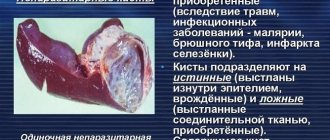
A thyroid cyst can be considered a type of colloid or non-toxic goiter. It looks like a bubble filled with jelly-like or dense contents. Pathology more often develops in women, especially in old age, although there are also gender-independent factors that provoke changes in the tissues of the gland. Small cysts do not have a negative effect on the human body; they only require observation and regular ultrasounds. Large tumors are subjected to sclerotherapy. In addition, they are prone to accelerated growth rates, relapses and the risk of compression of adjacent tissues, which becomes a reason for surgical intervention.
Classification
Depending on the contents, the following classification of cysts is distinguished:
- Colloidal, consisting of a mass of colloidal substance. The growth of such a cyst leads to the appearance of a diffuse goiter; treatment is not required; monitoring of development is necessary.
- Follicular (adenoma) – with newly formed follicular cells. There are no cavities in the colloidal contents, the structure is dense.
- A solid cystic formation includes epithelial cells and is usually filled with blood. This type of cyst does not resolve on its own and more often than others transforms into cancer.
- Cystadenoma occurs when blood circulation in the gland is impaired. Thyroid nodules transform into cysts. The tissue becomes necrotic and a cavity appears. Organ function decreases and hypothyroidism develops.
- Multiple thyroid cysts. A condition caused by iodine deficiency, considered the initial pathological hyperplasia of the tissue structure.
There are the following types of cystic formations:
- right-sided – large in size, complex in morphology, widespread;
- left lobe cyst – smaller and simpler in structure, less common;
- an isthmus cyst has a greater tendency to malignancy (degeneration into cancer), causing compression of the larynx earlier than others;
- small cysts;
- a cyst of both lobes of the thyroid gland, which is rare.
Causes
The main reason for the appearance of formations is a violation of the outflow of secretions or colloidal fluid from the follicles. This leads to the accumulation of fluid inside them and the formation of cavities. This situation can arise under the influence of many factors, since the thyroid gland is a very sensitive organ that responds to any disturbances in homeostasis. The prerequisite for the formation of cavities in the gland is excessive consumption of the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland - thyroxine (T3) and triiodothyronine (T4). This is facilitated by excessive psycho-emotional stress and excessive changes in body temperature. This leads to impaired elasticity and the formation of cysts.
In addition to these reasons, there are a number of additional factors that contribute to the formation of cavities in the thyroid gland.
- iodine deficiency;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathological processes of an inflammatory nature occurring in the thyroid gland;
- environmental pollution, life in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- intoxication of exo- and endogenous nature;
- traumatic neck injuries;
- hereditary and congenital pathologies.
Frequent pregnancies, non-compliance with the daily routine, bad habits, and violations of the diet and diet can also contribute to the occurrence of colloidal cavities.
Cysts and nodules that arise in the thyroid gland should not be confused. Nodules have a less favorable prognosis - according to statistics, 20% of patients diagnosed with a nodule develop malignant neoplasms. Cystic cavities can become cancerous in 7% of cases. Cavities larger than 4 cm in diameter are also highly likely to form a cancerous tumor.
Stages of development of nodal formations
The processes of development of thyroid nodules are distinguished by sequential stages, determined by the degree of their echogenicity during ultrasound examination:
- isoechoic homogeneous node. The density of the internal contents of the node corresponds to the surrounding tissues of the thyroid gland. At the stage of inechogenicity, there is an increase in blood circulation and an expansion of the network of vessels surrounding the node.
- isoechoic heterogeneous node:
- with minor fabric changes
- with pronounced tissue changes
- with hypoechoic inclusions (areas of cystic degeneration)
Isoechogenic heterogeneous nodes form as thyroid cells and follicles are depleted and die.
- hypo- or anechoic node. It is characterized by complete destruction of the node tissue, filling the cavity with fluid and destroyed cells, which leads to the formation of a thyroid cyst.
- stage of resorption of the contents of the thyroid cyst;
- stage of scarring of the thyroid cyst.
The process of staged transformation of thyroid nodules is lengthy; its speed depends on the size of the node, the functioning of the immune system, the state of the compensatory and adaptive mechanisms of the thyroid gland and the body as a whole. To speed up the scarring process, thyroid cysts are sometimes treated with sclerotization.
Surgery
Removal of the cyst will be required if the formation grows rapidly and already exceeds the size of one centimeter, which leads to pressure on the organs of the neck. In such situations, a hemistrumectomy is performed - removal of one lobe of the thyroid gland. The function of the gland when using such an operation is mainly preserved. If a cyst is detected in both lobes, a bilateral subtotal strumectomy is prescribed - complete excision of the gland.
If a malignant nature of the formation is detected, a total strumectomy will be required. During the operation, the entire gland is removed along with fatty tissue and lymph nodes. The operation is quite traumatic, but necessary to completely remove cancer cells. The most common consequence of strumectomy is functional impairment of the vocal cords. After surgery, the patient is required to take thyroid hormones. In addition, calcium supplements must be prescribed, since total resection also removes the parathyroid glands.
In all other cases, surgery is a method that allows the patient not to experience all further symptoms of the disease and avoid complications. If the disease is benign, partial resection of the thyroid tissue is performed; this does not disrupt the hormonal levels of the patient’s body.
Symptoms
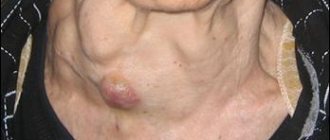
At the initial stage of development of the disease, there are no obvious signs of manifestation of the disease, nodular cyst of the thyroid gland. The main symptoms can be determined during a medical examination. A progressive condition can be suspected at the first visual enlargement of a neoplasm (nodule or cyst).
If you have suspicious symptoms, you should contact a specialist. A routine examination by an endocrinologist can confirm or refute the symptoms of the disease. On palpation, dense elastic nodular neoplasms stand out and are easily palpated. The reason for contacting a specialist is a noticeable increase in nodular seals in the thyroid gland. The size of the cyst can exceed 4 cm in diameter.
The main symptoms of thyroid cysts in women and men can be identified by the following signs:
- An enlarged thyroid gland is determined visually and palpated by palpation. Neglected conditions can be divided into several degrees of increase.
- There are problems with swallowing. A discomfort is felt when swallowing tablets and small pieces of food.
- The resulting thyroid cyst gives a feeling of squeezing in the throat. This symptom increases as the formation becomes more compact.
- When walking and intense movement, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing appears. The cyst begins to grow, narrows the lumen in the larynx, so full breathing becomes difficult.
- The voice becomes hoarse and hoarse. In some cases, complete loss of voice is possible.
- The pain syndrome can begin spontaneously and also disappear unexpectedly.
All of the above symptoms and signs are a reason to visit a doctor. Only a specialized specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Thyroid cyst in children
The formation of thyroid cysts in children is most often observed during puberty and intensive growth. The organ does not have time to adapt to the changes occurring in the hormonal background, as a result of which cysts and lumps form in its tissues.
In addition, the following factors may cause the formation of thyroid cysts in a child:
- Frequent colds;
- Weak immunity;
- Long-term treatment with any medications;
- Neck injuries;
- Postponed surgeries;
- Lack of iodine in the body;
- Bad ecology;
- Diseases of the mother suffered during pregnancy;
- Stress and increased physical activity.
If a thyroid cyst is detected, the child is registered with an endocrinologist and carefully observed, periodically undergoing a comprehensive examination. Young children and adolescents have a very high risk of degeneration of a benign process into a malignant tumor.
Parents of the child should be alert to the following symptoms that occur in the child:
- Refusal to eat, complaints of difficulty swallowing;
- Increased sweating;
- Lethargy, irritability, moodiness;
- Increase in body temperature to high levels (over 39 degrees);
- Cough and hoarseness;
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
If such symptoms appear, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.
Cyst in pregnant women
Since during pregnancy all the organs and systems of a woman work in an enhanced mode, the load on the thyroid gland accordingly increases.
A thyroid cyst in women in an interesting position develops as a result of a powerful hormonal surge, or an old neoplasm progresses under the influence of the same hormonal changes.
When the doctor palpates the front of the woman’s neck, noticeable lumps and nodules of the thyroid gland are detected. As a rule, cysts formed during pregnancy, after childbirth and completion of the lactation period, resolve on their own and do not require special treatment, but only observation by an endocrinologist.
During pregnancy
Often the first ultrasound of the gland is performed during pregnancy and cyst-like formations are detected. If there are no abnormalities in the function of the gland, then there is no threat of miscarriage. The threat exists only in a hypothyroid state. There is also no data on the danger of benign formations for the development of a child if the function of the gland is within normal limits. A pregnant woman can undergo dynamic ultrasound of the gland and even a fine-needle biopsy if necessary, but scintigraphy with iodine isotopes is contraindicated.
If a nodular pathology is detected, the pregnant woman must be sent for examination to endocrinological institutes or dispensaries. Benign formations, including nodular goiter , cyst , adenoma , are not an indication for termination of pregnancy and are not subject to surgical intervention during pregnancy. If a diagnosis of “follicular tumor” is received, surgical treatment is carried out after childbirth.
For cysts with normal gland function, iodine is prescribed (200 mcg/day) and ultrasound monitoring is done every three months. The main goal of conservative treatment is to prevent the growth of the formation or reduce its size. In forms that occur with hypofunction, hormone replacement therapy ( Eutirox , L-thyroxine ) is prescribed. The dose is selected under the control of TSH ( thyroid-stimulating hormone ).
Considering that during pregnancy the need for hormones increases, therefore TSH is monitored once every 3 months and the dose of the drug is adjusted accordingly. A pregnant woman's diet should be complete and contain a sufficient amount of protein (cottage cheese, meat, eggs) and iodine (seafood, fish, tomatoes, beets, seaweed, kiwi, persimmon), given that the need for it during pregnancy is 150-200 mg per day. day.
Are thyroid cysts dangerous?
A disease such as a thyroid cyst has a specific pathogenesis. If you run the case? the following risks will arise:
- hemorrhage process;
- inflammation;
- degeneration into a malignant disease.
When hemorrhage begins to flow inside the cyst, tolerable pain appears. The size of the “bump” increases. Medical intervention is not necessary when there is no secondary infection. This formation will resolve itself.
Rarely does such a dangerous phenomenon occur as the degeneration of a gland cyst. This is more typical of the so-called cyst nodes. So that the cyst starts to become inflamed? accompanying factors are required:
- Intoxication of an organ or the whole body.
- Severe pain.
- Increase in the size of lymph nodes in the neck.
- Quite high, dangerous temperature (40-41 degrees).
This symptomatology indicates the onset of the stage of pathogenesis. According to statistics, 90% of diagnosed patients with thyroid cysts are not at risk of developing cancer. Risks are signaled by the root causes of the appearance of cysts:
- gland hyperplasia,
- attack of thyroiditis,
- dystrophic changes in follicles,
- infectious processes.
An endocrinologist can answer concerns about whether a thyroid cyst is dangerous after some research. This conclusion is reached after obtaining data on the propensity for neoplasms of suppuration and inflammation. Certain manifestations indicate complications and pathogenesis:
- Hyperthermia, a significant increase in temperature.
- Growth of cervical lymph nodes.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Painful manifestations in the localized area of cyst formation.
Should the size of the cyst not be allowed to become large? then knots are formed. They carry a great risk of malignancy.
Diagnostics
Thyroid cyst is the field of activity of an endocrinologist. Determination of pathology and accurate diagnosis are always based on the results of a diagnostic study. The initial examination includes collecting complaints from the patient and palpating the thyroid gland area. The lymph nodes are also examined to determine their size and tenderness.
However, to obtain accurate information, research is used:
- To determine the type, volume and structure, ultrasound is prescribed.
- To find out which cells form the cyst, a fine-needle biopsy is used.
- To determine the possible malignancy of a tumor, pneumography is used.
- When a patient complains of problems with the throat, they also resort to laryngoscopy to examine the larynx and bronchoscopy to examine the trachea.
- Separate tests are carried out for the level of hormones in the blood, magnetic resonance imaging and scintigraphy.
For further work with thyroid cysts, a puncture is taken.
Monitoring small cysts
Small cysts after the introduction of a solution of sclerosants into them can be treated in the future using a conservative method - an endocrinologist in this situation may prescribe the use of iodine preparations and thyroid hormones. The patient must also undergo monitoring of the condition every month and once a trimester undergo an examination of the neck organs using an ultrasound machine. When such observations are made, a sharp increase in the level of hormones or antibodies in the blood will require immediate action. It will be necessary to quickly abandon further therapy and examination of the patient, the effect of which is to prevent the development of autoimmune thyroiditis. If, upon examination of the puncture, purulent contents of the thyroid gland or part thereof are revealed, then the use of antibiotics and detoxification therapy will be mandatory as part of the treatment. Also, based on the results of microbiological and bacteriological examination of the obtained biopsy, careful selection of drugs will be required.
How to treat a thyroid cyst?
An effective treatment for a benign thyroid cyst is emptying by puncture followed by the administration of sclerosing agents. This is a non-invasive procedure that can be repeated if a relapse occurs.
Provided that the detected cyst is not a malignant formation, conservative therapy is carried out. How to treat? Doctor's orders include the use of:
- drugs to regulate thyroid hormones,
- as well as anti-inflammatory, metabolic
- and improving blood circulation to reduce swelling and reduce the size of the cyst.
Antibacterial therapy is carried out when an infection occurs and requires accurate identification of the type of pathogen and determination of its sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs. Drug therapy is more effective in the early stages of the disease and can significantly reduce the frequency of surgical interventions. Only the attending physician determines how to treat a thyroid cyst in each individual patient.
When is surgical treatment indicated?
- With progressive growth of the cyst or with the addition of severe symptoms in the form of respiratory disorders and difficulty swallowing, the method of choice is surgical treatment of the thyroid cyst.
- If there is an increased risk of the cyst becoming a malignant tumor or if there are confirmed laboratory data, surgery is performed immediately, regardless of the stage of the disease and the size of the cyst. In this case, conservative therapy is not carried out, since the likelihood of deterioration of the patient’s condition and the development of severe cancer increases.
Should I remove the cyst?
And although in most cases thyroid cysts are benign, their “behavior” is unpredictable:
- In some cases, they do not give negative dynamics for years
- In others, they are growing rapidly
- Thirdly, they go away on their own
- Typically, the reason to consult a doctor is the growth of a cyst to a size (over 3 cm) that is noticeable to the eye and causes deformation of the neck, hoarseness or loss of voice, a lump in the throat, difficulty breathing and swallowing function, and neck pain.
If the cyst is less than 1 cm in diameter, it is only observed; if it enlarges, a puncture is performed, followed by a cytological examination. If, after the cyst is emptied, contents accumulate again in it, the issue of its removal is decided. Under no circumstances should any warming compresses or lotions be applied to cysts, as this can cause inflammation.
Surgical treatment for malignant disease usually includes bilateral resection of the thyroid gland (removal of most of both lobes). After this operation, careful monitoring of the level of thyroid hormones is required and, if necessary, its correction is prescribed with the help of hormonal medications (thyroid hormones).
A frequent complication of such an operation is dysfunction of the vocal cords with partial loss of voice. If a patient is diagnosed with a cyst of the left lobe of the thyroid gland, then surgery is performed only on the affected side (the same is the case with damage to the right lobe). Removal of a thyroid cyst is performed through a small incision in the neck in the area of the thyroid gland.
The removed lesion is subjected to histological examination to confirm a benign process. This allows you to carefully plan further treatment.
The postoperative period is easy. Return to normal life occurs within 1-2 days, and no restrictions on physical activity are required.
Features of treatment in pregnant women include the exclusion of radiological research methods. Biopsy and surgical treatment during pregnancy are not contraindicated. When planning treatment, the relative risks and benefits must be considered. If there are clear indications, the operation is recommended to be performed in the second trimester of pregnancy. In the absence of pronounced symptoms of compression of neighboring organs or dysfunction of the thyroid gland, treatment is carried out in the postpartum period.
Operation
Removal of a thyroid cyst by surgery is used when it is large in size, for example, when it makes breathing and swallowing difficult, or for a cosmetic effect. Note that there are cases when the removal of a thyroid cyst is done for health reasons, an example is the malignant course of this disease.
For surgical treatment, certain indications must be identified:
- Large cyst size.
- Compression syndrome on nearby organs and blood vessels in the neck.
- Frequent occurrence of rapid relapses, which happens after a puncture procedure.
- Malignization.
If the indications are present, it is necessary to remove a lobe of the organ (hemistrumectomy).
Only an endocrinologist can determine whether removal of a thyroid cyst is necessary. Today, progressive doctors have begun to abandon the previously popular total operations for cysts, adenomas or thyroid nodules.
The prognosis for further growth of the tumor directly depends on the results of the histological analysis. Usually, the use of medications in such cases is not required. It is quite enough to follow a limited diet that includes the following products:
- Seafood;
- Dishes containing iodine.
Folk remedies
The effectiveness of treating the disease with traditional methods is obvious. In combination with prescribed drug therapy, home treatment for thyroid cysts gives good results. However, you should not self-medicate. Consultation with an endocrinologist regarding the combination of these two treatment methods is necessary.
Here are some recommended treatments:
- Green nut shell. Pour boiling water over three tablespoons of shells and let steep for one hour. This remedy will be a good compress before bed;
- Walnut. Pour 200 ml of alcohol into walnut partitions (50 g). Leave for a week in a dark place. After this, strain and take one teaspoon daily three times a day. The recommended course of treatment is at least six months. This folk remedy can be used as a prophylaxis for thyroid diseases;
- Beetroot and honey. Grate the beets on a fine grater and mix with natural honey. Take 50 g of each ingredient. After that, put the whole mass on a cabbage leaf and apply it to the throat. This therapeutic compress can be left overnight. The course of treatment is unlimited;
- Bloodroot. Pour the crushed root of the plant (100 g) into one liter of vodka. Leave in a thermos for a month. Strain the resulting tincture and take 50 drops half an hour before eating. The course of treatment lasts one month;
- Walnut. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over several walnut leaves. Leave for 30 minutes. Strain the resulting product and take ½ glass three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is two weeks;
- Celandine. Pour crushed celandine into half a liter of vodka. Leave in a dark, cool place for 10 days. After this, strain the tincture and take 50 ml daily before meals once a day. The course of treatment is 21 days.
A balanced diet is of great importance; seafood and iodine-containing foods should be the main ones. All plant-based foods will help the body's immune defense. Natural juices should also be present on the dinner table.
Diet
Diet for thyroid disease
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1600-1700 rubles per week
Nutrition for thyroid pathology should be complete. If you live in an area with a natural iodine deficiency, then your diet must include seafood (mussels, squid, seaweed, scallops). It is advisable to use iodized salt. On the advice of a doctor, you can take iodine preparations ( Iodomarin ) orally. For any pathology of the gland, you need to pay attention to the content of vitamins and microelements in the diet. Useful:
- Selenium - bran, beans, eggs, whole grains, chickpeas.
- Zinc, which is rich in seafood, pumpkin seeds, peas, beans, peanut butter, sesame seeds.
- Magnesium is found in bran, nuts (cashews, almonds), soybeans, buckwheat, oatmeal, brown rice, and spinach.
- Vitamin D , which can be obtained by introducing cottage cheese, cheeses, vegetable oil, fish oil, cod and other fish liver, and seafood into the diet.
- Antioxidants, which are rich in vegetable oils, nuts, vegetables, fruits.
- Sea fish of fatty varieties contains vitamins A and D , omega-3 acids , B vitamins , and essential amino acids . Fish, seafood, olive and flaxseed oil should prevail in the diet of patients. In addition, sea fish are a source of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis for thyroid nodules is determined by their histological form. With a benign structure of thyroid nodules and cysts, a complete cure is likely. Thyroid cysts can recur again. Thyroid tumors of moderate malignancy in the absence of metastatic screenings are cured in 70-80% of patients. The worst prognosis is for malignant neoplasms that invade neighboring organs and give distant metastases.
Preventing the formation of thyroid nodules and cysts involves daily iodine consumption within the age-related physiological norm, a sufficient amount of vitamins, avoidance of insolation, radiation, and physiotherapy on the neck area. After treatment of a thyroid cyst, it is necessary to conduct control ultrasounds once a year. Patients with small nodules and cysts of the thyroid gland should be registered and monitored by an endocrinologist.
Cyst in the mammary gland Hypothyroidism Thyrotoxicosis of the thyroid gland: what is it and how to treat it? Hyperthyroidism Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) Bartholinitis
Iodine-containing products table
| Products | Iodine content (mcg of iodine per 100g of product) |
| Seafood after heat and other processing | 5-400 |
| Freshwater fish (raw) | 245 |
| Freshwater fish (cooked) | 75 |
| Fresh herring | 65 |
| Pickled herring | 6 |
| Fresh shrimp | 190 |
| Cooked shrimp | 11 |
| Fresh mackerel | 100 |
| Raw oysters | 100 |
| Canned oysters | 5 |
| Trout | 3,5 |
| Cod | 130 |
| Cod liver | 370 |
| Saida | 200 |
| Flounder | 190 |
| Salmon | 200 |
| Sea bass | 145 |
| Smoked fish fillet | 43 |
| Haddock | 245 |
| Seaweed (seaweed) | 500-3000 |
| Atlantic sardines in oil (canned) | 27 |
| Frozen fish fillet | 27 |
| Meat | 3 |
| Pork | 16,7 |
| Beef | 11,5 |
| Ham sausage | 55 |
| Chicken eggs | 10 |
| Champignon | 18 |
| Dairy | 4-11 |
| Whole milk | 19 |
| Processed cheeses (with additives) | 18 |
| Hard cheeses | 11 |
| Butter | 9 |
| Broccoli | 15 |
| Vegetables | 1-10 |
| Greenery | 6-15 |
| Spinach | 12 |
| Beans | 12,5 |
Click Next to see more.