As soon as the name of the antibiotic is read in the doctor’s prescription, the question immediately pops up: “Why and how much should you take antibiotics for a sore throat?” And it’s ideal if this question is asked right away in the doctor’s office.
An antibiotic course in the case of tonsillitis is necessary to combat microorganisms that provoke the disease. If they are not destroyed by these drugs, the disease can become chronic and cause serious complications in the heart, kidneys and joints. And, unfortunately, these are not just scary words, but millions of real, life cases.
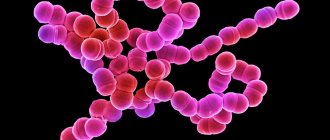
In the most common cases, the provoking agent is streptococcus. It is this that, if neglected, can spread from the tonsils throughout the human body, causing a variety of serious diseases.
Streptococcus is a gram-positive representative of the Streptococcaceae family, numbering 15 subspecies in its ranks, called letters of the Latin alphabet, from A to U. Bacteriologists call the most common species Alpha, Beta and Gamma. Of these, Alpha and Gamma can be considered components of the normal flora of the membranes, but Beta, in turn, provokes various human diseases.
You can get the bacterium through contact with a sick person through airborne droplets, as well as through unwashed hands, food, and food that has not undergone proper heat treatment.
Also, staphylococcus can be the cause of sore throat. Staphylococcus is another microorganism that belongs to gram-positive bacteria. Having seen it under a microscope, one can come to the conclusion that it is immobile and has a yellow, white or golden color. There are aureus, saprophytic, epidermal and hemolytic streptococci, and any of the species can develop resistance to penicillins.
Doctors, based on many studies of sore throat provocateurs, have found that the fight against streptococcus or staphylococcus should last, on average, at least 10 days. When selecting a course individually, the doctor may adjust the duration, but definitely not to a lesser extent.
What is sore throat and how does it manifest in children?
According to statistics for 2021, the incidence of children with sore throat of any complexity increases by 2-3% every year, which is associated with the uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
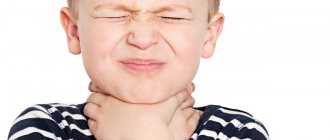
Tonsillitis is an acute infectious lesion. It is diagnosed with a sharp increase in temperature, sore throat, hyperemia and swelling of the pharynx, weakness, lack of appetite, and enlarged cervical lymph nodes are also noted. Vomiting or diarrhea rarely occurs. The cause is streptococci and staphylococci, less commonly fungi and viruses. The method of spread is airborne, household, fecal-oral.
A separate, dangerous and severe type of sore throat is herpetic. It is caused by the Coxsackie virus. This virus is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature to 40 °C, muscle pain, severe intoxication and malaise. When examining the throat, red blisters are visible. Requires immediate consultation with a specialist and hospitalization.
Classification of sore throat:
- Catarrhal;
- Follicular;
- Lacunarnaya;
- Fibrinous;
- Phlegmonous;
- Herpetic;
- Ulcerative-membranous;
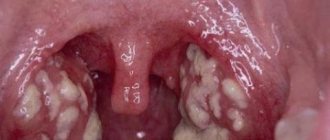
The statistically common type is follicular. With reduced immunity, bacteria attack the respiratory tract, acute purulent inflammation of the follicles occurs, the temperature rises, and malaise occurs.
more about purulent sore throat in the article.
Antibiotics for the treatment of sore throat in children are a priority if they are bacterial in nature. A list of additional measures will be prescribed after determining the etiology of the disease and collecting additional information about the symptoms.
Complications
Without treatment over a long period of time, sore throat leads to the following conditions:
- acute rheumatic fever. This occurs when antibodies that try to neutralize bacteria on the tonsils begin to attack the skin, joints and heart. Symptoms of acute rheumatic fever develop two to four weeks after the onset of sore throat;
- sinusitis. This condition develops when the paranasal sinuses become blocked, causing the sinus cavity to become obstructed in the flow of abnormal secretions. The bacteria then multiply, leading to disease. Symptoms of sinusitis include severe nasal congestion, cough, and nasal discharge;
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. This is a kidney disease characterized by damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering fluids and toxins from the blood. This may lead to bloody urination, decreased urine output, and pain or swelling in the joints;
- Toxic shock syndrome occurs when group A streptococcus is in the body. It releases toxins and leads to toxic shock syndrome, a life-threatening illness. Symptoms include fever, low blood pressure and rash;
- abscesses. These are limited accumulations of pus. With sore throat, abscesses can develop around the tonsils or in the back of the throat. In severe cases, they completely block the ability to swallow, speak, or breathe.
When is antibiotic therapy indicated for a child?
In the absence of drug therapy, the patient's condition will worsen. The infection will spread to the lower respiratory tract, and complications will arise in the form of tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia.
Based on the characteristic symptoms, the doctor can visually recognize the type of tonsillitis. Severe inflammation of the tonsils and enlarged lymph nodes are a symptom of bacterial origin.
With sore throat without antibiotics in children, the temperature does not drop for several days and does not respond to antipyretic drugs.
Note: Self-medication leads to complications and subsequent hospitalization.
With other pathogens of the inflammatory process, the symptoms will be less pronounced.
The viral type is amenable to antiviral and immunomodulators. For fungal infections, antimycotic agents.
Why take a throat swab before starting treatment.
Without collecting biomaterial from the tonsils, it is impossible to correctly determine the type of causative agent of the disease. The complex is selected based on the results of tests that determine the type of microorganisms inhabiting the pharynx and sensitivity to the class.
After confirming the bacterial origin of the infection, the healthcare professional will prescribe an antibiotic that is best suited for your child.
Antibacterial agents are recommended for any child of any age.
General information about sore throat
Sore throat is an infectious contagious disease manifested by inflammation of the tonsils
Sore throat is an infectious disease that occurs under the harmful influence of pathogens.
Most often it is transmitted by airborne droplets and through household utensils or clothing, rarely through blood. To protect your body from damage, you need to avoid contact with the patient or take safety measures - follow the rules of personal hygiene, protect your face with a bandage, take vitamins to boost immunity.
Most often, tonsillitis occurs during the period of all diseases, that is, in winter, autumn or spring. It is at this time that there is a greater risk of hypothermia or infection, when the body is more weakened, compared to the summer season.
The main causative agent of the disease is streptococcus or staphylococcus.
There are also several other types of sore throat, in which the causative agents are fungi or viruses.
There are several types of sore throat:
- primary is the one that arose due to infection or hypothermia
- secondary occurs as a complication after influenza, ARVI, sinusitis, rhinitis or other diseases of the respiratory system
- special is a rare type of pathological process resulting from injuries, fungi and other uncharacteristic lesions.
After the disease, the first symptoms appear within 10 hours. Usually, the throat starts to hurt first and it becomes painful to swallow. Next, a runny nose, cough, and redness of the throat may occur. Most often, sore throat is accompanied by high fever.
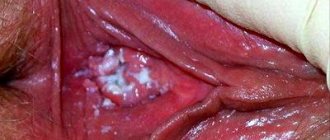
In the purulent form of the disease, you can see small pustules on the tonsils in the form of white or yellowish patches. A characteristic feature of angina is the acute onset of the disease. That is, symptoms appear almost spontaneously, and do not develop over several days, as with a cold or other similar diseases.
Features of its treatment
Treatment is complex and depends on the clinical manifestations of the disease
Sore throat is not a terrible treatment if you start timely and correct treatment. If the symptoms are ignored, a number of side effects and complications can occur. There are several ways to treat a sore throat - traditional medicine and medications.
The main condition for quality treatment is an integrated approach to neutralize the symptoms and act on the root cause at the same time:
- lowering the temperature to improve well-being. For this you can use antipyretic drugs - Paracetamol, Amiksin, Ibufen
- soothing the throat with tablets, mixtures, teas or decoctions of medicinal plants
- Gargling is a must! During this procedure, bacteria are washed from the tonsils, which affect the soft tissues and cause inflammation and pain. In addition, you can soothe your throat a little, relieve swelling and pain. For rinsing, you can use salt and soda, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, string, milk and honey, aloe juice, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin and other drugs
- when you have a runny nose, it is recommended to apply vasoconstrictor drops to your nose to relieve swelling of the nasopharynx
- taking antibacterial drugs when exposed to staphylococcus or streptococcus. Only an antibiotic can cope with the causative agent of sore throat
During illness, it is recommended to provide the patient with bed rest and proper nutrition. You should not eat hard foods or those that can irritate a sore throat - hot, cold, spicy, sour, salty, etc.
Antibiotics
When antibiotic therapy is indicated by a pediatrician, it is prohibited to change prescriptions, adjust the dose and duration.
The best antibiotic will be useless and sometimes even harmful if taken incorrectly. Each strain of bacteria is sensitive to a specific group of bactericidal agents. If the duration is shorter, the surviving microorganisms develop resistance and medications of a different effect will be needed; this will delay recovery and thereby negatively affect the child’s well-being.
For the treatment of inflammatory processes of the tonsils, depending on the severity and areas of spread, the attending physician will select a convenient method of application. A targeted complex effect on microbes quickly relieves unpleasant symptoms. For school-aged patients, rinsing with antiseptic solutions will be prescribed as an additional measure. Children are recommended to irrigate the throat with sprays with a targeted effect on pathogenic flora.
The following forms are produced:
- For oral administration (suspensions, tablets, capsules);
- For injection;
- Sprays;
- Solutions for inhalation;
- Preparations for oral administration.
When prescribing a medicine, the doctor relies on the child’s age, weight, and symptoms. The choice of active substance depends on the pathogen, which will be determined by laboratory analysis of the patient’s mucus.
New generations actively affect the vital activity of microorganisms and cause less damage due to low toxicity and a short course.
Classification of antibacterial drugs by class:
Penicillins. First generation. Effective, but toxic, and more often than others causes allergic reactions. Bacteria have been recorded that have developed resistance to it. List of drugs: Benzylpenicillin, Ampicillin trihydrate, extended spectrum group Amoxicillin.
Cephalosporins. Varied structure. Used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of all parts of the respiratory tract. Drugs: Cefazolin, Cephalexin, Cefuroxime, Cefotaxime and Cefepime.
Macrolides. Least toxic with high activity against pathogenic microorganisms. According to the results of studies and independent examinations, it is a safe group, well tolerated, and rarely causes unwanted effects. Prescribed for intolerance to the Penicillin class. Trade names: Erythromycin and Roxithromycin,
Clarithromycin, Midecamycin, Spiramycin, Josamycin, Azithromycin, Sumamed, Azitrox and Azitral.
Tetracyclines. Multidirectional action. Destroy strains of bacilli that cause inflammation in the respiratory tract. Used in medical practice since 1950. Highly active against all known bacteria. Categories of microorganisms that exhibit resistance to this group have been recorded. First choice when bacterial tonsillitis is diagnosed. Often cause digestive disorders and diarrhea. The main representative is Tetracycline.
Lincosamides. Low bactericidal activity. The most common side effect is allergic reactions.
Fluoroquinols. Strong bactericides. They have great toxicity and many contraindications, so they are rarely prescribed to children. Contraindicated for children under 12 years of age. These include the following trade names: Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Tsiprolet, Tsifran, Moxifloxacin, Zinnat and Glevo.
Sumamed
Representative of the macrolide group. It has a stabilized formula and high bioavailability. The short course sets it apart from other classes. Active ingredient: Azithromycin. Analogs of Sumamed on the market: Hemomycin, Zi-factor, Azitrox, Azitral and Zitrolide.
Available in the following forms:
- Powder for preparing a suspension;
- Capsules;
- Dispersible tablets (soluble in water).
It is well absorbed and distributed, so after 12 hours it reaches the required concentration at the site of inflammation. Long half-life, high bioavailability in infected organs.
Contraindications include severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, hypersensitivity to the components.
For tonsillitis, a short course of three days is prescribed once a day.
The dosage is calculated at 20 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight.
For babies weighing less than 10 kg, the doctor will prescribe Sumamed 100 mg/5 mg.
Side effects are rare and temporary. Research has revealed the following disorders: candidiasis, rhinitis, allergic reactions, dizziness, taste disturbances, nervousness, visual disturbances, tachycardia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence and constipation.
Overdose symptoms are similar. Lighten with activated carbon and other sorbents.
Amoxiclav
Penicillin group. Contains Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid to stabilize the formula and enhance the effect. Trade names of analogues based on the active substance: Augmentin, Flemoklav, Flemoxin, Flemoxin Solutab and Amoxicillin.
Dosage forms:
- Powder for preparing a suspension;
- Dispersible tablets;
- Film-coated tablets.
Both components of the drug are quickly absorbed and are also well distributed in tissues affected by bacteria.
Indicated starting from three months of age at 30 mg per kilogram of body weight. Over three years old, take 20-40 mg per kilogram of body weight, depending on the severity of the disease, twice a day with an interval of 12 hours at the same time. The course of therapy ranges from 5 to 14 days. The duration of the course is regulated only by the attending physician.
Negative effects are rarely recorded. The instructions indicate the following disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, urticaria, dizziness, headaches, development of candidiasis. All disorders disappear after discontinuation of the drug.
Contraindications for use: hypersensitivity and a history of allergic reactions to penicillins or components, as well as severe liver dysfunction and infectious mononucleosis.
No life-threatening cases of overdose have been identified.
Klacid
Group of macrolides. Active substance clarithromycin. Analogs: Fromilid, Klabaks and Clarithromycin-Teva.
Laboratory studies have recorded high activity in the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms that cause purulent inflammatory processes. This drug quickly penetrates into the affected tissues and organs.
Contraindications: individual intolerance, simultaneous use of cardiac medications.
The following forms are produced:
- Powder for preparing a suspension;
- Pills.
Suspensions are used from 6 to 12 months of age.
Klacid 125 ml/5 mg is prescribed according to the child’s body weight (milliliters):
- body weight 8-11 kg 2.5;
- 12-19 kg 5;
- 20-29 kg 7.5;
- 30-40 kg 10.
For a suspension with a dosage of 250 mg/5 ml, the serving size is doubled.
If you weigh less than 8 kg, the dose is calculated using the formula 7.5 milligrams per kilogram of body weight 2 times a day.
The course is continued until complete recovery occurs, but no more than 14 days.
Side effects are mild or not noticeable. Studies have revealed the following undesirable effects: diarrhea, nausea, headache, urticaria.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Suprax
The first of the third generation of cephalosporins. The main active ingredient is Cefixime. There are no analogues for the main component. It is highly resistant to microbial enzymes that destroy the active components of other classes. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and certain types of staphylococci have shown resistance to the action of Suprax in laboratory studies.
Of the contraindications, the manufacturer indicates only individual intolerance.
The main characteristics of Suprax are high bioavailability and a long half-life, which is why it is so convenient for use in children. This drug quickly penetrates into the foci of infection.
Suprax in powder form for the preparation of a suspension is prescribed from birth to 12 years. Dosage is 8 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight every 12 hours.
The dosage form in the form of capsules is used from 12 years of age, weighing more than 50 kg.
The course of treatment for tonsillitis is at least 10 days.
Side effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, urticaria, impaired renal and liver function.
Macropen
Representative of the macrolide genus. There are no analogues for the active substance. The active ingredient is midecamycin. They are produced in two forms: granules for preparing a suspension for infants from 2 months, tablets for adults and adolescents from 12 years of age.
Quickly penetrates the site of inflammation and reaches maximum concentration after 1-2 hours. Macropen has a long half-life.
The pediatrician will calculate the dosage using the formula 50 mg per kilogram of body weight, divided by 3 times a day.
The manufacturer indicated only hypersensitivity to components and liver failure as contraindications.
The list of side effects is short: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rash and weakness.
No severe or dangerous cases have been identified in cases of overdose. Treatment is symptomatic.
Vilprafen
Representative of the macrolide group. There are no analogues for the active substance. The active ingredient is josamycin. Vilprafen is available in the form of dispersible (soluble) tablets. High antimicrobial activity, low toxicity and a minimal list of side effects make it safe for severe respiratory tract infections, as well as chronic and acute tonsillitis.
Patients weighing less than 10 kilograms are prohibited from taking Vilprafen.
Contraindications are minimal and therefore limited to hypersensitivity to components and liver dysfunction.
Dosage:
- Infants weighing from 10 kg to 20 kg take 250 mg 2 times a day;
- Children from 20 kg to 40 kg 500 mg every 12 hours;
- Adolescents weighing more than 40 kg and over 14 years of age are prescribed 1000 mg 2 times a day.
Bacterial sore throat is treated from 14 to 21 days.
Side effects: nausea, diarrhea, urticaria, liver dysfunction, headache.
In case of overdose, the side effects intensify and disappear after discontinuation.
Choice of medicine
Every parent wonders which antibiotic is best for a child with a sore throat, and how to take it. There is no best medicine; the drug whose action is aimed at suppressing the causative agent of inflammation will be effective. In each case, a separate drug is indicated.
There is no need to self-medicate. A smear from the tonsils for a sore throat and bacterial culture of the resulting material will help you choose a truly effective medication.
Pharmacy chains offer different names of drugs to choose from, the range of which is easy to get confused.
You need to select it according to the following criteria:
- Possibility of use for children from birth or from the age of one year;
- effectiveness against the identified pathogen;
- convenient release form.
For children from birth to 4 years of age, the medicine is recommended in powder form for preparing a suspension. Capsules and tablets are acceptable for children from five to six years of age; a younger child may have difficulty swallowing a large capsule.
Antibiotic nasal spray
With bacterial infection of the tonsils, a common complication is sinusitis or rhinitis. After diagnosing concomitant diseases, the medical professional will prescribe additional measures in the form of nasal sprays containing antibacterial substances.
There are only two trade names on the nasal spray market that contain bactericidal components: Isofra and Polydexa. They are used as part of complex therapy for sinus infections.
The strong bactericidal effect of Isofra and Polydex helps prevent the spread of infection and complications in the form of sinusitis. Dosing according to instructions: one spray into each nostril 3 times a day.
The Polydex spray contains the additional ingredient Phenylephrine, which has vasoconstrictor properties and makes breathing easier. Use no more than 7 days. Side effects in the form of allergic reactions develop very rarely.
Can they cause side effects?
Using antibiotics incorrectly can cause side effects!
If the drug is not suitable, it may cause side effects:
- stomach disorders and intestinal dysfunction - nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence
- allergic reaction, skin redness, itching, irritation
- candidiasis, thrush is a fungal disease that occurs due to the active growth of the Candida fungus, which develops due to a violation of the microflora
- damage to the nervous system – insomnia, drowsiness, irritability
Sometimes antibiotics spoil your appetite and change your tastes and preferences in food.
When is it prohibited to take antibiotics?
Not everyone can take antibiotics, and before using such drugs you should consult your doctor and read the instructions. Contraindications:
- liver and kidney failure
- pregnancy and breastfeeding period
- simultaneous use with alcohol
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug
In the end, it should be noted that sore throat is considered a fairly simple disease with timely and correct treatment. If you do not start the course from the initial stage of development of the disease, a number of side effects may occur. If the pathology began due to bacteria, then the treatment should be antibacterial.
? Ctrl+Enter
Antibiotics for injection
In severe cases of the disease, in order to urgently improve the patient’s condition, relieve inflammation and improve well-being, the introduction of fast-acting drugs in the form of injections intramuscularly or intravenously is indicated. With this method, the active substance reaches the site of inflammation 5-10 minutes after the injection.
These medications include: Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, Cefazolin, Ceftazidime, Bicillin and Amikacin.
Characteristics of solutions for injections:
- High bioavailability;
- Quick action in emergency cases;
- Use in patients who cannot take the medicine orally;
- Treatment of patients with impaired absorption through the gastrointestinal tract.
Ceftriaxone is a member of the cephalosporin family, which is used for acute illness. The half-life is longer than its analogues, and it also quickly eliminates inflammation.
To prepare a solution for intramuscular administration per 1 gram of medication, the manufacturer recommends using 2 ml of water for injection and 2 ml of lidocaine.
The amount of active substance is calculated only by a medical specialist.
Treatment with injections usually takes place in a hospital setting.
Penicillin preparations
There are a large number of penicillin preparations on the market today. Moreover, in different products the antibiotic is contained in two different chemical forms:
- Benzylpenicillin potassium salt;
- Sodium salt of benzylpenicillin.
Penicillin is sold in this form in pharmacies.
Procaine and benzathine salts of benzylpenicillin are also actively used, but they have different pharmacokinetics and are used as part of bicillins - long-acting drugs for the prevention of complications of angina.
Here are just the main penicillin preparations:
- Bicillins - Bicillin-1, Bicillin-3, Bicillin-5, Retarpen, Extensillin
- Capicillin;
- Angincillin;
- Novopen;
- Cracillin;
- Christacillin;
- Pradupen;
- Pharmacillin;
- Lanacillin;
- Falapen...
Procaine salts of penicillin are used in bicillins
…and others. Basically, all of them are imported products, some are no longer produced today. In our country, benzine penicillin salts, packaged in special vials, are usually used for injection.
Inhalations with antibiotics
Therapy with inhalation antibacterial agents is carried out after consultation with the attending physician. At home, the solution is added to a nebulizer. There are many inhalation forms on the market: Dioxidine, Ceftriaxone, Tobramycin, Ciprofloxacin, Gentamicin and Fluimucil-Antibiotic.
Note: Choosing an antibiotic for inhalation based on reviews on the Internet or advice from people without medical education is prohibited!
Doctors recognize Fluimucil-Antibiotic as safe and effective for bacterial tonsillitis in children, since this medicine destroys the causative agents of sore throat. Analogs for the active substance are not commercially available. This drug can be used from birth. Doctors prescribe it for complications in the lower respiratory tract: bronchitis, pneumonia.
Among the adverse reactions, the instructions indicate allergies.
conclusions
As we can see, in many cases, effective treatment of sore throat without the use of antibiotics is not possible unless the pathogen is viral. These funds can and should be used as part of therapy in children. In order for their use to be effective and allow you to quickly and without consequences cope with the disease, it is extremely important to carefully choose a medicine and use it strictly in the dosage indicated by the doctor. In this case, you will be able to get rid of a sore throat in just 10 days.
Read more about the causative agents of tonsillitis in this article.
Rules for taking antibiotics
Drug treatment is indicated after consultation with a pediatrician, who examines the history of the disease, having the results of mucus tests.
The basis of the correct approach is to take medications at regular intervals and follow the prescribed duration.
The child may feel better the very next day, but this is not a reason to stop the course, since the infection still remains in the child’s body. When treating children with antibiotics, doctors note the likelihood of developing allergic reactions, often to the Penicillin group.
To exclude manifestations of allergies, the doctor will prescribe antihistamines. At the first symptoms of serious side effects, stop the course and seek advice from specialists. Antibiotics often cause digestive disorders, diarrhea, bloating, constipation and dysbiosis.
Antibacterial drugs kill microbes, both pathogenic and beneficial. Therefore, in addition to therapy, a course of probiotics is indicated to restore normal intestinal microflora: Linex, Acipol, Hilak Forte, Bak Set, Normobakt, Lactobacterin and Bifidumbacterin.
Why can't you stop treatment if it gets better?
It is forbidden to stop the course of antibiotics immediately with the first relief due to the fact that not all bacteria have yet been defeated. A small amount may still exist in the inflamed tonsils, and the condition and temperature may already be within normal limits. But this norm of sensations is not at all an indicator of refusal of treatment.
In addition, there is a risk of life-threatening complications affecting the heart muscle, nervous and auditory systems, joints and kidneys.
Therefore, if a doctor has prescribed a 10-day course of antibiotics, for the sake of your own health and well-being, it is worth going through this period with honesty and regularity.
What if my child is allergic to antibiotics?
Infectious and inflammatory diseases are treated with the use of antihistamines, which reduce the likelihood of developing allergies. Life-threatening allergic reactions: angioedema and angioedema. At the first sign, you must urgently call an ambulance. If a child is diagnosed with hypersensitivity to a drug, they will hospitalize the patient and change the drug.
Preferred forms of drugs
For oral administration, children will be prescribed a convenient suspension form or a dispersible form (soluble in water). Tablets and capsules are produced for adults and adolescents from 12 years of age.
General recommendations for parents
Proper therapy is based on bed rest and a full course of all necessary medications. Without an examination by a pediatrician and a smear test for the presence of pathogenic flora, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis. It is not allowed to replace what is prescribed with others without consulting a doctor, this will cause irreparable harm to health.
During illness, children need to be given more warm drinks.
Note: Drinking hot drinks if you have a sore throat is prohibited. A high temperature will irritate an already sore throat.
Normally, bacteria live in every person in an inactive form. When hypothermia occurs, the infection enters the active phase and causes inflammatory diseases.
Folk remedies in combination with medications will speed up the relief of unpleasant symptoms.
A good addition would be multivitamins that will boost your immunity. It is necessary to ventilate the room more often and carry out wet cleaning.
When the temperature rises, antipyretics are given in the form of release that is indicated for each age. There are candles for infants, and sweet syrups are produced for slightly older children. Pharmaceutical companies have developed a separate line of drugs for schoolchildren. At high temperatures, you cannot take hot baths, and it is also prohibited to use mustard plasters. If the temperature does not decrease after taking antipyretic drugs, you should immediately call a doctor and the ambulance team will quickly bring down the temperature by giving an injection. Medical workers will examine the patient and decide on hospitalization.