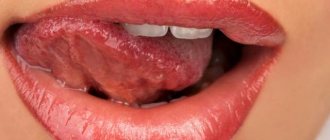
Warts are unsightly benign growths that appear on the skin when infected with the human papillomavirus. Invading the upper layers of the epidermis, the virus provokes the proliferation of its cells, resulting in the appearance of warts of different shapes, sizes and colors.
About 80% of people on the planet are infected with human papillomavirus, and not every patient knows about his diagnosis, since HPV in most cases is asymptomatic.
What causes warts
The content of the article
There is a common belief that touching a frog causes warts to appear. It's a delusion. The causative agent of the disease, which results in the formation of warts, is human papillomavirus infection. According to statistics, this infection causes about 20% of all cancers.
The risk of HPV infection increases significantly:
- when using other people's personal hygiene items and items of common use;
- in public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, etc.), especially when walking there barefoot;
- in case of skin damage;
- with increased sweating of the hands and feet;
- upon contact with an infected person (handshake, sexual contact, etc.);
- when walking in tight, uncomfortable shoes that cause friction on the skin of the foot;
- when using non-sterile instruments (in a beauty salon, etc.).
The infection can remain in the human body for 3 to 6 months without showing itself in any way. Its “activator” and indirect culprit for the appearance of warts is weakened immunity.
Strengthening the immune system
Modern medicine has not yet learned to kill viruses. But an important fact is that HPV carriage is not lifelong. In addition, medicine has a small number of means at its disposal that allow it to remove some of the viruses from the body. The use of these drugs is fully compatible with immunomodulatory therapy.
The amount of virus in the body is directly related to the state of the body’s immunity - the better the immunity, the less virus. Therefore, the most promising way to reduce the concentration of HPV in the body is to strengthen the immune system. For this purpose, a separate course of treatment is carried out, after which the person begins to feel much better.
Finally, there are very effective preparations for topical use - creams, gels, sprays that increase local immunity and reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected tissues.
Are warts always dangerous?
Most warts are completely harmless and can theoretically disappear in a few weeks or at most a month. In this case, patients are more likely to be concerned about a serious cosmetic defect, which causes psychological discomfort and interferes with leading a full lifestyle.
Warts are often painless unless they are on the soles of the feet or another part of the body that is subject to shock or constant contact. But there are cases of itching and discomfort in the affected area.
But as mentioned above, warts are viral in nature, so you cannot expect that the neoplasm will go away on its own or will not bother you for the rest of your life. Any wart should be shown to a dermatologist, and if he deems it necessary, it should be removed using one of the safe methods.
How to recognize warts: symptoms and signs
An inexperienced person may confuse warts with other skin growths, for example, moles, calluses, melanomas.
The main differences between warts and moles:
- moles have a dark or black tint, while warts have a light color;
- warts grow tightly together with the skin, moles are separate structures, as if glued to the body;
- moles are soft and smooth to the touch, warts are hard, hard and rough.
It is also easy to distinguish a wart from a callus. When pressing on the growth, painful sensations will occur, and if it peels off, traces of hemorrhages will be visible underneath it. Under the callus is new, tender skin.
You can distinguish a wart from a melanoma by color and shape. This dangerous disease is characterized by heterogeneous red and black shades, proliferation and an uneven contour.
It is not difficult for a dermatologist to make the correct diagnosis using a visual examination. But a good specialist will not be content with just a simple inspection. He will definitely use a special magnifying device - a dermatoscope. If there is a suspicion of a pathogenic process, scraping of the surface layer will be required.
In the case of anogenital warts (located around the anus and on the genitals), consultation with a gynecologist or proctologist is necessary.
How to get rid of them?
There are many methods: from the most common - removal with celandine - to laser burning. Mokina conventionally divides them into physical and chemical. The latter include liquids like the aforementioned celandine, with which warts can be very carefully removed at home. Dermatologists, as a rule, include medical interventions as physical methods. “They are removed with liquid nitrogen (freezing), a laser beam, an electrocoagulator, or a radio wave method. The mechanism is approximately the same. This is burning with high temperature or some type of radiation,” the doctor explains to AiF.ru.
Common (simple, vulgar) warts
Common warts are dense, dry growths characterized by an uneven and rough surface to the touch, variable size and rounded shape. They look like a hard, keratinized bubble up to 1 cm in diameter, significantly rising above the surface of the skin.
The surface of common warts is often covered with grooves and projections, which is why the new growth vaguely resembles a cauliflower or raspberry with black dots inside.
This is the most common type of wart, accounting for up to 70% of all such skin neoplasms. Simple warts can appear on the skin at any age, but most often they affect children and young people. This is due to the fact that they have weaker immunity than adults.
Common warts usually appear on the hands (fingers and backs of the hands), knees and elbows, sometimes on the face or feet, and extremely rarely on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
A scattering of small growths may form next to the large “parent” wart. Young neoplasms usually remain flesh-colored; over time, they acquire a dirty gray or grayish-brown tint, less often yellow or pinkish. This is due to their uneven porous surface, which accumulates dirt.
Vulgar warts usually do not cause concern: they do not cause unpleasant symptoms, do not hurt or itch. However, they may cause pain if they are in areas subject to impacts or in contact with clothing. The growths may heal on their own over time, especially if they occur in childhood.
Causes of warts on hands
Warts form between the fingers due to a large number of reasons:
- As a result of a decrease in the protective functions of the body;
- Poor nutrition, consumption of large quantities of harmful foods;
- Frequent stressful situations;
- Insufficient amount of vitamins in the body;
- The appearance of small scratches and cuts that were not promptly treated with an antibacterial agent;
- Malfunction of the sebaceous glands on the hands;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Improper hand hygiene.
A very common reason for the appearance of warts on the hands is the lack of normal living conditions, the presence of accumulation of dirt in the room where a person lives or in the place of work.
Plantar (spike) warts
Plantar warts are a type of vulgar wart. The manifestation of the disease is most often observed in children and at the age of 20-30 years. Of all skin warts, plantar warts occur in 30%.
Warts on the soles appear as hard, round lumps with papillae in the middle. Inside the wart, characteristic black dots are visible - many small thrombosed capillaries. Along the edges there is a small roll of keratinized skin. The visible part, rising above the surface of the skin by only 1-2 mm, can reach 2 cm in diameter and is only a quarter of the total size of the plantar wart, which mainly forms in the deep layers of the epithelium (skin).
Externally, the spine resembles a callus. A plantar wart can be differentiated (distinguished) from a callus by the visible interruption of the skin pattern in accordance with the wart.
This type of neoplasm usually affects the feet (sole, sides and toes), and less commonly the palms. They appear on the skin as small whitish, pinpoint skin lesions, sometimes itchy. Over time, their surface becomes rougher and changes color - from yellow to dark brown.
Plantar warts themselves do not pose a threat to health, but when walking they cause a person significant discomfort, cause pain, which often intensifies, and can even bleed. This is due to the location of the tumor and the specifics of its growth. Since the spine grows inward, the weight of the body when walking compresses the pain receptors.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several days to several years. The infection enters the body and goes into waiting mode for a favorable environment to activate. Plantar warts regress without treatment in 50% of cases. But this process lasts from 8 months to one and a half years.
Without treatment, plantar warts will enlarge and multiply, even to the point of producing large clusters of tumors. This can even lead to temporary loss of a person's ability to work due to unbearable pain that prevents walking.
Based on the characteristics of the lesion and its location, plantar warts are divided into 3 types:
- simple;
- periungual;
- mosaic.
Periungual plantar warts
Periungual warts are small, rough formations with cracks on the surface, located on the hands and feet of a person, namely near the nail plate or deep under it. Externally they resemble cauliflower heads.
They can be flat, pointed or hemispherical. As a rule, periungual warts are gray, but they can also be flesh-colored. They are not too dense, like simple plantar ones, but have a fairly deep root.
This disease mainly affects children and young people. The main factor in contracting the infection is skin microtraumas around the nail. At particular risk are those who bite their nails and pet stray animals, as well as people who carelessly remove cuticles, use undisinfected tools, and work in water without gloves.
This type of neoplasm does not pose a threat to human health; it is mainly only a cosmetic defect. Periungual plantar warts do not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. However, a wart under the nail is not so harmless - over time, the neoplasm provokes depletion of the nail plate and its further destruction.
In addition, various bacteria and viruses enter through cracks on the surface of the growths, which easily form due to frequent hand work, causing re-infection. Also, as warts grow, the cracks can cause pain. The cuticle is often lost and a tendency to become inflamed (paronychia) develops.
Removal of the tumor is necessary to stop the proliferation of growths, which easily spread to healthy fingers. Localization of the wart under the nail plate makes treatment and removal very difficult. When it appears in childhood or adolescence, it can go away on its own.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of warts on the hands, the following prevention methods must be followed:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with antibacterial agents;
- Treat skin damage with an antiseptic in a timely manner;
- Consume special vitamin complexes to increase the immune system’s resistance to viruses;
- After visiting places with high humidity, take a shower;
- Avoid contact with infected people.
Such simple prevention methods will help reduce the risk of warts on the hands, as well as other types of skin diseases.
Mosaic plantar warts
Mosaic warts are a special type of neoplasm. They are plaques, so-called clusters, formed as a result of the fusion of many small plantar warts tightly pressed together. The arrangement of the plaques resembles a mosaic (hence their name).
This formation is usually observed in a small and localized area. It can reach a diameter of about 6-7 cm. In the early stages of development, mosaic warts look like small black punctures. As they develop, they take on the appearance of a white, yellowish or light brown cauliflower, with dark spots in the middle. These spots are formed due to thrombosis of blood vessels.
This type of wart is quite rare. They usually affect the hands or soles of the feet, and are especially common under the toes. Unlike simple plantar warts, mosaic warts cause little or no pain when walking because they are flatter and more superficial.
Mosaic warts are highly contagious. They are difficult to treat due to the multiplicity of foci of viral infection. The success of treatment is facilitated by its timely initiation. As a rule, mosaic growths are prone to recurrence even after surgical removal.
Flat (juvenile) warts
Flat warts are a fairly common type of tumor and the least problematic. They present as small lenticular lesions (several mm in diameter) or smooth papular lesions. They can grow either singly, which is quite rare, or in large numbers, close to each other.
There are several stages of the disease:
- mild – one or several painless warts;
- medium – from 10 to 100 painless growths;
- severe – more than 100 neoplasms.
If they are localized in places that experience excess pressure (friction from clothing, shoes, etc.), they cause pain.
Flat warts are easily identified and have a white, brown, yellowish or pink hue, similar to the color of meat. They are about the size of a pinhead and, compared to other types of warts, are smoother and flatter. In fact, at the point where a flat wart develops, the skin rises slightly (to a height of about 5mm), forming a sort of raised circular area.
The growths typically appear on the face, knees, elbows, back, legs, and arms (especially the fingers). People of absolutely any age become victims of this disease. But most often it affects children and adolescents (20% of schoolchildren have it), hence the second name for warts - juvenile.
In a close group of schoolchildren, 80% show resistance (resistance) to the virus. In adults, irritation and inflammation after shaving contribute to the proliferation of tumors.
The incubation period of infection can last up to 8 months. Mostly the disease is only a cosmetic defect. Juvenile warts are painless unless caused by mechanical pressure or injury and can sometimes cause itching, but are extremely contagious.
The virus is practically not transmitted through shared objects; the main route of infection is skin contact. Flat warts multiply so easily that it is enough to touch a healthy part of the body to cause the birth of a new formation.
The peculiarity of this type of wart is that in most cases no treatment is required: they can disappear as suddenly as they appeared, especially in children. In adults, the disease must be treated, and the virus is very resistant to drug treatment.
Anogenital warts (condylomas)
Among sexually transmitted diseases, anogenital warts are especially common. They are flat and elongated neoplasms or elastic elastic growths in the form of cauliflower or cockscomb. Such warts reach 1-1.5 cm and are gray, pink or flesh-colored.
Typically, this type of neoplasm is transmitted sexually: during vaginal/anal sex or even simply through contact with intimate areas without penetration. After oral sex, warts can appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, vocal cords or trachea. Such growths are called oral, or acute, condylomas. In rare cases, infection occurs through household contact or from mother to newborn.
Based on their appearance and structure, there are several types of genital warts:
- Pointed - loose polyps of pink, flesh-colored or red color, on a stalk or a wide base, reminiscent of cauliflower. They can occur either individually or in the form of multiple clusters. Genital warts are prone to rapid reproduction;
- Papillary - round, smooth growths without a stalk, rising above the surface of the skin by several millimeters;
- Keratotic - very dense, thickened formations that protrude significantly above the skin. Typically affects the female labia majora;
- Giant (Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas) are a rare type of wart. They are prone to rapid growth, accompanied by destruction of surrounding tissues. In extremely rare cases, giant condyloma degenerates into a malignant form;
- Flat - formed both singly and in the form of multiple clusters. There are practically no symptoms, sometimes itching and discharge may occur. The affected area of flat growths is the vaginal mucosa and cervix in women.
The appearance of anogenital warts and the deterioration of their condition are often accompanied by other sexually transmitted diseases (ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.). It is impossible to protect yourself or your partner from infection using a condom, since in this case it is ineffective. It is necessary to completely abandon intimate relationships until complete recovery.
Anogenital warts occur equally often in people of both sexes who are sexually active (usually from 20 to 25 years). The incubation period for this disease varies from three weeks to nine months, with an average of about three months.
In men, condylomas are most often found on the foreskin, scrotum, inside the urethra and on the penis. They can be localized around the anus and rectum, especially in homosexual men. In women, warts appear mainly at the level of the vulva, vaginal wall, cervix and perineum; The urethra and anal area may also be affected.
Genital warts are more common in immunocompromised patients. The rate of growth varies, but pregnancy, immunosuppression (suppression of the immune system), discharge from the urethra, vagina or rectum, accumulation of smegma, or skin maceration (the natural process of swelling of the epidermis (layer of skin) with prolonged contact with liquid) can accelerate the growth and spread of warts.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- severe itching at the location of the growth;
- painful and uncomfortable sensations;
- burning;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse;
- foreign body sensation;
- problems with defecation when the wart is located in the anus;
- bleeding when condyloma is damaged.
In most cases, anogenital warts are benign, but they can degenerate into carcinoma. For this reason, in order to prevent cancer, condylomas, regardless of their position, shape and size, are always removed.
Anogenital warts are usually diagnosed clinically. Their morphology distinguishes them from typical lateral condylomas of secondary syphilis, but in any case, serological tests for syphilis are necessary in the initial phase and after 3 months. A biopsy is required to rule out carcinoma and is mandatory in cases of bleeding, ulceration or persistent warts.
Endocervical and anal warts can only be visualized by colposcopy and anoscopy. Application of a solution of 3-5% acetic acid for a few minutes before colposcopic examination causes the growth to change color to white, improving visualization and detection of small warts.
Recurrence of anogenital warts is promoted by:
- promiscuity;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- installation of an intrauterine device, termination of pregnancy using surgical traumatic methods or other medical procedures.
This type of wart is dangerous due to a number of complications:
- Lack of careful intimate hygiene or irritation of growths due to constant friction against underwear leads to ulceration of growths by secretion of purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- In the absence of timely treatment, genital warts are prone to suppuration;
- Lack of therapy leads to the formation of a large number of warts. In particularly advanced cases, not even a small area of healthy skin remains;
- In the presence of anogenital warts, a strong decrease in immunity is observed, which is associated with a person’s susceptibility to any infectious disease. If the patient already has a chronic inflammatory disease (in particular, of the pelvic organs), it will necessarily get worse;
- Threat of degeneration into a malignant form.
Folk remedies against warts: herbs
- Grind, sift and mix celandine herb with Vaseline. Apply to warts daily.
- Every other day, rub the wart with juice squeezed from a freshly cut celandine stem.
- Grind a fresh calendula flower, apply it to the wart and tie it or cover it with adhesive tape overnight. The procedure should be repeated until the wart disappears.
- Small young warts can be cured with dandelion juice by applying it to the affected areas 2 times a day.
- Mix dandelion root juice with butter in a ratio of 1:4. Apply ointment to warts 2-3 times a day.
- Lubricate warts located on the soles of the feet with flax seed oil.
- Crush the fruits of mountain ash and apply it to the warts as a cold compress. Make compresses daily.
- Lubricate warts with fresh rowan juice.
- Grind and apply thuja occidentalis leaves to the warts, securing them with a strip of adhesive tape.
- Pour 3 tablespoons of crushed wormwood with 1 cup of boiling water, leave for 2 hours in a sealed container, strain. Make a compress. Repeat the procedure daily. The product is effective for flat warts.
- Grind the seeds of blue cornflower and apply the powder from the seeds to the warts daily, securing it with a strip of adhesive tape.
- Lubricate warts and condylomas with duckweed juice. Warts disappear painlessly.
Filiform (acrochord) warts
Filiform warts, also known as facial warts, are the most unusual type of these growths. They are thin, long, racem-like shoots that are usually found on the eyelids and surrounding areas, on the neck, near the lips and nose, and less commonly on the legs, in the groin folds, under the mammary glands and in the armpits.
The typical color of acrochords is flesh-colored, which is why people do not immediately notice them. Sometimes they may turn yellow, brown or pink. Usually they reach a length of 5 to 10 mm, extremely rarely - several centimeters. Depending on the severity of the virus, acrochords form singly or in multiple clusters. This distinctive type of filamentous wart is usually diagnosed visually.
Filiform warts form when a strain of the human papillomavirus causes the top layer of skin to grow too quickly. At the inception stage, the growth looks like a yellowish bump. As it grows, it stretches out, transforming into an elongated formation on a stalk. To the touch, the wart has an elastic and dense structure.
People of absolutely any age can become a “target”, but often elderly patients suffer from this disease. According to statistics, about 50% of the world's population over 50 years of age have facial warts.
Infection with the virus often occurs through cracks and abrasions on the face, so people with dry skin are at high risk. Also, the appearance, growth and spread of facial warts is facilitated by various hormonal changes (pregnancy, obesity, menopause, ovarian dysfunction, diabetes, etc.).
Although highly contagious (infectious) and unattractive in appearance, this type of wart is benign, painless, and often responds well to treatment.
When they appear in sensitive areas, such as skin folds, or areas often subject to pressure and injury, some symptoms may occur:
- itching;
- bleeding;
- soreness;
- irritation.
This type of wart almost never develops into a malignant form. However, if the acrochord is injured, there is a high risk of developing an inflammatory process. Unlike many other similar neoplasms, the filamentous type does not disappear on its own. When a wart falls off, a new one grows in its place. Sometimes there is keratinization of the growth and its transformation into a cutaneous horn.
Facial papillomas are contagious and can be spread by sharing towels or facial cosmetics. Touching the acrochords puts a person at risk of spreading them to other parts of the body. Warts will increase in size and number if they are not removed.
Their location and ugly appearance make facial growths a cause of emotional stress and embarrassment for many people, sometimes affecting their self-esteem and self-confidence.
Senile (age-related keratomas, seborrheic keratoses) warts
Senile warts are one of the most common skin lesions that appear in old age as a general sign of skin aging. Despite their name, they are not caused by the human papillomavirus.
Seborrheic keratoses are extremely common. According to statistics, more than 90% of the population over the age of 60 have one or more of them. They are equally common in both men and women. It is not uncommon for the disease to affect people aged 30-40 years, as well as young people under 20 years of age.
Keratomas and keratoses can appear on any part of the body, including the scalp, face and genitals. The exception is the palms, soles of the feet and mucous membranes. It is rare for a person to develop only one growth. Over time, age-related keratomas become more and more numerous. Many people inherit a tendency to develop a very large number of these tumors. Some of them may have hundreds of wart-like growths scattered throughout their body.
In the early stages, aging warts appear as slightly raised light brown spots or papules. They can remain very flat and resemble freckles in appearance, or they can gradually thicken and develop a rough, warty surface, like a tumor on the skin. In most cases, they darken slowly and may eventually turn black.
These color changes are harmless. Many senile warts remain pinkish in color. Typical of these are small keratin plugs that can be seen on the surface of the wart.
Keratoses are usually round or oval in shape. Some seborrheic warts are irregular in shape. Their size can vary from one to several centimeters in diameter.
The cause of age-related keratomas is unknown. They are generally considered to be degenerative in nature and appear in large numbers as the skin ages. It is assumed that ultraviolet radiation increases the likelihood of their development.
There are five traditional forms of age-related warts:
- Spotted, or popularly “death freckles” . They form in numerous clusters on the hands and face. Such growths are round with an uneven contour and a smooth or slightly rough surface. It has several color options: light brown, brown-brown or pinkish-yellow;
- Papular or nodular . Larger growths tend to grow. Their typical color is gray or yellow. The surface of the wart is covered with horny layers;
- Classic keratoma . It is a collection of plaques tightly connected to each other. It is characterized by a jagged outline and a copper or pinkish color. As it grows, the middle part of the wart sinks;
- Cutaneous horn. It is a modification of keratoma. It is expressed as a cluster of dense keratinized dark brown plaques up to 1.5 cm.
Adverse reactions to certain medications and many chemotherapy drugs can contribute to the formation of irritated seborrheic keratoses—inflamed, red, crusty lesions. This leads to the development of eczematous dermatitis around the growth. Dermatitis can also cause new seborrheic keratoses to appear.
Age-related keratomas are always benign. This means that they do not spread and do not degenerate into a malignant form. The main problem is a cosmetic defect, especially if they develop on the face.
There are rare cases of skin cancer called melanoma that develops in a seborrheic wart. It is unknown whether this is just a coincidence or represents a true change in the cells in a seborrheic wart. A large number of age-related keratomas may be a sign of cancer of internal organs.
Typically, seborrheic keratoses are treated for cosmetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Diagnosis of the disease is usually made through a clinical examination. This type of wart is difficult to distinguish from skin cancer without histological examination. Therefore, very dark lesions that have changed in some way or that are growing rapidly require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out the possibility of cancer. Darker lesions should also be checked by a doctor to make sure they are not melanoma.
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor if neoplasms, nodules, compactions, or areas of discoloration appear on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs or anus.
During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the clinical manifestations and examine the affected areas.
To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests may be performed:
- PCR diagnostics with determination of the genotype of the virus; it is additionally possible to determine the degree of viral load. Biomaterial – vaginal smear, scraping from the urethra, cervical canal.
- Morphological, cytological examination to assess the risk of oncological pathology.
The severity of the condition is assessed by the number of tumors, the volume of affected tissue during examination and laboratory testing (the number of copies of HPV DNA in the test samples is determined).
Important ! Anogenital warts are treated using destructive methods (cryodestruction, laser destruction, electrocoagulation). In this regard, before treatment, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis are required.
Diagnosis is carried out by specialists from dermatovenerology departments. Additionally, consultations with specialized doctors may be required:
- a urologist if the tumors are localized inside the urethra;
- a proctologist if warts grow extensively in the anal area;
- obstetrician-gynecologist when planning and managing pregnancy;
- immunologist (for relapses of the disease or immunodeficiency states).
Treatment of warts in St. Petersburg
Treating warts requires a lot of patience. Warts may appear and disappear for no apparent reason or for reasons that are difficult to identify. High infectivity and autoculation of warts are arguments in favor of removal.
There are many different treatment methods. Therapeutic choices differ depending on the type of wart, its location, depth, number and extent of the affected area of skin.
Treatment for warts can produce very different results. Some warts respond to treatment while others do not, even if it is given to the same person.
Treatment often requires repetition over several weeks, months and in extreme cases even years before success is achieved. But in any case, wart removal should be performed in a clinic by a dermatologist. Self-medication is highly discouraged, as the consequences may be irreparable.
The most gentle and universal ways to get rid of warts of all types are laser and radio wave therapy.
Self-medication is harmful
Do not try to diagnose and treat HPV infection on your own! Firstly, there is a risk of improper use of drugs. Secondly, only a doctor can distinguish papilloma from a malignant tumor. In addition, self-treatment is fraught with consequences.
Today, there are celandine-based preparations on sale that are intended to eliminate warts. Celandine juice is similar in composition to iodine. Therefore, prolonged exposure to the drug causes skin burns. In this case, papillomas are seriously injured and can provoke the development of skin cancer. Cauterization with iodine is even more dangerous - it is more aggressive than celandine. Trying hard to get rid of papillomas with iodine, you can get scars on the skin. Vinegar is no better in this regard. Attempts to bandage warts and papillomas with a thin silk thread often only provoke the growth of these formations.
If you suspect the appearance of warts or genital warts, you should definitely seek advice from a dermatologist, urologist or gynecologist, depending on the location of the source of infection. Only a professional can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
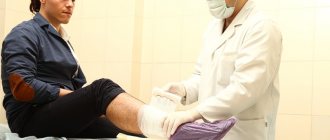
Laser wart removal
Today, laser surgery is one of the best ways to get rid of warts. This is a painless and safe procedure that can be used in areas of maximum sensitivity. Laser removal of tumors is very effective: the likelihood of relapse is minimal. This is significantly influenced by the severity of the disease.
Warts are removed by layer-by-layer cauterization of the affected area, thanks to which the doctor controls the depth of the effect. At the same time, the laser beam cauterizes the blood vessels, thereby preventing bleeding at the site of exposure.
Three methods of laser coagulation are common:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Procedures using this laser are more painful. Although the CO2 laser seals the blood vessels, it also kills the wart tissue. In this process, there is a possibility of damage to healthy tissue. Wound healing usually takes longer, and scar formation is possible. The efficiency is about 70%.
- Erbium laser. It is characterized by a shorter wavelength. The likelihood of scar formation after healing is significantly reduced.
- Pulsed dye laser. This laser more effectively seals the blood vessels that feed the wart. It does not damage much of the healthy tissue like a CO2 laser does. It is also the only type of laser approved for use on children. The effectiveness of this treatment method is about 95%.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Minimum likelihood of scar formation (depending on the degree of neglect of the pathology) | High price |
| Fast tissue healing | |
| High efficiency of the method | |
| Minimal damage to healthy tissue | |
| Speed of the procedure |
Wart removal is performed under local anesthesia. A crust remains at the cauterization site, which disappears within 14 days. After the procedure, the patient quickly returns to his normal lifestyle, provided that all doctor’s recommendations are followed.
Removal with a radio knife
The most effective modern method of getting rid of warts is removal by radio waves. First of all, this is due to the fact that in this procedure the instruments do not contact the patient's body: they are produced at a radio wave frequency.
Under the influence of radio waves, the skin does not overheat, blood vessels do not bleed, and all types of viruses die instantly. Thus, the growth is easily removed, and the likelihood of further development of the virus is completely eliminated.
Other advantages of radio wave wart removal should be noted:
- complete painlessness;
- speed of the procedure;
- exclusion of edema and infiltration;
- absence of postoperative complications;
- absence of scars at the site of wart removal;
- quick rehabilitation period.
The procedure is also performed under local anesthesia. After exposure, a crust forms on the affected area of the skin, which disappears on its own within 7-10 days.
As noted above, warts often affect the genital area. Removing anogenital growths (condylomas) usually frightens patients. However, the radio wave method in this case is the most effective and causes minimal pain.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Drug treatment
Very often, special treatment of warts with medications is used. The action of medications helps eliminate the disease on the hands and prevent re-infection.
Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs
The action of such drugs is aimed at increasing the resistance of the immune system to viral infections.
The most common types of drugs are:
- Interferon is a drug aimed at increasing immunity and developing the body’s natural resistance to viral infections. Used twice a day, morning and evening, course of use is 10 days. The use of the drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance and mental disorders. Permitted for use after reaching 5 years of age under strict medical supervision. Average cost 220 rubles ;
- Isoprinosine has an antiviral effect and is widely used to treat benign tumors. It is recommended to use three times a day during meals. Treatment period is up to 15 days. Allowed for use from the age of 7 years, average cost 900 rubles ;
- Cycloferon - used to suppress viral infection, often used in combination with external preparations to remove warts. Used once a day before meals, the course of treatment is up to 20 days. Not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Prescribed for children over 3 years of age under the supervision of a physician, the average cost is 350 rubles .
Interferon Isoprinosine Cycloferon
Most often, this drug treatment is used in the first stages of the disease.
If warts on the hands are neglected, it is necessary to use other methods of removal.
Chemicals
To treat lesions on the hands, chemical preparations for external use are often used. The action of such drugs is aimed at gradually removing warts on the hands.
Solutions have an increased level of toxicity and require careful use during treatment; when they come into contact with healthy areas of the skin, they tend to leave burns.
Very often, such chemical solutions are used at home and are sold in free quantities in pharmacies.
The most popular include:
- Solcoderm is a special chemical solution that quickly removes benign formations using the burning method. The drug contains a large amount of acids that destroy damaged cells and eliminate formations. Before using the drug, it is necessary to treat the wart on the hand with an antiseptic drug, and apply one drop of the chemical solution directly to the center of the wart on the hand. After a few minutes, repeat the procedure, the wart should change its color, after which it is necessary to remove the formation with tweezers. Not used in childhood and during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The cost of the drug is 900 rubles ;
- Feresol - the drug is used for the gradual removal of warts on the hands, used once a day until the formation completely disappears. Using a special applicator, the substance is applied to the center of the wart, which can cause discomfort. In case of contact with skin, rinse with plenty of water. Not used under the age of 7 years and during pregnancy and lactation. Average cost 300 rubles ;
- Lapis pencil is a special chemical that is designed to eliminate the infection that causes warts on the hands, used twice a day for 7 days. Before use, it is necessary to treat the formation with an antiseptic and apply a wart remedy. Not used for children under 10 years of age, as well as for those with individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is prohibited. The average cost is 150 rubles .
Solcoderm Ferezol Lapis pencil
Chemicals are toxic and can cause poisoning and burns on healthy skin.