Causes of gastroduodenitis
As with any chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, the main cause of the disease is an imbalance between protective and aggressive factors affecting the mucous membrane of the organ.
Protective factors include:
- mucous barrier (mucous membrane) - mucus covering the inner walls of the stomach and intestines;
- high ability of cells to recover;
- sufficient blood supply (this means that a sufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen is supplied for normal restoration of the mucous membrane);
- antroduodenal acid brake (in the antrum of the stomach, special cells produce an alkaline secretion, changing the pH of food before it enters the duodenum).
Damaging factors:
- excess production of hydrochloric acid (hereditary factors, increased activity of the parasympathetic nervous system);
- impaired blood supply to the mucous membrane;
- insufficiency of antroduodenal acid brake;
- bile acids.
Most often, the balance between damaging and protective factors is disrupted by an infection - the acid-fast bacterium Helicobacter Pylori (Helicobacter pylori). The products of its vital activity destroy the mucous barrier, damage the cells of the mucous membrane themselves, and change the activity of the parietal cells that produce hydrochloric acid.
Their excessive activity contributes to an increase in acidity in the stomach, which is why food in the pyloric area does not alkalize to the desired pH. Constantly entering the duodenum, excessively acidic food changes the environment in its lumen (normally, the environment in the intestine is alkaline). The properties of the mucosa change, the cells metaplase (degenerate) into the gastric epithelium. After this, they also become accessible to Helicobacter, and the inflammation spreads to the duodenum.
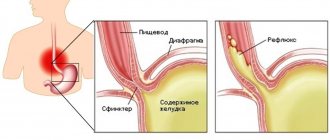
Another mechanism for the occurrence of gastroduodenitis is also possible. Under the influence of inflammation in the duodenum, where biologically active substances that regulate the functions of the entire gastrointestinal tract are produced, normal peristalsis is disrupted. The contents of the duodenum are thrown into the antrum of the stomach (this condition is called duodenogastric reflux). Bile acids from intestinal contents damage the gastric mucosa, causing chronic inflammation. The “trigger” of such a condition can be a parasitic infestation, for example, giardiasis, which affects up to 35% of children attending kindergarten[2].
Relatively rarely, the cause of gastroduodenitis is a serious general disease - for example, with cardiovascular failure, the normal blood supply to the mucous membrane is disrupted, with severe liver or kidney failure, autointoxication occurs, and so on.
Classification of gastroduodenitis
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common causes of gastroduodenitis.
Gastroduodenitis can be primary or secondary in origin. Primary develops “on its own”: under the influence of Helicobacter or parasitic infection, poor-quality food, and so on. Secondary develops against the background of other diseases: cardiovascular, liver, kidney failure.
Based on the changes that appear in the mucous membrane, gastroduodenitis can be:
- superficial,
- catarrhal,
- hyperplastic,
- erosive,
- atrophic.
Gastroduodenitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is most often associated with food toxic infection and usually accompanies acute gastritis, which is described in detail in the corresponding article.
Is it possible to do without medications?
It is possible to help the body cope with a high temperature without the use of antipyretic medications.
- First of all, you need to ventilate the room. The room temperature should not exceed 23 ˚C with a humidity of 40-60%.
- Rubbing with water at room temperature helps a lot , but not with ice or alcohol. They cause spasm of peripheral vessels and reduce heat transfer.
- Follow your diet. Fever develops with acute gastritis or exacerbation of chronic gastritis. In such cases, complete fasting is recommended on the first day. In the future - the most gentle diet.
- Drink more. You are allowed to drink mineral water without gas, with a moderate exacerbation - warm milk with honey, rosehip decoction, with hypoacid gastritis - cranberry juice.
An increase in temperature is an important symptom that you should definitely pay attention to. Even low fever with gastritis is a sign of a severe course of the disease. Therefore, despite the fact that you managed to cope with the temperature in just a couple of days, it is still advisable to visit a doctor.
There may be a need to undergo a comprehensive examination and correct treatment. If the fever reaches high levels and persists for a week, then a visit to the doctor becomes mandatory. The sooner you seek medical help, the lower the risk of complications.
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis
Manifestations of gastroduodenitis can be local and general. Local are symptoms of inflammation of the mucous membrane:
- pain in the epigastric region;
- dyspeptic manifestations: nausea, belching, heaviness in the abdomen.
The types of pain syndrome may vary depending on which area of the mucous membrane the inflammation is most active.
When the duodenal bulb is damaged, the pain resembles ulcerative pain - it appears on an empty stomach or at night. If the outflow of bile or pancreatic secretion is disrupted due to inflammation, a cholecyst-like or pancreatic-like variant of gastroduodenitis develops. Pain migrates to the right hypochondrium with a cholecyst-like variant or to the left with a pancreatic-like variant and occurs in response to eating fatty foods. A gastritis-like variant appears against the background of duodenogastric reflux: after eating, there is a feeling of fullness in the stomach, heaviness, and bloating.
General manifestations are the body’s reaction to chronic inflammation: weakness, increased fatigue, dizziness, and possibly an increase in temperature to 37 degrees. Typically, such symptoms do not exist constantly, but intensify during an exacerbation and disappear for several months during remission.
Chronic duodenitis is characterized by such symptoms as:
- Dizziness
- Sleep disorder
- Fast fatiguability
- Drowsiness, increased sweating (especially a couple of hours after eating)
- If the patient does not eat anything for a long time, he may experience bodily tremors and general weakness.
The above symptoms are only part of the signs that gastroduodenitis makes itself felt in different phases. Other manifestations of the disease, in particular, the strength of their severity will depend on how the disease progresses. For example, in the phase of exacerbation, incomplete or complete remission, the patient will feel differently.
In most cases, the exacerbation phase occurs in the spring and autumn periods, when infectious and viral diseases are especially active. Spontaneous pain lasts, as a rule, 7-10 days and then subsides. Chronic gastroduodenitis can be in the acute stage for 1 to 1.5 months.
The first attack usually appears unexpectedly - a person feels (especially on an empty stomach) contractions in the upper abdomen, and then nausea and vomiting are added to them. Diarrhea with gastroduodenitis is also a common occurrence.
Diagnosis of gastroduodenitis
Gastroduodenitis - causes, symptoms, treatment, dietary table
The main diagnostic method is esophagogastroduodenoscopy. This is an endoscopic examination that allows the doctor to see inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane and take a biopsy - a piece of mucous membrane for laboratory testing. A biopsy is the only way to reliably confirm changes in the structure of the mucous membrane: hypertrophy, atrophy, depth of the lesion.
To detect increased pressure in the duodenum (which can cause duodenogastric reflux), antroduodenal manometry is performed.
Gastric and duodenal intubation, during which secretion samples are taken, allows one to study the activity of enzymes, and intragastric pH-metry allows one to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
To determine Helicobacter pylori infection, breath tests, PCR diagnostics are performed, or antibodies to the bacterium are determined in the blood. One positive result is sufficient to confirm infection. The absence of infection must be confirmed by at least three different methods because no test is 100% sensitive.
Superficial tissue inflammation
According to the degree of damage to gastritis and duodenitis, superficial inflammation of the tissues of the organ is considered the mildest.
Visually, upon examination, the doctor sees that the surface is red, swollen, and thickening appears in the folds. This disease has two types:
1. Superficial gastritis, duodenitis with foci. This type of inflammatory process is quickly treated because it does not penetrate deep into the walls of the organs. But once this disease starts, it can turn into an ulcer and provoke disease in other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
2. Superficial diffuse gastroduodenitis. The disease does not cover individual superficial areas of the mucous membrane, but its entire area. Accordingly, it is much more difficult to treat this type.
Treatment of gastroduodenitis
During an exacerbation, a diet is prescribed that mechanically, thermally and chemically spares the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Gradually the diet expands. During remission, there is no need for a diet, but it is better to exclude foods that cause discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract in a particular patient. A food diary can help identify individual triggers.
To restore the normal structure of the mucous membrane and the protective functions of mucus, gastroprotectors (rebamipide) are recommended. They reduce the activity of inflammation, accelerate healing and improve the effectiveness of Helicobacter eradication. Rebamipide is the basis for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
If Helicobacter pylori infection is confirmed, a complex of two antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor is prescribed. Such a complex is necessary because the bacterium is very resistant to external influences and is extremely difficult to destroy. The duration of eradication therapy is at least 14 days. If the infection cannot be killed, another set of antibiotics is prescribed and the result is checked again after treatment. By the way, rebamipide enhances eradication therapy, so that with it the chances of destroying the bacteria on the first try increase.
When a parasitic infestation is detected, specific drugs directed against protozoa are prescribed.
Depending on the acidity of the gastric contents, either antacids (Almagel, phosphalugel, Maalox), H2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine) and proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole), or enzyme preparations are recommended.
Duodenogastric reflux requires the use of drugs that normalize motility (itomed).
Folk remedies
You should not rely solely on alternative methods of therapy, but as an auxiliary alternative treatment for gastroduodenitis, it is ideal.
- A decoction of fresh mint significantly improves the condition. If you don’t have fresh mint, then dry mint, which is poured with boiling water overnight, will do. The ratio of water and mint is taken arbitrarily, according to your taste. You need to drink the decoction in the morning before meals, the liquid should be lukewarm. If you wish, you can drink this decoction after meals instead of your usual tea.
- Flax seeds. For infusion, take 3 tbsp. l. seeds and a liter of boiling water. After 15 minutes, the mixture will swell and become like jelly. Mucus has a coating effect on the stomach. You should drink 100 ml in the morning on an empty stomach. The rest is drunk throughout the day.
- Oat decoction. This product also has excellent protective and healing properties. In the store, in the medical nutrition department, you should buy unrefined oats and prepare a decoction daily based on 1 tbsp. l. oats and 200 ml of water. It is enough to boil the composition for 15 minutes, leave for 2 hours, strain and take 100 ml before meals.
- Boil a spoonful of nettle in a glass of milk for five minutes. Set aside to cool. Stir a spoonful of honey into the resulting milky-nettle infusion. You need to drink the product three times a day, a third of a glass, about forty minutes before meals.
- Calendula is also widely known for its healing properties. Pour 500 ml of boiling water into one spoon. After a quarter of an hour, strain. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- Leaves of nettle, plantain, St. John's wort, chamomile inflorescences - equally. Preparation and use: 2 tablespoons of pre-crushed (in a coffee grinder or meat grinder) collection, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, pour into a thermos along with the herbs, leave overnight. Take 1/3-1/4 cup 3-4 times a day before meals. The course is 1-1.5 months.
Prevention and prognosis for gastroduodenitis
Fried and fatty foods can cause pain with gastroduodenitis
Gastroduodenitis itself is not dangerous to life and health. But it often transforms over time into a peptic ulcer, which in turn can cause dangerous complications. Prolonged inflammation leads to atrophy of the mucosa and a decrease in secretory activity; against this background, malignancy often occurs. Therefore, if gastroduodenitis is detected, you should strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and not try to treat yourself or with traditional methods.
To prevent gastroduodenitis, a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and timely examination of relatives of patients for Helicobacter pylori are recommended.
[1] G.V. Beketova. Chronic gastroduodenitis in children and adolescents (etiology, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment). Health of Ukraine, 2011.
[2] V.P. Novikova, E.A. Osmalovskaya, E.Yu. Kalinina. Helicobacteriosis and giardiasis in chronic gastroduodenitis in children. RMJ, 2014.
Why you shouldn’t lower the temperature
Fever is considered a protective reaction to inflammation and the penetration of a foreign object into the body. According to medical literature, against the background of rising temperatures, antibodies to microbes are more actively produced, the concentration of protective cells in the blood - leukocytes - increases, vital processes and the rate of reproduction of many bacteria slow down.
That is why you should not reduce low-grade fever, as you will only complicate the body’s process of fighting infection and inflammation.
All the negative consequences of high temperature appear only when the threshold is reached at 39 ˚C or prolonged low-grade fever.
Particular care should be taken in lowering the temperature in children. Due to imperfect thermoregulation mechanisms, their fever always reaches higher numbers. Even a temperature of 39˚C is not considered critical for children.
Dr. E. O. Komarovsky talks in detail about how to properly assist children with fever in this video: