Release form and composition
Dosage form - solution for subcutaneous administration: transparent light yellow or colorless liquid (0.5 ml in syringe tubes, 1 syringe tube in a cardboard pack, complete with a sterile injection needle, packed in a sealed polyethylene container).
Active substance: interferon alpha-2a, in 1 syringe tube 3 million IU (international units), 4.5 million IU, 6 million IU or 9 million IU.
Auxiliary components: polysorbate 80, benzyl alcohol, water for injection, sodium hydroxide or glacial acetic acid, sodium chloride, ammonium acetate.
Analogs
Viferon
LLC Feron, Russia
Price from 168 rubles
Viferon is a complex medicine with antiviral activity, containing human interferon alpha-2. It is quite effective in combination with other agents in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by viruses and bacteria. Prescribed for influenza, ARVI, chlamydia, herpes. Available in pharmacy kiosks in the form of suppositories and ointments.
Pros:
- Allowed for use in pediatrics
- At the first manifestations of viruses, a very effective remedy
- Convenient dosage forms.
Minuses:
- Not recommended for use by pregnant and lactating women
- There are many side symptoms.
Laferobion
Biopharma, Ukraine
Price from 450 to 580 rubles
Laferobion is practiced as an immunostimulating and antiviral substance. It includes interferon and additional components such as ascorbic acid, sodium tocopherol, etc. These components can actively fight infections and strengthen the immune system.
Pros:
- Symptoms of the disease are quickly eliminated
- Safe product
- Can be used by children.
Minuses:
- Long-term use is undesirable
- Possible increase in allergic reaction
- With prolonged treatment, monitoring of blood counts is necessary.
Indications for use
Viral diseases:
- genital warts;
- chronic active hepatitis B in patients who have identified markers of viral replication, i.e. positive for HBV DNA, DNA polymerase or HBeAg and increased ALT (alanine aminotransferase) activity without signs of hepatic decompensation (class A according to the Child-Pugh classification);
- chronic active hepatitis C in adult patients with antibodies to the hepatitis C virus or HCV RNA in the serum and increased ALT (alanine aminotransferase) activity without signs of hepatic decompensation (class A according to the Child-Pugh classification) (usually Roferon-A is prescribed in combination with ribavirin; this combination is indicated both for patients who have not previously received therapy and for patients who responded to interferon alfa therapy but had a relapse of the disease after treatment was discontinued).
Solid tumors:
- metastatic malignant melanoma;
- advanced renal cell carcinoma;
- melanoma after surgical resection in the absence of regional and distant metastases;
- Kaposi's sarcoma in patients with AIDS without a history of opportunistic infections.
Neoplasms of the lymphatic system and hematopoietic system:
- thrombocytosis in myeloproliferative diseases;
- multiple myeloma;
- Ph-positive chronic myeloid leukemia;
- cutaneous T-cell lymphoma;
- hairy cell leukemia;
- low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (in the form of adjuvant therapy to chemotherapy, including radiation therapy).
Medicinal properties
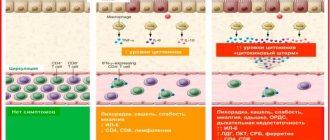
The therapeutic effect of Roferon is due to its constituent interferon (purified protein), which has antiviral, immunomodulatory effects, and suppresses tumor cells. Interferon, penetrating into cells, stimulates the immune system to activity aimed at destroying viruses and bacteria. The medication acts on tumor formations, suppressing their growth. It penetrates quickly and is well absorbed. The maximum concentration of the drug is achieved at 4 hours of administration. Excreted through the urinary system; in patients with kidney problems, the elimination period is longer.
Contraindications
- severe dysfunction of the liver, kidneys, myeloid lineage of hematopoiesis;
- chronic hepatitis in patients who are receiving or have recently received immunosuppressive drugs, with the exception of short-term treatment with steroids;
- chronic hepatitis with severe decompensation;
- convulsive disorders and/or other disorders of the central nervous system;
- chronic myeloid leukemia in patients who have an HLA-identical relative, as well as those who are scheduled (or possible) to undergo allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in the near future;
- existing or past severe heart disease;
- children under 3 years of age;
- pregnancy - if combination therapy with ribavirin is necessary;
- lactation;
- hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
Directions for use and dosage
Roferon-A is intended for subcutaneous administration.
Chronic active viral hepatitis B
The initial dose is usually from 4.5 million IU to 9 million IU 3 times a week, the duration of treatment is 4-6 months. Further, if necessary, the dose is adjusted depending on the tolerability of interferon alfa-2a. If after 3-4 months there is no improvement, therapy is stopped.
For children over 3 years of age, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 7.5 million IU/m2.
Metastatic melanoma
The drug is prescribed at the maximum tolerated dose or 18 million IU 3 times a week.
After approximately 12 weeks, the effectiveness of therapy is assessed. If improvement is noted, treatment is continued; if not, Roferon-A is discontinued.
The maximum known duration of therapy was 24 months.
Advanced renal cell carcinoma
a) Monotherapy with Roferon-A
Treatment begins with a daily dose of 3 million IU, gradually over 8-12 weeks it is increased to 18 million IU, and if the drug is well tolerated - to 36 million IU.
Recommended dosage increase regimen:
- days 1–3 – daily 3 million IU per day;
- days 4–6 – daily 9 million IU per day;
- Days 7–9 – daily 18 million IU per day.
If well tolerated, on days 10–84 the daily dose is increased to 36 million IU daily.
For maintenance therapy, Roferon-A is used in the maximum tolerated dose, but not more than 36 million IU 3 times a week.
The maximum known duration of therapy was 16 months.
b) Combination therapy in combination with vinblastine
Application of Roferon-A:
- first week – 3 million IU 3 times a week;
- second week – 9 million IU 3 times a week;
- further - 18 million IU 3 times a week; in case of poor tolerance, it is possible to reduce the daily dose to 9 million IU with a frequency of use 3 times a week.
Vinblastine is administered intravenously during this period in accordance with the instructions for its use - usually at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg once every 3 weeks.
The minimum duration of treatment is 3 months, the maximum is 12 months or until the disease progresses. If remission is noted, the drug is discontinued 3 months after its onset.
c) Combination therapy in combination with Avastin (bevacizumab)
Roferon-A is prescribed at a dose of 9 million IU 3 times a week, treatment is carried out for 12 months or until the disease begins to progress. If necessary, therapy can be started with a daily dose of 3 million IU or 6 million IU and gradually increased to the recommended dose over the first 2 weeks. In case of poor tolerability of the drug, it is possible to reduce the dose to 3 million IU 3 times a week.
Roferon-A is administered after Avastin infusion - on the same day or on days 2-3. Avastin is prescribed in accordance with the instructions for its use.
Melanoma after surgical resection
Interferon alfa-2a is used as an adjunct in addition to the main therapeutic regimen (adjuvant therapy).
The drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 3 million IU 3 times a week. Therapy in small doses can increase the duration of the period without relapse of the disease in patients without regional and distant metastases after resection of melanoma (tumor thickness >1.5 mm).
Treatment with Roferon-A should begin no later than 6 weeks after surgery. Duration – 18 months.
Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS patients over 18 years of age
The initial dose is 3 million IU daily, gradually over 10–12 weeks the daily dose is increased to 18 million IU, and if the drug is well tolerated, to 36 million IU.
Recommended dosage increase regimen:
- days 1–3 – daily 3 million IU per day;
- days 4–6 – daily 9 million IU per day;
- Days 7–9 – daily 18 million IU per day.
If well tolerated, on days 10–84 the daily dose is increased to 36 million IU daily.
For maintenance therapy, Roferon-A is used in the maximum tolerated dose, but not more than 36 million IU 3 times a week.
To determine the effectiveness of the therapy, it is necessary to periodically evaluate and document the dynamics of tumor changes. Before the first assessment of response, the duration of treatment should be at least 10 weeks, and preferably 12 weeks, since the result usually becomes noticeable after 3 months of treatment. If after this time a positive effect is noted, therapy is continued; if not, it is stopped.
The maximum known duration of therapy was 20 months. In case of positive dynamics due to the use of the drug, it is recommended to continue treatment at least until the tumor disappears.
Note: after stopping treatment with Roferon-A, a relapse of Kaposi's sarcoma often occurs.
Thrombocytosis associated with myeloproliferative diseases (except chronic myeloid leukemia)
In the first 3 days, 3 million IU is prescribed daily, from days 4 to 30 - 6 million IU daily.
The maximum tolerated dose is selected individually for each patient. Typically, to maintain platelet counts within normal limits, a daily dose of 1–3 million IU is sufficient, administered 2–3 times a week. In addition, this dose is well tolerated by patients.
Thrombocytosis associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (in patients over 18 years of age)
Treatment begins with a daily dose of 3 million IU, gradually increasing over 8–12 weeks to 9 million IU according to the following scheme:
- days 1–3 – 3 million IU daily;
- days 4–6 – 6 million IU daily;
- Days 7–84 – 9 million IU daily.
Treatment should preferably be carried out for 12 weeks (but not less than 8 weeks). If after this time a positive effect is noted, therapy is continued until complete hematological remission is achieved, but not more than 18 months. Otherwise, the drug is discontinued.
After achieving complete hematological remission, Roferon-A is prescribed in a daily dose of 9 million IU daily, in case of poor tolerance - 9 million IU 3 times a week. Treatment is carried out until cytogenetic remission is achieved, but as soon as possible. There are observations of cytogenetic remissions lasting 2 years after the start of therapy.
Myeloma
Treatment begins at a dose of 3 million IU 3 times a week.
The maintenance dose is determined by the doctor depending on the individual tolerability of the drug. If required, the dose is gradually increased once a week until the maximum tolerated dose is reached, which usually ranges from 9 million IU to 18 million IU 3 times a week.
The duration of therapy is determined individually. In the absence of disease progression and severe drug intolerance reactions, treatment is long-term.
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (in patients over 18 years of age)
Treatment begins with a daily dose of 3 million IU, gradually increasing over 12 weeks to 18 million IU according to the following scheme:
- days 1–3 – 3 million IU daily;
- days 4–6 – 9 million IU daily;
- Days 7–84 – 18 million IU daily.
For maintenance therapy, Roferon-A is used in the maximum tolerated dose, but not more than 18 million IU 3 times a week.
Treatment should preferably be carried out for 12 weeks (but not less than 8 weeks). If after this time a positive effect is noted, therapy is continued, otherwise the drug is discontinued.
Partial remission is usually observed after about 3 months of treatment, complete - after about 6 months, although in some cases 12 months of use of the drug are required to achieve the best effect.
The maximum known duration of therapy was 40 months.
Hairy cell leukemia
At the beginning of treatment, 3 million IU is prescribed daily for 16–24 weeks. In case of intolerance to the drug, reduce the daily dose to 1.5 million IU and/or reduce the frequency of administration to 3 times a week.
The maintenance dose is 3 million IU 3 times a week, with poor tolerance - 1.5 million IU 3 times a week.
After 6 months, therapy is assessed. If there is no positive effect, treatment is stopped; if an effect is observed, therapy is continued.
The maximum duration of use of the drug, according to clinical data, was 20 months.
Low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Roferon-A is prescribed as a maintenance agent after standard chemotherapy (including in combination with radiation therapy) at a dose of 3 million IU 3 times a week. It is recommended to start using the drug as early as possible - after the patient’s condition improves, usually 4-6 weeks after the end of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Duration of therapy is at least 12 months.
The drug can also be prescribed simultaneously with chemotherapy if traditional treatment regimens are used, for example, vincristine, prednisolone, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin. In this case, Roferon-A is prescribed at a dose of 6 million IU/m2 from the 22nd to the 26th day of each 28-day therapy cycle.
Condylomas acuminata
Roferon-A is prescribed at a dose of 1–3 million IU 3 times a week.
The duration of treatment is 1-2 months.
Chronic viral hepatitis C
The effectiveness of interferon alfa-2a increases when it is used simultaneously in combination with ribavirin. It is prescribed as a single drug if ribavirin is intolerant or there are contraindications to its use.
a) Combination therapy
Previously untreated patients with chronic hepatitis C are prescribed interferon 3 million IU 3 times a week, the duration of treatment is 6 months. Ribavirin is used in accordance with its instructions.
In case of relapse - 4.5 million IU 3 times a week, course of therapy - 6-12 months, depending on the initial data, including the genotype of the virus. Ribavirin is used in accordance with its instructions.
b) Monotherapy
Roferon-A is prescribed at a dose of 3-6 million IU 3 times a week. Duration of treatment is 6–12 months. If after 3 months the ALT level does not return to normal, the drug is discontinued.
In case of good tolerability and partial or complete response to therapy, but if the disease relapses after discontinuation of interferon alfa-2a, the effect of a repeated course of Roferon-A at the same or higher dose is possible.
Solution for subcutaneous administration of Roferon-A (Roferon-A)
Instructions for medical use of the drug
Description of pharmacological action
Interferon alpha-2a is a highly purified protein containing 165 amino acids with a molecular weight of about 19,000 daltons. It is produced using recombinant DNA technology using a genetically engineered E. coli strain, the DNA of which encodes the synthesis of this human protein. Roferon-A has an antiviral effect, inducing a state of resistance to viral infections in cells and modulating the response of the immune system aimed at neutralizing viruses or destroying cells infected by them. Roferon-A has an antiproliferative effect on a number of human tumors in vitro and inhibits the growth of some human tumor xenografts in athymic mice with the nude mutation. Clinical efficacy In human tumor cells treated with Roferon-A (HT29 cells), the synthesis of DNA, RNA and protein is significantly reduced. A limited number of human tumor cell lines grown in vivo in immune-deficient nude mice were tested for sensitivity to the effects of Roferon-A. In vivo, the antiproliferative activity of Roferon-A was studied on tumors such as mucoid carcinoma of the mammary gland and adenocarcinoma of the cecum and transverse colon), as well as the prostate gland. The degree of antiproliferative activity varies. Roferon-A leads to clinically significant tumor regression or disease stabilization in patients with hairy cell leukemia and in AIDS patients with Kaposi's sarcoma. Roferon-A is also effective for treating patients with multiple myeloma. Roferon-A has activity in patients with advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma who are refractory to or unsuitable for conventional therapy. Roferon-A is effective for the treatment of patients with Ph-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Roferon-A leads to hematological remission in 60% of patients in the chronic stage of CML, regardless of previous therapy. Complete hematological remission still persisted 18 months after the start of treatment in two thirds of the patients studied. Unlike cytotoxic chemotherapy, interferon alfa-2a can lead to stable cytogenetic remission lasting more than 40 months. Roferon-A in combination with intermittent courses of chemotherapy increases overall survival and inhibits disease progression compared to chemotherapy alone. Roferon-A is effective for the treatment of thrombocytosis in chronic myeloid leukemia and other myeloproliferative diseases. Roferon-A reduces the number of platelets within a few days, reduces the incidence of concomitant thrombohemorrhagic complications and does not have leukemia potential. In patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, when prescribed in addition to chemotherapy (with or without radiation therapy), Roferon-A prolongs disease-free survival and progression-free survival. In patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma, Roferon-A in combination with vinblastine is more effective in terms of survival compared to chemotherapy alone. In patients with advanced malignant melanoma, treatment with Roferon-A led to objective regression of tumors of the skin and visceral localization. Roferon-A also increases the length of time without relapse of the disease in patients without lymph node involvement and distant metastases after resection of melanoma (tumor thickness >1.5 mm). Roferon-A is effective for the treatment of patients with confirmed compensated (without signs of hepatic decompensation) hepatitis B and C. Roferon-A is effective for the treatment of patients with genital warts.
Indications for use
Neoplasms of the lymphatic system and hematopoietic system: - hairy cell leukemia; - multiple myeloma; — cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; — Ph-positive chronic myeloid leukemia; - thrombocytosis in myeloproliferative diseases; - low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (in the form of adjuvant therapy to chemotherapy - with or without radiation therapy). Solid tumors: - Kaposi's sarcoma in patients with AIDS without anamnestic indications of opportunistic infections; - advanced renal cell carcinoma; - metastatic melanoma; — melanoma after surgical resection (tumor thickness >1.5 mm) in the absence of lymph node involvement and distant metastases. Viral diseases: - chronic active hepatitis B in adults with markers of viral replication, i.e. positive for HBV DNA, DNA polymerase or HBeAg and increased activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT); - chronic active hepatitis C in adults with antibodies to the hepatitis C virus or HCV RNA in the serum and increased ALT activity without signs of hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh class A); in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, the combination of Roferon®-A and ribavirin is optimal; Roferon-A in combination with ribavirin is indicated both for patients who have not previously received therapy and for those who previously responded to therapy with interferon-alpha and then had a relapse of the disease after discontinuation of therapy; - genital warts.
Release form
charges for injections 18 million MO; cartridge 0.6 ml, cardboard pack 1; dose for injections 3 million MO / ml; 0.5 ml syringe tube with tip(s), cardboard pack 1; dose for injections 4.5 million MO / ml; 0.5 ml syringe tube with tip(s), cardboard pack 1; doses for injections 6 million MO / ml; 0.5 ml syringe tube with tip(s), cardboard pack 1; dose for injections 9 million MO/ml; 0.5 ml syringe tube with tip(s), cardboard pack 1; dose for injections 3 million MO / ml; 0.5 ml syringe tube with tip(s), cardboard pack 1;
Pharmacokinetics
After administration, bioavailability exceeds 80%. After subcutaneous administration of a dose of 36 million MO, Cmax in the population (from 1250 to 2320 pg/ml, on average 1730 pg/ml) was achieved in an average of 7.3 years. Rozpodil. In humans, the pharmacokinetics of roferon-A in doses ranging from 3 million to 198 million MO is linear. After intravenous infusion of 36 million IU to healthy volunteers, the volume in the same study ranged from 0.22 to 0.75 l/kg (average 0.40 l/kg). Both in healthy volunteers and in patients with metastatic cancer, large individual variations in the concentration of interferon alfa-2a in serum are observed. Metabolism and elimination The main route of elimination of alpha-interferon is nitric catabolism. Hepatic metabolism and elimination from the liver are the least significant routes of elimination. In healthy individuals, the T1/2 period of interferon alpha-2a after intravenous infusion of 36 million MO becomes 3.7-8.5 years (on average 5.1 years), and the extragal clearance is 2.14-3.62 ml/ hw / kg (average 2.79 ml / hw / kg).
Use during pregnancy
Men and women who are taking Roferon-A are required to use reliable methods of contraception. In case of pregnancy, the drug should only be used in cases where the measles from treatment exceeds the possible risk to the fetus. Although we want to confirm teratogenicity in animals, we cannot exclude the possibility that stagnation during pregnancy can cause harm to the fetus. When rhesus monkeys were given doses in early and mid-gestation that significantly exceeded clinical recommendations, they experienced an increase in the number of days off. It is unknown whether Roferon-A is seen with breast milk. Nutrition for breastfeeding or for taking medications must be taken seriously due to the importance of bathing for the mother. Benzyl alcohol, which is placed in the container of Roferon®-A, ready for drying, can penetrate the placenta. If Roferon®-A is found to be present directly in front of the canopy or cesarean tissue, remember the toxic effect on premature babies. Vaginal women are not to blame for using Roferon-A in combination with ribavirin. Women of the childbearing age and male partners of women of the childbearing age who are taking Roferon-A in combination with ribavirin are likely to use reliable methods of contraception (see also instructions for use). ribavirin).
Contraindications for use
— Increased sensitivity to recombinant interferon alfa-2a or any component of the drug; - Obviously or having suffered an important illness of the heart; — Severely impaired function of the liver, liver, and myeloid hematopoiesis; — Suspicious disorders, other dysfunctions of the central nervous system; — Chronic hepatitis with severe decompensation or liver cirrhosis; — Chronic hepatitis in patients who are recovering or have recently stopped immunosuppressants, due to short-term treatment with steroids; — Chronic myeloid leukemia, if the patient has an HLA-identical relative and is due, or possible allogeneic cerebrovascular transplantation in the nearest future; — Children's age up to 3 years (as a preservative, use benzyl alcohol); — Vaginism — during combination therapy with ribavirin (see also instructions for medical administration of ribavirin).
Side effects
The following data are provided about the side effects of the drug based on the early treatment of patients with various malignant illnesses, often refractory before treatment and who were in advanced stages, as well as patients for chronic hepatitis B and C. Additional symptoms: often - influenza-like syndrome (flatness, elevated temperature , chills, loss of appetite, pain and headaches, pain in the joints and sweating), loss of vagina. These acute side effects tend to weaken or subside with immediate administration of paracetamol, and their severity during treatment or when changing the dose of roferon-A tends to change, although with prolonged therapy drowsiness, weakness and bloatiness may occur. ShCT: often - approximately two-thirds of cancer patients have anorexia, half have boredom; Drink often - vomiting, change in taste, dry mouth, diarrhea, as well as mild or severe abdominal pain; rarely - constipation, flatulence, increased peristalsis and liver, acute viral illness, intestinal bleeding that does not threaten life, severely impaired liver function, pancreatitis. Change the functions of the liver: inodes - increase the level of ALT, ALP, LDH and bilirubin, which, as a rule, do not require dose adjustment; rarely - changes in transaminase activity in hepatitis B; very rarely - severely impaired liver function, liver failure. Central nervous system: sometimes - systemic and confusion, impaired vision, mental depression, forgetfulness, depression, drowsiness, confusion, impaired behavior (anxiety, nervousness) and sleep disturbance; rarely - severe drowsiness, seizures, coma, impaired cerebral blood flow, temporary impotence and ischemic retinopathy, as well as suicidal behavior (at the first signs of suicidal behavior, the drug must be taken off). Organs of the vision: inodі - damage to the vision; rarely - ischemic retinopathy; Very rarely - retinopathy, including hemorrhage in the retina and cotton wool exudates, swelling of the disc of the visual nerve, thrombosis of the central vein and artery of the retina, posterior ischemic neuropathy. Peripheral nervous system: some - paresthesia, spinal cord loss, neuropathy, itching and tremor. Cardiovascular and respiratory systems: treat frequently - in approximately one in five cancer patients - transient arterial hypo- or hypertension, swelling, cyanosis, arrhythmias, palpitations and chest pain ; rarely - cough and shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, pneumonia, congestive heart failure, heart failure and shortness of breath, myocardial infarction. In patients with hepatitis B, cardiovascular damage is rarely observed. Skin, appendages and mucous membranes: drink often - in the fifth part of the patient - lightly or evenly, the hair will fall out, and after the application of the bath. Severe hair loss can be treated with a few tens of pulls. Rarely - exacerbation of herpetic swellings on the lips, swelling, itching, dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, nasal discharge and nosebleeds, exacerbation or manifestation of psoriasis. Nirka and sechovividnye paths: rarely - decreased function of nirok, gastrointestinal deficiency (mainly in cancer patients with such factors as risk of illness or immediate treatment with nephrotoxic drugs), electrolyte impairment, especially with anorexia or anemia, proteinuria, increased cellular elements in the sediment, increased blood level, as well as creatinine and sechoic acid in the blood. Hematopoietic system: often - transient leukopenia (rarely requires a dose change), in patients with myelosuppression - thrombocytopenia, decreased hemoglobin level; Others - thrombocytopenia in patients without myelosuppression; rarely - changes in the level of hemoglobin and hematocrit. The reversal of severe hematological disorders to the final level was observed within 7-10 days after administration of roferon-A. Very rarely - idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Others: rarely - hyperglycemia, blood diabetes, reactions at the injection site; very rarely - necrosis, autoimmune pathology (vasculitis, arthritis, hemolytic anemia, impaired thyroid function, wolf-like syndrome), very rarely - asymptomatic hypocalcemia, sarcoidosis, hypertriglosis Ceridemia/hyperlipidemia. In rare cases, therapy with alpha-interferon drugs, including Roferon-A, in combination with Copegus is associated with pancytopenia; very rarely - for aplastic anemia. Antibodies to interferon. In some patients, after the administration of drugs that replace the homologous protein, the neutralizing active protein of the antibody can be neutralized. It is therefore certain that a large proportion of patients will have antibodies to all interferons, both natural and recombinant. In case of certain illnesses (cancer, systemic diarrhea, ringworm), antibodies to leukocyte interferon can spontaneously develop in patients who have never previously eliminated interferon. There are no indications that, if clinically indicated, the presence of such antibodies may negatively affect the patient’s reaction to Roferon-A. When combined therapy with ribavirin was carried out - div. Also “Side effects” for ribavirin.
Directions for use and doses
Roferon-A is administered subcutaneously for hairy cell leukemia Pochatkova dose: 3 million MO subcutaneously, daily, over a period of 16-24 years. In case of intolerance, change the additional dose to 1,500,000 IU/or reduce the frequency of administration to 3 times per week. Maintenance dose: 3 million MO s/c 3 times per week. In case of intolerance, change the dose to 1,500,000 MO 3 times per week. The severity of the treatment: if a positive effect is evident, continue the treatment after 6 months; if it is present, take it. The maximum duration of treatment was 20 months. Myeloma Initial dose: 3 million IU subcutaneously 3 times a week. Maintenance dose: depending on individual tolerance, the dose can be increased to reach the maximum tolerated dose (9-18 million MO) 3 times per week. Treatment duration: treatment according to this scheme should be continued for three hours if the disease progresses and there is severe intolerance to the drug. Skin T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) (from 18 years) Roferon-A may have an effect in patients with progressive CTCL, incl. refractory to traditional therapy or not suitable for its implementation. Corn dose: 3 million IU/dobu, s/c, incrementally increasing the dosage up to 18 million IU/dobu for 12 days per scheme: 1-3rd day - 3 million IU/dobu, 4-6th day - 9 million MO / dobu, days 7-84 - 18 million MO / dobu. Maintenance dose: maximum tolerated dose (not exceeding 18 million MO) 3 times per day s.c. Treatment duration: treatment duration before assessing the response to therapy should be no less than 8 doses, most importantly - 12 doses; If a positive effect is evident, continue the treatment; if it is present, administer it. The maximum duration of treatment was 40 months. In patients who respond positively to therapy, it is necessary to wait for at least 12 months in order to maximize the likelihood of achieving a new remission and promote the acceptability of a permanent remission. Partial remission occurs within 3 months of treatment, and full remission occurs within 6 months, although 12 months of therapy are required to achieve the best effect. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) 18 years of age and older Pochatkov dose: 3 million IO / dose with progressively increasing doses over 8-12 days per regimen: 1-3 days - 3 million IO / dose, 4-6 days - 6 million IO / dobu, days 7-84 - 9 million MO/dobu. The length of the treat: not less than 8 years, most important - 12 years; If an effect is evident, continue therapy until a complete hematological remission is achieved, or no more than 18 months. If there are no changes in hematological indicators, therapy is administered. For further hematological remission, treatment should be continued at a dose of 9 million IU/dose (optimal dose) or 9 million IU 3 times per week (minimal dose), until cytogenetic remission is achieved in the shortest possible time. Є prevention of cytogenetic remissions of trivalism 2 years after the start of harvesting. The effectiveness, safety and optimal doses of roferon-A for children with CML have not been established. When combined with cytotoxic chemotherapy, interferon alfa-2a can induce a stable cytogenetic remission that lasts more than 40 months. Roferon-A reduces the number of platelets within a few days, changes the frequency of concomitant thrombohemorrhagic complications and does not increase leukemia potential. Thrombocytosis associated with myeloproliferative diseases (CML cream) Today: 1-3 days - 3 million MO / dob, 4-30 days - 6 million MO / do. Maintenance dose: 1-3 million MO 2-3 times per week. For skin patients, select the maximum dose individually. Low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in the context of supportive therapy after standard chemotherapy (with or without chemotherapy): 3 million IU s/c 3 times per day for at least 12 months Treatment should be started earlier in case of advanced illness, starting 4-6 days after chemotherapy and exchange therapy. In combination with traditional chemotherapy regimens (for example, with a combination of cyclophosphamide, prednisolone, vincristine and doxorubicin) - 6 million MO / m2 from days 22 to 26 of a 28-day skin cycle. In this condition, treatment with roferon-A can be started simultaneously with chemotherapy. In patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, when treated in addition to chemotherapy (with or without exchange therapy), Roferon-A has a long-term disease-free survival and survival without progression. Kaposi's sarcoma in patients with SNID It is likely that patients with Kaposi's sarcoma and SNID respond positively to therapy, especially if they have no history of opportunistic infections, group B symptoms (in Vagi waste is more than 10%, temperature is more than 38 ° C at in the presence of visible infection, latent fluidity), and the output number of T4 lymphocytes exceeds 200 cells per 1 μl. Cotal dose (from 18 years of age and older): 3 million MO / dose, daily, with progressive dose increases over 10-12 years up to 18 million MO / dose, if possible - up to 36 million MO / dose per scheme: 1-3 days - 3 million MO/dobu, 4-6 days - 9 million MO/dobu, 7-9 days - 18 million MO/dobu, 10-84 days - up to 36 million MO/dobu (depending on tolerance). Maintenance dose: the maximum tolerated dose is 3 times per day, but not more than 36 million MO / dose. The severity of the treatment: by measuring the reaction to the treatment, we can document and evaluate the dynamics of the change in swelling. The duration of treatment before assessing the response to therapy should be no less than 10 years, most importantly - 12 years. If a positive effect is evident, the therapy is continued; if it is present, it is administered. The effect begins to appear after 3 months of treatment. The maximum duration of treatment was 20 months. If the effect of curing is evident, it is necessary to continue chewing until the swelling disappears. Note: after initiation of roferon-A therapy, Kaposi's sarcoma often recurs. In patients with recurrent swelling or metastases, the greatest therapeutic effect was achieved with large doses of Roferon-A (36 million IU/dose) in the form of monotherapy or small doses of Roferon®-A (18 million IU 3 times per day) in combination with vinblastine, combined with monotherapy with moderate doses of roferon-A 3 times a day. The survival rate and survival rate of roferon-A monotherapy and combination therapy of roferon-A with vinblastine are similar. In patients who took small doses of roferon-A (2 million MO/m2 per dose), the effect of treatment was daily. The combination of roferon-A with vinblastin resulted in a slight increase in the incidence of mild and mild leukopenia and granulocytopenia similar to monotherapy. a) Monotherapy of roferon-A Occasional dose: 3 million OD/dose with progressive dose increases over 8-12 days up to 18 million OD/dose, and if possible - up to 36 million OD/dose in an incremental scheme: 1-3 days - 3 million MO/dobu, 4-6 days - 9 million MO/dobu, 7-9 days - 18 million MO/dobu, if tolerated, a larger dose on days 10-84 up to 36 million MO/dobu. Maintenance dose: the maximum tolerated dose is 3 times per day, but not exceeding 36 million MO / dose. The duration of the bath: no less than 8 years, most importantly - no less than 12 years. If the effect is evident, continue the therapy; if it is present, administer it. The maximum duration of treatment was 16 months. b) Roferon-A + vinblastine In the first period, Roferon-A is prescribed at a dose of 3 million MO 3 times per week, in the other year - 9 million MO 3 times per week, then - 18 million MO 3 times per week (depending on dose intolerance You can change up to 9 million MO 3 times per week). During this period, vinblastine is administered intravenously at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg 1 time per 3 days. Duration of treatment: not less than 3 months, maximum - up to 12 months or until illness begins to progress. In cases of remission, treatment can be started after 3 months. after this day. Metastatic melanoma 18 million MO 3 times per day or at the maximum tolerated dose for 12 days. The duration of treatment before assessing the effectiveness of therapy is important - no less than 12 days. If the effect is evident, continue the therapy; if it is present, administer it. The maximum duration of treatment is 24 months. In patients with advanced malignant melanoma, treatment with roferon-A led to an objective regression of scalp and visceral swelling. Melanoma after surgical resection Adjuvant therapy with small doses of roferon-A is more effective without relapse of illness in patients without lymph nodes and distant metastases after resection of melanomas and (tovshchina puffiness> 1.5 mm). Treatment must be performed no later than 6 days after the operation. Dose - 3 million MO 3 times per week. Trival of Likuvannya - 18 months. Chronic viral hepatitis B is prescribed 4.5-9 million MO s/c 3 times a day for 4-6 months. Further dose adjustments should be made depending on tolerability to the drug. If after 3-4 months the swelling is not prevented, you should take a look at the diet and interrupt therapy. Children from 3 years of age and older. Roferon-A at a dose of 7,500,000 MO/m2 is safe and effective. Chronic viral hepatitis C The effectiveness of interferon alfa-2a is increasing when it is prescribed in combination with ribavirin. Roferon-A may be prescribed as monotherapy if intolerance is evident and / or contraindicated before ribavirin. a) Combined therapy with roferon-A and ribavirin Combined therapy with roferon-A and ribavirin before serious illnesses with chronic hepatitis C: 3 million IU p/c 3 times per day for at least 6 months. Ribavirin dosage regimen: div. More instructions for medical administration of ribavirin. Combined therapy with roferon-A and ribavirin for relapse in adult patients in whom prior monotherapy with interferon-alpha gave an immediate effect. Dosing mode: 4,500,000 MO 3 times per week for 6 months. The standard duration of therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C depends on the patient’s characteristics (for example, the genotype of the virus) and becomes 6-12 months. Ribavirin dosage regimen: div. Instructions for medical administration of ribavirin. b) Monotherapy of roferon-A Roferon-A may be prescribed in addition to monotherapy in case of intolerance or contraindication to ribavirin. 3-6 million MO 3 times per week for 6-12 months. If after 3 months the treatment of rhubarb ALT is NOT normalized, therapy should be continued. If tolerated and with frequent or repeated response to roferon-A therapy, or in case of relapse of illness after treatment, there may be an effect of repeated therapy with roferon-A at the same or higher doses i. State condylomata 1-3 million MO 3 times per week s/c for 1-2 months.
Overdose
There is no information about overdose. Symptoms: repeated administration of large doses of interferon may be accompanied by profound lethargy, bloat, prostration and coma. Treatment: such patients should be hospitalized for precautions and to carry out routine follow-up visits.
Interactions with other drugs
Alpha interferons can disrupt oxidative metabolic processes, reducing the activity of liver microsomal enzymes of the cytochrome P450 system. This should be used in the case of immediately recognized drugs that are metabolized by this substance. A decrease in theophylline clearance has been described after one-hour administration of alpha-interferons. Interferons may potentiate neurotoxic, hematotoxic or cardiotoxic drugs previously prescribed or concomitantly with them. Interactions can be prevented after one-hour administration of central drugs. When combined therapy with ribavirin was carried out - div. Also “Interaction” with ribavirin.
Special instructions for use
Roferon-A should be administered under the supervision of a physician, who will provide evidence of care for typical symptoms. Treatment of the underlying illness and deterioration of the patient is appropriate if adequate diagnostic and therapeutic options are identified. In case of mild or moderate impairment of the functions of the liver, liver or bone marrow, their functional state must be carefully monitored. Change the oven functions. Changes in the activity of transaminases in hepatitis B should indicate an increase in the clinical status of the patient. It is necessary to exercise caution when treating patients with interferon-alpha for chronic hepatitis with a history of autoimmune diseases. Skin patients who show pathological changes in liver function tests when treated with Roferon-A must be carefully monitored and, if necessary, discontinue the drug. Psychoneurological changes in patients who recover from interferons, incl. and Roferon-A may exhibit important psychiatric side effects. Depression, suicidal ideation, and suicide may occur in patients with or without a history of mental illness. Caution should be exercised when using roferon-A in patients with a history of depression. It is recommended to carefully monitor patients who are taking Roferon-A in case of depression. Before treatment begins, patients should be informed about the possibility of developing depression, and patients should be sure to inform the doctor of any signs of depression; In cases where depression develops, consultation with a psychiatrist and additional attention to the importance of therapy are necessary. Myelosuppression With caution, use Roferon-A in patients with severe myelosuppression, because the drug suppresses the cystic spores, causing a decrease in the number of leukocytes (especially granulocytes), the number of platelets and, sometimes, equal to hemoglobin. This may lead to an increased risk of infection or bleeding. It is necessary to carefully monitor these changes and perform blood tests before starting treatment with Roferon-A and, regularly, during this process. Infections Fever may be associated with an influenza-like syndrome, which is often encountered with interferon therapy. In case of persistent fever, especially in patients with neutropenia, turn off the infection (bacterial, viral, fungal). In case of severe infectious complications, discontinue interferon and initiate auxiliary therapy. Ophthalmological changes As well as during therapy with other interferons, during therapy with roferon-A, episodes of retinopathy have been registered (bleeding in the retina, cotton wool, swelling of the disc of the visual nerve, thrombosis of the center arteries and veins of the retina) and posterior ischemic neuropathy, which can lead to loss of vision . If scargas appear on increased vision or loss of vision, these patients should undergo ophthalmological closure. Patients with blood diabetes and arterial hypertension must undergo ophthalmological testing to identify pathology of the fundus before starting therapy. Therapy with roferon-A or roferon-A / ribavirin should be discontinued in case of severe or advanced ophthalmic illnesses. Hypersensitivity reactions. Under the hour of therapy with interferons, incl. and interferon alpha-2a, beware of serious hypersensitivity reactions of the nongain type (urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm and anaphylaxis). Occasionally, the development of similar reactions during therapy with roferon-A or roferon-A / ribavirin therapy is canceled and a similar drug therapy is safely prescribed. Minute visiping does not affect therapy. Change endocrine organs. Hyperglycemia is rarely observed during roferon-A therapy. If clinical symptoms of hyperglycemia are evident, it is necessary to monitor the level of glucose in the blood and a corresponding observation. If you have diabetes, you may need to adjust the dosage of your cutaneous medications. Autoimmune disorders During therapy with alpha-interferons, episodes of the creation of various autoantibodies have been recorded. Clinical manifestations of autoimmune diseases during therapy with interferons occur more often in patients who are susceptible to the development of such diseases. Alpha interferon therapy is rarely associated with acute or acute psoriasis. In patients after transplantation (for example, cerebral or bone marrow), drug immunosuppression may be less effective, because interferons may have a stimulating influx on the immune system. There are indications of direct cardiotoxicity of the drug on a daily basis, however, it is clear that acute, self-existing toxic effects (such as fever, chills) often accompany treatment with roferon-A may Wiklikati zagostrennya nayavnykh sertsevikh zakhvoryuvan. It is not recommended to administer Roferon-A to newborns, especially premature babies, and children under 3 years of age, since benzyl alcohol may be used as a preservative, which, as is known, can cause permanent damage to the neuropsychic sphere and multiple organs. ї insufficiency. When combined therapy with ribavirin was carried out - div. Also “Zapobizhni go” for ribavirin. Preclinical vaccination. In rhesus macaques, which were prescribed doses of the drug that significantly exceeded clinical recommendations, transient disturbances of the menstrual cycle were observed, incl. Subsequent to the period of menstruation. Instructions for use with the drug Bagatadose cartridges 18 million MO in 0.6 ml are intended for use by only one patient. The stench will only be present in the Roferon-Pen syringe. Together with the syringe pen and the cartridge, only a few Penfine heads are stuck. For skin injection, scrub with a new sterile tip. Cartridges containing Roferon-A are liable to malfunction within 30 days after the first injection. After skin injection, the syringe pen with the inserted cartridge should be stored in the refrigerator, protected from a light place, however, if necessary, the syringe pen with the cartridge can be stored at room temperature temperature (up to 25 ° C) up to 28 days. Mark the date of the first cartridge cartridge on the sticker that came with the cartridge and stick it on the box with the syringe pen. Detailed instructions for Vikoristan Roferon-Pen are included in the package. Pour into the building of transport vehicles and work with machines and mechanisms. Carefully following the dosing regimen and the individual sensitivity of the patient, Roferon-A can be applied to the fluidity of the reaction, adding to the vicariousness of the songs. operations, such as water transport, work with machines and mechanisms.
Storage conditions
Store in a light place, at a temperature of 2-8 ° C (Do not freeze).
Best before date
24 months
ATX classification:
L Antineoplastic drugs and immunomodulators
L03 Immunostimulants
L03A Cytokines and immunomodulators
L03AB Interferons
L03AB04 Interferon alfa-2a
Side effects
- general symptoms: often - weight loss, flu-like syndrome (sweating, chills, lethargy, joint pain, loss of appetite, fever, muscle pain and headaches) (these side effects can be weakened or eliminated by the simultaneous use of paracetamol);
- central nervous system: sometimes - sleep disturbances, drowsiness, anxiety, nervousness, depression, deterioration of mental state, confusion, dizziness, forgetfulness; rarely - cerebrovascular accidents, severe drowsiness, temporary impotence, suicidal thoughts and attempts, convulsions, coma;
- cardiovascular and respiratory systems: relatively often - chest pain, palpitations, transient arterial hypo- and hypertension, arrhythmias, cyanosis, edema; rarely - slight shortness of breath, cough, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, respiratory arrest, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrest (in patients with hepatitis B, cardiovascular disorders are observed in very rare cases);
- gastrointestinal tract: often – nausea, anorexia; relatively often - dry mouth, mild or moderate abdominal pain, diarrhea, changes in taste, vomiting; rarely - flatulence, constipation, heartburn, exacerbation of peptic ulcer, increased peristalsis, pancreatitis, non-life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding;
- kidneys and urinary tract: rarely - an increase in the content of cellular elements in urine sediment, proteinuria, electrolyte disturbances (especially in the case of dehydration and anorexia), deterioration of kidney function, increased levels of urea, uric acid and serum creatinine, acute renal failure (mainly in cancer patients with risk factors such as kidney disease and/or concomitant use of nephrotoxic drugs);
- liver: sometimes - increased levels of LDH, ALT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase; rarely - a change in transaminase activity (with hepatitis B, this reaction usually indicates an improvement in the patient’s clinical condition);
- peripheral nervous system: sometimes – neuropathy, itching, paresthesia, tremor, numbness of the extremities;
- hematopoietic system: relatively often – transient leukopenia; in patients in a state of myelosuppression - a decrease in hemoglobin levels and platelet counts; sometimes – thrombocytopenia in patients without myelosuppression; rarely – a decrease in hematocrit and hemoglobin levels; very rarely - idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- skin, its appendages and mucous membranes: relatively often - mild or moderate hair loss (reversible after cessation of treatment); rarely - itching, rash, nasal discharge and nosebleeds, dry mucous membranes and skin, exacerbation of herpes;
- organ of vision: sometimes – visual impairment; rarely – ischemic retinopathy; very rarely - posterior ischemic neuropathy, papilledema, retinopathy, including cotton wool exudates and retinal hemorrhages;
- other: rarely - diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, reactions at the injection site, including necrosis (very rare); in some cases - autoimmune pathology (dysfunction of the thyroid gland, arthritis, lupus-like syndrome, hemolytic anemia, vasculitis), hypertriglyceridemia or hyperlipidemia, sarcoidosis, asymptomatic hypocalcemia, transplant rejection.
When Roferon-A is combined with ribavirin, pancytopenia occurs in rare cases, and aplastic anemia occurs very rarely.
Side effects
Negative symptoms are often recorded in patients with severe cancer, as well as with hepatitis B and C. Among the most common manifestations are:
- Flu syndrome. Weakness, high temperature, chills, soreness in the muscles and head, excessive sweating, weight loss, lethargy, general weakness. These symptoms decrease when taking Paracetamol tablets and reducing the dosage of Roferon.
- Digestive tract. Nausea, attacks of vomiting, development of anorexia, dry mouth, impaired taste, abdominal pain, constipation, sometimes diarrhea, bloating, heartburn, exacerbation of existing pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Nervous system. Dizziness, memory loss, depression, drowsiness, anxiety, nervousness. In more rare situations, cerebral circulation disorders, convulsions, coma, and suicidal behavior are possible. Numbness of the arms and legs, trembling, and itching may also develop.
- The cardiovascular system. The formation of hypertension, swelling, disturbances in heart rhythm, chest pain, very rarely myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest.
- Respiratory system. Constant shortness of breath, swelling of the lungs, cough, development of signs of pneumonia.
- Skin and mucous membranes. Hair loss, body rash, dryness, irritation.
- Urinary system. Decreased renal function, renal failure, urinary disturbances, proteinuria, changes in urea, creatinine and uric acid.
- Circulatory system. Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, decreased hemoglobin levels, rarely thrombocytopenic purpura may develop.
- Liver. Impaired liver test results, organ dysfunction
- Organs of vision. Vision problems, retinopathy, hemorrhages, papilledema, etc.
- Other violations. Thyroid dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, arthritis, vasculitis, allergies at the injection site.
special instructions
Therapy with the drug should be carried out under the supervision of a physician who has experience in treating the relevant indications.
In cases of mild or moderate functional impairment of the bone marrow, liver or kidneys, their functions must be carefully monitored.
Caution must be observed when treating patients with chronic hepatitis who have a history of autoimmune diseases.
Roferon-A can cause severe psychiatric side effects even in patients without a history of mental illness. During treatment, it is recommended to monitor the condition of patients in order to identify possible signs of depression in time.
The drug should be used with extreme caution in cases of severe myelosuppression, since interferon alfa-2a inhibits the bone marrow, resulting in a decrease in the number of leukocytes and platelets, and less often in hemoglobin levels, which can lead to the development of infections or bleeding. You should closely monitor these indicators, as well as conduct detailed blood tests before prescribing Roferon-A and regularly during its use.
In case of complaints of deterioration or loss of vision, an ophthalmological examination is indicated. Before starting therapy, patients with arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus must undergo an examination to identify fundus pathologies.
Sometimes Roferon-A contributes to the development of hyperglycemia. In this case, it is necessary to monitor blood glucose levels. Patients with diabetes mellitus may require dose adjustment of hypoglycemic drugs.
When carrying out combination therapy, it is necessary to take into account the precautions specified in the instructions for the relevant drugs.
Precautionary measures
The use of Roferon a should be accompanied by the strict supervision of a specialist.
During treatment, kidney and liver function should be monitored, and laboratory blood parameters should also be monitored.
Treatment should be carried out with caution in patients with autoimmune pathologies.
If a depressive state or any other psychological adverse reactions develop, the use of the medication should be discontinued immediately.
If problems with the organs of vision are detected, you should be examined by an ophthalmologist.
Patients with diabetes need a dose adjustment, which is prescribed by a doctor, after assessing their health status.
When carrying out therapy with Roferon in combination with Ribavirin, you must adhere to certain rules.
Reusable cartridges are used for one patient only. For each injection, you must use a new sterile needle.
Cartridges are suitable for use within 30 days after unpacking; they are best stored in the refrigerator.
Depending on the dosage and susceptibility of the drug, Roferon may have an inadequate reaction from the central nervous system, therefore, during the period of therapy with the drug, it is advisable to refrain from driving and work that requires special attention.
Drug interactions
Interferons can enhance the cardiotoxic, hematotoxic and neurotoxic effects of drugs used simultaneously or previously.
Interferon alfa-2a can disrupt oxidative metabolic processes and reduce the activity of hepatic microsomal enzymes of the cytochrome P450 system, which should be taken into account if it is necessary to simultaneously use drugs that are metabolized by this pathway.
Interactions may occur when centrally acting drugs are coadministered.
When conducting combination therapy with ribavirin, its possible drug interactions must also be taken into account.
Similar drugs:
- Ergoferon () Lozenges
- Groprinosin Oral tablets
- Groprinosin Oral tablets
- Tea tree DN Ointment for external use
- Valtrex Oral tablets
- Zanamivir Powder for inhalation, dosed
- Valacyclovir Oral tablets
- Oseltamivir Capsule
- Anaferon for children (Anaferon filios) Lozenges
- Laripront Lozenges
** The Drug Directory is intended for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions. Do not self-medicate; Before starting to use the drug Roferon-A, you should consult a doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal. Any information on the site does not replace medical advice and cannot serve as a guarantee of the positive effect of the drug.
Are you interested in the drug Roferon-A? Do you want to know more detailed information or do you need a doctor's examination? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home . Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
** Attention! The information presented in this medication guide is intended for medical professionals and should not be used as a basis for self-medication. The description of the drug Roferon-A is provided for informational purposes and is not intended for prescribing treatment without the participation of a doctor. Patients need to consult a specialist!
If you are interested in any other drugs and medications, their descriptions and instructions for use, information about the composition and form of release, indications for use and side effects, methods of use, prices and reviews of drugs, or you have any other questions and suggestions - write to us, we will definitely try to help you.