Fibroadenoma is a benign breast tumor with clear contours, dense consistency, and is easily displaced relative to the breast tissue. As a rule, there is no sharp pain in the area of education. The characteristic structure of fibroadenoma tissue is the predominance of connective tissue stroma over glandular parenchyma.
It occurs more often in girls and women under 40 years of age (20-60%). In adolescents, fibroadenomas are called juvenile fibroadenomas. As a rule, fibroadenoma has a diameter of 1-3 centimeters, but larger formations occur. Most often one breast is affected, less often both. Some patients have multiple nodes.
The presence of fibroadenoma in the mammary gland is not life-threatening, but the risk of developing cancer in such women is 3-5 times higher than in others. This is why it is important to have regular breast examinations.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a mammologist.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
What is fibroadenoma
The content of the article
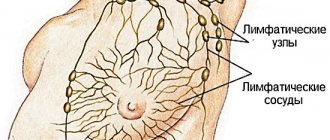
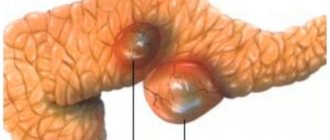
Fibroadenoma of the mammary gland is a mobile benign neoplasm of glandular and connective tissue. The pathology affects the chest, less often tendons, skin, and internal organs.
It is more often found in women under thirty years of age.
Glandular tissue is soft in nature, but overgrown with connective tissue, it takes on the appearance of a dense ball. In this form, the tumor is not dangerous - it does not extend beyond the frame and, unlike cancerous formations, does not metastasize. But if the capsule contains cysts (accumulations of purulent fluid) or inclusions of calcium deposits - calcifications, the neoplasm becomes dangerous as it can become malignant.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Doctors do not know the exact reason why the disease occurs. Scientists believe that there are several factors for the appearance of pathology:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Chronic diseases of the endocrine or reproductive systems;
- Excess weight in women;
- Alcohol and nicotine abuse;
- The influence of constant stress;
- Use of hormone-based oral contraception;
- Artificial termination of pregnancy or miscarriage;
- Disturbances in the metabolic process.
Why do fibroadenomas form?
This type of pathology belongs to the category of little-studied. There are only assumptions about the causes of fibroadenomas, the most recognized among them being hormonal disorders.
It has been proven that any factors associated with hormonal fluctuations contribute to the occurrence of fibroadenoma:
- Independent, uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, emergency contraception;
- Pregnancy, frequent abortions, in which the body, which is in the gestation stage, is forced to sharply adjust to a new rhythm;
- Intermittent lactation, breast refusal or inability to feed;
- The presence of pathologies, stressful situations, overload;
- Menopause.
Often fibroadenoma forms during the childbearing period, and after entering menopause it resolves. This indicates the important role of female sex hormones in this process.
Complications after treatment
Modern treatment methods have minimal risks and complications. The use of minimally invasive treatment allows you to preserve the appearance of the breast as much as possible.
The following complications are rarely possible after removal:
- infection of the surgical wound;
- scar (cosmetic defect);
- compaction after removal of fibroadenoma;
- inflammation of the wound.
It is important to remember that even after surgical treatment, a recurrence of the disease and the formation of a new tumor in the same place or in another is possible.
Types and form of breast tumors
Kinds:
- Nodular
- a change in the shape of connecting tissues together with the ducts of the gland, ingrowth of connecting tissues into the ducts. - Leaf-shaped
. This is a dangerous, rare tumor. It actively increases in size and carries the risk of degeneration into sarcoma. This fibroadenoma gets its name from its structure: it consists of layers that look like leaves. - Mixed form
, which combines the symptoms of both cases.
Fibroids are divided into forms: immature and mature. In the first case, the tumor appears at an earlier age; there is no external capsule, which makes it possible to do without surgery. In the second case, the tumor is diagnosed after 20 years. The formation has a dense shell, so it cannot be treated with drugs.
Recovery period
The duration of the postoperative period depends on the operation performed. Rehabilitation can be short or, conversely, take a long time. It is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations for caring for the suture to prevent the development of complications.
The patient is placed in the ward. Intensive monitoring takes place to monitor blood pressure, heart rate and breathing. The external well-being of the patient is monitored. Ice should be applied to the wound - this will prevent the development of a hematoma. Hospital monitoring is required to manage the adverse effects of the operation.
The stitches are removed after 7-10 days. Recently, threads have been used that dissolve independently into the tissue. After a certain time, the stitch will dissolve on its own. Therefore, it does not require removal, which avoids a rough scar.
It is forbidden to take a bath to avoid infection in the wound. Only showers are allowed. Restoring the body involves proper and balanced nutrition. The menu should contain vitamins and microelements - zinc, copper, folic acid, iron and others. Diet is required to replenish the body with important mineral elements.
Prevention of relapse requires the use of compression garments and light sports without heavy loads.
Symptoms of the disease
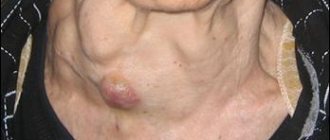
First, a strange lump appears in the mammary gland, it is called a node. The nodule has a dense structure, can be easily felt and does not hurt. If the tumor is small, then it is difficult to notice at home; it is detected only by ultrasound of the mammary glands. There may be several fibroadenomas.
It is possible to recognize fibroadenoma more quickly if it appears near the nipples. In this case, in addition to compaction, the following may appear:
- Sores;
- Cracked nipples;
- Leakage of light fluid from the nipples;
- Pain on contact with the chest.
When a benign tumor becomes malignant, additional symptoms appear:
- The skin of the chest changes color to pale bluish or red;
- The tumor can grow quickly.
In any case, if you notice the slightest lump, you should immediately visit a gynecologist - mammologist. If necessary, after the examination he will redirect you to an oncologist.
Important questions
Every patient is concerned about issues related to the health of the breast when diagnosing a benign tumor. At a doctor's appointment, a woman should ask all her questions to the attending physician. A qualified specialist will give detailed answers.
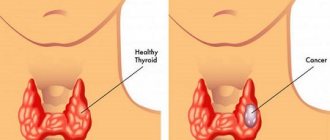
Can fibroadenoma turn into cancer?
Many women are concerned about whether fibroadenoma can develop into cancer. Leaf-shaped and pericanalicular tumors are most often susceptible to this phenomenon. However, the percentage of their degeneration into a malignant process is not high. Fibroadenoma degenerates into cancer only in 20% of cases; the lump remains benign and rarely hurts.
A benign neoplasm requires constant monitoring and biopsy. Histological analysis of the biomaterial will determine the nature and morphology of the neoplasm cells.
Fibroadenoma and pregnancy
In many cases, the development of a benign tumor in the breast is diagnosed during pregnancy. Fibroadenoma during pregnancy does not have a negative effect on the course of pregnancy, but can create discomfort and problems during breastfeeding.
A pregnant woman should be constantly under medical supervision. Doctors decide the need for surgery individually.
IVF and fibroadenoma
A medical specialist will answer whether glandular fibroadenoma is compatible with IVF. A benign neoplasm is considered safe and cannot threaten the development of the embryo and the birth of a child. The tactics of doctors depend on the characteristics of each case - doctors recommend that some women undergo surgery before IVF, others refrain from surgery if there are contraindications.
Ultrasound table with norms and deviations of fibroadenoma
| Glandular tissue thickness | Fibroadenoma size | ||
| Normal up to 40 years – up to 14 mm | Deviations - more than 14 mm | Normally does not exceed 2-3 cm | Deviations – up to 9 cm |
| The norm after 40 years is up to 20 mm | Deviations - more than 20 mm | ||
If cancer is suspected, a fine-needle biopsy is prescribed. This is quite unpleasant, but the only adequate procedure that allows you to accurately determine whether there is cancer in the mammary gland.
The mammologist, using a thin hollow needle, inserts it into the tumor, capturing a small amount of tissue. To avoid mistakes, the doctor monitors the process using ultrasound. The cells obtained in this way are sent to the laboratory for cytological (cellular) examination. Under a microscope, the structure of cells is clearly visible: it is different for benign and malignant ones.
After the tests obtained, the doctor will prescribe further treatment, and if necessary, surgery.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers many effective recipes for the treatment of benign tumors. For fibroadenoma, it is useful to take a decoction of pomegranate bark. To prepare it, 1 part of pomegranate peels is mixed with viburnum and oak branches. The mixture is poured with boiling water and left in a water bath under a lid for 10 minutes. Then the infusion is filtered and taken 5 tablespoons 3 times a day on an empty stomach.
Another recipe has been known since ancient times. It is useful to drink a decoction from a collection that contains St. John's wort, pine buds, rose hips, and wormwood for fibroadenoma. The herbal mixture is brewed in a thermos or sealed container, then placed in a water bath and 200 ml of alcohol or cognac is added. The broth is cooled and infused. Alcohol tincture is taken with honey and aloe juice 30 minutes before meals, 1 teaspoon. The course of treatment is 6 days.
How is fibroadenoma treated?
Having received the results, the mammologist resorts to the following types of treatment:
Monitoring the dynamics of tumor growth is suitable in several cases:
- The dimensions of the seal do not exceed two centimeters.
- Fibroadenoma is hormone-dependent and responds well to hormonal treatment.
- The tumor is not growing.
If drug treatment does not bring visible results, the breast hurts or cancer cells are found, surgery is required.
One type of surgery may be enucleation, where the tumor is excised from the breast. And the second type is sectoral resection. Excision is carried out locally, in a specific area. But low-traumatic interventions are especially popular:
- Radiofrequency ablation, in which the node is destroyed by radio waves. The operation is carried out under ultrasound control.
- Cryotherapy is the treatment of a tumor with liquid nitrogen delivered to the tumor through a thin probe.
After the operation, you need to take very good care of yourself so as not to miss the formation of new nodes.
Diagnosis of pathology
It is difficult to determine the disease on your own. Sometimes fibroadenoma is not visible on mammography and ultrasound. It can be differentiated from breast cancer by performing a thorough examination of the sternum. A localized lesion in the sternum may show visual signs - the nipple is pulled inward, the dermis changes shade above the tumor, and the capillary pattern becomes clear. But these symptoms may not always characterize the disease. Therefore, you cannot focus on visualization.
But if suspicious signs appear, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a detailed diagnosis. Fibroadenoma is often confused with breast cancer, cyst and cystadenopapilloma. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you will need to undergo the following procedures:
- A physical examination of the patient is performed. Visually, the tumor is not yet visible, but when pressed, a dense foreign tumor is felt. The doctor collects a detailed verbal history of the course of the disease.
- Mammography shows the local lesion with detailed information.
- Ultrasound (US) can examine the breast and perinodular blood flow for signs of clinical changes. You can examine the diseased area and determine the boundaries of the node.
- To clarify the structural composition, a fine- or thick-needle puncture of the biological material is performed and a biopsy with cytology is performed.
- Histological examination of the biological sample is recommended. This will allow us to determine the exact composition and degree of malignancy.
- Blood must be donated for a general clinical analysis, to identify hormones and tumor markers.
- Doctors often perform an ultrasound of the liver and adrenal glands with the pancreas to identify the presence of dangerous changes.
- Magnetic resonance imaging provides a more detailed picture of the disease. An MRI of the brain (pituitary gland) is also performed, which shows structural abnormalities in development.
- Nipple discharge is examined using cytology.
- Elastometry and radiothermy provide additional information that helps exclude other pathologies.
When the examination results are ready, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and decide how to treat the patient.
Is it possible to prevent the formation of fibroadenoma and its degeneration into cancer?
Any female pathology can be prevented by observing the principles of careful hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and timely diagnosis. Regular visits to a gynecologist-mammologist should be the norm in the life of any woman, starting from adolescence.
In our clinic you will meet qualified specialists who are ready to carefully examine each patient and help her get rid of any pathologies. An accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment using modern diagnostic equipment will help you forget about breast fibroadenoma.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Prevention
Since the cause of fibroadenoma has not yet been studied, effective methods for preventing the disease have not been identified. But you can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Perform regular breast self-examinations;
- visit a gynecologist and mammologist if symptoms of the disease are detected;
- undergo a medical examination in accordance with age recommendations;
- lead an active healthy lifestyle;
- take oral contraceptives only as prescribed by a gynecologist;
- fight excess weight.
These methods will help not only to identify the disease in the early stages of its development, but also to stop its growth and development.
General signs
The following signs are distinguished:
- Weight fluctuations (rapid weight gain or loss, with normal nutrition).
- Enlargement of the mammary glands.
- Pulling sensations.
- Pain when pressing on the upper outer part of the breasts.
- Cycle disruption.
Soreness of the glands (during the period when menstruation is not expected) requires an urgent visit to a mammologist. At the initial stages, self-examination will not reveal nodules, so instrumental research methods are needed - ultrasound, mammography. Only hardware images show the layer of tissue and pathological disorders. The course and prognosis are determined based on the form of the disease.