| Pharyngitis | |
| ICD-10 | 02., 31.231.2 |
| ICD-9 | 462462, 472.1472.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 24580 |
| MedlinePlus | 000655 |
| eMedicine | emerg/419 |
| MeSH | D010612 |
Pharyngitis
(from Latin pharynx “throat” + suffix -itis “inflammatory process”) is an inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx.
What it is?
Throat diseases, including pharyngitis, can be a consequence or cause of the development of other diseases. This specific definition refers to inflammation of the mucous tissue at the back of the throat and lymph. It can form against the background of many factors, the basis of which is throat irritation - one-time and severe or constant minor. Accordingly, acute and chronic forms of the disease are distinguished.
This is a very diverse disease and it is impossible to determine it on your own. Traditional methods of treating colds in the form of milk with honey and tea with jam will have a beneficial effect on the throat, but the disease will not be cured. Moreover, a delay in appropriate treatment can turn the acute form into chronic pharyngitis with all the ensuing consequences or contribute to the spread of infection to other organs.
Etiology
Acute pharyngolaryngitis is most often associated with the effect of the virus on the human body (upper respiratory tract).
The disease can be caused by the following viral pathologies:
- diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- whooping cough;
- measles;
- rubella.
Very rarely, the acute form of the disease is provoked by a fungal infection. In adult patients, this type of pathological process is observed due to a weakened immune system.
Pharyngolaryngitis is more often diagnosed in adults than in children. The development of the disease can be triggered by:
- the presence of foci of infection in the nose - sinusitis, rhinitis, pulpitis;
- the presence of enlarged adenoids;
- inhalation of harmful chemicals or coal dust;
- constant overstrain of ligaments;
- allergic reactions of the body to some pathogen;
- eating spicy or too hot food;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
Severe everyday stress can reduce the immune system, as a result of which a person is susceptible to all kinds of negative influences from the outside.
Types of disease
Considering the causes and symptoms of the disease, we can distinguish several types according to severity:
- Catarrhal or simple - easy to treat and the most common, most often refer to the acute form, but it can also be chronic;
- The hypertrophic variant is more serious; its characteristic feature is strong thickening of the walls of the mucous membrane, their inflammation and difficulty breathing. Refers to the chronic form.
- Atrophic pharyngitis is a characteristic feature of which is rapidly developing sclerosis of lymphatic and mucous tissues, the most dangerous and difficult to treat. It is accompanied by severe pain and thinning of the membrane, vessels can already be seen through it, the mucus thickens and is difficult to remove.
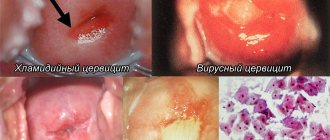
Photos of the throat with different types of pharyngitis can be seen below. Diseases are also divided depending on the pathogen or cause:
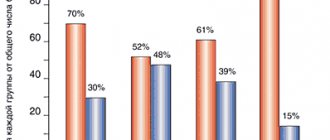
- Viral (especially common - about 70% of all cases, most of it is caused by rhinovirus);
- Bacterial;
- Allergic, if allergens are the cause of development;
- Fungal;
- Caused by trauma, that is, traumatic;
- Occurred against the background of irritating factors, for example, a constant large amount of dust or the need to talk a lot.
In addition, the disease is divided into already known forms: acute - with a one-time manifestation and chronic - with a series of remissions and exacerbations.
Objective examination
It is possible to clarify the location of the lesion by performing a visual examination of the pharynx and pharyngoscopy. An objective study consists of directly examining the pharyngeal mucosa using an additional light source and a spatula, which, by pressing on the tongue, allows the specialist to examine the lining of the pharynx and tonsils. This study allows us to determine the nature of the morphological changes in the pharynx.
For the acute course, catarrhal inflammation is most typical. It is characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the pharynx, palatine arches, hard and soft palate. At the same time, the mucous membrane looks lacquered. Single enlarged bright red follicles may be located along the back wall of the pharynx. There are no changes characteristic of the inflammatory process in the tonsils. It is not possible to make a differential diagnosis between viral and bacterial inflammation based solely on the results of pharyngoscopy. An objective examination can only clarify the inflammatory process and its form.
It is necessary to take into account that streptococcal pathogens can cause the development of infections such as scarlet fever. In this case, an important role in diagnosis is given to the presence of skin manifestations and the study of the epidemiological situation. The peculiarity of the rash with scarlet fever is the presence of pinpoint rashes, widespread against a hyperemic general background. An important sign is the thickening of the rash elements in skin folds and places of natural abrasions.
Causes of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis symptoms and treatment in adults, which can only be correctly determined by a doctor, can be diagnosed against the background of the causes of its occurrence. They are:
- Infections, that is, bacteria, for example, staphylococci, viruses (influenza), Candida fungi (candidiasis), chlamydia;
- If there is no specific immunity against diseases such as measles or whooping cough;
- If there is inflammation somewhere nearby, for example, with sinusitis, caries, tonsillitis, if there is a curvature of the nasal septum and this makes breathing difficult;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract, which include hiatal hernia or certain types of reflux;
- Diseases of the glands, for example, diabetes. The cause may also be menopause, changes in the functioning of the body against this background;
- Allergy;
- Various insufficiencies - renal, cardiac, pulmonary;
- Features of the structure of the throat and gastrointestinal tract;
- Reduced immune function due to fatigue or poor nutrition, persistent lack of vitamin A.
Prevention
Methods for preventing pharyngitis in adults include:
- hardening the body - walking in the fresh air, playing sports, swimming;
- giving up bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol;
- strengthening the immune system - introducing the maximum amount of vegetables and fruits into the diet, taking vitamin complexes (as prescribed by a doctor).
Pharyngitis is one of the diseases that significantly disrupts the normal state. It is necessary to consult a doctor promptly and undergo treatment. This way you can forget about the problem once and for all.
Main factors that increase the risk of developing the disease
In addition to the reasons that increase the risk of developing pharyngitis, there are also certain risk factors:
- The presence in the air regularly appears of a lot of dust, other pollutants, including harmful chemicals, in or near industries, corrosive gases;
- Failure to comply with the temperature regime for food and drink, inhalation of very hot or cold air;
- Regular drinking of alcohol or smoking tobacco products of any kind;
- Constant overstrain of the vocal cords due to specific professions, for example, if a person sings or talks a lot;
- Removal of tonsils, which leads to an increase in harmful microorganisms in the throat;
- Breathing through the mouth due to difficulty passing air through the nasal passages.
If a person knows about any problem from the list of causes of pharyngitis, he should carefully avoid the mentioned risk factors - their combination greatly increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
Acute form of pharyngitis
The acute version of the disease involves exposure of the larynx to a sufficient number of negative factors, for example, half an hour in an icy room or two servings of ice cream on a hot day, which allows an infection to develop. It can also be caused by a large dose of alcohol, burning tender areas and other risk factors.
Let's consider what symptoms acute pharyngitis has, how to treat it, carry out prevention, and what to be afraid of in advanced forms.
Symptoms
The disease can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Suddenly, a fairly strong sore throat appears;
- When the muscles of the larynx are tense, the patient feels a sharp and severe pain;
- Cough, and there is no sputum with it, and the longer it continues, the more sore and irritated the throat;
- A person constantly swallows unconsciously, as the accumulating mucus feels like a foreign object;
- The pain may radiate to the ears;
- The temperature can rise to 37.5 degrees, higher - very rarely;
- General malaise, weakness, sluggish appetite;
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
The externally acute form is easy to notice when looking at the back wall of the larynx in the mirror. It will turn red, swell, and small but visible ulcers will appear. With some types, plaque is possible.
Complications
If left untreated, the acute form can lead to:
- Chronic pharyngitis;
- Some species may cause a peritonsillar abscess with erythema and edema;
- Inflammation can descend to the lower organs and cause specific diseases such as bronchitis or tonsillitis, including pneumonia;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Possible development of rheumatism.
Treatment
Acute pharyngitis can be guaranteed to be cured only after the correct diagnosis has been made. The course should be comprehensive and take into account everything:
- Nutrition. The diet should not contain anything that irritates the throat - hot tea, ice-cold juices, sour, spicy, pungent foods are strictly contraindicated. You need teas, milk, soups, purees and soft porridges.
- Mode. Be sure to lie in bed, in a warm place, talk less, sing less, and generally open your mouth. The room needs to be ventilated and moistened. Be sure to keep your feet wrapped; foot baths with essential oils will be helpful. Be sure to quit all types of smoking.
- Gargling with medications (chlorhexidine) or herbal decoctions (chamomile, propolis). Sprays such as Bioparox or Eucalyptus are possible.
- Immunity helpers. Lisobact and similar tablets will be relevant. You need to constantly replenish your vitamin C reserves, drink tinctures from Eleutherococcus or Schisandra chinensis.
- Antiviral drugs and antibiotics are prescribed depending on the type of pharyngitis and the causes of its occurrence.
- Treatment of symptoms is prescribed individually, for example, if the patient cannot sleep due to a severe cough, this condition is alleviated.
Treatment
Photo: volkovysk.by
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The indication for hospitalization is the development of complications, the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs, accompanied by a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition. Conservative therapy includes drug and non-drug methods:
- Protective mode . The patient is advised to stop smoking, drinking alcohol, and eating foods that irritate the mucous membranes. You should avoid staying in dusty rooms or in the cold.
- Drug therapy . The main role in drug therapy for pharyngitis is given to local agents. If the disease is bacterial in nature and complications develop, antibiotic therapy may be possible.
- Physiotherapy . For acute pharyngitis, laser therapy, electrophoresis with potassium iodide, paraffin treatment and mud applications to the submandibular area are used. For atrophic pharyngitis, nicotinic acid electrophoresis is prescribed.
Sanitation of infectious foci is necessary: carious teeth, paranasal sinuses, tonsils. For chronic granular pharyngitis, cryotherapy, laser coagulation and ultrasonic disintegration of granules, and radio wave shading of the pharynx are used. Novocaine blockades of the lateral parts of the pharynx are performed.
Patients with pharyngitis caused by gastroesophageal reflux require treatment of the underlying disease by a gastroenterologist. In the presence of endocrine and somatic pathologies, observation by an endocrinologist, cardiologist, nephrologist, hepatologist, and other specialists is indicated.
Surgical interventions are required when complications develop, nasal breathing disorders due to other diseases of the ENT organs. For patients with parapharyngeal and paratonsillar abscesses, the abscesses are opened and drained. For chronic tonsillitis, a tonsillotomy or tonsillectomy is performed. For diseases of the nasal cavity, septoplasty, polypotomy, and vasotomy are performed.
Chronic form of pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis is a more serious disease than acute pharyngitis. It occurs either against the background of an untreated simple form, or due to a regular destructive effect on the mucous membrane of the throat.
Symptoms
It is important to understand that chronic pharyngitis is a change of two stages - exacerbation, during which the disease has symptoms of the acute stage and remission, which has specific, more vague symptoms.
When the patient is not in an acute state, the state of the larynx is as follows:
- In the simple form, this is swelling, a mild but constant soreness, a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, coughing up mucus, and there may be a burning sensation and dryness. There will be no pain or fever;
- The hypertrophic form also increases lymph flow, the throat begins to hurt, it becomes raw, you constantly want to cough, an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth due to the accumulation of mucus;
- Atrophic form - the mucus becomes thicker, it is difficult to get rid of it, dense crusts form on the larynx. There is pain and when coughing, particles of keratinized tissue may come out, breathing becomes more and more difficult, as the desire to cough increases.
The chronic form of pharyngitis greatly affects the voice; when talking, a person quickly gets tired and experiences discomfort.
Complications
The consequences of the neglected chronic form are disastrous:
- Autoimmune reactions;
- Damage to internal organs - kidneys, brain, heart;
- In childhood, swelling may develop and suffocation may occur during sleep.
Treatment
To treat the chronic form in an adult, it is necessary to distinguish between the time of exacerbation, during which it is necessary to be treated as in the acute form, and the latent course of the disease. During the latter, it is good to carry out typical folk or preventive measures, for example, relax in a warm climate by the sea or drink warm milk with honey and butter at night, wear warm socks and insulate yourself in off-season weather.
Diagnosis of the disease
After looking at photos and videos in articles or books, you can form a pretty decent idea about pharyngitis, but there is no way to learn how to diagnose it. In order to make such a diagnosis, the doctor, and the patient himself, can look at the larynx and understand that it is. However, only a specialist with a trained eye and test results can determine the stage, type, and causative agent of the disease.
For diagnosis, a visual examination is performed, after which the doctor will prescribe a smear to determine the type of infection and a specific group of pathogens. Sometimes, for a more detailed study, pharyngoscopy is performed. Without accurate knowledge of the type of disease, treatment will likely be ineffective and the patient’s condition will worsen.
Traditional methods
How can you cure pharyngitis without a doctor and medications? No way! But it is quite possible to support the throat, alleviate symptoms and saturate the body with vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
Regular sea water works well. It can be made from purified, warm, non-mineral water by adding special salts. It's easier to buy at a pharmacy. This liquid should be used to gargle and rinse your nose.
Warming baths have a beneficial effect on the entire body, and with the addition of fragrant eucalyptus oils, they stimulate the immune system, provide light inhalation, relax and relieve stress. In addition, thyme infusions can be added to baths, which will speed up the recovery process.
Liquid plays a special role. You need to drink at least 2, but no more than 4 liters of warm water per day. These may be non-strong teas with or without jam, herbal infusions, neutral, non-sour and non-spicy juices. It is also worth thoroughly humidifying the air in the room; this can be done using a special device or simply by placing a damp towel on the radiator.
The throat should be kept warm throughout the entire treatment. There is no need to apply hot compresses, they can make things worse, but wrapping yourself in a warm woolen scarf would be a great idea. The main thing to remember is that any folk treatment should be combined with medication.