When a baby is sick, you need to urgently go to the clinic, especially if herpes sore throat is detected in children, because it is children who tolerate it very hard. The main thing here is to correctly diagnose the disease, because herpangina can be confused with both stomatitis and purulent tonsillitis. You also need to know that treatment of herpes sore throat in children can differ significantly from treatment in adults. Therefore, do not self-medicate and urgently show your baby to a specialist.
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat
The first cold symptoms appear within 1-2 weeks after infection with the Coxsackie virus. The pathogenic virus enters the body through the fecal-oral or contact route. The disease state begins with a flu-like illness:
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling unwell;
- fever;
- body aches;
- irritability.
Over time, herpetic sore throat acquires more defining symptoms - pain in the pharynx and nasopharynx, acute rhinitis, anterior cervical lymphadenopathy on both sides, profuse salivation.
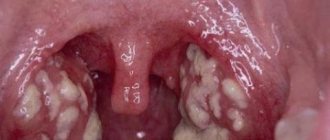
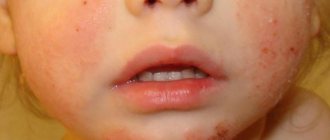
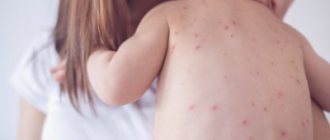
The mucous membranes of the inflamed throat become covered with blisters with a hyperemic halo, inside of which serous contents can be found. Such herpetic rashes are localized on the tonsils, back of the throat, uvula, and soft palate. The rash dries out over time and becomes crusty.
If the disease is aggravated by a bacterial infection, the herpetic blisters suppurate. Signs of intoxication also appear - vomiting, diarrhea, nausea.
Incubation period
From the moment the virus enters the body until the first symptoms of the disease develop, some time passes when the presence of the disease cannot be judged by external signs. In medicine, this is referred to as the incubation period. For different diseases, it amounts to different time periods, which can vary from several hours to several years and even decades.
In the case of herpetic sore throat, caused in most cases by the Korsaki virus, it ranges from 6 to 20 days. This depends on the concentration of the virus in the blood, the state of immunity, the patient and other individual characteristics.
Important! A child becomes a transmitter of infection long before the first symptoms appear - 3-4 days after infection.
Diagnosis of herpetic sore throat
The doctor can make a diagnosis only when characteristic rashes are already visible. Before this, the disease is easily confused with the flu. Several factors play a role in the diagnosis of herpetic sore throat:
- age;
- seasonality (summer-autumn);
- type of inflammation in the throat;
- localization of bubbles.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes serological or virological examination methods. For serological testing, special sera labeled with fluorescein are used. Material for analysis should be taken during the first few days of illness, and repeated after 1-2 weeks. For virological examination, swabs and swabs are taken from the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
It can be difficult for an inexperienced doctor to recognize herpetic sore throat and distinguish it from diphtheria, scarlet fever, pneumonia or meningitis. In children, the examination should begin with a visual examination of the pharynx and nasopharynx, a general blood test should be prescribed, and a swab from the nasopharynx should be taken.
Photo
With the herpetic form, there are characteristic rashes in the throat, but the disease must be differentiated from many other forms of throat damage.
Content may be difficult to view
Herpetic sore throat in children and its features
Herpetic sore throat in children has its own characteristics. Thus, children under 3 years of age are more susceptible to various viruses and infections than infants, who receive a full range of vitamins and minerals from breast milk. After the baby is weaned, the immune system begins to weaken slightly. In kindergartens, outbreaks of this disease sometimes occur, since the main route of transmission of the virus is through contact.
By the age of three, the baby has formed its own immune system, which protects it from various diseases. Up to 10 years of age, herpetic sore throat is rare in children.
The risk group includes schoolchildren, allergy sufferers, and malnutrition sufferers. The provoking factors are frequent colds, hypothermia, chronic stomatitis, tonsillitis, and reduced immunity.
How is herpes sore throat transmitted?
Acute herpetic stomatitis in children often occurs while attending preschool institutions. In infants, the disease occurs in isolated cases, since their immunity is reliably protected by antibodies from mother's milk. During the entire feeding period, passive immunity protects the child from contracting a viral infection.
There is a congenital form of the pathology. The virus is small and freely penetrates the placental barrier. If a mother has herpes, the risk of having a baby with the infection is high.
The disease can be contracted through household contact and airborne droplets. The carrier is an infected person.
Provoking factors
The development of the disease begins after the virus enters the body. This is facilitated by weakened immunity and frequent respiratory diseases. The pathological condition is dangerous because it quickly takes on an epidemiological course in small preschool and school groups.
The virus penetrates the cells of the oral mucosa. There they actively begin to share. The cells swell and gradually die. As a result, bubbles with pathological fluid are formed. If they are damaged, liquid leaks out. During this process, a small part of the viruses die. The rest are destroyed by the body's own antiviral system.
Herpetic sore throat in adults and its features
The peculiarity of herpangina in adults is that the disease is diagnosed much less frequently than in childhood, and its course is easier. An adult can catch the virus from a child who became infected in kindergarten, summer camp, or school.
In addition, after suffering the disease once, a stable immunity is formed, which prevents the pathogen from becoming active again. Re-infection can be caused by a severe cold or weakened immune system.
Complications and consequences
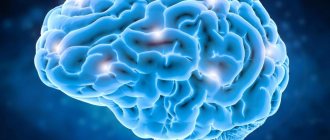
If herpetic childhood tonsillitis is not treated or therapy is abandoned when the disease has not yet been completely defeated, serious complications may occur. These pathologies significantly affect the child’s health. The Coxsackie virus, which most often causes the formation of herpetic sore throat, can infect not only the cells of the throat mucosa, but also the nerve fibers.
If treatment is not started in time, this can lead to many serious consequences, namely:
- nephritis,
- encephalitis,
- meningitis,
- rheumatism,
- liver damage,
- myocarditis,
- heart defects,
- conjunctivitis,
- sepsis, etc.
All these diseases are quite serious. They undermine the child’s health irreversibly for the rest of his life. Some of them complicate not only physical, but also mental development. This means that the disease must be dealt with in the early stages and the prescribed treatment must be carried out fully. In addition, preventive measures should not be ignored if your child is healthy.
Treatment of herpetic sore throat
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for herpetic sore throat. It consists of symptomatic therapy. Antibiotics can be prescribed only in case of concomitant bacterial infection - Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Penicillin. Rioflora, Imudon, Immunal and other analogues successfully cope with strengthening the immune system and fighting viruses.
For the purpose of successful and effective treatment, the patient needs to follow some rules:
- The patient must be isolated. It is necessary to provide him with separate hygiene products and dishes to prevent infection of other family members.
- Bed rest - it will take some time to regain strength.
- Special diet - it is necessary to exclude foods that can irritate the already inflamed mucous membranes of the throat. The patient will have to abstain from confectionery, spices, hot and cold foods, and hard fruits. The diet should consist of cottage cheese, liquid cereals, and soups.
- Lots of liquids - drink plenty and warm. It is recommended to drink warm tea, fruit juice, and neutral juices.
During colds, including during herpetic sore throat, the herpes virus can be activated. In this case, the doctor prescribes the following drugs:
- Cycloferon;
- Cytovir;
- Viferon.
To relieve a sore throat, you can take Strepsils, Septolete and other cough lozenges and lozenges. Antiseptic sprays are also effective - Ingalipt, Hexoral, Yox, Kameton.
To reduce the temperature, the doctor prescribes Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Panadol, as well as antihistamines in case of a possible allergic reaction - Zyrtec, Loratadine, Claritin, Diazolin.
Popular about sore throat
Sore throat is one of a number of infectious diseases that occurs due to the penetration of various pathogenic agents into the body. This can be bacterial or viral microflora, protozoan fungi of the genus candida, in rare cases the disease is caused by a herpes virus.
Most often, the disease occurs in children aged 4 to 14 years. This is facilitated by the weakened immune status of the body.
The disease primarily begins in an acute form after inhaling atmospheric air that contains harmful microflora. Pathogenic pathogens settle on the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, which causes activation of the body's immune cells.
This condition leads to vasodilation and tissue swelling, causing pain when swallowing. The development of pathogens is accompanied by the release into the bloodstream of toxic substances that they produce during their life activities.
This is a consequence of intoxication of the body, and if appropriate methods of therapy are not applied, the disease can move to other organs, causing dangerous consequences.
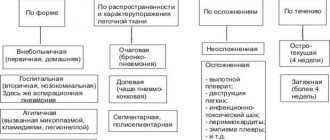
Main types
Before starting treatment for angina, it is especially important to establish its type. This is necessary because each form of the disease requires an individual approach.
The following types of this pathology are distinguished:
- Catarrhal. It occurs in people even if they have a good immune system, which is why inflammation in the tonsils occurs without the presence of pus. It can also be the beginning of complex and severe forms of tonsillitis.
- Lacunar tonsillitis . The most frequently recorded cases are when a person's tonsils were removed. It is considered a particularly contagious (infectious) disease, since the pathogenesis includes staphylococci, streptococci and adenoviruses. It can also occur after surgery in the oral cavity. Sometimes it appears after prolonged hypothermia or being in a damp room. Most often, the inflammatory process is recorded in children.
- Follicular tonsillitis . In the vast majority of cases, it occurs when the seasons change. The pathogenesis of development may involve various pathogenic agents (streptococci, staphylococci, adenoviruses). This type of sore throat is characterized by the fact that it damages the follicles that are located in the tonsils. A concomitant sign of this pathology is the presence of a diagnosis of regional lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes).
- Herpetic sore throat. In the etiology of the disease, the main role is played by the parasitic effect of the Coxsackie virus. Adults rarely suffer from this pathology. In a child, the disease is severe, and in some cases, in the absence of proper therapy, serious consequences occur with damage to the meningeal membranes of the brain or heart muscle. The virus can be transmitted both through the air and through dirty hands.
- Phlegmonous form of sore throat. The second name is paratonsillitis. Most practicing specialists in the field of ENT pathology consider it the next stage after lacunar or follicular tonsillitis. It is most likely to occur in people between 15 and 40 years of age. With it, purulent lesions of the tonsils occur mainly on one side. The disease occurs in an acute form. This form of sore throat has a distinctive symptom. The patient experiences a severe disturbance in the act of swallowing. At the same time, he is unable to swallow not only food, but also any liquid.
- Fibrous form. The main symptom is the development of a film on the affected areas of the tonsils. It is a serious pathological process, since its rapid development can pose a threat to the life of the patient.
- Ulcerative-necrotic . Although the disease is called tonsillitis, it differs from all previous ones in that the pathogenesis of its development involves a symbiosis of a spirochete and a spindle-shaped rod. This form of the disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses. Moreover, the chance of development increases significantly if the patient has chronic cardiac diseases. The risk of a sore throat also increases if a person does not sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner (dental caries, not removed roots).
Possible routes of infection and risk groups
Both in an adult patient and in a child, the ways of contracting tonsillitis are the same.
They are:
- Transmission of infection through the air (airborne droplets) . Occurs when communicating with a sick person, as he releases pathogenic microorganisms into the environment when he sneezes or coughs. This route of infection occurs in places with increased crowding of people (shops and public transport, preschool and school institutions, work teams at enterprises).
- Contact and household. Infection occurs through contact with the saliva of a sick person or through dirty hands. A child may become infected through toys or clothing. Failure to maintain personal hygiene can lead to infection if one of the family members is sick and personal items (towels, cutlery) are not provided for him.
- Food. They are very rare. Occurs when foods contaminated with staphylococci or streptococci are eaten. Therefore, vegetables and fruits must be thoroughly washed before eating, and ideally they should be doused with boiling water. Cooking must be accompanied by long-term heat treatment.
The occurrence of sore throat occurs more often in people who are at risk.
They are the following categories of the population:
- Children. Every child has imperfect immunity. This is due to anatomical development. The immune system reaches its peak development around the ages of 16 to 18 years.
- Women who are carrying a child. In this case, the immune system is in a suppressed (inhibited) state. This condition is considered physiological, otherwise fetal rejection would occur. A negative manifestation of this condition is increased susceptibility to any type of pathogenic microflora.
- People with chronic diseases. A long course of chronic infection causes depletion of the immune system, which often causes a complication in the form of a sore throat.
- Category of people who suffer from vitamin deficiency. Lack of vitamins leads to a decrease in the body's barrier function. The reason for this is insufficient intake of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). This problem can arise in the off-season or when mono-diets are used to lose weight.
- Systemic diseases. The process of development of angina is recorded more often in people who have diseases associated with impaired renal function, with cardiac pathologies and systemic lesions of the joints.
The impetus for the development of sore throat, both in a child and an adult, can be the following situations:
- Wearing clothes that are not appropriate for the weather causes general hypothermia of the body.
- If colds, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections or influenza occur more often than twice a year.
- When an adult or child, due to an unbalanced diet, experiences a constant lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements.
- Chronic diseases of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis or sinusitis).
- Allergic manifestations and intestinal infections.
- Violation of the psycho-emotional state as a result of prolonged stressful situations and prolonged depression.
Why is herpetic sore throat not considered a manifestation of herpes?
In the pathogenesis of herpetic sore throat, the main role is played by the active reproduction of the Coxsackie virus within the velopharyngeal ring. It belongs to the group of enteroviruses, and has nothing to do with herpes infection.
Herpangina gets its name due to the similarity of clinical signs that resemble the blistering rashes of herpes. Their appearance causes a feeling of pain, which is also inherent in herpetic rashes.
Possibility of occurrence in newborns
The main feature of herpetic sore throat is that a child of the first year of life does not suffer from it.
This is due to the fact that some antibodies are transferred from mother to child during prenatal development.
The period when the baby is breastfed is also associated with the supply of antibodies that prevent the development of sore throat.
This is the main advantage of natural feeding over artificial feeding.
And that’s why babies don’t get herpetic sore throat.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating herpetic sore throat can also be supplemented with folk remedies. But you should agree on the chosen prescription with your doctor. The most effective traditional medicine recipes are:
- Propolis. 2 grams of propolis should be chewed in the mouth for 15 minutes. The procedure must be repeated three times a day.
- Honeycomb can also be consumed as chewing gum three times a day.
- 1 teaspoon of aloe juice twice a day.
- Kalanchoe leaf will help cope with pain in the nasopharynx - you need to chew it until the juice stops secreting. Kalanchoe can be chewed three times a day.
- Propolis in the form of an alcohol tincture for gargling - dilute 1 teaspoon of solution in one glass of water.
Before using this or that folk remedy, you should make sure that the patient does not have allergies. Honey and propolis are fairly common allergens.
Rinse for herpangina
The procedure is intended to wash out pathogenic microflora from the mucous membrane affected by the virus, as well as to prevent infection of ulcers that form after the vesicles open.
When choosing a pharmaceutical rinse, pay attention to the following drugs:
- Furacilin - 1-2 tablets dissolved in a glass of warm water, used as directed 3 times a day.
- Hydrogen peroxide - 5 ml of 3% hydroperite is combined with 100 ml of water, gargle up to 4 times throughout the day.
- Stomatidin - used after 6 years. The solution is not diluted - rinsing is done by taking 1 tablespoon of the drug. The frequency of the procedure is three times a day.
Price – about 270 rubles
A good rinse is baking soda. Take a teaspoon of soda per glass of boiled water, wait until it dissolves, and rinse up to 6 times a day. To enhance the therapeutic effect, add a teaspoon of salt and a couple of drops of iodine to the soda solution.
Decoctions of medicinal plants - oak bark, chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, yarrow, string, sage - effectively relieve the inflammatory process . To prepare the product, pour a teaspoon of dry herb into a glass of boiling water, leave for 15-20 minutes, then filter and use as directed every 2-3 hours.
Recommendations
At the first signs of discomfort, you should consult a doctor. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, serious complications may develop:
- meningitis with inflammation of the meninges;
- encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue);
- hemorrhagic conjunctivitis - an infection of the eyes;
- rheumatism – connective tissues become inflamed;
- myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart muscle.
By following all the doctor’s recommendations and adhering to the course of treatment, you can avoid the development of these complications and significantly speed up the recovery process.
The difference between herpes sore throat and diseases with similar symptoms
Clinical manifestations of herpes sore throat may have similar symptoms to diseases such as purulent follicular sore throat and herpes stomatitis. Therefore, sometimes there is a need for differential diagnosis.
The main difference between herpetic sore throat and a disease of bacterial etiology is the presence of a runny nose and vesicles located behind the tonsils. With bacterial sore throat, there is no nasal discharge, and pustular formations are located on the tonsils.
As for herpes stomatitis, this disease is caused by a typical herpes virus infection. This disease is characterized by blistering rashes covering the tongue, gums, inner surface of the cheeks and palate. The external difference between herpes stomatitis and tonsillitis lies in the location of the vesicles. In addition, it is with stomatitis that relapses develop. All other manifestations, including increased body temperature, are more pronounced with angina.
When conducting self-diagnosis at home, herpes sore throat at the beginning of its development can be confused with Quincke's edema. The nature of the rashes at this stage of the disease is identical. In addition, during this period, the manifestations of herpes sore throat are similar to food poisoning.
A pediatrician will tell you how to distinguish herpangina from streptococcal in a video from the Doctor Komarovsky channel.
Prevention
As mentioned above, herpetic sore throat is transmitted from person to person by contact or airborne droplets, then the main method of prevention is the introduction of quarantine, that is, isolation of a sick family member or team, limiting contacts with him.
Preventive measures also include:
- systematic strengthening and maintenance of immunity.
- Maintaining a routine means getting enough sleep.
- Proper nutrition.
- Getting rid of bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the house, regular ventilation and wet cleaning.
- Reducing stress levels.
- Timely treatment of colds.
If a child shows signs of a cold, he should not be taken to kindergarten or school. It is better to take the baby to the doctor and let him rest at home. Such measures will allow the child’s body to regain strength. In addition, the likelihood of infecting other children will be reduced.
Preventive actions
If a child in a team falls ill, quarantine is declared for a period of two weeks for everyone who has been in contact with him. There is no vaccination against the pathological condition; emergency preventive measures are the administration of gamma globulin.
Other measures:
- early diagnostic measures;
- carrying out work to prevent viral infection in a team;
- vitamins and medicines to support immunity;
- after visiting crowded places, the child needs to wash his hands with hot water and soap;
- if contact with a sick child is suspected, the oropharynx is rinsed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. It is lightly pink so as not to burn the oropharynx;
- In public catering establishments, before eating, wipe hands with a damp antibacterial wipe.
Attention must be paid to the possible addition of a bacterial etiology infection as a secondary one. It is important to prevent complications that arise when bacteria spread from the lesion through the lymphatic and blood vessels to all tissues of the body. As a result, sepsis will develop.
Question answer
Can you have herpetic sore throat without fever?
During herpetic sore throat, the temperature always rises. In the initial stages, the temperature rises slightly, as with a cold, but when a rash has already appeared on the mucous membranes, the temperature can rise to 40. Hyperthermia lasts from 3 to 6 days.
Is it possible to wash with herpetic sore throat?
You can wash with this disease. The rash appears only on the tonsils and in the nasopharynx; there are no signs of vesicles or papules on the skin, so there are no contraindications to showering. But with hyperthermia, all measures should be taken to avoid hypothermia.
Is it possible to get herpangina again?
After experiencing the disease once, immunity is formed. But sometimes a re-exacerbation of herpetic sore throat occurs. A recurrent disease can be diagnosed many years after the first case, and only with reduced immunity and a weakened body.
Is it possible to go to the pool with herpetic sore throat?
You will have to refuse to visit the pool during a herpetic sore throat. Swimming in the pool is physical activity that should be limited. And the water in the pool is quite cool, which can lead to hypothermia. The pool is considered a public place - you should not become a source of infection for many people.
Who is at risk of getting sick?
There is a risk of getting herpetic sore throat:
- In children attending organized children's groups (kindergartens, schools, camps). Children in groups are more likely to catch an infection than unorganized children.
- In frequently ill children. Often sick children have weakened immunity, and therefore the risk of getting sick increases.
- In children with chronic diseases.
- In children with systemic diseases being treated with drugs that suppress the immune system.