Peripheral circulation is a continuous process of blood circulation in small veins and arteries, capillaries, as well as arterioles and venules. A variety of factors lead to impaired blood circulation, including: tumors, injuries, heart and vascular diseases, kidney diseases, metabolic disorders, etc.
Signs of poor circulation may include: pain in the legs, swelling, discoloration of the limbs, headaches, hearing problems, imbalance, numbness in the limbs, etc.
Reasons and indications
Sometimes pills to improve blood circulation in the brain are necessary due to a person’s injury. The need may arise from a systemic illness. High blood pressure, atherosclerotic plaques, poisoning, and infection negatively affect the vascular condition. Stress factors and vascular spasms and osteochondrosis play a role. Such pathological conditions lead to insufficient blood supply to the brain. As a result, cells do not receive the necessary oxygen and nutritional compounds. This leads to disruption of brain functionality. It is no secret that this organ is responsible for regulating the activity of the entire human body, so insufficient blood flow in it leads to catastrophic consequences.
On pharmacy shelves there is a wide variety of tablets to improve blood circulation in the brain. Choosing the right option among them is quite difficult. The most effective and accurate method is to seek the help of a qualified doctor. If you suspect a need for such drugs, there is no need to delay contacting a doctor. The progress of the diseases mentioned above can provoke a stroke and other serious consequences, even death.
Which doctor should I contact?
Disorders of blood microcirculation are a common process, so contacting a specific specialist depends on the presence of primary pathology and clinical manifestations.
If you notice frequent or, conversely, rare urination, accompanied by high blood pressure numbers, as well as heart symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath, heart failure), you should consult a therapist or cardiologist.
In case of swelling, coldness and changes in the color of the extremities (pallor, blueness or redness), it is necessary to visit a vascular or at least a general surgeon. Diabetic foot syndrome is jointly treated by endocrinologists and surgeons.
Disorders of microcirculation of cerebral vessels due to strokes, hypertension or spinal osteochondrosis (the so-called DEP of complex origin) are the prerogative of neurologists.
Correction of impaired blood flow in the skin and associated skin aging is carried out by cosmetologists and dermatologists.
What will help?
There are several types of pills to improve cerebral circulation and memory. Sometimes the doctor prescribes nootropics. Others benefit from agents that expand the vascular lumens. Sometimes medications are indicated to thin the blood and prevent excessive clotting. All of the above tools must be used in combination. The drug regimen is drawn up by an experienced doctor. Ancillary drugs are selected based on the characteristics of the patient’s condition. Self-treatment can provoke undesirable consequences, even irreversible.
Xanthine derivatives
This category of drugs exhibits a moderate vasodilator effect and relieves spasm. Thus, blood movement is activated and the required level of oxygen saturation and its supply is maintained. Let's consider how drugs in this category have a pronounced vasodilating effect.
Pentoxifylline SR Zentiva
Vasodilators for the head are prescribed when normal blood flow is disrupted, prevent brain hypoxia, and thin the blood. Published in tablets and injections for injections. Contraindications for use are: heart attack, sudden hemorrhage. Secondary effects: swelling, bleeding, decreased visual acuity, liver dysfunction and allergies.
Teonicol
Belongs to the group of artificial substances prescribed to improve blood microcirculation and metabolism. The product is available in pills and solution form. The medicine restores blood circulation with oxygenation in the cells of the brain and spinal cord, and prevents thrombus formation. Vasodilators are not prescribed in the case of: cardiovascular insufficiency of the second and third stages, predisposition to hemorrhages.
Eufillin
It is used not only for severe vascular conditions, but also for the treatment of many diseases: migraine, heart failure, angina pectoris, asthma, high blood pressure, and cervical osteochondrosis. Do not use for epilepsy or peptic ulcer disease.
Vasodilation
Among the variety of tablets to improve blood circulation in the brain, those belonging to this class are prescribed almost most often. They expand the vascular ducts, so that blood flows more actively to the brain, bringing more useful compounds. This eliminates hypoxia and provides sufficient nutrition. The drugs improve energy metabolism and stabilize brain functionality. Quite often, drugs from the class of calcium antagonists are prescribed. They have been known for a long time and have a good reputation. Modern doctors have access to the third generation of drugs of this type. Calcium antagonists expand arterial lumens, relaxing the muscle fibers of the vascular walls. They do not affect the condition of the veins. Under their influence, blood flow in the brain is activated, the organ receives the nutritional compounds and oxygen it needs.
Calcium antagonists are known to have systemic effects on the body. They can be prescribed only after a preliminary examination proving the reasonableness of such therapy. The duration of the course, the dosage - all this is chosen by a qualified, experienced doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the patient. Among the drugs presented on pharmacy shelves, calcium antagonists include Diltiazem, Verapamil, Cordipine (first generation), Nimodipine, Tiapamil, Clentiazem (second generation), Stamlo, Norvasc ( third generation).
Based on natural products
In pharmacies you can also find tablets to improve memory and blood circulation, made using herbal ingredients. They are used to treat and prevent blood flow problems. A distinctive feature is a narrow range of contraindications. Some drugs are sold without a prescription. You can take them yourself, after reading the accompanying instructions. These medicines are produced using plant alkaloids. Most often, ginkgo and periwinkle are used as the main active ingredient.
Medicines for veins
The most common vein diseases are varicose veins and thrombophlebitis, which occurs in both sexes from the age of 20 (although previously the pathology was considered age-related and developed after 40 years). Preparations for blood vessels throughout the body strengthen not only arteries, but also veins and capillaries. For veins, medications can be used both orally and externally.
You need to take medications as prophylaxis in courses 1-2 times a year or for treatment as prescribed by a doctor:
- Dioflan is available in tablets and has venotonic and angioprotective properties. Used to treat superficial veins.
- Troxevasin ointment has a vascular strengthening effect. The active component of the composition is troxerutin, which has an anti-edematous and vasodilating effect. Reduces the permeability of small capillaries and prevents the formation of blood clots.
About periwinkle
Periwinkle alkaloid (proven by tests!) eliminates vascular spasms, stabilizes local metabolism, eliminates the formation of blood clots, and improves the quality of blood flow. Among the pharmaceutical products produced using this product, it is worth noting the Telektol tablets for cerebral circulation and memory. Vinpocetine and Bravinton are quite well known and often prescribed. Periwinkle alkaloid is also used, "Vero-Vinpocetine". It is noted that it is undesirable to use Vinpocetine and Cavinton before obtaining the doctor’s consent. This is due to the possible negative impact if the dose and duration of the course are chosen incorrectly.
About ginkgo
Tablets for blood circulation and memory based on ginkgo have a complex effect on the body, improve blood circulation in the smallest vessels, strengthen tissues and relieve swelling. The walls of the vascular system are protected from radicals. Among the names are o and “Bilobil”. Quite safe and reliable products Ginkum, Vobilon, and Memory are popular. Sometimes a specialist recommends taking a closer look at pharmaceutical products presented under the names “Ginkor Fort” and “Tanakan”.
Medicines produced with the inclusion of plant materials are intended for long-term use - from a quarter of a year or more. During the treatment program, blood thinners should not be used; Aspirin is prohibited. This combination can cause bleeding in the brain. Many people note signs of improvement after just a month of regularly taking the pills, but a stable effect is achievable only after three months or more.
Give your brain a job
In light of recent research into brain problems, scientists note a direct connection between the degree of mental stress and a decrease in functional disorders of the brain in the future. Those who do not spare their “central processor”, but load it by solving crossword puzzles, memorizing poetry and taking on something new and difficult, significantly reduce the chances of encountering Alzheimer’s disease or dementia in old age. Experts recommend special activities to “shake up” the brain: become left-handed for a day if a person is right-handed, or vice versa, go to the store or to work another way, move around the apartment from time to time blindfolded, forcing both the senses and cells to activate brain under the pressure of new impressions.
A nicotinic acid
Tablets available on the pharmaceutical market that improve blood circulation in blood vessels also contain nicotinic acid. They do not affect large vessels, but expand the capillaries. The main substance strengthens vascular walls, reduces the content of dangerous cholesterol inclusions, stabilizing the blood lipid profile. Among the popular ones, “Nicotinic acid”, “Acipimox”, “Enduratin” deserve mention. The medicines “Nikoshpan” and “Nicofuranose” have a good reputation.
All drugs in this category are intended for course use. Some medications are produced for injection strictly under medical supervision. After the first stage of the complex course, the patient is transferred to a tablet form for oral administration.
Noopept
Among the nootropic drugs described above (Piracetam, Aminalon, etc.), the most effective is the new generation nootropic drug - Noopept.
Nootropic drugs are aimed at stimulating brain function, improving memory and protecting the brain from adverse effects. The pharmacological effect of this group of medications is based on improving blood circulation through capillaries and large blood vessels, as well as increasing the intensity of metabolism in the vessels.
Noopept stands apart in the group of nootropic drugs because it has a prolonged effect and virtually no side effects. It is prescribed to persons with pronounced ischemic manifestations resulting from injuries, atherosclerotic changes, etc.
Still, despite the effectiveness of the drug, manufacturers do not recommend taking it to persons under 18 years of age, pregnant and lactating women, as well as persons with disorders of the liver and excretory system. The drug is characterized by a minimum of side effects. Still, you should not take Noopept uncontrollably.
Strengthening the vascular wall
Tablets are in demand to improve cerebral circulation, affecting primarily the walls of blood vessels. They are effective because they make these elements more elastic. There are mineral and vitamin preparations. You can take Blueberry Forte. Ascorutin tablets are useful. Preparations containing silicon, potassium, and selenium have a good effect on the state of the circulatory system. There are a lot of vitamin and mineral complexes with such inclusions on sale. Dihydroquercetin has a good effect. It is present in the industrial products “Dihydroquercetin NTG”, “Flaol”, “Flavit”.
Mineral and vitamin preparations are used to improve the quality of blood flow and prevent treatment of emerging health problems. It is advisable to consult a doctor first and only then start using it. If it is impossible to see a doctor, you can simply study the instructions before taking it. The products are sold without doctor's prescriptions.
Statins
Prescribed to eliminate atherosclerosis. Therefore they are suitable only for a limited number of cases.
This group of drugs should not be recommended to patients without cholesterolemia or at least a tendency towards it, confirmed by anamnesis and laboratory data.
The mechanism of action is based on the ability of statins to dissolve plaques consisting of fatty substances, also remove lipids from the body and prevent them from depositing on the walls of the arteries.
Atoris is actively used as the main medicine.
There are many analogues, there is no fundamental difference between them. The point is one thing. The drug is used for the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis.
Strictly speaking, statins do not improve cerebral circulation per se. They relieve the main causes of cerebrovascular insufficiency by eliminating mechanical obstruction to blood flow.
Therefore, the number of cases when medications in this group can be prescribed is quite small. Not all patients have excess cholesterol and atherosclerosis.
Nootropics
If you ask the average person about pills for blood circulation in the brain, the person will probably first of all remember nootropics. Such medications improve local metabolism, make the brain more resistant to hypoxia, increase mental abilities, and improve memory. Some products are made from animal brains. They contain natural amino acids. Among the popular drugs are Cerebrolysin and Phenotropil. Piracetam and Glycine have a good reputation. Glutamic acid is quite in demand. Sometimes the doctor advises stopping at Actovegin or Cortexin. Some people find the drug “Pantogam” useful.
All of the listed pharmaceutical products can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment for various diseases caused by blood flow problems. They are prescribed for dementia, coma and asthenia, cerebral ischemia and VSD, acute disturbance of blood flow, and delayed mental development. Before prescribing, it is necessary to study the patient's condition.
Effective medications for stroke
Competent treatment tactics for acute cerebrovascular accident can not only save the patient’s life, but also improve his prognosis for the restoration of motor and speech functions and quality of life.
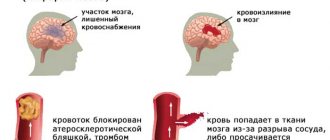
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is a consequence of blockage of a vessel by a thrombus or embolus. The following drugs are used to treat it:
- Means for reducing and destroying blood clots. Today they are not widely used (Prourokinase is used only in research centers, Streptokinase has not proven itself due to low evidence, tissue plasminogen activator is not available everywhere).
- Low molecular weight heparins (Fraxiparin, Clexane) can reduce thrombus formation and reduce the risk of embolism after a stroke.
- Indirect anticoagulants continue the work of heparins after 3-4 weeks. This is Warfarin, Sinkumar.
- Treatment of the acute period of stroke begins with antiplatelet agents (150 mg of aspirin is chewed at the first signs of the condition). If you are intolerant to aspirin, use Ticlopedin, Clopidogrel, Dipyridamole.
- Low molecular weight dextrans: Reopoliglucin, rheomacrodex increase the volume of circulating blood and improve the delivery of oxygen to the brain.
- Remedies for high blood pressure. ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers are started when blood pressure is more than 180 over 105. This protects patients from recurrent strokes.
- Vasodilators Vinpocetine, Pentoxifylline and drugs that improve microcirculation (Curantil, Trental).
- Nootropics are prescribed during the recovery period.
Hemorrhagic stroke
It becomes the result of a rupture of a vessel in the brain and requires slightly different tactics with the mandatory use of antihypertensives and dextrans to replenish the volume of circulating blood. Most often, hemorrhagic stroke is operated on, since without surgical treatment the mortality rate from it is quite high.
Instead of a conclusion: the problem of treating cerebrovascular accidents, despite its relevance, has not yet been optimally solved and represents a wide field for clinical and pharmacological research. For patients, timely prevention of cerebral blood flow disorders should be a reasonable tactic:
- to give up smoking
- balanced diet
- physical activity, frequent exposure to fresh air
- timely treatment of osteochondrosis and neuroinfections
- reduction of irrational visual loads and time spent at the computer
- a balanced attitude towards drug treatment, with the rejection of a large number of unnecessary nootropics
- attention to the recommendations of neurologists and angiosurgeons.
Author:
Postnova Maria Borisovna general practitioner
Blood quality
When choosing tablets that are suitable for the patient to improve blood circulation, the doctor may recommend anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. They reduce the viscosity of the blood, making it more fluid. These drugs are more often prescribed when there is a risk of transistor ischemia, in case of transient blood flow disturbances. Antiplatelet agents reduce the risk of blood clot formation and reduce the risk of thromboembolism. Among the popular pharmaceutical products, it is worth mentioning Aspirin, Curantil and Ticlopidine. The medications Clopidogrel and Pentoxifylline have a good reputation. Before starting the course, you need to study the patient’s condition and determine whether there are any contraindications. The duration of the course is selected individually.
Taking anticoagulants can improve the quality of blood flow in small vessels and control the level of coagulation. Warfarin and Fragmin are prescribed. Doctors often recommend taking unfractionated heparin. The medications Clexane and Fraxiparin are known to have a good effect. Improper use of such medications is accompanied by a risk of complications, so it is very important to use medications under the supervision of a doctor, regularly checking the quality of your blood. Incorrect and unjustified use is accompanied by the risk of formation of hematomas and areas of bleeding. A person may vomit and may have a bowel movement with blood in the discharge. All these symptoms require urgent medical attention.
"Actovegin"
When studying the features of tablets designed to improve blood circulation in the brain, you should refer to the instructions for this popular medication. It comes in the form of greenish or yellowish capsules, convex on both sides. One tablet contains 0.2 g of veal hemoderivative, from which proteins have been extracted. Officially, the medication belongs to the category of tissue regeneration stimulators. It is an antihypoxic agent that protects the nervous system, improves metabolism, and affects microcirculation. The active ingredient increases oxygen absorption with subsequent utilization of molecules. The product contains phospho-oligosaccharides, which have a positive effect on the movement and utilization of sugars. Consequently, cellular metabolism improves and lactate is generated less actively, which is especially important during ischemia.
"Actovegin" prevents apoptosis, modulates the work of kappa B, which is necessary for regulating apoptosis and inflammatory processes in the PNS and central nervous system. The drug affects the enzyme poly(A) polymerase, which is responsible for identifying and repairing single-strand DNA. Excessive enzyme activity can cause cell death in some pathologies. The drug controls the activity of polypolymerase, due to which the state of the central nervous system and PNS becomes better, more stable - morphology and functionality return to normal.
Alpha blockers
A broad category of pharmaceuticals aimed at restoring the activity of the central nervous system and brain.
Sermion
The drug is an effective vasodilator and improves blood circulation in the brain. You can buy injections or pills at the pharmacy in 15 or 25 pieces. in blisters. Cannot be used in the following cases: with manifested bradycardia, after a critical myocardial infarction, with severe bleeding. The use of such drugs is usually well tolerated by patients, and the likely secondary effects are moderate. In some cases, therapy causes pathologies in the functionality of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, which are accompanied by dizziness, a feeling of heat and a marked decrease in blood pressure.
Phentolamine
Prescribed for pathologies of the peripheral nervous system, ulcers of the extremities, poorly healing wounds, and peripheral circulatory disorders. They sell pills containing 25 mg of phenthalamin hydrochloride, 30, 60 tablets per package. You can buy a solution of 5 mg in ampoules. Side effects: redness and irritation of the skin, swelling of the nasal mucosa. If symptoms are severe, you should stop taking the medicine or reduce the dosage.
Admission rules
When planning to take Actovegin tablets to improve blood circulation in the brain, you need to read the instructions describing the rules for safe use. Take into account that the effect can be noticed half an hour after the drug enters the body - this has been proven by clinical trials. The maximum result is observed approximately 2-6 hours after taking the capsule orally.
Tablets are used shortly before meals. Do not chew, cut, crush or otherwise damage the integrity of the outer shell. The medication should be taken with a relatively small volume of clean water. For acute stroke, the drug is used by the end of the first week. First they inject it, then switch to tablets: three times a day, a couple of capsules. The duration of therapy reaches six months.
Diagnoses and doses
Useful for improving brain activity and cerebral circulation, Actovegin tablets are prescribed for dementia. The optimal regimen is a couple of capsules three times a day. Duration of treatment – 20 weeks. If blood flow in the periphery is impaired and there is a need to correct the consequences of such health problems, the drug is prescribed in a 4-6-week course, using one capsule three times daily or twice as much. For polyneuropathy due to diabetes, the drug should be consumed first by injection, then in tablet form three times daily, three capsules. The duration of therapy varies between 4-5 months.
"Pentoxifylline"
You can take Pentoxifylline tablets to improve cerebral circulation. One capsule contains 0.1 g of the active ingredient of the same name. The drug belongs to the category of products that improve microcirculation and also protects blood vessels. The ingredient that ensures the effectiveness of the intake is made from dimethylxanthine. It reduces blood viscosity, makes red blood cells more elastic, improves blood flow in small vessels, and increases the oxygen content in tissues. The content of cAMP in platelets increases. In red blood cells, while taking the drug, the concentration of ATP increases. The energy potential is saturated, vasodilation is observed, peripheral vascular resistance decreases, and the heart rate is not adjusted.
Indicated for improving blood circulation, Pentoxifylline tablets contain an ingredient that dilates arterial lumens and activates the flow of oxygen to the heart muscle. The tone of the muscles responsible for breathing increases. If occlusive pathology of the arteries in the periphery is diagnosed, taking the drug allows you to increase the walking distance, reduce cramps at night, and pain that plagues the patient at rest.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy for cerebrovascular accidents is carried out at all ages, but with varying duration and effectiveness. The price of the issue is also different.
I would immediately like to draw attention to the fact that all drugs without exception that directly improve metabolic processes in brain cells and are called nootropics, work only in pathologically altered tissues and do not have any effect on healthy tissue.
Therefore, a great direction is to use these funds to stimulate the mental activity of children, youth and healthy adults:
- in preparation for exams
- during intense stress at work
- in children starting school
- or those who do poorly in it
- and even more so for preschoolers
can be safely attributed to the TRICK of PHARMACEUTICAL CONCERNS in collusion, expanding the indications for the use of these drugs and receiving huge amounts of money from gullible but unenlightened buyers.
The greatest role in the development of cerebral blood flow disorders is played by vascular spasm or thrombus formation in the arteries. Therefore, the most relevant groups of drugs that improve cerebral blood flow are vasodilators and drugs that prevent platelet aggregation during the formation of blood clots.
Indications and rules
Pentoxifylline tablets, which stimulate blood circulation, are prescribed for chronic occlusive disorders, problems of blood flow in the periphery, ischemia of brain tissue, and stroke. The drug is indicated during the recovery period after a stroke. It is used in the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis and some forms of encephalopathy. "Pentoxifylline" is recommended for neuroinfection, ischemic heart disease, and during the recovery period after a heart attack. It is prescribed for angiopathy due to diabetes, in case of acute disruption of blood flow in the visual system. The pharmaceutical product is used for otosclerosis, degeneration of the inner ear due to problems with blood vessels, asthma and COPD, impotence caused by vascular disorders.
The dose, course duration, and treatment features are chosen based on the diagnosis. It is known that Pentoxifylline tablets that improve blood circulation can provoke undesirable consequences. Some people experience headaches and dizziness, their faces turn red, and their quality of sleep deteriorates. There is a risk of seizures, anxiety, and hot flashes. There are known cases of nail plate brittleness. Scotoma, disturbances in heart rate and rate, hepatitis, intestinal atony, thrombocyto-, pancyto-, and leukopenia are possible. There is a danger of hypofibrinogenemia, bleeding, and allergies.
Microcirculation correctors
Betahistine (Betaserc)
This is an effective drug that helps not only to correct blood flow in the capillaries, but also eliminates dizziness and unsteadiness of gait in case of chronic problems with cerebral blood flow. Application: in tablets of 8 or 16 mg in courses. The daily dose ranges from 24 to 48 mg in three doses. Contraindications: pregnant or lactating, requires caution in case of peptic ulcer, bronchial asthma. Side effects: can cause hives or digestive disorders. Price: Betaserk 30 pcs. 650 RUR, Betaver 30 pcs. 250 RUR, Betahistine 30 pcs. 100 rub., Vestibo 30 pcs. 280 rub., tagista 30 pcs. 100 rub.
Popular and available: Piracetam
The product is sold in tablets. One capsule contains 0.4 g of the active ingredient of the same name as the drug. The medicine belongs to the class of nootropics. It has a positive effect on local cerebral metabolism and blood flow, activates the utilization of sugars, improves microcirculation, has a positive effect on areas affected by ischemia, inhibits the aggregation of certain forms of platelets, and protects the brain during hypoxia, electric shock, and poisoning. The drug increases integrative brain activity, but does not have a mental depressant or psychostimulating effect.
"Piracetam" is intended for oral administration, is quickly and effectively absorbed, after half an hour it is observed in the blood serum in maximum concentration. After 2-8 hours, maximum saturation of the cerebrospinal fluid is achieved. The drug penetrates the organic barriers of the body and accumulates in the brain tissue. The medication is prescribed when the ability to concentrate and remember has deteriorated. It is used to prevent dizziness and in the fight against emotional lability and dementia. "Piracetam" is indicated for Alzheimer's disease, after injury, and for elderly people. It is used for coma of various origins, to correct problems caused by chronic dependence on alcohol. Piracetam is prescribed for children with learning disabilities. The indication for use is sickle cell anemia.
For adults, the medicine is prescribed in an amount of 30-160 mg/kg. The daily dose is divided into 2-4 servings. Duration of treatment is up to 8 weeks. For children, 30-50 mg/kg is indicated. The daily volume is divided into 2-3 servings. The course lasts at least three weeks.
Drugs that improve cerebral circulation
Home Medical encyclopedia Medicines Cardiovascular medicines
See also aminalon, acephen, dibazole, dihydroergotamine, dihydroergotoxin, caffeine, iaftidrofuril, no-spa, paitogam, papaverine hydrochloride, picamilon, piracetam, pyriditol, theophylline, pentoxifylline, aminophylline, cerebrolysin, etc.
AVAMIGRAN
A combined drug containing ergotamine tartrate, mecloxamine citrate, camilofine dihydrochloride, caffeine, amidopyrine.
Pharmachologic effect. Avamigran relieves (relieves) migraines and migraine-like headaches caused by cerebral (brain) vascular disorders. It is not prescribed for the prevention of migraine.
Indications for use. Migraine, migraine-like headaches with cerebral angiopathy (impaired tone of the blood vessels of the brain), histamine cephalalgia (unilateral headaches appear 1-2 hours after falling asleep).
Method of administration and dose. At the first signs of a migraine attack, 2 tablets are prescribed, and the dose is repeated if necessary. The maximum daily dose is 4 tablets, weekly dose is 10 tablets.
Side effect. Possible dry mouth and dizziness.
Contraindications. Lactation period (breastfeeding) in women, liver and kidney dysfunction, vascular diseases, angina pectoris, hypertension (persistent rise in blood pressure), glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure), prostate adenoma (benign tumor) with urinary retention, cardiac tachyarrhythmias ( rapid irregular heartbeat), megacolon (significant dilation of part or all of the colon).
Release form. Coated tablets containing ergotamine tartrate 0.75 mg, mecloxamine citrate 20 mg, camilofin dihydrochloride 25 mg, caffeine 80 mg, amidopyrine 125 mg.
Storage conditions. List B. In a cool place.
VAZOBRAL (Vasobral)
Pharmachologic effect. A combined drug whose effect is determined by the properties of its constituent components. Dihydroergocriptine, a dihydrogenated derivative of ergot, which is part of vasobral, blocks alpha]- and alpha2-adrenergic receptors of smooth muscle cells and platelets. It has a stimulating effect on dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors of the central nervous system. When using the drug, the aggregation (sticking together) of platelets and red blood cells decreases, the permeability of the vascular wall decreases, blood circulation and metabolic processes (metabolism) in the brain improve, and the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia (lack of oxygen due to insufficient oxygen supply or impaired absorption) increases.
Vasobral has been shown to have a preventive effect against migraine.
Indications for use. Cerebrovascular insufficiency (mismatch between the need of brain tissue for oxygen and its delivery), including due to cerebral (brain vessels) atherosclerosis; residual effects after cerebrovascular accident; decreased mental activity, memory impairment regarding recent events, decreased attention, orientation disorders; preventive treatment of migraine; cochleovestibular races
disorders (dizziness, tinnitus, hypoacusia) of ischemic origin (developed due to insufficient blood supply to the cochlea of the inner ear); retinopathy (damage to the walls of blood vessels in the retina), in particular diabetic (associated with high blood sugar) and Raynaud's disease (narrowing of the lumen of the vessels of the extremities); chronic venous insufficiency.
Method of administration and dose. Prescribe 1-2 tablets or 2-4 ml (1-2 pipettes) 2 times a day. The drug should be taken with meals, with a small amount of water.
Side effect. In rare cases - nausea, pain in the epigastrium (the area of the abdomen located directly below the convergence of the costal arches and the sternum). Skin itching, rash. Possible decrease in blood pressure. Vasobral does not have a long-term hypotensive (blood pressure-lowering) effect, therefore, when prescribing it to patients with arterial hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure), the need to use antihypertensive (blood pressure-lowering) drugs is not excluded. With the simultaneous administration of Vasobral and antihypertensive drugs, the development of arterial hypotension (a decrease in blood pressure below normal values) and fainting is possible.
Contraindications. Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Safety of use in pregnant women has not been proven. Prescribing vasobral to nursing mothers can lead to a decrease in lactation (milk production).
Release form. Pills; oral solution in a bottle with a 2 ml pipette attached. 1 tablet contains: alphadihydroergocriptine - 2 mg, caffeine - 20 mg. 2 ml of solution contain: alphadihydroergocriptine - 2 mg, caffeine - 20 mg.
Storage conditions. List B. In a cool place.
VINCANOR (Vincanorum)
Purified sum of alkaloids from Vinca minor L.
Pharmachologic effect. The drug has an antispasmodic (relieving spasms), vasodilator, hypotensive (lowering blood pressure) and moderate sedative (calming) effect.
Indications for use. Used for cerebral circulatory disorders (spastic and atherosclerotic), initial forms of hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure), after ischemic stroke (acute cerebral circulatory disorder), as well as for neurogenic sinus tachycardia (rapid heartbeat).
Method of administration and dose. Take orally (regardless of meal times) 1-2 tablets 3 times a day, if necessary, up to 2 tablets 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 10-30 days. The course of treatment can be repeated, selecting an individual maintenance dose.
Side effects and contraindications. Not identified.
Release form. Tablets of 0.02 g (20 mg), film-coated, in a package of 50 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
VINCAPAN
Synonyms: Winkaton.
Contains the sum of vinca alkaloids (Vinca minor L).
Pharmachologic effect. It has an antispasmodic (relieving spasms), vasodilator, hypotensive (lowering blood pressure) effect.
Indications for use. Used for spasms (sharp narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels, neurogenic tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), initial forms of hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure).
Method of administration and dose. Take orally, starting with 0.005 g ('/2 tablets), then 0.01 g (10 mg = 1 tablet) 2-3 times a day. After achieving a therapeutic effect, maintenance doses are selected individually. Children are prescribed starting from 0.0025 g ('/4 tablets) per day.
Side effects and contraindications. Not identified.
Release form. Tablets 0.01 g.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place.
INSTENON
A combination drug containing three separate medicinal substances: hexobendine, etamivan and etophylline.
The pharmacological action consists of the effects of the components included in the drug.
Hexobendine has antispasmodic (relieving spasms) and vasodilator activity. Moderately dilates coronary vessels (heart vessels). The drug somewhat increases cerebral circulation and improves metabolic (metabolic) processes in the brain, which is the basis for its inclusion in the composition of the drug instenon.
Etamivan's pharmacological action is similar to cordiamine.
Etophylline is similar in structure and pharmacological properties to theophylline and diprophylline.
Improves cerebral circulation, stimulates the vasomotor center, has a positive inotropic effect (increases the force of heart contractions); It also has bronchodilator (bronchodilator) and moderate diuretic (diuretic) activity.
The combination of these substances justifies the use of instenon to improve brain functions in conditions of impaired blood flow, ischemia and hypoxia (insufficient oxygen supply to tissue or impaired absorption).
Indications for use. The drug is proposed for use in ischemic stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident), residual effects after a stroke, discirculatory encephalopathy, post-traumatic encephalopathy, vegetative-vascular dystonia and other manifestations of cerebrovascular insufficiency (lack of blood supply to the brain).
Method of administration and dose. Instenon is prescribed orally, intravenously and intramuscularly.
Taken orally, mainly for chronic forms of cerebrovascular insufficiency, 1 tablet of instenon forte or 2 tablets of instenon 2-3 times a day for 3-4 weeks.
Instenon is prescribed intravenously (or intramuscularly) mainly for acute forms of ischemia and cerebral hypoxia (inadequate oxygen supply to the brain). Administer 1 ml (1 ampoule) 1-2-3 times a day for 3-5 days. or until clinical improvement occurs. Intravenous injections are given slowly
(drip). The contents of the ampoule are diluted in 200 ml of 5% glucose solution or isotonic sodium chloride solution.
Side effect. With rapid intravenous administration, tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), headache, and facial hyperemia (redness) may develop.
Contraindications. The use of instenon is contraindicated in cases of increased intracranial pressure, intracerebral hemorrhages, and epilepsy.
Release form. Dragees containing 20 mg of hexobendine, 50 mg of etamivan and 60 mg of etophylline; dragees forte containing 60 mg of hexobendine, 100 mg of etamivan and 60 mg of etophylline; in ampoules containing 10 mg of hexobendine, 50 mg of etamivan and 100 mg of etophylline.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
CAVINTON
Synonyms: Vinpocetine, Inex.
Cavinton is a semi-synthetic derivative of the alkaloid devincan, contained in the periwinkle plant (Vinca minor L. and Vinca erecta Rgl. et Schmalth.); family Kutrovye (Arosupaceae).
Pharmachologic effect. Cavinton dilates brain vessels, increases blood flow, improves oxygen supply to the brain, and also promotes glucose utilization. By inhibiting (suppressing) phosphodiesterase, the drug leads to the accumulation of cAMP in tissues; reduces platelet aggregation (sticking together). There is only a slight decrease in systemic blood pressure.
The vasodilating effect of Cavinton is associated with a direct relaxing effect on smooth muscles. The drug enhances the metabolism (exchange) of norepinephrine and serotonin in brain tissue, reduces pathologically increased blood viscosity, and promotes deformability (increased plasticity) of red blood cells.
Indications for use. Used for neurological and mental disorders associated with cerebral circulatory disorders (after a stroke, post-traumatic, atherosclerotic origin); for memory disorders, dizziness, aphasia (speech impairment), etc.; with hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure), vasovegetative symptoms (impaired vascular tone) during menopause, etc.
In ophthalmological practice, Cavinton is prescribed for atherosclerotic and angiospastic (associated with a sharp narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels) changes in the retina and choroid of the eye, degenerative changes (with disruption of the tissue structure) of the macula (the most sensitive area of the retina), secondary glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure), associated with partial thrombosis (blockage) of blood vessels, etc.
It is also effective for hearing loss of vascular or toxic (medicinal) origin and dizziness of labyrinthine origin (associated with a disorder of the vestibular apparatus).
Method of administration and dose. Take orally in the form of tablets (5 mg each), 12 tablets 3 times a day. Maintenance dose - 1 tablet 3 times a day. Use for a long time. Improvement is usually observed after 1-2 weeks; course of treatment is about 2 months. and more.
Intravenously (drip only) is used in neurological practice for acute focal ischemic disorders of cerebral circulation (discrepancy between the need of brain tissue for oxygen and its delivery with blood), in the absence of hemorrhage
(cerebral hemorrhages). First, 10-20 mg (1-2 ampoules) are administered in 500-1000 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution (drip infusion). If necessary, repeat (3 times a day) slow drip infusions are prescribed, then switch to taking the drug orally.
There is evidence of the use of Cavinton for the prevention of convulsive syndrome in children who have suffered brain injury. The drug is administered intravenously by drip at a rate of 8-10 mg/kg per day in a 5% glucose solution with a transition after 2-3 weeks. for oral administration at 0.5-1 mg/kg per day.
Side effect. Cavinton is usually well tolerated. When administered intravenously, hypotension (low blood pressure) and tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) are possible.
Contraindications. Severe ischemic heart disease, severe arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances); not used during pregnancy. It is not recommended to prescribe the drug for labile (unstable) blood pressure and low vascular tone.
The injection solution is incompatible with heparin. Do not inject the solution under the skin.
Release form. Tablets of 0.005 g (5 mg) in a package of 50 pieces; 0.5% solution in ampoules of 2 ml (10 mg).
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
XANTHINOL NICOTINATE (Xantinoli nicotinas)
Synonyms: Teonicol, Complamin, Xavin, Sadamin, Angioamine, Complamex, Contamex, Megemin, Vedrin, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Improves cerebral circulation, reduces the phenomena of cerebral hypoxia (insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain). The drug increases cerebral blood flow and improves metabolic (metabolic) processes of the brain in the postoperative period after removal of brain tumors, brain contusions, etc.
Dilates peripheral vessels, improves collateral circulation (bypassing the affected artery), enhances oxidative phosphorylation and ATP (adenosine triphosphoric acid) synthesis.
Indications for use. Atherosclerotic disorders of cerebral circulation. Obliterating endarteritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the arteries of the extremities with a decrease in their lumen) in the vessels of the lower extremities, Raynaud's disease (narrowing of the lumen of the vessels of the extremities), acute arterial thrombosis (blockage of the lumen of the arteries), diabetic retinopathy (damage to the walls of the retinal vessels associated with increased sugar content in blood), retinopathy (non-inflammatory damage to the retina), acute thrombophlebitis of the superficial and deep veins (inflammation of the vein wall with blockage) and postthrombophlebitis syndrome (a condition after restoration of blood flow through a blocked vein), trophic ulcers of the extremities, Meniere's syndrome (attacks of dizziness when the internal ear), dermatitis (skin inflammation), to increase cerebral circulation.
Method of administration and dose. Inside, intramuscularly or intravenously. In tablets of 0.15 g 3 times a day, if necessary, the dose is increased to 0.3-0.6 g 3 times a day. Take after meals without chewing. The course of treatment is at least 2 months.
Intramuscularly, 0.3 g (2 ml of 15% solution) 1-3 times a day with a gradual increase in dose to 0.6-0.9 g (4-6 ml of 15% solution) 2-3 times a day. Duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
For acute blockage of blood vessels or hemorrhage into the brain, inject intravenously (very slowly)
0.3 g 1-2 times a day for 5-10 days. Can be administered intravenously at a rate of 40-50 drops per minute. To do this, 1.5 g (10 ml of a 15% solution) is diluted in 200-500 ml of a 5% glucose solution or in 200 ml of an isotonic sodium chloride solution, administered dropwise over a period of 2-4 hours up to 4 times a day. Course duration is 5-10 days.
Side effect. Dizziness, fever, tingling and redness of the skin of the upper body, especially the head and neck.
Contraindications. Heart failure stage II-III, acute myocardial infarction, acute hemorrhages (bleeding), the first 3 months. pregnancy.
Release form. Tablets of 0.15 g in a package of 60 pieces; ampoules of 2 ml of 15% solution in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
MEXIDOL (Mexidolum)
Pharmachologic effect. Mexidol is an inhibitor of free radical processes (/antioxidant/drug that prevents lipid peroxidation of cell membranes), but has a more pronounced antihypoxic (increasing tissue resistance to lack of oxygen) effect.
Mexidol has a wide spectrum of biological activity. It is effective for various types of hypoxia (with insufficient oxygen supply to the tissue or impaired absorption). The drug increases the body's resistance to oxygen-dependent pathological conditions (shock, cerebrovascular accidents, etc.), improves mnestic functions (memory processes), reduces the toxic effects (damaging effects) of alcohol, etc.
Indications for use. Mexidol is proposed for the treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents, discirculatory encephalopathy (a brain disease caused by a chronic cerebral circulatory disorder), vegetative-vascular dystonia (impaired vascular tone due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system), atherosclerotic disorders of brain function, to relieve withdrawal syndrome (to relieve the condition resulting from a sudden cessation of taking drugs or alcohol) in alcoholism and drug addiction, in other conditions accompanied by tissue hypoxia.
Method of administration and dose. Mexidol is used intramuscularly or intravenously (stream or drip). The drug is recommended to be administered as a stream to relieve withdrawal symptoms and vegetative and sympathoadrenal paroxysms (a sharp increase in the concentration of adrenal hormones / adrenaline / in the blood), and as a drip for acute cerebrovascular accidents.
When administered intravenously, it is recommended to use sterile water for injection as a solvent. Mexidol is administered in a stream over 5-7 minutes, and dropwise at a rate of 60 drops per minute. Doses are prescribed individually.
Begin treatment with a dose of 100 mg 1-3 times a day, gradually increasing the dose until a therapeutic effect is obtained. The duration of treatment and the choice of individual dose depend on the severity of the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of treatment. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 800 mg.
For the treatment of acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke), Mexidol is prescribed intravenously at a dose of 200-300 mg in the first 2-4 days, and then intramuscularly at a dose of 100 mg 3 times a day.
For patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy and vegetative-vascular dystonia, the drug is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 50-100 mg 3 times a day.
For withdrawal symptoms, Mexidol is administered at a dose of 100-200 mg intramuscularly 2-3 times a day or intravenously (drip) 1-2 times a day, and for neurotic and neurosis-like disorders it is prescribed intramuscularly at a dose of 50-400 mg per day.
For the treatment of atherosclerotic dementia in elderly patients, Mexidol is used intramuscularly at a dose of 100-300 mg per day.
In case of acute neuroleptic intoxication (poisoning with neuroleptics), the drug is used intravenously in a dose of 50-300 mg per day.
Side effect. Mexidol is usually well tolerated. Some patients may experience nausea and dry mouth.
Contraindications. The drug is contraindicated in cases of severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, or in the presence of a history (medical history) of an allergy to pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
Release form. 5% solution in ampoules of 2 ml.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
NIMODIPINE
Synonyms: Nimotop.
Pharmachologic effect. Belongs to the group of calcium ion antagonists and has the basic properties characteristic of these drugs. However, a specific feature of nimodipine is its predominant effect on the blood supply to the brain, the ability to reduce the resistance of resistant vessels (arterioles) of the brain, improve cerebral circulation, and reduce hypoxic (associated with lack of oxygen) phenomena.
Indications for use. Nimodipine is used as a preventive and therapeutic agent for ischemic disorders of cerebral circulation (a discrepancy between the need of brain tissue for oxygen and its delivery through the blood).
Method of administration and dose. Nimodipine is prescribed immediately after the onset of acute ischemia (subarchnoid hemorrhage /bleeding under the membranes of the brain/) and treatment is continued for 5-14 days. In the first 2 hours, adults are administered intravenously (as a slow infusion) 0.001 g (1 mg) of nimodipine (5 ml of 0.02% solution) 2 times per hour. After 2 hours, increase the dose to 2 mg (10 ml) in 1 hour (about 30 mcg/kg per hour), monitoring hemodynamics to avoid too sharp a decrease in blood pressure. For administration (preferably using a perfusion pump), the solution is diluted in isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution.
Preventively prescribed orally in the form of tablets (30 mg) - every 4 hours, 2 tablets (total 360 mg per day). Take from the 4th day of hemorrhage (bleeding in the brain) for 21 days.
For patients weighing less than 70 kg and labile (frequently changing) blood pressure, the drug should be administered starting with reduced doses (0.5 mg per hour).
Side effect. With intravenous administration, hypotension (low blood pressure) may develop; when taken orally, headache, nausea and other dyspeptic symptoms (digestive disorders) are also possible.
Contraindications. The drug should not be administered orally at the same time as its infusion. Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Caution should be exercised in case of cerebral edema and acute increase in intracranial pressure, as well as in cases of renal dysfunction.
Release form. Tablets of 0.03 g (30 mg) in a package of 20; 50 or 100 pieces; 0.02% solution in vials or polyethylene (not polyvinyl chloride to avoid interaction) packages of 50 ml (total 10 mg) for infusion.
Storage conditions. List B. In a cool place.
NICERGOLINE (Nicergoline)
Synonyms: Sermion, Nicotergoline, Dazovaz, Dospan, Ergotop, Physilax, Nargolin, Nimergoline, Sinskleron, Varsan, Niceline.
Pharmachologic effect. Belongs to the group of alpha-blockers. Reduces the tone of cerebral and peripheral vessels. Reduces cerebrovascular resistance (resistance of blood vessels in the brain) and increases cerebral blood flow. Activates metabolism in the brain.
Indications for use. Acute and chronic disorders of cerebral circulation, especially in the early stages (vascular-metabolic disorders; cerebral atherosclerosis; consequences of thrombosis - blockage of cerebral vessels); prevention of migraine and vascular headache; maintenance treatment for high blood pressure.
Method of administration and dose. Take nicergoline orally before meals in the form of tablets of 0.01 g (10 mg) 3 times a day. Treatment is carried out for a long time (2-3 months or more, depending on the severity of the disease, the effectiveness of treatment and tolerability). The effect develops gradually.
Intramuscularly, 2-4 mg is distributed over 1-2 injections per day. Intravenously 4-8 mg in 100 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution. Methods of administration, doses and time of therapy depend on the individual patient's characteristics. Intra-arterially, 4 mg in 10 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution over 2 minutes. The solution, ready for injection, can be stored at room temperature for up to 48 hours.
Side effects and contraindications. See page 110.
Release form. Powder in bottles of 4 mg and ampoules with solvent of 4 ml; tablets of 0.01 g in a package of 30 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dark place.
THEOBROMINE (Theobrominum)
Synonyms: Teosten, Tezal.
An alkaloid extracted from the husks of cocoa seeds (Semina Cacao).
Pharmachologic effect. It has a stimulating effect on cardiac activity, slightly dilates the coronary (heart) vessels and bronchi, and increases urination. The diuretic (diuretic) effect is associated primarily with a decrease in tubular reabsorption (reabsorption in the kidneys) of water, sodium and chloride ions. Theobromine causes mild stimulation of the central nervous system.
Indications for use. It is used mainly for mild spasms (sharp narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels, sometimes for edema due to heart and kidney failure.
Method of administration and dose. Orally 0.25-0.5 g 1-2 times a day.
Side effect. Weak stimulation of the central nervous system.
Contraindications. Gout, peptic ulcer of the stomach (an ulcer that develops as a result of the destructive effect of gastric juice on the mucous membrane).
Release form. Powder; tablets 0.25 g.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
TABLETS "THEMINAL" (Tabulettae "Theminalum")
A combination drug containing theobromine, amidopyrine and phenobarbital.
The pharmacological action is due to the properties of its constituent components.
Indications for use. It is used as an antispasmodic (relieving spasms) agent for spasms (sharp narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels, migraines, and initial forms of angina.
Method of administration and dose. 1 tablet 2-3 times a day.
Release form. Tablets containing theobromine and amidopyrine - 0.25 g each and phenobarbital - 0.02 g, in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
TABLETS "THEOVERIN" (Tabulettae "Theoverinum")
A combined drug containing theobromine, papaverine hydrochloride and barbamyl.
The pharmacological action is due to the properties of its constituent components.
Indications for use. It is used as a vasodilator and antispasmodic (relieving spasms) for spasms (sharp narrowing of the lumen) of cerebral vessels, migraines, the initial form of hypertensive heart disease (persistent increase in blood pressure) and angina pectoris.
Method of administration and dose. 1 tablet 2-3 times a day.
Release form. Tablets containing theobromine - 0.25 g, papaverine hydrochloride - 0.03 g and barbamyl - 0.075 g, in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
TABLETS "TEODIBAVERIN". (Tabulettae "Theodibaverinum")
A combined drug containing theobromine, papaverine hydrochloride and dibazole.
The pharmacological action is due to the properties of its constituent components.
Indications for use. As a vasodilator and antispasmodic (relieving spasms) agent for hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure).
Method of administration and dose. 1 tablet 2-3 times a day.
Release form. Tablets containing theobromine - 0.15 g, papaverine hydrochloride and dibazole - 0.02 g each, in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
Theobromine is also included in menopausal medications, neoclimastilbene, theophedrine tablets, theophedrine N tablets, and tepaphylline tablets.
FLUNARIZIN
Synonyms: Flunarizine hydrochloride, Sibelium, Amalium, Flufenal, Flugeral, Flunagen, Flunar, Flurpax, Fluxarten, Nabratin, Niflucan, Nomigran, Vasculoflex, Vertix.
Pharmachologic effect. Like cinnarizine, flunarizine blocks calcium channels. The drug relaxes smooth muscles (muscles of blood vessels and internal organs), improves cerebral circulation and oxygen supply to the brain; reduces vestibular disorders (impaired coordination of movements). Has antihistamine activity. It has an anticonvulsant effect and reduces the frequency of seizures in epilepsy.
Indications for use. Particularly effective for dizziness associated with brain disorders
blood circulation (vertigo), vestibular disorders and migraines.
Method of administration and dose. Well absorbed when taken orally; has a long half-life, which allows it to be taken once a day.
For the prevention of migraine, or vertigo, cerebrovascular accidents and vestibular disorders, adults are prescribed 0.01 g (10 mg) per day, children weighing up to 40 kg - 0.005 g (5 mg) per day.
In epilepsy, flunarizine is recommended mainly as an additional agent in cases of resistance to conventional anticonvulsants. Adults are given 0.015-0.02 g (15-20 mg) per day, and children weighing up to 40 kg - 0.005-0.01 g (5-10 mg) per day. Due to the hypnotic effect, flunarizine is recommended to be taken before bedtime.
Side effect. The drug is usually well tolerated. May cause drowsiness, weight gain, extrapyramidal phenomena (impaired coordination of movements with a decrease in their volume and tremors) (especially in elderly patients with long-term use).
Contraindications. Be careful when prescribing it to patients whose work requires quick physical and mental reactions.
Release form. Tablets of 0.005 and 0.01 g (5 and 10 mg); capsules containing 5 mg flunarizine.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
Cinnarizine
Synonyms: Stugeron, Stutgeron, Cinniprin, Dimitronal, Glamil, Labyrin, Marizan, Midronal, Mitronal.
Pharmachologic effect. According to modern data, the pharmacological properties of cinnarizine are largely due to its ability to block membrane calcium channels (see Calcium ion antagonists). It inhibits (suppresses) the entry of calcium ions into cells.
Cinnarizine has a positive effect on cerebral, peripheral and coronary (heart) circulation; improves microcirculation. Increases the ability of red blood cells to deform (increase plasticity) and reduces increased blood viscosity. Increases tissue resistance to hypoxia (insufficient supply of oxygen to tissues or impaired absorption of oxygen).
The drug has a direct antispasmodic (relieving spasms) effect on blood vessels, reduces their response to biogenic vasoconstrictor substances. Potentiates (strengthens) the effect of CO2 (carbon monoxide) on brain vessels. Systemic blood pressure, heart rate, contractility and cardiac conductivity are not significantly affected.
The drug also has antihistamine activity. Reduces the excitability of the vestibular apparatus (brain structures responsible for coordinating movements), suppresses nystagmus (involuntary movements of the eyeballs).
Indications for use. As a cerebrovascular (affecting the blood vessels of the brain) drug is prescribed for cerebral circulatory disorders associated with spasm (sharp narrowing of the lumen) of blood vessels, atherosclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and stroke. The drug reduces cerebroasthenic phenomena (weakening of brain function), headache, tinnitus, and improves general condition.
Cinnarizine is prescribed for migraines and Meniere's disease (disease of the inner ear).
Cinnarizine is also used to reduce spasms of peripheral vessels and improve blood circulation in obliterating endarteritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the arteries of the extremities with a decrease in their lumen), thromboangiitis (inflammation of the arterial wall
rium with their blockage), Raynaud's disease (narrowing of the lumen of the vessels of the extremities), acrocyanosis (blue discoloration of the tips of the fingers, lips, nose) and other disorders of peripheral circulation.
Method of administration and dose. Cinnarizine is taken orally after meals: for cerebrovascular accidents - usually 25 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day or 75 mg (1 capsule) 1 time a day; for peripheral circulatory disorders - 50-75 mg (2-3 tablets) 3 times a day or 2-3 capsules (75 mg each) per day. The drug is used for a relatively long time (courses from several weeks to several months).
For vestibular disorders, it is recommended to give 25 mg 3 times a day. In case of severe arterial hypotension (low blood pressure), the drug is prescribed in reduced doses (0.025 g 2 times a day).
Side effect. The drug is usually well tolerated, sometimes moderate drowsiness, dry mouth, and gastrointestinal disorders are possible; in these cases
reduce the dose. In some elderly patients, extrapyramidal symptoms appear (or intensify) (impaired coordination of movements with a decrease in their volume and tremors).
Cinnarizine enhances the effect of sedatives (drugs that have a calming effect on the central nervous system) and alcohol. The possibility of a sedative effect of the drug (especially in the first days of treatment) should be taken into account when prescribing it to transport drivers and other persons whose work requires a quick mental and physical reaction.
Contraindications. It is not recommended to prescribe the drug to pregnant women and while breastfeeding.
Release form. Tablets of 0.025 g (25 mg) in a package of 50 pieces; capsules of 75 mg of cinnarizine (stugeron forte) in packages of 20 and 60 pieces, as well as in the form of drops in 20 ml bottles containing 75 mg of cinnarizine.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dark place at room temperature.
| print version | This information is not a guide to self-treatment. A doctor's consultation is required. |