Albinism is a hereditary disease associated with a disorder of pigment metabolism in the body. With this pathology, there is a deficiency of melanin - a special substance that gives color to the skin, pigment and iris of the eye, hair, and nails. It would seem, what’s wrong if it’s just a matter of skin, eye, and hair color? But it's not all that simple in reality.
The absence or decrease in melanin content leads to not only cosmetic defects, but also a number of health problems. In particular, this is sun intolerance and visual impairment. Albinos have an increased risk of developing skin cancer. Albinism is not a disease that threatens the patient's life, but it can significantly affect its quality. From this article you can learn more about what albinism is, why it occurs, how it manifests itself in humans and how it is treated.
Causes of albinism
The main reason for the development of this pathology is a violation of the metabolism of the amino acid tyrosine due to the lack of the enzyme tyrosinase, resulting in a weakening of synthesis or a complete block of melanin deposition. This condition can be caused by various genetic mutations that are indirectly or directly involved in the process of pigment formation.
Various disorders may occur in the genes responsible for the formation of tyrosinase. The degree of melanin deficiency depends on their character. In some people with this disorder, the production of tyrosinase is normal, in which case it is assumed that there is a mutation in the genes that regulate the formation of another enzyme necessary for the formation of pigment.
Discrimination against albinos
In some countries, albinos are often targets of ridicule, persecution and discrimination. In Tanzania, in recent years, more than 20 albinos have become victims of beliefs and superstitions according to which the skin, meat and bones of albinos can be successfully used to treat all sorts of diseases. These rumors are sometimes deliberately spread by local healers. As a result of these superstitions, the lives of many albino Tanzanians are put in daily danger. Rumors about the healing properties of albinos began to gradually spread in neighboring Kenya. In Israel, there was a case of granting asylum to a refugee family from Cote d'Ivoire, in which an albino girl was born.
What are the different types of albinism?
According to the degree of prevalence, it is customary to distinguish:
- Complete or total albinism. It is diagnosed from the moment the child is born. Melanin is absent in all tissues of the body: skin, hair, nail plates and pupils.
- Incomplete albinism (albinoidism). With this form, there is a decrease in pigmentation of the skin, hair and iris of the eyes.
- Partial albinism. Albinism is most common in the eyes, although the abnormality can be observed on the head, anterior abdominal wall, nail beds, or face.
Types of albinism
1. Oculocutaneous albinism 1 - this disorder occurs due to a defect in the tyrosinase enzyme gene, which is located on chromosome XI. A mutation can lead to a complete absence or decrease in the level of its formation. In the first case it will be subtype 1A, and in the second - 1B.
2. Oculocutaneous albinism 1A is the most severe form of this type of disease. As a result of the mutation, a completely inactive tyrosinase enzyme is formed, which leads to a lack of melanin production throughout the patient's life. Typical features include white skin, hair, and translucent blue irises. Due to the lack of pigmentation, the skin is not able to tan. In addition, there is an increased risk of sunburn and skin cancer. Visual acuity is usually reduced. Also in this subtype, photophobia and nystagmus are most pronounced.
3. Oculocutaneous albinism 1B - in this case, a genetic mutation leads to a decrease in tyrosinase activity. Differences in pigmentation range from very weak to almost normal. Since some enzyme activity is still present, the pigmentation of the skin, hair and eyes may increase with age in some people, and over time you may even begin to tan in the sun. Such patients tend to darken their eyelashes, and they often become darker than the hair on their head. Brown pigmentation may appear on the iris, sometimes only to a limited extent along the edge of the pupil. Visual acuity may increase with age.
4. Temperature-sensitive (heat-dependent) albinism is a subtype of the latter. It is caused by a mutation resulting in the formation of the heat-sensitive enzyme tyrosinase. Its activity at 37°C is approximately 25% of normal and increases at lower temperatures. Since melanin is formed in “cold” areas of the body, the hair on the legs and arms is usually dark, while on the head and in the armpits it remains white (sometimes becoming yellowish over time).
5. Oculocutaneous albinism 2 (tyrosine-positive) is the most common type of pathology in all races. In this case, the synthesis of the enzyme tyrosinase remains normal. There are different variations in the phenotype of this form of the disease, which can range from almost normal levels of pigmentation to complete absence of pigmentation. It gradually appears with age, although the exact mechanism of this delay is unknown. The intensity of pigmentation also depends on race. In addition, visual acuity improves over time. At birth, the amount of pigment in Europeans can vary greatly. The skin is white and does not tan. The hair is pale yellow or darker with a reddish tint. The color of the iris is gray-blue, and the degree of light transmission depends on the saturation of the pigment. Pigmentation increases with age and freckles and age spots appear in sun-exposed areas.
The phenotype of representatives of the Negroid race is different. At birth, their hair is usually yellow and remains that way throughout their lives, but some darkening is still possible. The iris of the eyes is gray-blue. The skin is white and does not tan, but some patients may experience age spots.
6. Brown oculocutaneous albinism is a subtype of type 2, exclusively manifested only in representatives of the Negroid race. Their hair and skin are light brown, and their irises are gray. Hair and irises may darken over time, but skin color remains largely unchanged.
7. Oculocutaneous albinism 3 (red or ginger). In this case, the mutation leads to a disruption in the formation of tyrosinase, as a result of which the pigment is synthesized not black, but brown. African patients have a characteristic phenotype of light brown or reddish-brown skin and hair, as well as brown-blue irises. Some patients lack iris transparency, strabismus, and nystagmus. The phenotype in Asians and Europeans is currently unknown.
8. Ocular albinism affects only the eyes. These patients have normal skin, but may be slightly paler than their immediate family members. The ocular manifestations are as follows: strabismus, nystagmus, decreased visual acuity, transparency of the iris, etc. Only men suffer from this form, and women are only carriers. Thus, the phenotype appears entirely in males, and female carriers may have a fundus with muddy spots and hypopigmented lines along the periphery, as well as a transparent iris.
Autosomal recessive ocular albinism has not yet been linked to any specific genetic disorder. However, it is assumed that some cases of this disease are ocular forms of oculocutaneous types 1B and 2.
Classification
The following types of diplopia are known to medicine:
- binocular diplopia - develops in three forms (sensory, motor, mixed), the most common type of pathology;
- monocular diplopia is much less common; monocular diplopia has its own forms of development: refractive, aberration, papillary, retinal.
There is also temporary diplopia, which appears after a head injury or after severe alcohol poisoning. This deviation passes very quickly. There is also a strong-willed one, when a person himself provokes this state.
There are horizontal and vertical diplopia, depending on the plane in which the image splits.
Symptoms of albinism
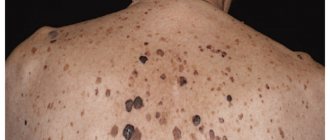
The main clinical manifestations of albinism include pale skin, especially noticeable at birth. Often, due to translucent blood vessels, it has a pinkish tint. The eyes are blue at birth, however, in some angles they can also have a reddish color. As you grow, depending on the type of disease, the signs of albinism may change somewhat. With type 1A, melanin synthesis does not occur in the body at all, so such a patient retains white hair and skin color and blue eyes for life. Type 1B is characterized by the rapid accumulation of yellow pigment in the hair, which is why it takes on a light straw color; pigmentation of the cornea and eyelashes often occurs with age.
Heat-dependent albinism is manifested by a peculiar distribution of melanin - normal pigmentation is observed on the limbs, while the skin and hair remain white. The eyes of such patients remain blue. Type 2 is also characterized by noticeable variability in clinical signs: from imperceptible lightening of hair and skin to an almost complete absence of pigmentation. This form of the disease is also often characterized by an improvement in melanin synthesis with age: freckles begin to appear, hair darkens, and a tan appears. An albino must be extremely careful when exposed to the sun, since his skin is very sensitive to ultraviolet radiation and burns occur quite easily.
Another characteristic symptom in patients with this pathology is impaired visual acuity. It is more pronounced the weaker the formation of melanin in the body, especially in the pigment layer of the retina and cornea. In addition, common manifestations of albinism are strabismus, nystagmus, and astigmatism, which occur immediately after birth or in the first years of a child’s life. In ocular forms, similar symptoms of the disease appear without disturbing the pigmentation of hair and skin. Patients with albinism often also experience photophobia, which sometimes develops into day blindness.
Patients with albinism need to wear sunglasses and also protect their skin with special products with a protection factor (SPF) of at least 30, even if the sun is not shining that much outside the window. In very hot weather, going outside is not recommended at all. Clothing should be chosen exclusively from natural materials, and it should cover the entire surface of the body. It is also advisable to wear hats with fairly wide brims.
Forecast
Albinism does not change life expectancy, although people with albinism are more likely to develop skin cancer.
The condition is not getting worse. For example, any vision problems a person has will remain the same as they age.
Albinism does not affect intelligence, although it may affect social development. For example, if children are laughed at because they look different, they may have difficulty making friends and playing with other children in a group.
Young children may also appear clumsy as their limited vision affects their ability to learn certain actions and movements, such as picking up an object or learning to crawl. As the child develops and with the help of vision aids, the condition may improve.
Albinism itself does not require treatment, but people with albinism will need to take care of themselves in the sun as without melanin in their skin they can easily burn.
Treatment and prognosis for albinism
To date, there is no specific treatment for this disease; only preventive measures have been developed that can improve the patient’s quality of life.
In order to maintain the existing level of visual acuity, mandatory eye protection from sunlight is necessary. This is achieved by wearing special contact lenses or sunglasses. You should avoid exposure to bright sun or protect your skin with special lotions or creams.
If you adhere to all these recommendations, the prognosis for albinism is generally favorable - patients will be able to live a full and long life. At the same time, such patients need regular consultations with an ophthalmologist and dermatologist in order to prevent and timely detect complications such as retinal detachment or skin cancer.
Diagnostics
The disease albinism can be diagnosed by the symptoms described above and complaints of pain in the eyes from any light, sunburn from short exposure to the sun, and myopia. The ophthalmologist should conduct a general examination of the eyes, skin, hair and prescribe additional methods for detecting the disease.
In particular, the following can be carried out:
- examination of the fundus of the eye (ophthalmoscopy) – helps to detect hypopigmentation, manifested in the form of absence or reduction of pigment;
- ERG is a way of recording electrical signals coming from the brain to the retina. Helps determine the ocular form of albinism;
- visometry – identification of visual acuity;
- registration of VEP (visual evoked potentials);
- DNA analysis - special tests that help detect the albinism gene;
- biomicroscopy – using a special device to examine the eyes under additional lighting;
- chemical examination of the hair follicle to detect tyrazine, the type of which can determine a form of albinism.
It is also advisable to additionally consult a dermatologist or geneticist.
A little history
The concept of "albino" comes from the Latin word albus, which means "white". The term was first introduced by the Filipino poet Francisco Baltazar, thus naming “white” Africans. The writer mistakenly believed that the unusual skin color of these people was explained by marriage with Europeans.
Mentions of mysterious people can be found in the history of almost every country, but the attitude towards them was very different. Misunderstanding of the problem led to various reactions of the population towards albinos, ranging from worship and attribution of magical properties to complete rejection and demonstration of pathology in traveling circuses.
In African countries, life for people with hereditary syndrome remains difficult to this day. Some tribes consider the birth of an albino a curse, others attribute magical, healing properties to his flesh, which is why they often kill innocent people.
In the modern world, there is more loyalty towards albinos. With the development of television, the problems of people with unusual appearance features have become well known. Among albinos there are many famous and talented people: actors, singers, models (Dennis Hurley, Sean Ross, Connie Chiu, Diandra Forrest).
Albinos people - character: features
Albinos - character
In fact, albinos are no different in character from others. Generally, young people do not like daytime because they are too sensitive to light. Therefore, many people note that they go to bed late at night, because they feel much more comfortable this way. Children often bully peers who are different from them, but this does not prevent them from achieving great success. For the most part, these are kind, cheerful people.
By the way, today the topic of albinism is gaining more and more popularity on the Internet, and some people even deliberately pretend to be such because they like to stand out and be different from everyone else.
conclusions
Albinism is a hereditary pathology that almost every person has heard of. But despite the high availability of information, there are many myths about this disease, and the life of “special” people cannot be called simple. Parents of unusual children need to understand that their health and quality of life in the future depends on proper care for their child.
The birth of a baby should not be perceived as a test, because these children can live a long and fulfilling life, and they especially need the help and support of their parents.
Discrimination against albinos
In some countries, albinos are often targets of ridicule, persecution and discrimination. In Tanzania, in recent years, more than 20 albinos have become victims of beliefs and superstitions according to which the skin, meat and bones of albinos can be successfully used to treat all sorts of diseases. These rumors are sometimes deliberately spread by local healers. As a result of these superstitions, the lives of many albino Tanzanians are put in daily danger. Rumors about the healing properties of albinos began to gradually spread in neighboring Kenya. In Israel, there was a case of granting asylum to a refugee family from Cote d'Ivoire, in which an albino girl was born.
Disease prevention
The following tips will help minimize the risk of diplopia:
- Don't abuse alcohol.
- Quit smoking.
- Follow sleep, rest and nutrition schedules.
- Don't forget about daily physical activity.
- Monitor your blood pressure.
If signs of diplopia occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. A split image indicates the development of diseases in the body. You can avoid their consequences if you take the necessary measures in time.
What causes visual problems in people with albinism?
Melanin is the most important pigment that is involved in the visual process. When we perceive a visual image, it passes through the optical media of the eyeball and enters the retina. The retina contains photoreceptors that convert light signals into nerve impulses, which then travel to the brain. These receptors with their tips are immersed in the pigment epithelium of the retina, which, in turn, must absorb all light rays passing through the photoreceptors. Thanks to the absorption of light by the pigment epithelium, we obtain a high-contrast, clear image.
In people with albinism, there is no pigment in the retinal epithelium or there is too little of it to fully absorb light rays. As a result, light passing through the photoreceptors is not absorbed by the pigment epithelium and enters the choroid of the fundus. It begins to be reflected from it in a chaotic manner and again passes through the photoreceptors, which reduces the sharpness and clarity of the image.
If the pigment is also absent in the iris, then it cannot retain part of the light flux. As a result, a large amount of light enters the retina and its focusing is disrupted. This is why people with albinism see worse than those who have normal amounts of melanin in their bodies.
A common pathology in albinos is nystagmus, in which the eyes make uncontrolled oscillations. The disturbance intensifies when a person tries to use as many photoreceptors as possible in looking at a particular object.
Albinos often have one or another refractive error (farsightedness, nearsightedness, astigmatism). According to research, the optical system of the eye can change in such a way as to achieve a clear image on the retina. This explains the change in the optics of the eye towards myopia or farsightedness with albinism.
It is impossible to cure albinism today, but correcting visual impairments is possible and necessary. To do this, you should consult an ophthalmologist.