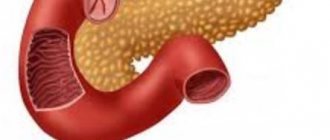
Gastritis is an inflammatory or inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the stomach, which is characterized by damage to its mucous membrane. If inflammation spreads to the duodenum, they speak of gastroduodenitis.
The disease can be acute - occurring for the first time, or chronic - with periodic relapses.
Unfortunately, the symptoms of gastritis are often ignored by most patients. According to statistics, about 50% of the Russian population suffers from chronic gastritis, but 10-15% seek medical help. This leads to sad consequences - untreated acute gastritis becomes chronic, and chronic gastritis turns into a stomach ulcer and even cancer. But if you consult a gastroenterologist in time and undergo a course of treatment, you can get rid of the disease once and for all.
What does a gastroenterologist treat?
A gastroenterologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. If you experience abdominal pain, irregular bowel movements, frequent constipation or diarrhea, belching or regular heartburn, you should contact a gastroenterologist who treats:
- colitis;
- gastritis;
- duodenitis;
How to treat intestinal dysbiosis? dysbacteriosis;- peptic ulcer;
- pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal diseases.
In the initial stages, many digestive disorders have similar symptoms. To make an accurate diagnosis, examinations are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- endoscopic examinations: gastroscopy, colonoscopy;
- X-ray examination methods: for example, irrigoscopy;
- urine, stool and blood tests.
Studies show the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract, identify the concentration of digestive enzymes, which allows the gastroenterologist to make a diagnosis and select a treatment regimen.
Is gastritis contagious or not?
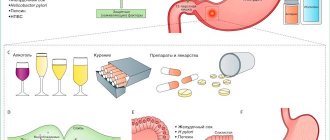
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs for various reasons. For example, it can be caused by uncontrolled use of medications, abuse of spicy and smoked foods, and constant stress.
Scientists also consider the bacterium Helicobacter pylori to be an important factor in the development of gastritis. Microorganisms attach to the walls of the stomach and produce substances that reduce the acidity of the environment. As a result of their vital activity, the mucous membrane is gradually destroyed, ulcerations of the walls occur and gastritis develops.
The Helicobacter bacterium can be infected through food, water, or kissing a carrier of the pathogen. But in 90% of cases, the presence of this microorganism in the stomach does not lead to the development of chronic gastritis. In order for the disease to develop, other factors are also necessary: for example, reduced immunity, systematic poor nutrition. Therefore, gastritis is not considered a contagious disease.
Why do gastritis worsen in the off-season?
Spring and autumn are transitional periods between summer and winter. In the off-season, the daily routine changes (the days become shorter, the nights become longer), the nature of the diet (the diet becomes less fresh fruits and vegetables, preference is given to meat, cereals, and pickles). Colds begin to intensify, depleting the immune system, and as a result, existing chronic diseases worsen. The emotional depression characteristic of autumn also affects the state of health.
Whether we like it or not, shortening daylight hours has a depressing effect on our mood, but practice shows that the emotional sphere is very closely related to the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, a person living in a state of chronic stress has a much higher chance of developing gastritis than those who treat any problem philosophically. And all because during stress, a large amount of adrenaline is released into the blood - a hormone that causes vasoconstriction.
As a result, the blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract deteriorates, the nutrition of the cells of the gastric mucosa is disrupted, some of them atrophy and die, forming zones of inflammation, that is, gastritis. If this condition is not treated, over time, defects, erosions and ulcerations appear on the mucous membrane.
How to recognize gastritis with high or low acidity?
Stomach diseases are often accompanied by impaired secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Normally, the environment in the human stomach is highly acidic, but with gastritis it can change: the acidity either increases or decreases.
With increased acidity, the following symptoms are observed:
- severe heartburn;
- belching with a bitter taste;
- burning in the esophagus and throat;
- sudden attacks of pain;
- pain radiating to the right hypochondrium.
The main danger of high acidity is the risk of developing stomach ulcers and perforation of its walls.
With reduced acidity, the clinical picture changes. The patient complains of:
- belching with the smell of sulfur (rotten eggs);
- frequent stool disorders (constipation);
- regular pain in the intestines, accompanied by bloating;
- dry skin and brittle nails due to low absorption of nutrients.
Gastritis with low acidity provokes stomach cancer. Special studies can determine the acidity and type of disease. For example, during an endoscopic examination, a sample of gastric juice is taken using a probe, and then its acidity is measured in the laboratory.
Diagnosis of the disease
A doctor can identify the disease by a number of characteristic symptoms. To find out the causes of the pathology, a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination is necessary; the nature and composition of further treatment depends on this.
Main types of studies for gastritis:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a study of the condition of the inner wall of the stomach using a device with a probe equipped with a video camera. The analysis helps to identify areas of affected epithelium and the presence of ulcers and erosions on the mucosa.
- X-ray with contrast to identify nodes and erosions.
- Intragastric pH-metry - determination of stomach acidity to prescribe specific treatment.
- The Helicobacter breath test is a modern and highly informative method for determining the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body by analyzing the carbon concentration in exhaled air.
- Study of gastric juice to assess the secretory function of the stomach.
Mandatory laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests, stool analysis.
Treatment of gastritis
Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases involves compliance with
Do you need a diet for gastritis? diets and taking specially selected medications. The diet excludes from the diet coarse fibrous foods, spicy, smoked, salty foods, which additionally irritate the walls of the stomach. The tablets normalize acidity, relieve pain, eliminate bacteria and accelerate tissue healing. Both diet and medications are selected depending on whether the patient’s acidity is low or high.
Folk remedies for gastritis
The experience of the older generation can be used as additional measures to combat the disease at home. Following popular advice should not interfere with taking the pills prescribed by your doctor. Before using any recipe, check its ingredients for allergenicity.
Folk remedies for the treatment of gastritis of the stomach involve the use of:
- It is necessary to pour 100 grams of wheat grains with water. After the sprouts appear, rinse and grind in a meat grinder. The resulting mass is diluted with several tablespoons of sunflower oil. The product should be consumed every day, on an empty stomach.
- Milk. This product helps to quickly reduce stomach acidity at home. In addition, drinking a glass of warm milk quickly eliminates the symptoms of heartburn.
- Juice from raw potatoes. Has powerful healing properties. Before meals you need to drink 1 tablespoon of freshly squeezed juice.
- Flax oil. It is better to use it in capsules, so you can be sure of its freshness. If stored improperly, bottled oil quickly becomes rancid and unfit for consumption. Capsules are taken in the morning before meals and in the evening after the last meal, washed down with warm water.
- A decoction of buckthorn and yarrow. A tablespoon of dry herbal mixture is poured into a liter of boiling water and left for about 2 hours. The finished decoction is filtered and taken on an empty stomach once a day. In addition, it is recommended to drink the product for gastralgia and constipation. Buckthorn is strictly contraindicated for pregnant women and children under 15 years of age.
- Aloe juice. Today, in any health store you can buy ready-made 100% aloe juice. If you have this plant at home, you can prepare the medicine yourself. The only rule is that aloe must grow for at least 3 years. You need to drink 1 tablespoon of juice in the morning on an empty stomach.
If your health condition worsens, you must immediately stop self-medication and urgently seek advice from a specialist.
Treatment of erosive gastritis of the stomach
After the examination, the doctor prescribes an effective radiation regimen. But there is a standard scheme by which you can quickly cope with the disease of erosive gastritis.
- First, if Helicobacter is present, it is necessary to destroy the pathogenic microflora. For this purpose antibiotics are prescribed.
- In the case of gastrointestinal reflux, when food that has had time to oxidize is thrown into the esophagus, medications are prescribed that can restore motility in the stomach.
- It becomes possible to eliminate high acidity with the use of effective non-absorbable antacid medications.
- Medicines that help sufficiently oxygenate tissues that have been damaged as a result of the disease help cure erosion quickly.
- Drugs that contain enzymes reduce the stomach's ability to properly digest food.
- To protect the walls of the stomach, medications are prescribed that can significantly increase acidity. They restore the mucous membrane, which is very important for gastritis.
- Preparations that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid create an acceptable microclimate in the stomach that is safe for the mucous membrane.
Even after the disease is defeated, it is necessary to adhere to the correct regime, eat healthy foods, lead an active lifestyle and not abuse alcohol.
Ulcer or gastritis - how to determine?
A gastric ulcer may resemble gastritis in its course: the patient complains of belching, heartburn, and sharp pain in the upper abdomen. But, if gastritis causes inflammation of only the mucous membrane, then with ulcerative gastritis both the mucous and the submucosal layer are destroyed. The source of inflammation is localized, the tissues are gradually destroyed under the action of digestive enzymes. According to statistics, about 4% of the world's population suffers from stomach ulcers.
How to distinguish an ulcer from gastritis? Ulcers are characterized by “hunger pains” that subside immediately after eating. With gastritis, eating can increase pain, nausea, and a feeling of heaviness will appear. But it is impossible to independently distinguish gastritis from an ulcer. To do this, you need to undergo instrumental and laboratory tests, which will be directed by a gastroenterologist.
Signs of gastritis of the stomach: first symptoms in women
https://youtu.be/5O1y61Nyo94
Gastritis is a modern disease; recently, almost every third person lives with gastritis of the stomach. Gastritis has no age; it is diagnosed in middle-aged people, pensioners, youth and children.
The first symptoms of gastritis are the same in both men and women. Gastritis occurs from poor nutrition, or rather from the fact that the stomach cannot cope with the food that we eat every day.
All of the following symptoms should help you pay attention to your health; if such symptoms do not go away within a few days, then you immediately need the help of a qualified gastroenterologist.
What are the first symptoms of gastritis:
- discomfort and unpleasant sensations, similar to squeezing, in the upper abdominal area;
- severe pain that occurs immediately after eating or during hunger;
- Frequent heartburn can often indicate that you have gastritis;
- carefully examine your tongue before and after brushing your teeth and the surface of the tongue itself; if there is a white coating left on it, then you already have gastritis;
- regular nausea or vomiting may indicate gastritis;
- increased body temperature, which does not rise above 37.2 degrees;
- belching with a putrid unpleasant odor, as well as not fresh breath even after brushing your teeth;
- after eating, you may notice that you feel “hard” for a very long time; this symptom may indicate chronic gastritis;
- a decrease in appetite should at least alert you;
- Constipation very often appears due to gastritis, because the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted and metabolism slows down.
Acute and chronic gastric ulcer
Doctors distinguish two forms of gastric ulcers: acute and chronic. An acute ulcer causes damage to the mucous membrane and submucosal layer, and can reach muscle fibers. The disease develops due to injuries, recent surgical interventions, poisoning, and uncontrolled use of certain medications.
A chronic ulcer develops in the absence of treatment for gastritis and is an advanced form of the disease. Often, ulceration is affected by Helicobacter bacteria, and a purulent-necrotic area forms at the bottom of the ulcer. This disease can lead to dangerous complications: gastric bleeding and perforation of the stomach walls.
How to treat a stomach ulcer?
Before treatment is prescribed, the patient undergoes a series of examinations. If the tests revealed the presence of Helicobacter pylori, the gastroenterologist selects antibacterial drugs. Other medicines:
- regulate stomach acidity for speedy tissue healing;
- relieve abdominal pain;
- restore and maintain healthy microflora in the gastrointestinal tract.
During therapy, a diet is prescribed that eliminates the risk of additional irritation of the gastric walls.
What's worse: gastritis or gastroduodenitis?
Another disease with symptoms similar to gastritis is gastroduodenitis. But if with gastritis only the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, then with gastroduodenitis the irritation also affects the duodenum.
Pathology occurs due to chronic stress, abuse of spicy and salty foods, against the background of gastritis, pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal diseases. It cannot be said that gastritis or gastroduodenitis is better or worse - each disease is dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
Prevention
To protect yourself from gastritis, it is important to build the right diet for yourself. Diet and the quality of food eaten play an important role in preventing the disease. Reduce the amount of alcohol and tobacco consumed.
Stress is one of the causes of gastritis - eat slowly, in a good environment and with positive thoughts. Do not use harmful chemicals.
Video on the topic: Gastritis: causes, symptoms and treatment
How to treat duodenitis?
Duodenitis requires complex therapy. Depending on the general condition of the patient, treatment of duodenitis may include taking the following medications:
- antacid medications (if the acidity in the stomach is increased);
- medications that relieve inflammation and accelerate the healing of the mucous membrane;
- painkillers that relieve spasms.
Vitamin complexes are often prescribed. Recovery depends on following the rules of a healthy lifestyle: the patient needs to give up cigarettes and alcohol, balance nutrition and daily routine.
What is pancreatitis and its treatment
An attack of acute gastritis is almost impossible to independently distinguish from another disease - pancreatitis. Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, in which enzymes do not enter the gastrointestinal tract, but are activated in the gland itself, causing its gradual destruction.
Symptoms of pancreatitis are:
- sharp paroxysmal pain in the abdomen. In the chronic course of the pathology, the pain is constant, aching, with short periods of relief;
Nausea and vomiting Nausea and vomiting;- bowel disorder.
Gastroenterologists divide pancreatitis into acute and chronic. Treatment of pancreatitis depends on its form and the degree of damage to the pancreas.
Forecast
To avoid acute gastritis, which can lead to chronic gastritis, it is important to follow proper nutrition and its regimen, as well as eliminate harmful factors from your life.
If the first stage of the disease appears, as indicated by symptoms, it is important to seek help in time and begin to follow preventive methods so as not to aggravate the disease and, with prompt action, treatment will not be very long.
In the second stage it will be more difficult to cure, but it is possible. The main thing is to prevent the third stage. Atrophic gastritis can be fatal.
What causes pancreatitis?
In 70% of cases, pancreatitis develops with regular alcohol consumption, and it can also occur as a complication of gallstone disease. If you have been diagnosed with pancreatitis, the reasons may be:
- mechanical abdominal injuries;
- poisoning;
- infection of the gastrointestinal tract by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- parasitic infestations (for example, opisthorchiasis);
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the pancreas.
Only a gastroenterologist after examination can identify the cause of pancreatitis.
How to determine: pancreatitis or gastritis?
With gastritis and pancreatitis, the main symptom is one – severe abdominal pain. If the pancreas is damaged, it can be localized in the right hypochondrium or extend to the back. The pain does not decrease after taking antacids; it intensifies when eating fatty foods or alcohol. With chronic pancreatitis, abdominal pain occurs regularly, bowel movements are disrupted, and the patient can suddenly lose weight. But it is impossible to recognize pancreatitis on your own; if you have abdominal pain, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
Nothing dyspeptic is alien to us
Every person has experienced the main symptoms of gastritis at least once in their life. Even someone who has never visited a gastroenterologist is unlikely to be able to answer all the questions below in the negative:
- Have you ever experienced discomfort in the epigastric region?
- Do you know the feeling of a full stomach that occurs for no reason?
- Have you experienced bloating?
- Have you ever felt nauseous after eating?
Anyone who answers yes to at least one question may not be a potential patient of a gastroenterologist. But the presence of the sensations described above clearly indicates that you should be more careful about your diet and lifestyle in general.
How to treat pancreatitis?
Therapy for pancreatitis depends on the form of the disease: acute or chronic. Treatment of acute pancreatitis involves maximum unloading of the gland: the patient is prescribed fasting for the first day, then a gentle diet with a minimum content of fats and carbohydrates is developed. Symptomatic therapy may be carried out to eliminate pain and maintain gastrointestinal functions.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis consists of several steps:
- taking painkillers;
- ensuring functional rest of the gland through replacement therapy (prescribed drugs with enzymes) and diet.
It is important for the patient to completely abstain from alcohol and lead a healthy lifestyle. Chronic pancreatitis can cause peritonitis, abscess, jaundice and other diseases).
When to do an abdominal ultrasound?
What diseases can ultrasound diagnose? Pancreatitis, urolithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, benign and malignant tumors. An ultrasound examination is prescribed by a gastroenterologist if the patient complains of:
- sudden weight loss;
- abdominal pain;
- stool disorder;
- nausea after eating food;
- flatulence;
- heartburn.
You need to prepare for an ultrasound. Three days before the procedure, exclude from the diet foods that cause increased gas formation (whole-ground black bread, legumes, grains). You should come for an ultrasound scan on an empty stomach, and your last meal should be no later than 8 hours before the examination. Patients with diabetes are allowed to drink tea and eat one or two crackers for breakfast. Other patients need to undergo an ultrasound scan on an empty stomach.
Symptoms of gastritis in women
Manifestations of gastritis in women can be very diverse. Symptoms can be expressed or hidden. Very often, the first sign is pain in the solar plexus. They intensify after taking food or medications that have an aggressive effect on the mucous membrane. But there are cases of pain present during periods between meals. In this regard, during illness it is prohibited to consume spicy foods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, and much more.
Accompanying symptoms are heartburn and vomiting. The stomach is often bloated and gases are released. If these signs coincide in time with abdominal pain, there should be no doubt about the presence of inflammation. There are no special changes in the condition of a patient with chronic gastritis, except that the unpleasant manifestations of the disease bring discomfort. But its severe form is characterized by anemia, drowsiness, and cold sweating.
There is no direct relationship between symptoms and the severity of the inflammatory process on the epigastric mucosa. This suggests that even with severe inflammation there may be no symptoms at all. There are other cases when minor lesions of the mucous membrane are accompanied by severe pain, vomiting and nausea. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of illness, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Signs of gastritis in women with high acidity are as follows:
Manifestations of gastritis in women can be very diverse; symptoms can be pronounced or hidden.
- prolonged pain in the solar plexus area, which may subside after eating;
- very frequent diarrhea;
- the appearance of heartburn after eating sour food;
- frequent belching.
A woman with reduced stomach acidity may have the following symptoms due to inflammation:
- discomfort in the oral cavity;
- after eating food - heaviness;
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- rumbling in the abdominal cavity;
- morning sickness;
- the regularity of bowel movements is disrupted.
The chronic form of the disease, or rather its relapses, causes much greater damage to a woman’s health. With this form of gastritis, pain in the solar plexus area constantly torments a person. This occurs regardless of food intake, its volume and frequency. A burning sensation in the chest, pain from heartburn, a metallic taste in the mouth. Nausea, which very often turns into vomiting of undigested food. It is sour and comes with bile.
Saliva production increases, a feeling of thirst appears, and the body weakens. A pronounced dispersion with all its manifestations is observed. Constant headaches and dizziness in parallel with an increase in heart rate.
Erosive forms of the disease may be accompanied by vomiting of blood or dark masses. Black stool indicates the presence of gastric bleeding. But there are cases when this can only be determined using laboratory diagnostics. Massive internal bleeding is reflected in pale skin and the appearance of tinnitus.
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach
Another type of study that a gastroenterologist can prescribe is gastroscopy or FGDS. This is an endoscopic examination that involves inserting a thin tube (endoscope) into the stomach through the esophagus.
You need to prepare for this procedure:
- the day before the examination, do not eat after 22.00;
- in the morning do not drink or eat;
- Avoid drinking alcohol or smoking the night before the procedure.
If FGDS is scheduled for the evening, the last meal should be 5-6 hours before visiting the doctor. In this case, gastroscopy without pain is guaranteed.
What to do to prevent illness
In fact, dealing with Helicobacter pylori, stopping frequently taking painkillers, not drinking too much alcohol and not taking too long breaks between meals is the best prevention of gastritis. And in order to prevent functional dyspepsia (after all, it is this that most often causes stomach discomfort), Alexey Golovenko advises not to forget about training: regular physical activity reduces unpleasant symptoms. It is also useful to learn how to cope with stress more easily - meditation can help with this.
Read more here:
https://ru.tsn.ua/lady/zdorovye/aktualnaya-tema/gastrit-kak-izbezhat-sezonnogo-obostreniya.html
https://ru.tsn.ua/lady/zdorovye/aktualnaya-tema/gastrit-kak-izbezhat-sezonnogo-obostreniya.html
https://www.wonderzine.com/wonderzine/health/wellness/232787-gastritis
https://www.segodnya.ua/lifestyle/food_wellness/kak-ponyat-chto-u-vas-yazva-ili-gastrit-771424.html
Who is prescribed irrigoscopy?
A gastroenterologist can refer you for irrigoscopy - an x-ray examination of the large intestine, which shows the condition of the intestine, the diameter of the lumen, and the elasticity of the walls. Irrigoscopy is performed for the following complaints:
- bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation or diarrhea);
- abdominal pain;
- the presence of mucus, blood, and undigested pieces of food in the stool;
- intestinal bleeding.
To obtain accurate results, the patient needs to prepare for the procedure: cleanse the intestines using laxatives or an enema. The gastroenterologist will tell you about additional preparation for irrigoscopy and the diet that must be followed before the study.
Abdominal pain, constipation or flatulence may indicate other gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, if you experience unpleasant symptoms in the stomach or intestines, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and develop a treatment that will normalize the functioning of the stomach and intestines and restore health and well-being.
Medicines for atrophic gastritis
To normalize the functioning of the stomach, drugs are prescribed that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid (prozerin, limontar) and agents with replacement properties (pepsin, trypsin). They promote complete digestion of food and protect the mucous membrane from pathogenic microflora.
Prokinetics are prescribed to improve gastrointestinal motility. This group of drugs includes domperidone, metoclopramide, itopride hydrochloride. They prevent stagnation of food, relieve spasms, and protect the stomach from reflux of intestinal contents.
A necessary condition for the restoration of damaged, atrophic mucosa is the administration of cytoprotectors (De-Nol®). The drug increases the synthesis of prostaglandins and gastric mucus, activates regeneration processes[3].