Keratoacanthoma of the skin is a benign type of neoplasm of epidermal origin. It affects an open area of skin, sometimes occurring under the nail plate or on the mucous membranes. The tumor is also often called a sebaceous mollusk. The neoplasm grows dangerously fast – it takes on large sizes in a short period of time. The peculiarity of the disease is that after a certain time it can go away on its own, in some cases it degenerates into a malignant tumor. With favorable development, only a scar remains at the site of the pathology.
Keratoacanthoma of the skin: what is it?
Keratoacanthoma of the skin produces a double impression. On the one hand, it in itself is a safe pathology, on the other hand, it often degenerates. It is interesting that in some patients, cutaneous keratoacanthoma remains benign even with relapses and in aggravating circumstances (dermatological diseases, skin injuries), while in others it transforms into malignant neoplasia. In every twentieth case (and this is 6% of patients), the neoplasm degenerates into squamous cell skin cancer.
Important
Due to the danger of malignant degeneration, keratoacanthoma of the skin requires constant monitoring - such patients should undergo a preventive examination by a dermatologist and oncologist not once a year, but twice, preferably more.
Keratoacanthoma of the skin is diagnosed approximately three times more often in men than in women. It is more often detected in older people - from 40 to 60 years, with a peak incidence observed after 50 years. The disease is not typical for childhood and adolescence; juvenile forms are rare. Malignant degeneration of the tumor in children and adolescents is also rare.
Geographical features of the appearance of cutaneous keratoacanthoma have not been found - it is detected in different populations around the world.
Surgical removal of this tumor is indicated not only because of the risk of malignancy. The scars that form after the keratoma has disappeared spoil the aesthetic appearance of the skin. Therefore, removal of keratoacanthoma on the face is especially important.
Keratoma of the skin is also called tumorous keratosis.
Why should you visit a dermatologist at Odrex Medical House?
The staff of the Odrex Medical House consists of highly specialized specialists who are not so easy to get an appointment with in a regular clinic - oncologists, dermatologists, immunologists and other doctors of the first and highest categories. And most often, a patient diagnosed with keratoacanthoma needs consultation with several doctors to choose an effective treatment regimen.
We value your time and accept patients by appointment, so there are no queues at Odrex. To remove benign tumors, the clinic uses expensive electrosurgical equipment, which reduces the risk of postoperative complications and shortens the rehabilitation period.
Causes
The true direct causes of the development of cutaneous keratoacanthoma are currently unknown, as are the causes of many similar skin neoplasias. Factors that are regarded as contributing to the development of the described pathology have been identified. This:
- viruses;
- smoking;
- chemical factors;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- radioactive radiation;
- skin injuries;
- inflammatory lesions of the skin;
- genetic predisposition;
- somatic pathologies;
- environmentally unfavorable situation.
note
The involvement of viruses in the development of this pathology has been proven by the fact that in almost 50% of patients, DNA of the human papilloma virus is detected in tumor tissues using PCR analysis.
Nicotine is one of the most well-known oncogenes. Smoking provokes the development of not only benign, but also malignant tumors - in this case, keratoacanthoma of the skin.
The likelihood of the described pathology increases in those people who often come into contact with a number of chemicals - mainly tar, polycyclic hydrocarbons, and ordinary soot.
A connection has been established between this tumor and ultraviolet radiation - skin keratoacanthoma often occurs in people who like to sunbathe for a long time on the beach or visit a solarium. The risk of developing this tumor increases in children who have been exposed to excessive sun exposure.
The significance of radioactive radiation for the appearance of skin keratoacanthoma is no less than the value of ultraviolet radiation. Such patients often come into contact with its sources:
- due to professional duties that involve contact with radioactive substances and similar equipment;
- during diagnostic procedures;
- during radiation therapy;
Injuries to the skin lead to the development of keratoacanthoma of the skin due to the fact that its cells react to mechanical irritation. This can be either minor damage to the skin (but regular) or serious trauma - cut, torn, stab, bitten, gunshot wounds. Also, skin keratoacanthoma can occur after surgery, in particular, to remove other tumors.
note
Inflammatory lesions of the skin may precede the formation of the described neoplasm. But this happens more often with a genetic predisposition to the formation of skin keratoacanthoma.
In turn, a genetic predisposition to the occurrence of the described pathology is characteristic only of its individual varieties - at the moment it has been established that such types are multiple and generalized forms of skin keratoacanthoma.
Somatic pathologies, the connection of which with this neoplasm has been noticed, can be very different - mainly these are:
- metabolic disease;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the respiratory (breathing) system.
It has been noticed that skin keratoacanthoma more often appears in people who live in environmentally disadvantaged regions. First of all, drinking contaminated water and inhaling atmospheric air with an increased concentration of harmful substances (car exhaust and industrial emissions) are important.
Based on clinical observations, it is assumed that not one, but several factors play a role in the development of cutaneous keratoacanthoma.
Folk remedies
Skin keratoma in some cases is treated using folk remedies.
The most common folk recipes for the treatment of keratoma:
- Take 2 juniper leaves, 10 laurel leaves, 10 g fir oil, 100 g butter, crushed into powder. Mix everything well so that you end up with a homogeneous mass. This composition must be used to treat the tumor daily, without skipping days.
- You need to cook several potatoes, rinse them well and grate them on a very fine-toothed grater. The resulting pulp is applied to the neoplasm and fixed with a cloth or film. The holding time is at least 40 minutes. Residues are washed off with warm running water.
- Take a little castor oil and heat it in a water bath, and use a cotton pad or swab to treat the keratoma daily.
- The onion is cut in half and applied with the cut to the neoplasm. You can secure it with a bandage or cotton cloth. Such manipulations are performed before bedtime. Their duration depends on the speed of disappearance of symptoms.
- Another effective decoction is made from celandine leaves. To use, dry celandine leaves need to be brewed and wiped with the new growth composition.
- You can wipe the keratoma with an infusion of walnuts and vegetable oil. To do this, you need to bring the vegetable oil to 90 degrees and add a few walnuts to it. It is important that the nuts are unripe. It is necessary to create thermal conditions for the resulting mass, so you should place it in a specialized thermos. You need to infuse the composition for 12 hours. Before using, the liquid is allowed to cool and filtered to get rid of any small particles. The course of treatment is 14 days. The liquid is used to wipe the new growths daily.
- Internal treatment of keratosis using agrimony root. For this procedure you need to brew tea. To prepare it, take 4 tbsp. l. agrimony root and 2 tbsp. boiling water Then let it sit in the thermos for at least 4 hours. The infusion should be consumed daily before meals, ½ cup. The main thing is that the tea is warm. You should not sweeten the infusion with sugar; if you need to improve its taste, it is recommended to add 1 tsp. honey
Any use of folk remedies at home must be coordinated with a qualified specialist. It will help adjust the dosage. For greater effectiveness, procedures should be performed daily.
Development of pathology
The mechanism of development of the described pathology is as follows. Skin cells have receptors (sensitive structures) that respond to the “inhibition” of division - thanks to their presence, skin cells do not grow. All the factors mentioned above affect the sensitivity of such receptors and prevent them from correctly assessing cell growth and division. Since control over division is lost, it turns into a spontaneous unregulated process. Many new cells are formed, which form a tumor.
This pathological process consists not only of an increase in the number of cells. The following are launched simultaneously:
- increased keratinization;
- deterioration of skin tissue nutrition. Since there are many cells, and there is not enough “food” for all of them, this significantly increases the risk of their “breakdowns”. This explains the malignant degeneration of keratoacanthoma of the skin.
It is expected that the neoplasm stops growing and developing, and then completely degrades due to the fact that the mentioned receptors are freed from the block and again begin to control the division process. But it is unknown what is the factor that can unblock the receptors.
Tumor types
Several clinical types of cutaneous keratoacanthoma have been identified, which differ in structure, size, location and number of lesions. Why a patient develops one and not another type of this tumor remains unknown. They are trying to explain this phenomenon by a hereditary factor. But this does not mean that skin keratoacanthoma is passed on from generation to generation - this happens with genes that model the characteristics of normal cells, from which, under unfavorable conditions, this tumor begins to form. It is possible that a spontaneous gene mutation may occur in a healthy person who has healthy relatives in previous generations.
note
The relationship between the type of neoplasm and the likelihood of its malignant degeneration has not been identified. Clinical observations show that any type of keratoacanthoma with the same risk can provoke the development of skin cancer.
There are such types of tumors described as:
- solitary (or single);
- multinodular;
- subungual;
- gigantic;
- keratoacanthoma of the skin with peripheral growth;
- mushroom-shaped;
- tubero-serpiginous;
- multiple keratoacanthomas.
Solitary keratoacanthoma is the most common type of this tumor. Only one pathological focus is formed up to 3-4 cm in diameter. Located on the skin of the face, arms and legs.
Multinodular keratoacanthoma is so called because it has several pathological growth foci on its surface. This type of tumor should be distinguished from the multiple form, in which nodes located nearby merge into one. Multimodular keratoacanthoma can grow to large sizes.
Giant keratoacanthoma always reaches large sizes; reverse development is not typical.
note
Cases of giant keratoacanthoma, 20 cm in diameter, have been described.
Skin keratoacanthoma with peripheral growth is characterized by a specific growth that distinguishes it from other types - it grows along the edges, while most varieties of this tumor grow in its central part.
Subungual keratoacanthoma forms on the nail bed or fold. In the initial stages of development, it grows quickly, preventing the patient from doing work with his hands.
Keratoacanthoma fungoides looks like a mushroom. It has a smooth hemispherical surface, but there is no central ulceration, which can be detected in other types of tumors, but multiple areas of keratinization occur.
The tuberoserpiginous variety of this tumor is characterized by reduced keratinization. Keratoacanthoma may be partially covered by normal (albeit slightly thinned) skin. The tumor itself is hemispherical in shape.
Multiple keratoacanthomas are hereditary. Often, when diagnosing them, other disorders are also discovered - most often these are a deterioration of the immune response and defects of embryonic development. Some clinicians associate the appearance of such formations with a deterioration in the functioning of the immune system. It is also suggested that the malignant degeneration of a tumor depends on the reactivity of the body, and not on the cause of its occurrence.
note
Different types of keratoacanthoma differ only in appearance, but at the tissue level they all have almost the same structure. Therefore, different types of this neoplasm are similar in clinical course and risk of developing squamous cell skin cancer.
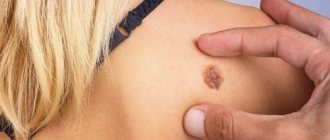
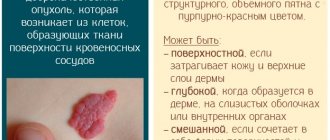
What does a keratoma look like at the initial stage?
Once a skin keratoma begins to form, regardless of its type, the main signs and symptoms will be the same:
- Keratoma (photo - the initial stage proceeds almost unnoticed - shown in the article) implies the appearance of a small spot of a pale yellow hue.
- The spot then becomes darker in color.
- At the next stage, the neoplasm begins to rise above the skin and resemble a wart-like appendage.
- The last stage is characterized by the growth of the neoplasm in width and height with noticeable peeling and darkening.
Important! Keratoma cannot be scratched or removed on your own; this may lead to infection and development into an oncological form.
Symptoms of skin keratoacanthoma
The first signs of cutaneous keratoacanthoma usually appear over the age of 40 years, although an earlier onset of pathology is increasingly observed.
The stages of development of this disease are traced. This phasing can last for 2-10 months, the clinical picture is different.
The first stage is the emergence of a pathological focus. At this point there are:
- slight redness;
- skin itching and/or tingling;
- after a few days, the skin keratoacanthoma itself appears, which quickly increases in size and can reach 1-15 cm in diameter.
If several tumors form, they all develop at approximately the same pace. Such neoplasms appear on the skin:
- faces;
- neck;
- extensor surfaces of the hands;
- less often - the torso.
After the keratoacanthoma increases to a certain size, an ulceration appears in its center, which is filled with desquamated keratinized skin cells. There may be other options:
- absence of ulceration (in mushroom form);
- the formation of several ulcers (with the multimodular variety).
The skin around the node becomes inflamed and red (sometimes turns blue).
Next comes the stabilization phase of skin keratoacanthoma - during which tumor growth stops. In this form, the tumor can persist for several months.
In the last stage, which is called the regression phase, several options for the development of the clinical picture are possible. Most often, the tumor begins to gradually decrease on its own, the scarring process begins - after a few weeks the tumor disappears, and an atrophic scar remains in its place. But clinicians are also aware of cases of long-term existence of skin keratoacanthoma in the form of relapses - in this case, the regression phase was replaced by a period of new growth. In both cases, the tumor can degenerate into squamous cell skin cancer.
How does it affect the patient’s well-being?
A neoplasm in the form of a keratoma in most cases does not cause any discomfort to a person if it is not located in open areas of the body.
According to statistics, the main complaints are:
- itching;
- burning;
- tingling;
- cosmetic defect;
- uncomfortable wearing clothes.
Important! Not all types of keratomas can manifest themselves; some of them are invisible to humans, especially if the location is not visible to the eye.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cutaneous keratoacanthoma can be made based on the patient’s complaints about the formation of nodes, anamnesis (history) of the disease and examination results. From the anamnesis, the variability of the tumor is important - rapid development over several months with spontaneous cessation of growth and reduction of the node until its disappearance. Instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis. You should remember about the possibility of developing different forms of this neoplasm.
The results of the physiological examination will be as follows:
- upon examination, neoplasms of various sizes and shapes are revealed on the skin of the face, limbs and/or torso, with a central depression filled with horny masses. Upon re-examination, a decrease in the nodes and their disappearance with the formation of scars is noted;
- upon palpation (palpation) - the nodes have a medium elastic consistency, painless, sometimes characterized by increased sensitivity.
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods used:
- inspection with a magnifying glass;
- biopsy – removal of tumor tissue and subsequent examination under a microscope. If several neoplasms have arisen, a fragment is plucked off from each of them for examination.
The following laboratory research methods are used in the diagnosis of skin keratoacanthoma:
general blood test - its value is that in the case of benign growth of tumors, the analysis is unremarkable, but in the case of malignant degeneration, the ESR sharply increases. With the further development of malignant neoplasia, signs of anemia are observed - a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin;- histological examination - examination of the tissue structure of a biopsy specimen under a microscope. It is important for excluding the malignant nature of the tumor and conducting differential diagnosis with other neoplasms. The picture during histological examination is very different - depressions in the cells, “deposits” of keratinized cellular structures and a complete absence of keratinization, cellular strands and “islands”, immune cells are revealed;
- cytological examination - examination of the cellular structure of a biopsy specimen under a microscope. It is also important for understanding the nature of this neoplasm - benign or malignant.
What drugs are used for cauterization
Keratomas are cauterized with drugs containing active substances such as:
- glycolic acid,
- fluoruacil,
- podophyllin,
- trichloroacetic acid.
The procedure must be performed only in a specialized clinic. Self-administration of such drugs can lead to chemical burns. As a result, an irreversible process of transition of the keratoma into a malignant formation may occur.
Treatment of skin keratoacanthoma
Since the tumor is prone to spontaneous regression, some clinicians adhere to a wait-and-see approach. However, they recommend that patients undergo only antiseptic treatment of the tumor to prevent secondary infection.
But this tactic is risky because:
- malignant degeneration of the tumor may begin at any time;
- antiseptics are essentially chemical irritants and can provoke the malignant degeneration of keratoacanthoma into squamous cell skin cancer.
Therefore, the following tactics are more justified:
- removing nodes;
- if the patient refuses radical treatment, follow-up with a dermatologist and/or oncologist until the tumor is completely resolved.
Removal of nodes is carried out using the following methods:
- surgical operation - excision of a neoplasm from the area of skin on which it grew;
- laser destruction - “cutting off” the tumor with a laser knife;
- cryodestruction – removal of a tumor by freezing (liquid nitrogen is used for this purpose);
- electrocoagulation – excision of a tumor using an electric current.
Indications for surgical removal of keratoacanthoma are:
- high risk of malignant degeneration;
- large size of keratoacanthoma.
After radical treatment, the following are prescribed:
- dressings;
- gentle toilet of the peri-wound skin surface;
- Antibacterial therapy - to prevent the addition of a secondary infection.
Which doctor should I contact?
Keratoma (what it is, how to treat it must be clarified in consultation with a doctor) is diagnosed by a dermatologist. If necessary, he will refer you for a consultation with an oncologist. But there is no reason to panic, because... this tumor can be removed.
The main thing you should not hesitate to do is visit a qualified medical specialist, otherwise you may miss the transition of the disease to an oncological form.
Prevention
Since the true nature of the described pathology is still unknown, no specific prevention methods have been developed. But the risk of developing cutaneous keratoacanthoma can be significantly reduced if you follow certain recommendations. This:
prevention of viral diseases, and if they have developed, their timely diagnosis and treatment;- to give up smoking;
- avoiding exposure to any chemicals on the skin, developing clear principles of labor protection at work and observing them;
- avoidance of ultraviolet radiation, dosed stay on the beach on a sunny day, refusal to visit the solarium;
- justified prescription of radioactive diagnostic methods, correct dosage during radiation therapy, search for an alternative to such treatment;
- avoiding situations that are fraught with skin trauma, performing manipulations with skin invasion only when indicated using gentle methods;
- prevention of inflammatory lesions of the skin, and if it occurs, timely diagnosis and therapy;
- prevention, detection and treatment of somatic pathologies;
- regular visits to a dermatologist and oncologist as part of periodic preventive examinations;
- skin hygiene;
- living in environmentally friendly conditions;
- healthy lifestyle in general.
Forecast
The prognosis for cutaneous keratoacanthoma remains uncertain - even with the possibility of its spontaneous disappearance. The risk of developing skin cancer is quite high.
It is recommended to remove the tumor not only because of possible malignancy, but also because of the development of quite noticeable atrophic scars that spoil the aesthetic appearance of the skin (especially the face).
note
Even after a radical intervention, there is a risk of re-formation of skin keratoacanthoma. This is mainly observed after cryodestruction, so it is not the method of choice in the treatment of this pathology.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
5, total, today
( 42 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)
Argyrosis, or silver deposition in the body: symptoms and treatment
Red spots on a child’s legs, under the knees: what is it?
Related Posts
Preventive ways to get rid of the disease
As preventive measures, you can use ways to protect yourself from any harmful carcinogenic substances. Smokers should get rid of the bad habit, since a large percentage of patients with keratoacanthoma are from among them. In this category of patients, tumor foci are localized in the oral cavity or near it.
If possible, such an important organ for a person as the skin system should be protected from all kinds of damage and injury. This applies to a greater extent to the main risk group – older men. It is recommended to spend less time in the open sun and wear long sleeves.
Nutrition should be balanced. The food should include a sufficient amount of protein products. Pickled and spicy foods should be removed from the diet, since it is these foods that already provoke cancer.
Usually all problems with this type of disease are resolved positively, but do not forget that keratoacanthoma is a provocateur of cancer. It won’t hurt anyone to remember this once again.
Those who once resorted to surgery should also protect themselves from relapse, since even after cryodestruction there is every reason to think that the tumor can form again.