Sanguiritrin®
Externally, locally apply a 0.2% alcohol solution. An aqueous-alcohol solution prepared ex tempore from a 0.2% alcohol solution is also used. To do this, the drug is diluted 40 times (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of water).
As a preventative measure, newborns are treated with skin folds using a sterile cotton swab moistened with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug or an aqueous alcohol solution prepared from it daily, 2 times a day during the first 5-6 days of life. To prevent purulent-inflammatory complications, the wound is treated with a sterile gauze swab, generously moistened with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug, covered with a sterile napkin moistened with the same solution, and a fixing bandage is applied. After 3-4 days, the wound is re-treated with the drug and a dry sterile bandage is applied. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
Treatment of periodontitis is carried out after removing dental plaque and curettage of pathological gum pockets. Thin turundas, generously moistened with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug or an aqueous-alcohol solution prepared immediately before use, are injected into the gum pockets for 20 minutes. The procedure is carried out daily or every other day. The course of treatment is 4-6 procedures.
For stomatitis of various etiologies, an aqueous-alcohol solution of the drug prepared from a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug is applied to the lesions of the oral mucosa 2-3 times a day for 2-5 days. Children over 5 years old with stomatitis are prescribed rinsing with a warm aqueous-alcohol solution of the drug. For children under 5 years of age with stomatitis, the oral mucosa is lubricated with an aqueous-alcohol solution of the drug.
For tonsillitis, the tonsils are treated with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug once a day for 2-5 days. In addition, adults and children over 5 years of age are prescribed rinsing with an aqueous-alcohol solution daily 3-5 times a day for 3-7 days.
Treatment for external otitis is carried out after careful removal of discharge from the external auditory canal and the introduction of cotton wool moistened with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug for 10-15 minutes 2-3 times a day. The minimum course of treatment is 7 days.
In the treatment of chronic purulent otitis after removing pus from the ear, a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug is instilled into the ear of adults, 8 drops 3 times a day, for children - 3-4 drops 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
For the treatment of infected burns, long-term non-healing wounds and ulcers, the lesions are treated with a sterile gauze swab, abundantly moistened with a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug, covered with a sterile napkin moistened with the same solution, and a fixing bandage is applied. For infected burns, dressings are performed every other day, for long-term non-healing wounds and ulcers - daily 1-2 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the nature and severity of the disease. The minimum course of treatment is 10-12 days.
For endocervicitis, colpitis, vaginitis, cervical erosion, Sangviritrin® is used as douching or lotions with a warm aqueous-alcohol solution 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 5-10 procedures.
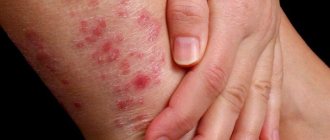
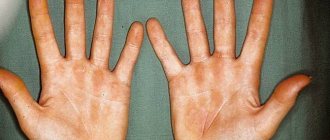
For pyoderma, dermatomycosis, including those complicated by mixed microflora, the drug is prescribed in the form of bandages soaked in a 0.2% alcohol solution of the drug 1-2 times a day. The duration of treatment is up to 3 weeks.
Sangviritrin
Active substance:
Sanguinarine hydrosulfate, Heleritrine hydrosulfate
Pharmgroup:
Antiseptics and disinfectants
Average price in pharmacies
| Name | Manufacturer | average price |
| Sangviritrin 0.2% 50ml solution | VILAR PHARMACY CENTER | 168.00 |
Analogs for the active substance:Sangviritrin liniment 1% | Application area:Abdominal surgery Adenomectomy Bacterial diarrhea Bacterial dysentery Bacterial vaginitis Bacterial vaginosis Bacterial intoxication Bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract Bacterial ear infections Bacterial colpitis Bacterial vaginitis Bacterial vaginosis Bacterial gastroenteritis Bacterial dysbiosis Bacterial colpitis Balloon coronary angioplasty Vaginal hysterectomy Gilchrist's disease Vaginal candidiasis Vaginal candidiasis Vaginitis Bacterial vaginitis Corona bypass Viral dysbiosis Visceral candidiasis Interventions on the vagina and cervix Bladder interventions Intervention in the oral cavity Inflammation after surgery and injury Inflammation after injury Inflammation of the middle ear Inflammatory gum disease Inflammatory diseases of the vagina and vulva Inflammatory diseases of the female genitalia Inflammatory diseases of the female genitalia Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity Restorative and reconstructive operations Restoration of intestinal flora Secondary infection of skin lesions and mucous membranes Secondary healing processes Secondary toxicosis Vulval candidiasis Vulvitis Vulvovaginal infections Vulvovaginal candidiasis Vulvovaginal candidiasis Vulvovaginitis Atrophic vulvovaginitis Bacterial vulvovaginitis Vulvovaginitis candidiasis Vulvovaginitis mycotic Estrogen deficiency vulvovaginitis Vulvovaginitis Limp granulating wounds Slow healing wounds Slow-healing wounds Gardnerellosis Hand hygiene of medical personnel Gingivitis Gynecological surgery Gynecological interventions Gynecological surgeries Hyperplastic gingivitis Hypovolemic shock during surgery Deep wounds Deep wounds Purulent wound Purulent wound Pustular dermatoses Pustular skin lesions Purulent-necrotic phase of the wound process Purulent-septic diseases Purulent allergic dermatopathies Purulent skin infections Purulent wounds Purulent wounds with deep cavities Gonococcal cervicitis Gonorrheal cervicitis Granulating wounds Small granulating wounds Fungal paronychia Fungal eczema Fungal nail disease Fungal nail infection Fungal vaginitis Fungal vulvovaginitis in girls and virgins Fungal dermatoses Fungal diseases of smooth skin Fungal diseases of smooth skin Fungal skin diseases Fungal nail diseases Fungal diseases of the oral cavity Fungal infections of the mouth Fungal infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity Fungal infections of smooth skin Fungal infections of smooth body skin Fungal infections of smooth body skin Fungal nail infections Fungal nail infections Disinfection of purulent wounds Disinfection of purulent wounds Disinfection of wound edges Dermatomycosis Ringworm in large skin folds Dermatomycosis of smooth skin Dermatomycosis of the groin area and smooth skin Dermatomycoses Dermatomycosis of smooth skin Dermatomycosis of nails |
Release form and composition
Dosage forms of Sangviritrin:
- Tablets, enteric-coated: biconvex, round, from dark orange to brownish-orange in color (10 pcs. in a blister pack, in a cardboard pack of 3 or 5 packs; 30 or 50 pcs. in a blister pack, in a cardboard pack 1 package);
- Solution for external and local use 0.2% (alcohol): transparent, orange liquid with the odor of alcohol (10, 25, 50 and 100 ml each in an orange glass bottle with a screw neck, sealed with a polyethylene stopper and a plastic screw cap; by 20, 30 and 50 ml in a dark glass bottle with a screw neck, closed with a plastic screw cap with a control ring and a dropper; 1 bottle in a cardboard box);
- Liniment 0.5%: a thick, homogeneous mass from pale orange to orange in color with a characteristic odor (10 or 20 g each in an orange glass jar with a triangular rim, sealed with a plastic pull-on lid with a sealing element; 10 or 20 g each in an aluminum tube with a high-pressure PE bushon; 1 can or 1 tube in a cardboard pack).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- Active substance: sanguiritrin (chelerythrine hydrosulfate and sanguinarine hydrosulfate) – 0.005 g;
- Additional components: magnesium stearate, low molecular weight povidone (low molecular weight medical polyvinylpyrrolidone 12600±2700), sucrose (sugar or refined sugar);
- Shell: opadry II white OY-LS-28911 (titanium dioxide dye, polyethylene glycol 4000 (macrogol-4000), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose), polydextrose, lactose monohydrate); white acrylic 93O18359 (sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, triethyl citrate, talc, titanium dioxide dye, copolymer of methacrylic acid with ethyl acrylate 1:1); opadry II red 85F25163 (iron oxide red (E172), polyethylene glycol 4000 (macrogol-4000), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose), polydextrose or lactose monohydrate).
Composition of 1000 ml solution for external and local use:
- Active substance: sanguiritrine (chelerythrine hydrosulfate and sanguinarine hydrosulfate) – 2 g;
- Additional components: purified water, ethyl alcohol (ethanol) 95%.
Composition of 100 g of liniment:
- Active substance: sanguiritrine (chelerythrine hydrosulfate and sanguinarine hydrosulfate) – 0.5 g;
- Additional components: purified water, sorbic acid, castor oil, Tween 80 (polysorbate 80), emulsifier No. 1, ethyl alcohol (ethanol) 95%.
Indications
In the complex therapy of acute and chronic purulent-inflammatory diseases:
— acute intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonellosis, food toxic infections);
- wound infections and various infectious complications caused by pathogenic microflora (convalescent bacterial carriage);
- diseases associated with disruption of normal microflora (dysbacteriosis), as well as diseases caused by pathogenic fungi (pharyngomycosis, candidiasis, microsporia).
As part of combination therapy of sensory and motor disorders associated with diseases and traumatic injuries of the nervous system (poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy).
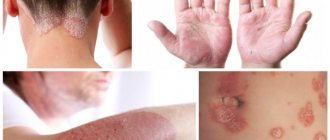
Prevention of purulent-inflammatory skin diseases in newborns and wound infections in surgical patients; infectious and inflammatory diseases of the skin and mucous membranes (including infected wounds, periodontitis, periodontal disease, alveolar pyorrhea, ulcerative necrotizing gingivostomatitis, aphthous stomatitis); tonsillitis, otitis media; pyoderma, eczema, dermatomycosis, onychomycosis, superficial blastomycosis; open infected fractures, burns, long-term non-healing wounds and trophic ulcers.
Diseases of the middle ear and external auditory canal.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the uterus and vagina (endocervicitis, colpitis, vulvitis, cervical erosion, infected postoperative wounds), incl. in pregnant women.
special instructions
The drug should not come into contact with the eyes. If Sangviritrin into your eyes, rinse them with plenty of water.
For long-term non-healing wounds and ulcers, endocervicitis, colpitis, vaginitis, cervical erosions, pyoderma, superficial blastomycosis and dermatomycosis (including those complicated by mixed flora), the combined use of Sanguiritrin in combination with liniment (1% or 5%) is possible. which is prescribed in the form of bandages or lubrication of the lesion.
pharmachologic effect
Antimicrobial drug for external and local use. Has a wide spectrum of action, is active against
gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria (including antibiotic-resistant strains), yeast-like and filamentous (mold) fungi. When used in therapeutic doses, it acts bacteriostatically. The mechanism of action is due to the suppression of bacterial nuclease, disruption of the permeability of cell membranes, division partitions and changes in the structure of the nucleotide.
pharmachologic effect
Has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action. Active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
(Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., Shigella spp., Escherichia spp., Salmonella spp., Proteus spp., Acinetobacter spp., Citrobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., Serratia spp., Klebsiella spp., Antracoides spp., Cryptococcus spp.), pathogenic fungi of the genus Microsporum, Trichophyton, Nocardia, Aspergillus, yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (including multiresistant strains of microorganisms), as well as Actinomyces and some pathogenic protozoa (Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis). The mechanism of the antimicrobial action of sanviritrin is based on the suppression of bacterial nuclease, disruption of the processes of permeability of cell walls, division septa, and nucleoid structure.
Active regarding
many multidrug-resistant strains of microorganisms.
Has anticholinesterase activity.
Showing
As a preventive use: for newborns to prevent purulent-fiery skin diseases and surgical diseases - to prevent early infections.
As a medical treatment: for infectious-inflammatory diseases of the skin and mucous membranes of bacterial and fungal etiology, including Candida albicans; in dentistry – for periodontitis, aphthous stomatitis, virulent-necrotizing gingivostomatitis and other diseases of the mucous membrane of the empty mouth; in otolaryngology – for sore throat, diseases of the middle ear and outer ear canal; in surgery – for infected wounds, wounds that will not heal for a long time, and wounds; in gynecology – with endocervicitis, colpitis, vaginitis, cervical erosion; in dermatology – for pyoderma, superficial blastomycosis, dermatomycosis.
Contraindications
For all forms:
- Severe kidney and liver diseases accompanied by functional disorders;
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Additionally for tablets:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Hyperkinesis;
- Epilepsy;
- Age up to 3 years.
Additionally, contraindications for liniment and solution also include the presence of skin lesions with symptoms of eczematization.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the solution and liniment are approved for use after consultation with a specialist. During these periods, tablets are used only as prescribed by a doctor, in the case when the intended benefit to the woman outweighs the possible threat to the child/fetus.