are currently different types of over-the-counter choline supplements, but no studies have compared the bioavailability (or how easily the body can use choline supplements) of these different forms.
You can buy high-quality choline with a 5% discount here.
Choline supplement
Buy at a discount
Lecithin is one of the most widely available supplements. It is a source of phosphatidylcholine, the main phospholipid in cells. Lecithin, which is usually derived from oils from soybeans (soy lecithin), sunflower seeds or canola (canola), is suitable for vegetarians. They contain 3% to 4% choline.
Other forms include:
- Choline bitartrate - 40% choline.
- Choline citrate – 50% choline.
- CDP-choline - 20% choline.
You can buy a high-quality supplement with a 5% discount here.
Lecithin supplement
buy with discount
It's worth discussing your options with your doctor to determine which supplement is best for you and whether you even need one.
Precautions and contraindications
Choline preparations for therapeutic purposes are prescribed only by the attending physician. The maximum permissible dosage for adult patients is 3500 mg per day. This amount will not harm the body. It is extremely difficult to obtain such a volume of the active substance with food. The use of pharmaceuticals must be under medical supervision.
Risk of high mortality
. A study of 80,978 women and 39,434 men showed that high doses of choline cause the development of cardiovascular disorders, leading to death [].
Risk of developing prostate and colorectal cancer.
Increasing recommended dosages over a long period of time causes the development of malignant processes in the prostate in men and in the colon in women [34-35].
History of discovery
The substance was first described in 1862. Scientists examined animal tissue and discovered this compound. However, its importance and necessity were clarified several decades later.
In 1930, tests were carried out on laboratory animals. Their pancreas was removed and insulin was injected. Although the animals survived after the intervention, they quickly developed fatty hepatosis. Soon all the individuals died.
Gradually, scientists came to the conclusion that there was a lack of choline in the animal tissues. Because of this, the liver was unable to utilize fat, and cirrhosis developed. The same processes occur in human tissues and organs.
Application[edit | edit code]
The effectiveness of choline in fatty degeneration and cirrhosis of the liver (usually alcohol-related) has not been proven. Because choline can be precursed by other methyl group donors, a well-balanced diet may alleviate symptoms of liver damage as much as choline itself. Fatty liver degeneration often develops in patients on total parenteral nutrition. Since parenteral nutrition solutions usually do not contain choline, choline deficiency may be the cause of liver pathology in such cases.
For diseases of the nervous system, which may be a consequence of decreased acetylcholine synthesis, it has been proposed to use large doses of choline or a related compound, citicoline (choline ester CDP). However, in none of these diseases (late neuroleptic hyperkinesis, Huntingon's disease, Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome, ataxia due to hereditary vitamin E deficiency, Alzheimer's disease) has the therapeutic effect of choline been reliably proven (Chapters 20 and 22). Recent controlled clinical trials suggest benefits for citicoline in stroke (Clark et al., 1997) and age-related verbal memory loss (Spiers et al., 1996), but these data require confirmation.