Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that affects the skin and sometimes mucous membranes. Statistics show that the disease is especially common among children aged 1-10 years. When a dangerous pathogen enters the body, a rash first appears on the skin, and at the end of the incubation period, small papules filled with a white cheesy mass form. To combat infection, various treatment methods are used: medications for external use (creams, ointments), laser removal of formations, diathermocoagulation. Effective folk remedies are used as a complement to the main therapy.
What are shellfish on the skin?
The causative agent of the disease is one of the varieties of smallpox viruses - Molluscipoxvirus (Molluscipoxvirus). Microorganisms multiply inside skin cells and mucous membranes.
Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease, and the peak prevalence occurs at the age of 3-5 years. The incubation period ranges from 1 week to 5-6 months. On average, its duration is in the range of 2-7 weeks.
If in adults rashes most often appear in the genital area (sexual route of infection), then in children papules can appear on any part of the body - from the eyelids to the outer part of the foot.
Molluscs on the skin of a child (photo) is a fairly common contagious disease
Molluscs on a child’s skin, photos of which in severe cases of lesions clearly show the degree of damage to the skin, not only create an unaesthetic appearance, but also cause the following complications:
- Development of the inflammatory process, secondary infection (most often with staphylococci or streptococci).
- The occurrence of structural changes in the subcutaneous layer, leading to tissue degeneration and the formation of small scars.
- Damage to the intraorbital region, conjunctivitis (in the presence of rashes on the eyelids).
Prevention
Special complications usually do not arise. Prevention lies in following the rules of skin care. It is necessary that each family member has their own means of cleansing the body.
Most often, molluscum contagiosum affects children. Parents must take care of the child's hygiene. Swimming pools are especially dangerous. Often the virus is contained in the water in which a large number of people bathe.
Most modern pools are thoroughly disinfected, but there are exceptions.
It is important to wash your hands after using public transport. It is advisable to use an antiseptic.
Reasons for appearance
Molluscs on the skin of a child, the photo and causes of which are outlined below, is a widespread disease. According to various estimates, at least 1 episode of pathology is observed in 22-80% of children. The main reason for the development of infection is reduced immunity. For the same reason, the virus also affects people in old age.
One of the reasons for the appearance of mollusks on the skin is lack of personal hygiene.
The incidence of infection increases in the presence of factors such as:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- high humidity;
- close physical contact with other children;
- tight-fitting clothing, leading to increased sweating, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of viruses;
- use of glucocorticosteroids or antitumor drugs;
- decreased local immunity and the protective barrier of the epidermis in children with dermatitis. In such cases, the pathology takes on the character of multiple lesions of the skin.
In immunodeficiency, the disease occurs with persistent relapses, despite treatment.
Forecast
Self-healing is possible, but with the spontaneous disappearance of external manifestations, the transition of the virus to a low-active stage and its reactivation with a decrease in immunity cannot be ruled out. Complex treatment allows you to get rid of the disease, but does not prevent re-infection, because immunity is not developed during this infection.
After proper removal of the nodules or their spontaneous regression, the skin becomes clear. If the deep dermal layers are not damaged, scars will not form. But with the development of molluscum contagiosum against the background of atopic dermatitis, eczema and some other dermatological diseases, healing can occur with scarring.
Routes of infection
The virus is transmitted both through direct contact with a sick child and through contact with contaminated household items . Children most often become infected when playing together in educational institutions or in the yard. The pathogen spreads only among humans and is not carried by animals.
The virus that causes molluscum on a child's skin (photo above) is spread when children play on the playground through touch and household items
In older children, this can happen when playing contact sports in sections (various types of martial arts - Greco-Roman wrestling, sambo, judo and others), or when visiting the pool. Among adolescents, transmission of infection also occurs through sexual contact.
Precautionary measures
If molluscum contagiosum appears on a child's skin, it is necessary to be examined by a doctor.
You should not treat diseases yourself without diagnostics.
It is very important to ensure that your baby does not scratch the knots. For disinfection, parents should treat the affected areas with miramistine or chlorhexidine.
Before visiting children's institutions, it is necessary to cover the formations with a plaster. If necessary, you can apply cream if the skin becomes dry. This is necessary to prevent the development of cracks and bacterial infection through them.
Symptoms in children
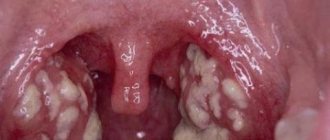
Molluscs on the skin of a child, whose photo clearly shows what they look like, appear in the form of papules with the following distinctive features:
- appearance - dense nodules rising above the skin;
- the shape of the formations is round, slightly flattened; sometimes on “legs”;
- the average size is 3-5 mm, in more rare cases, in patients with reduced immunity, the size of the papules can reach several centimeters (giant clams);
- location – group, most often in 1-2 areas of the skin;
- color - flesh-colored or pale pink, but with irritation there may be redness, expressed in the presence of a red rim around the formation;
- waxy shine;
- in the center there is a small depression;
- upon opening, a curdled mass is released, which contains a large number of viral particles;
- rapid growth of formations;
- the appearance of a bleeding wound when removing the mollusk.
There are also more rare forms of manifestation of the rash with this disease:
- formations with a diameter of more than 30 mm;
- keratinizing papules (the skin becomes rough and tough);
- molluscs in the form of cysts;
- ulcers;
- papules that look like acne or warts.
Associated symptoms include:
- itching, the intensity of which can range from mild to severe;
- soreness or discomfort;
- secondary inflammatory processes that occur as a result of violation of the integrity of the skin and scratching with hands due to itching.
Localization
The rash in children is most often located in the following places:
- face (eyelids, forehead);
- torso, especially its upper part;
- limbs;
- shoulders and neck;
- armpits.
Molluscs on the skin of a child (photo) can have different localizations - face, head, neck, arms, legs, torso.
The degree of distribution on the skin can be different. The disease develops gradually, with 1-2 papules and can take on the character of an extensive lesion. Usually the total number of these formations does not exceed 20 pieces, but sometimes reaches several hundred.
In some patients, the disease resolves spontaneously after 6-9 months, without taking any therapeutic measures. In children with dermatitis and immunodeficiency, independent recovery almost never occurs, and the persistence of the rashes persists for years.
Features of the disease
It’s worth mentioning right away that the subcutaneous mollusk has nothing in common with living mollusks or any other living creatures. Although officially this disease is called molluscum contagiosum. In fact, the virus got its name because of the contents that are inside this pimple. This is a kind of white opaque mass interspersed with keratinized skin epithelial cells. Under a microscope, a subcutaneous mollusk vaguely resembles mollusk shells, hence the name.
The good news for many is the fact that this disease does not spread over the entire surface of the skin. However, the patient is quite capable of becoming a carrier of this disease and beginning to actively transmit it to others. It is important in this case to get rid of subcutaneous molluscum contagiosum as quickly as possible. This should be done not only for the aesthetic effect, but also because of a number of possible unpleasant symptoms that constantly accompany this disease.
Which doctor should I contact for molluscum contagiosum?
If such formations occur on the skin, you should consult a dermatologist. The typical manifestation of symptoms can be easily recognized by a pediatrician. But if there is a specialized specialist in the children's clinic and for more accurate differentiation of the disease, it is better to contact a professional who specializes in skin pathologies.
For minor lesions, the doctor may first prescribe conservative treatment in the form of local remedies and immunomodulatory drugs. If such therapy turns out to be ineffective and there is a need to remove the papules, you will need to consult a surgeon.
Diagnostics
Mollusks on the skin of a child (photo above) usually do not require special research methods. The diagnosis is most often made clinically, based on external examination.
If necessary, a histological examination is prescribed. A small sample of skin is taken from the patient, which is then examined under a microscope. In this case, large brick-shaped viral bodies are observed inside the cells.
Similar symptoms may occur with diseases such as:
- Papular dermatitis. Its difference is that compacted nodules on the skin appear in children only on the knees or elbows.
- Papillomatosis , the formation of flat warts. They are usually smaller in size than clams and most often occur on the face and hands. The mother-of-pearl sheen and depression in the center, characteristic of mollusks, are absent.
- Soft fibroma is a benign tumor with a “pedicle”. The most common location is under the arms and on the back of the head.
- Milia. They occur in newborns and infants on the cheeks and under the eyes. The rashes are small and whitish in color.
- Dermatofibroma (sclerosing hemangioma). It looks like a single papule on a red-brown stalk with a dense consistency.
- Sebaceous gland adenoma. This type of benign formation looks like red-yellow nodules.
- Acne. Its difference is the inflammatory process, and the papules have a soft consistency, pink or red color.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children with drugs
There are no specific medical treatments for molluscum.
There is also no consensus among doctors about the advisability of therapy, since the rash may disappear on its own.
Factors that favor treatment at the first symptoms include:
- the impossibility of predicting the course of the disease in a particular child;
- the occurrence of complications in case of severe damage;
- highly contagious to other children.
All treatment methods can be divided into 2 groups:
- destructive (chemical, laser, mechanical removal, cryodestruction);
- conservative (immunomodulators, aniline dyes, antiviral agents).
The table below shows the most common medications used to treat this disease.
| Name of the drug and release form | Active substance, therapeutic effect | Features of application | Patient age | Average price, rub. |
| Acyclovir, 5% ointment for external use | Acyclovir, anti- viral | The instructions do not contain direct indications for use in molluscum contagiosum, but in practice the ointment shows quite high effectiveness. Skin formations are lubricated 3-4 times a day. | From birth | 25 |
| Isoprinosine, tablets | Inosine pranobex, immunostimulating | Daily dose – 50 mg/kg in 3-4 doses. The duration of therapy is 5-14 days until the signs of the disease are eliminated + 2 days to “consolidate” the effect. If necessary, conduct several courses | From 3 years (body weight >15 kg) | 1500 |
| Viferon, rectal suppositories and ointment | Human interferon, immunomodulatory | Suppositories of 150 thousand units are used 1-2 times a day, treatment is a course. The ointment is applied pointwise 3-4 times a day to the papules | From birth | 380 |
| Allomedin, gel | Allostatin, antiviral | In the form of applications 2 times a day. Duration of treatment – 1-2 weeks | From birth | 280 |
| Betadine, ointment for external use | Povidone-iodine, antiseptic and disinfectant | Most often used after treatment with Fukortsin and for disinfection during surgical removal of papules. Course of treatment – 10 days | From birth | 250 |
| 3% oxolinic ointment for external use | Oxolin, antiviral | Apply 2-3 times during the day. The duration of therapy can be 2 months. Shows a high degree of safety when used in children. 0.25% ointment can be used for the eyelid area. | From birth | 230 |
| Iodine, alcohol solution for external use | Iodine, cauterizing | Apply directly to the mollusk 3-4 times a day until it dries. May cause irritation on delicate areas of skin. Often used in combination with oxolinic ointment | From birth | 30 |
In a small child, when treating molluscum contagiosum on the skin, the following treatment tactics are advisable: if the number of formations is 1-2 pieces, then at the first stage you can resort to iodine. In case of a common form of the disease (see photo above), complex therapy is carried out using one of the destructive methods and immunomodulators.
Of the aniline dyes, you can use not only iodine, but also Fukortsin, brilliant green, and a 2% aqueous solution of gentian violet. They are applied 4-5 times a day to the mollusk (pointwise, without lubricating the surrounding skin surface). With a tendency to reduce the size of the formation, treatment is gradually reduced.
Possible complications
The difficulty in treating molluscum is that it does not leave the body completely.
There are no serious consequences; the disease is more cosmetic in nature, since the external signs resemble the symptoms of syphilis. Complications occur rarely, these include a large number of lesions, the possible development of dermatitis, and the addition of a secondary infection.
Difficulties arise in people with a weakened immune system, because the development of the disease can become serious and leave growths on the body, especially in the face. In this case, papules take on an atypical shape, and treatment is complicated.
Women, as can be seen in the photo, are not decorated with papules. In addition to systemic treatment of molluscum contagiosum, care should be taken to prevent relapse. Rashes should be treated under the supervision of a doctor to avoid serious complications.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Recipes and scheme for using folk remedies
In folk medicine, there are several methods for treating this pathology in children:
- Seed grass has pronounced antiseptic properties due to the presence of polyphenols in it. Baths with a decoction of the string are recommended for bathing children, starting from the newborn period.
A strong decoction is prepared from the string in a water bath, which is then used to lubricate the shellfish on the skin.
To eliminate the shellfish, prepare a strong decoction according to the following recipe: 3 tbsp. l. raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, and then simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes. The finished composition is kept at room temperature for about an hour, after which it is filtered. This product is used to lubricate the skin areas affected by the mollusk 5-6 times a day.
Long-term use of alternating baths for preventive purposes can lead to negative effects: increased irritability and bowel dysfunction. Rubbing the broth too often or for a long time also leads to increased dryness of the skin.
- Fresh garlic juice has a whole range of properties: antimicrobial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory.
In order not to cause irritation to delicate baby skin, it is recommended to use it together with butter according to the following recipe: chop 2-3 cloves of garlic in a garlic press and pour a small amount of melted butter over the pulp. Leave for 2 hours. Lubricate the nodules on the skin with a cotton swab 3-6 times a day.
- A strong decoction of calendula (marigold) not only has antimicrobial properties, but also helps relieve inflammation. The product is prepared in the same way as a decoction of the string, and the areas of the skin on which the mollusks have formed are lubricated several times a day.
It is not recommended to use celandine infusion when treating young children, as it can cause burns.
other methods
If there are very few rashes, then chemotherapy drugs are effective. But they are not recommended to be used for a long time, as this can lead to irritation to the skin.
For minor dissemination, UV therapy is also used. Healing ultraviolet rays have a desensitizing, restorative, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effect. The main thing is, before starting phototherapy with ultraviolet rays, to establish the presence of individual sensitivity to this method, as well as the optimal biodose, which is individual for each patient. It is determined by test irradiation of the skin of the forearm or buttock. Remember that UV therapy is contraindicated for precancerous skin lesions, albinism, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, severe sensitivity to light therapy, and xeroderma pigmentosum.
When treating minors, the tuberculin application method is often used. In pediatric dermatology it is used as one of the most painless and safe. This is a new and modern technique, but there is no more or less accurate data on its effectiveness yet. The main thing is that minors have been previously vaccinated with isoprinosine or BCG.
Removing shellfish from children
Elimination of mollusks is carried out using several methods:
- chemical (iodine, salicylic acid and other substances);
- mechanical (needle or tweezers);
- surgical;
- laser;
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
In addition to iodine, formations on the skin are cauterized using the following means:
- 5% potassium hydroxide solution (Molutrex, Molyustin);
- salicylic acid in the form of a patch;
- topical retinoids (Ferezol, Tretinoin and others);
- Podophyllotoxin applications;
- silver nitrate solution.
Local cauterization first leads to inflammation and then to the disappearance of pathological foci. Removal of the mollusk using destructive methods can begin at the earliest stage of the disease, when there are only 1-2 nodules on the skin.
After eliminating the formations, it is recommended to treat the affected areas with iodine for a week, and then apply ointments (Viferon, oxolinic ointment and others). This procedure is carried out once a day. Bed linen and toys must be disinfected, and a sick child must be isolated from other children.
The advantages and disadvantages of various shellfish removal methods are listed in the table below.
| Method of treatment | Advantages | Flaws |
| Use of chemical cauterizing agents | Simplicity and accessibility at home |
|
| Mechanical removal with a needle or tweezers |
|
|
| Desquamation with a surgical curette | No contraindications based on age |
|
| Laser removal |
|
|
| Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen) | No anesthesia required for small lesions |
|
If a child experiences an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, it must be treated before removing the molluscum. Methods associated with violating the integrity of the skin are also not applicable in case of immunodeficiency, since there is a high risk of infectious complications.
Mechanical removal
Self-removal of the mollusk is done using a needle from a disposable syringe or sterilized sharp tweezers. This method is recommended for “fresh” rashes.
The procedure is as follows:
- Treating hands and instruments with a sterilizing composition (hydrogen peroxide, alcohol).
- Antiseptic treatment of the skin in the affected area.
- Opening the top of the mollusk.
- Squeezing its contents out using a piece of sterile cotton wool. At the same time, it is necessary to try not to spread viruses to surrounding areas of the skin.
- Treatment with hydrogen peroxide, cauterization of the mollusk with iodine.
Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis leads to the fact that the virus enters healthy areas of the skin and the rash spreads even more. The reappearance of mollusks in this case is most often observed 4-8 weeks after the procedure.
Surgical removal
Surgical removal is performed using a sharpened curette and is the standard treatment. EMLA, the main components of which are lidocaine and prilocaine, is used as an anesthetic in children.
A bandage with an anesthetic is applied to the affected areas 1-2 hours before the procedure. Pain is also reduced by stretching the skin when curettage of the formation. For children with an increased level of anxiety, as well as in advanced cases, when the number of molluscs on the child’s skin reaches several dozen, surgical removal is carried out under general anesthesia.
After surgical removal of molluscum contagiosum, the skin is treated with an antiseptic (for example, chlorhexidine)
This procedure can be done at any age. After removing the mollusk, the skin is treated with an antiseptic (0.25% solution of gentian violet, chlorhexidine, dioxidine and others).
Laser treatment
Cauterizing a mollusk with a laser beam not only leads to its destruction, but also causes an immune response in the skin. A high-density light beam is aimed at the papule. The duration of exposure is several fractions of seconds. In this case, the upper layer of skin is heated and evaporated. Removal can be done pulsed or continuous radiation.
The technique of the procedure is similar to that for the surgical method of removal : first, the hands and the affected area are treated with antiseptic agents, then anesthesia is applied with applications or injections with an insulin syringe for each formation.
With laser treatment, mollusks are removed using a laser; this treatment is similar to surgery.
If necessary, laser treatment is repeated after 2–3 weeks. After the procedure, repeated antiseptic treatment with solutions is performed or a bactericidal patch is applied.
Liquid nitrogen removal
Cryotherapy involves creating a superficial burn of the skin using nitrogen at a temperature of -196°C. Each formation is affected for 6-20 seconds. As a result, the frozen areas die and disappear after a while.
Removal is carried out pointwise, using a tip on which cotton wool soaked in liquid nitrogen is attached. The absence of the need for anesthesia during the procedure is a significant advantage when treating children.
This method is also used if you are allergic to anesthetics. However, subsequently the treatment site causes discomfort, which makes repeating the procedure difficult.
Removing shellfish with liquid nitrogen
Effective treatment of molluscs on the skin, photos, causes and symptoms of which are given above, should also be accompanied by preventive measures.
For a child with weak immunity, it is necessary to follow a daily routine, monitor nutrition, engage in general strengthening procedures, take regular walks in the fresh air and avoid overwork. If the disease persists and there are repeated relapses, consultation with an immunologist is required.
Article design: Natalie Podolskaya