Colposcopy is a gynecological research method involving a targeted and detailed examination of the cervix using a specially designed microscope.
The main purpose of colposcopy is to identify foci of epithelial degeneration into erosion or even neoplasia (precancer).
The procedure is performed as part of a routine gynecological examination in a clinic or diagnostic center.
There are several different colposcopy methods that allow you to identify all possible anomalies in the structure of the cervix and cervical canal, which allows you to identify areas of erosion and dysplasia (degeneration) of the epithelium. This method is the earliest and life-saving diagnosis of tumor processes.
Cervix and its features
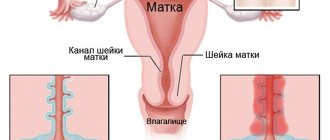
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, connecting its body to the vagina. It has the shape of a tube, inside of which the cervical canal is located in the form of a spindle. At one end it opens into the uterine cavity, forming the internal pharynx, and at the other end into the vagina, thereby forming the external pharynx. It is the external os of the cervix that is examined during a gynecological examination, as well as colposcopy.
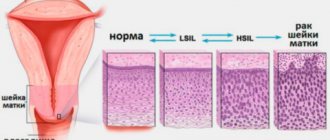
Along the entire internal surface, the cervical canal is covered with cylindrical (goblet) epithelium, secreting a special secretion that protects the uterus from penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, and also ensures the normal movement of sperm from the vagina into the uterine cavity. At the same time, the vagina and external os of the cervix are normally covered with stratified squamous epithelium. Typically, the border between the columnar and squamous epithelium, called the transition zone, is clearly visible and presents a clear edge. It is in this part that most often, namely in 90% of cases, pathological changes occur, which colposcopy is intended to diagnose.
In young girls, the presence of an area covered with goblet epithelium may be observed in the vaginal part of the cervix. If the transition boundary is clear and even, this is regarded as a variant of the norm. But such a condition should go away on its own by the age of 25, otherwise they say there is erosion.
Brief information
We are talking about a gynecological method for examining the female genital organs. This is a direct examination of the internal structures of the reproductive sphere under magnification. With the help of a special optical device, such a procedure becomes possible - magnification occurs several tens of times.
This examination technique is classified as a purely medical procedure, because it is performed exclusively by a doctor for the purpose of additional examination of mucous structures. The method is truly unique and in demand - it allows you to identify minimal primary changes that cannot be noticed when examined with the naked eye.
What is colposcopy
Colposcopy is one of the methods of gynecological examination of the cervix from the vagina using a special apparatus (colposcope). It is an optical device similar to a microscope, in which a light source is installed for high-quality illumination of the most inaccessible and darkened areas. The colposcope does not contact the patient’s body and allows you to examine the cervix with a magnification of up to 40 times, thanks to which the gynecologist can notice even minor changes in the structure of its tissues, and carrying out various tests and samples significantly expands the diagnostic capabilities of the method.
With its help, the doctor evaluates the color, character, surface relief of the mucous membrane of the visible part of the cervix, vascular pattern, and the condition of the glands. All this makes it possible to accurately determine not only the size of pathological changes in the cervix, but also their origin, i.e., make a diagnosis and prescribe optimal treatment.
Previously, all colposcopes were mechanical, but today digital colposcopes are becoming increasingly common, allowing real-time image display on a monitor screen. This allows both the woman herself to see all the existing changes in the cervix, and creates a basis for comparing the results of treatment with the initial state and assessing its effectiveness. Therefore, if there is a choice, digital colposcopy is always preferred.
Colposcopy is a safe, painless, highly informative procedure that often takes no more than 5 minutes, although in some cases it can last up to half an hour. Only sometimes women feel slight discomfort when treating the outer part of the cervix with solutions of chemicals.
Today the method has wide indications for use and is used for the following purposes:
- detection of areas of pathological epithelium on the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix, typical for erosion, dysplasia and cervical cancer;
- assessing the size and location of foci of pathological changes;
- choosing a treatment method for detected diseases;
- dynamic control over the condition of the cervix when choosing expectant management or active treatment of its pathologies;
- assessing the need for a biopsy followed by histological examination of the samples.
Historical facts
In 1924, Hinselmann was asked to write a chapter based on the etiology, symptoms and diagnosis of uterine cancer in the third edition of the Handbook of Gynecology. Hinselmann faced this challenge most successfully. He performed gynecological examinations and often encountered early detection of cervical cancer, which he believed could only be improved by optical means. He believed it was necessary to "provide an intense light source for the magnified image without sacrificing binocular vision."
Content:
- Historical facts
- Composition of a colposcope
- Indications for the use of colposcopy
- Differences between simple and extended colposcopy
- Preparing for the examination
- Methodology
- Complications after extended colposcopy
- Contraindications for the study
- Colposcopy and pregnancy
- Study protocol
By 1925, he reported the construction of the first colposcope. To this end, he connected a light source to Lake's binocular biological microscope. He connected the optical system to a stand that allowed movement in each direction and also supported a small screw for fine adjustment. After the invention of the colposcope, Hinselmann was able to state that “with regard to so-called early problems, colposcopy makes it possible to detect earlier cases.” Even a tiny tumor the size of a dot did not disappear and was visible even with an initial magnification of 7.5 times. Thus, Hinselmann discovered a completely new invention and proved its significance in the field of medicine.
Types of colposcopy
There are 3 types of colposcopy:
- simple (overview);
- extended;
- colpomicroscopy.
Initially, they always start with a simple colposcopy. If during the procedure the gynecologist discovers changes in the condition of the cervix, he will conduct an extensive study using chemicals: acetic acid and a 5% alcohol solution of iodine. After each stage of the procedure, the gynecologist carefully examines the cervix through a colposcope and records the detected changes.
Colpomicroscopy is performed extremely rarely and requires special equipment. It allows you to obtain an increase of more than 300 times, which is necessary for assessing the ratio of the size of the nucleus to the cytoplasm and detecting other features in the structure of cells.
Acid test
To carry out this test, use a 3% acetic acid solution or a 0.5% salicylic acid solution. Their treatment of the surface of the cervix leads to short-term swelling and pallor of the squamous epithelium, and narrowing of healthy capillaries. If the squamous epithelium is replaced by cylindrical epithelium, it does not react to the acid used and stands out against the healthy background as a bright red spot with clearly visible boundaries. Pathologically altered vessels also do not react to acetic or salicylic acid, so they retain their original shape and are clearly visible.
After 2 min. healthy mucous membrane returns to normal and becomes pale pink. A slight uniform whiteness of large areas is not regarded as a sign of the disease, but the more the epithelium whitens and the longer this effect persists, the deeper its damage. This is typical for inflammatory processes, in particular cervicitis, as well as mucosal atrophy. But if after application of acid the epithelium becomes thick and richly white, this is a sign of a precancerous condition.
Thus, the test allows you to obtain a lot of valuable information about the condition of the cervical mucosa, including:
- accurately determine the line between squamous and goblet epithelium;
- detect modifications of the squamous epithelium and assess the depth of the lesion, as well as areas modified by HPV;
- identify abnormal vessels;
- detect even small foci of leukoplakia and neoplasia (precancerous condition) and differentiate them;
- diagnose oncological diseases, in particular adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Schiller test
The Schiller test is also part of an extended colposcopy and is performed immediately after the end of the test with acetic or salicylic acid. It involves treating the cervical mucosa with Lugol's solution or a 5% aqueous solution of iodine. The method is based on the ability of iodine to interact with glycogen, so its use makes it possible to detect areas of the epithelium whose cells lack this compound. Thus, after smearing with an iodine solution, the healthy mucous membrane is uniformly colored brown, and if pathological changes occur in it, it either remains unchanged or turns unevenly yellow or another color.
Thus, the Schiller test allows you to detect:
- atrophied epithelium (brown color is uneven);
- areas of metaplastic, columnar epithelium and other benign changes (such lesions are weakly stained and have blurred edges);
- foci of inflammation (partially painted over);
- cervical dysplasia, severe atrophy (colored yellow or pale);
- leukoplakia (no coloring occurs, and the affected area has the appearance of a light shiny film with a smooth or embossed surface);
- atypical cells (take on a gray, olive color and have pronounced contours).
If, when performing a test with Lugol's solution, iodine-negative areas are detected, i.e., unstained, it is recommended to take a targeted biopsy from them and conduct a histological examination of the resulting biopsy. This is necessary to exclude cancer and establish an accurate diagnosis.
If the clinic where the colposcopy is performed has its own laboratory, the biopsy can be taken immediately.
Composition of a colposcope
Colposcopes come in two types: those with a fixed focal length lens whose magnification can be changed by changing the power of the eyepieces, and those with a fixed focal length lens but with multiple magnifications where the dial setting can be changed or a button pressed. .
Increase
Multiple magnifications are preferred, starting at ×5 or ×7.5, ×20 or ×30. The lowest magnification gives a bird's eye view and is great for locating or zooming in on an area of interest. The magnification commonly used for detailed examination is ×15. The modern colposcope is based on the original prototype, but differs from the original in that the magnification varies from 6 to 40 times, as opposed to the original 7.5 times. 10x magnification is suitable for everyday use. Higher magnification allows you to recognize some minor points, but it is not necessary to use it for an accurate diagnosis.
The most important accessories for a colposcope are photographic equipment and special spare parts for teaching. Also, simple low-power devices without any accessories are always available on the market, as well as more complex ones with electrical control, a zoom lens with fine tuning and a camera. For routine use, a simple colposcope is fine, but for training, both the camera and viewing tube are essential. All colposcopes have lenses, eyepieces, filters, a light source and a stand.
Lens
This in turn affects the focal length and therefore the working distance. The best focal length is between 250mm and 300mm. This allows you to easily operate and manipulate tools without interfering with your vision.
Eyepieces
Eyepieces must have the following good characteristics: the axes of the eyepieces can be straight or inclined at an angle of 45° to the optical axis of the device, they must have rubber cups installed on them, they must have independent focusing elements that adapt to human vision. Also one very important feature is the convergent line of sight for fatigue-free working.
Filters
Most colposcopes are equipped with green filters. They absorb red light and enhance the image of blood vessels that appear black. The contrast between normal and abnormal epithelium is also enhanced.
Light source
The light source must be at least 30,000 lux, must be constantly centered, and must have a rheostat to vary the light intensity. Some equipment has automatic brightness adjustment depending on the magnification used. Most colposcopes are equipped with a halogen lamp with a power of 6 to 12 W and 20 to 75 W. A recent innovation is the light emitting diode (LED), which is a better light source. They generate light through semiconductor processes rather than heating a wire filament, as in a halogen lamp. The advantages of an LED light source are that its light output is five to seven times higher than that of a lamp; this light uses a different optical system, significantly improving contrast, and with it overall visibility improves. The service life of an LED is also many times higher (up to 10,000 hours) than a halogen lamp. It lasts for approximately 10 years with daily use of approximately 4 hours.
Indications for use
The procedure is performed both routinely once a year during a routine examination by a gynecologist, and upon receipt of the results of a cytological analysis of a scraping from the cervix, indicating the presence of dysplasia, namely atypical squamous or glandular epithelial cells:
- ASC-US;
- LSIL;
- HSIL;
- ASC-H;
- AGC;
- AIS.
It is the diagnosis of true cervical erosion and pseudo-erosion that has acquired signs of atypia and dysplasia that is one of the most common indications for performing colposcopy.
The procedure is also used to diagnose cervical pathologies such as:
- cervicitis is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- endometriosis is a pathology in which the endometrium covering the uterus from the inside extends beyond the boundaries of the inner lining of the cervix, which is often accompanied by bleeding of varying severity and nagging pain;
- polyps - are growths of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- condylomas are small growths on the surface of the mucous membrane of a flat, papillary or pointed shape, which are a sign of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV);
- erythroplakia is a disease accompanied by the formation of areas of atrophy and dyskeratosis against the background of infectious diseases, hormonal disorders, chemical and mechanical damage;
- leukoplakia is a pathology characterized by the formation of zones with increased keratinization of the squamous epithelium;
- cancer is the formation of a malignant tumor of the cervix, which often results from the development of dysplasia against the background of pseudo-erosion, the formation of condylomas and other pathological changes.
The procedure is necessarily performed as part of monitoring the condition of the cervix in patients with mild erosive changes that may turn out to be physiological, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of treatment of detected diseases.
Popular questions
My daughter is suspected of having erosion; she has not given birth yet.
They prescribed Klion D suppositories. After she put them on, 2 hours passed, she went to the toilet and a burning sensation appeared inside the vagina. What can be done to relieve this discomfort? Can I continue to try taking this drug? To relieve the symptoms of burning after urination, you can perform hygiene with an antiseptic or intimate gel with an anti-inflammatory effect, for example Gynocomfort intimate gel. This will not only eliminate discomfort, but will also complement the anti-inflammatory effect. You should continue to use the suppositories, and if similar manifestations recur, consult your doctor. A year ago, cervical erosion was discovered. 2 cryodestructions were performed. To normalize hormonal levels, COC Jess Plus was prescribed. Now erosion has appeared again. According to the results of cytology CIN 1, leukocytes and erythrocytes are in moderate quantities. Last year's and current PCR tests for HPV, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, and torch infections were negative. The gynecologist prescribed excision followed by sending the tissue for histology. There were no pregnancies, now in the planning stage. I would like to hear an additional answer regarding the need for cervical excision; will this procedure affect conception and natural childbirth?
In this situation, it is necessary to know the conclusion of colposcopy, carry out additional sanitation of the genital tract and undergo a “liquid cytology” test, which will confirm or refute the presence of mild dysplasia. If the conclusion is repeated, then it is better to plan pregnancy and periodically monitor the smear for oncocytology, rather than carry out surgical treatment.
I was diagnosed with cervical erosion, the first gynecologist did not give me a conclusion. I learned this from the second gynecologist (the first gynecologist said cauterization, the second after childbirth). Cervical canal scraping revealed (1) HPV 31 q 1.8×10*6 HPV 31 in ye Hybrid Capture 12; (2) HPV 58 q 1.0×10*5 HPV 58 in ye Hybrid Capture 0.66 Material capture control 2.0x10*5. and so far 2 infectious diseases have been identified: Mycoplasma sp. (generic); Gardenella vaginalis. Question: I need to do a transvaginal ultrasound. When is the best time to do it? What tests should I take? I’m 28 years old and have no children; I really want to give birth.
Hello! In your case, you need to start with anti-inflammatory therapy for mycoplasmosis, gardnerellosis and carriage of the Human Papilloma Virus. Then perform a colposcopy and take an oncocytology test. Based on their results, decide on the need to treat cervical erosion before birth. Ultrasound is not performed in this situation.
Hello, I am diagnosed with cervical erosion, they suggest cauterization, I don’t want to, they don’t offer an alternative, there is no other doctor, can you tell me an alternative to cauterization. Thank you
Hello!
The treatment method depends on the type of cervical erosion. The nature of the changes is determined during colposcopy. The examination takes into account a cytology smear and an HPV test. I recommend an additional consultation with a doctor with the results of examinations to decide on treatment alternatives. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Preparing for colposcopy
Colposcopy can be performed on absolutely any day of the cycle, with the exception of menstruation, since the presence of bloody discharge will not allow a full assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix and will distort the test results. The optimal time for performing the procedure is considered to be the first 5 days after the end of menstruation.
There is no need to prepare specially for colposcopy, but to avoid getting false results, it is recommended that 2 days before your visit to the gynecologist you refuse:
- sexual intercourse;
- inserting tampons into the vagina;
- douching;
- use of vaginal suppositories and creams.
Douching, except when prescribed by a doctor for medicinal purposes, is harmful to the female body, as it leads to disruption of the microflora. Therefore, it should be abandoned in principle.
Before the procedure, you should empty your bowels and perform a standard toilet of the external genitalia. It is important to avoid getting soap solutions into the vagina.
On what day of the cycle should I do it?
The optimal time for diagnosis is the first week after the end of menstruation. At this time, the opportunity to obtain the most reliable research results is maximum. During ovulation, the presence of mucous discharge in the cervical canal prevents the doctor from assessing its condition. Also, diagnosis cannot be carried out during menstruation, due to the fact that the presence of blood in the vagina makes it difficult to see. In the second half of the cycle, the procedure is undesirable for the reason that at this time the mucous membrane needs more time to recover after a possible biopsy.
The essence of the procedure
Colposcopy is performed in a gynecological office equipped with a colposcope. The patient is placed on a gynecological chair, the doctor inserts a standard speculum into the vagina, expands it to the required parameters and fixes the cervix. If necessary, secretions and cervical cells are collected for laboratory tests. After this, the vaginal walls are cleaned of secretions with a tampon soaked in saline solution.
The doctor moves the optical device to the chair and places the colposcope at some distance from the vagina. It is equipped with two eyepieces and a magnification control, which allows you to view all areas of interest to the gynecologist in the required approximation. If a digital colposcopy is performed, a woman can monitor the progress of the procedure and see everything that the doctor sees on the monitor screen.
First, a survey colposcopy is always performed, during which the gynecologist examines the cervix at different magnifications for abnormalities. If they are not detected, the procedure ends there. But if the doctor sees pathological changes, he proceeds to conduct an extended colposcopy in the absence of allergies to iodine and acetic acid preparations.
At this stage, the gynecologist initially carefully treats the entire surface of the external os of the cervix with a tampon moistened with a 3% solution of acetic acid, holding it on the surface of the mucous membrane for 30-40 seconds. Afterwards, the tampon is removed and the cervix is examined again using a colposcope. As a result of the action of the drug, the changed areas of the mucous membrane become white, which is called acetowhite epithelium.
After this, a Schiller test is performed, which involves the use of an aqueous solution of iodine (Lugol's solution). A tampon soaked in it is used to treat the visible part of the cervix, which can sometimes lead to a slight burning sensation that causes slight discomfort to the woman. Areas with healthy mucosa are uniformly dark brown in color, while areas with pathological changes acquire lighter shades.
If during colposcopy areas with signs of pathological changes are detected, to accurately diagnose their nature, samples can be taken immediately after colposcopy for histological examination, i.e., biopsy.
Varieties of techniques
A simple examination with a colposcope is the most common. It is, in fact, a simple, exclusively survey colposcopy.
Sometimes such a study is not enough; many experts consider it to be of little effectiveness for diagnosing complex lesions. For better, in-depth diagnosis, additional tests are used. In such cases, colposcopy turns into an extended one. There is also colpomicroscopy - histological diagnosis of the vagina. This way pathological changes can be accurately determined. The results of the histological and colpomicroscopic diagnostic method have the highest percentage of coincidences.
In addition, in many private centers and clinics, the achievements of the examination have gone further. It became possible to perform video colposcopy. During diagnostics, the image is displayed on the screen, it becomes possible to take pictures and record video procedures. The patient sees the progress of the procedure in parallel with the doctor.
Decoding the results
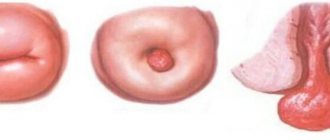
Normally, in a healthy woman, the cervix has a uniform, shiny, pale pink surface. If the patient consults a doctor in the 2nd half of the menstrual cycle, the mucous membrane may acquire a bluish tint, which is not a sign of pathological changes. The presence of the disease is indicated by bright red mucous membrane, which may also have a bumpy or velvety surface.
The external pharynx in nulliparous women has a rounded shape, and after natural childbirth it takes on the appearance of a slit and retains it until the end of life.
When the cervix is treated with acetic acid, the normal mucous membrane lightens for a while and after a couple of minutes returns to its normal pinkish color. The receipt of acetowhite epithelium after treating the cervix with a 3% solution of acetic acid, i.e., areas with an intense white color, may indicate HPV infection and the development of dysplasia, which requires further examination.
When performing the Schiller test, the degree of brown coloration of various parts of the cervix is assessed. If the entire surface has a uniform brown color, this indicates the absence of pathology. The presence of changes is indicated by the coloring of various areas in:
- yellow color – dysplasia;
- white color – atypia;
- lack of staining (the mucous membrane remains pink) – pseudo-erosion, i.e. covering the vaginal part of the cervix with an atypical columnar epithelium.
Thus, a healthy cervix has a conical shape, its mucosa is not swollen, pale pink or bluish, the border between the stratified squamous and goblet epithelium is clear. There are no glands, cysts, signs of keratosis and epithelial atrophy on the surface of the cervix. The vessels have a typical shape, the punctuation is gentle, and there is no mosaic. There is no acetowhite epithelium, the Schiller test is positive, i.e. there are no iodine-negative areas. Any deviations from these values are regarded as deviations from the norm, based on the nature of which the doctor can immediately make a diagnosis or refer the patient for a biopsy and other examinations to clarify the nature of the detected changes.
The diagnostic results are announced to the patient directly during the procedure or after completion of the examination. Additionally, they can be presented in the form of a schematic image of the cervix indicating the area and size of the affected area, photos or videos (only possible with digital colposcopy).
Does it hurt or not?
Many patients who have little understanding of the specifics of this form of examination ask the question: “Does it hurt to do colposcopy?” Normally, this procedure is painless and is done without anesthesia. Some women complain of slight discomfort due to the insertion of the Cusco speculum into the vagina, and also feel a slight tingling sensation during testing. However, if the walls of the vagina and cervix are subject to inflammatory processes, pain may still be present.
Actions after colposcopy
Since colposcopy is not a traumatic procedure, no restrictions are imposed after it is performed. A woman can continue to lead a normal life, including sexual intercourse, as well as play sports and perform her usual work. After the manipulation, there is no need to use any medications or perform procedures.
If extended colposcopy was used, brownish discharge may occur in the first 3 days after the procedure. This is normal, and the brown color of vaginal mucus is not caused by blood, but by leaching iodine residues. Therefore, these days it is worth using panty liners to protect your underwear.
Refraining from sexual activity, physical activity and visiting open water bodies, swimming pools, saunas, baths for 1-4 weeks will be required in cases where during colposcopy a biopsy was immediately taken or polyps and condylomas were removed. In such cases, the doctor may also prescribe the use of certain medications to speed up the healing of the wound surface. After such procedures, discomfort may occur in the lower abdomen or directly in the vagina, as well as spotting bleeding. This should not cause concern to a woman, as it is a normal reaction of the body to the intervention.
Thus, colposcopy is a simple, cheap, safe and at the same time very informative method for diagnosing a huge number of cervical diseases. Therefore, it is recommended to carry it out at least once a year for every woman.
The effectiveness of the technique
Today, such manipulation is rightfully considered accurate in terms of studying endometriosis, polyposis, oncological processes and precancerous conditions.
Normally, the epithelial area is light pink, shiny and smooth. Benign changes are characterized by true erosion, ectopia.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?