Cystic formations are often diagnosed pathologies of the central nervous system, which cause dizziness, a feeling of fatigue, headaches and other symptoms that bother the patient. After consultation with a specialist, diagnosis shows the formation of an arachnoid or retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain.
Untimely diagnostic measures lead to the destruction of neural connections, which is fraught with neurological disorders. In the article we will analyze in detail the reasons for the development of the anomaly, signs and treatment and preventive measures of retrocerebellar neoplasm.
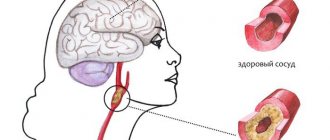
The formation of a head tumor causes dizziness, a feeling of fatigue, and pain in the head.
What it is
A retrocerebral cyst is a hollow capsule of a benign nature, which during its formation is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and affects those areas of the brain in which necrosis of the gray matter occurs. A characteristic feature of the neoplasm is that it directly affects the arachnoid membrane, which aggravates the clinical manifestations and complicates the treatment process.
The development of a retrocerebellar tumor in a child is considered a common phenomenon: in most cases, a cystic formation occurs as a result of a genetic mutation and precedes a cerebrovascular accident. Since a benign neoplasm is not aggravated by severe symptoms, it is impossible to detect it at an early stage of development and begin to eliminate it in a timely manner, which increases the risk of developing mental disabilities in the baby.
Classification
Based on the nature of the tumor, two types of tumors are distinguished:
- A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain is formed on the surface of the tissues that combine the outer membrane and the internal parenchyma and is filled with spinal substance.
- A retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain develops as a result of an inflammatory process, local hemorrhage or mechanical trauma. Often the reason for the formation of the retrocelebellar space is poor-quality surgery for pathologies developing in the head.
Depending on the origin, there are two types of cerebrospinal fluid cyst:
- A congenital tumor is formed as a result of a violation of embryonic development.
- An acquired tumor develops against the background of mechanical damage or inflammation of the brain structure.
Each type of cyst has its own developmental characteristics, which must be taken into account by the doctor when choosing treatment tactics.
Size and growth of the tumor
A hollow capsule, not exceeding two millimeters in diameter, develops asymptomatically over many years and is discovered mainly by chance - during a comprehensive examination. A small cyst in the brain is the norm and does not require therapeutic therapy: so that the doctor is able to monitor the condition of the tumor, the patient regularly attends an ultrasound procedure.
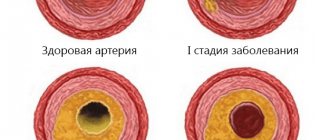
Since a retrocerebellar cyst often increases in diameter, patients ask their doctor about what size is dangerous. A cystic cavity reaching ten millimeters in diameter indicates a moderate severity of the pathological process and is a cause for concern if its volume continues to increase, provoking the destruction of brain cells.
If the cyst grows not only in width, but also in length, this process causes the rapid growth of a benign neoplasm into nearby tissues, as a result of which the risk of developing their necrosis increases. The main reason for the increase in cystic capsules is considered to be a disorder of cerebral blood flow: much less often the provoking factor is an infectious lesion and an inflammatory process.
Possible complications
A retrocerebellar cyst is a formation that can be large in size and clinically dangerous in location, which is associated with difficulties in treatment. Common complications:
- Ineffectiveness of therapy (medical, surgical).
- Formation of liquor-type hydromas (secondary cystic formation).
- Formation of intracranial hematomas with subsequent development of cerebral edema.
- Decompensation of impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Early postoperative complications include liquorrhea (leakage of cerebrospinal fluid), necrosis (tissue death) of the edge of the skin flap, and dehiscence of the surgical wound. Late complications include infectious lesions associated with the penetration of viral or bacterial agents into the wound.
Cystic retrocerebellar expansion is a formation most often located in the brain space behind the cerebellum. Symptoms of pathology depend on the size and exact location. It may be asymptomatic and then does not require treatment. In the presence of severe, progressive neurological symptoms, surgical intervention is usually performed.
Reasons for formation
The following are the causes of brain tumors:
- infectious diseases that contribute to central nervous system disorders - meningitis and encephalitis;
- damage to the cerebral cortex of an ischemic nature, caused by a failure of local circulation;
- abnormal structure of the organ, which is characterized by the absence of partitions between the cerebral hemispheres;
- receiving a brain injury as a result of poor-quality surgery;
- hereditary predisposition.
The main reasons for the appearance of congenital cysts are considered to be the use of medications by a pregnant girl that disrupt the embryonic development of the baby, as well as her prolonged stay in an area of poor environmental conditions. Marfan disease is also the cause of the formation of a primary tumor in a newborn.
Provoking factors
A neoplasm of this type can appear without obvious reasons, which significantly complicates its diagnosis. The factors that provoke its development are quite diverse. These include:
- circulatory disorders;
- concussions, head injuries;
- inflammatory processes caused by infectious influence;
- serious adverse changes in the brain;
- surgical interventions performed on the brain;
- previous stroke;
- genetic predisposition;
- birth injuries, negative effects on the fetus of medications taken by the mother during pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances in the body.
People with the above pathological conditions are at risk. The high probability of cyst formation requires regular monitoring by a specialist. It is necessary to visit him at least once a year to minimize the risk of unexpected development of this disease.
Symptoms and diagnosis
A retrocerebellar cyst, the diameter of which does not exceed two millimeters, develops asymptomatically, so the patient is not aware of its presence. When exposed to negative factors (blood flow disorder, development of an autoimmune process, infection), the cystic cavity begins to grow, which precedes the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
There are the following symptoms of a brain cyst:
- Headache that becomes constant and aggravated by migraine attacks.
- Disorder of the functioning of sensory organs: deterioration of hearing and vision.
- An unstable psycho-emotional state causes symptoms such as insomnia, apathy, and causeless irritability.
- A disorder of the vestibular system that causes constant dizziness and loss of balance in adult patients.
- Paralysis, which is temporary at the initial stage of tumor formation, becomes permanent as the pathological process progresses.
- Hydrocephalus, characterized by increased intracranial pressure. The main symptoms of hydrocephalus include drowsiness, excessive nervousness and nausea.
- Deterioration of brain activity: inhibition of thought processes.
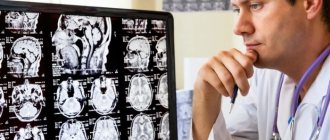
Diagnosis of pathology begins with an oral interview with the patient, during which the doctor determines the presenting symptoms and, based on the patient’s complaints, creates an individual history. Since the presence of specific symptoms is not enough to determine the diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient for a comprehensive diagnosis.
The examination traditionally begins with the patient taking a blood test, with the help of which the laboratory technician determines the concentration of cholesterol and assesses the degree of blood clotting. If the results of a laboratory test indicate an increase in cholesterol and a decrease in the coagulation rate, this is an indirect sign of a disorder of cerebral blood supply.
In order to determine the provoking factor, the patient also takes a blood test to detect autoimmune pathologies - sclerosis, infectious lesions of the central nervous system, arachnoiditis. Since stroke is considered a common cause of tumor development, the patient is monitored for blood pressure.
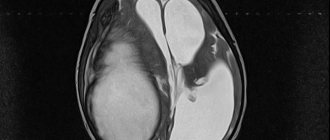
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered the fundamental diagnostic method. During the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the patient’s brain, which helps the doctor determine the exact size of the tumor and its location, as well as eliminate the possibility of the presence of malignant cells in the structure of the hollow capsule.
Another mandatory event is Doppler ultrasound. This procedure is aimed at assessing the patency of local blood vessels. If a pathological narrowing of the vascular walls was detected through diagnostics, this indicates a nutritional deficiency, which results in the development of necrosis of brain tissue.
Additional procedures
Additionally, the patient may be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- Blood tests. Indicators of coagulation and cholesterol levels will help clarify the condition of the blood vessels and existing blockages, due to which such a tumor often begins to grow. In addition, the presence of autoimmune and infectious pathologies is checked.
- Heart diagnostics. This procedure is necessary to identify disorders related to heart health, which is extremely important when performing surgery under long-term general anesthesia.
- Doppler ultrasound. Detection of areas of vascular constriction in the brain and spinal cord will mean that an insufficient volume of blood is supplied to the brain, and such a deficiency leads to the death of brain tissue cells and the appearance of pathological neoplasms.
- Pressure monitoring. Changes in blood pressure can provoke micro-strokes, as a result of which brain tumors begin to develop.
Immediately after determining the expansion of the retrocerebellar space and establishing a diagnosis, patients are prescribed the necessary treatment. It is necessary to start it quickly in order to exclude subsequent deterioration of the patient’s condition and the possible risk of complications.
Treatment methods
Depending on the size of the cyst, the characteristics of its development and the intensity of symptoms, the adult patient is treated conservatively or surgically. Retrocerebellar formation in children under 16 years of age is treated conservatively.
Conservative
The main goal of drug therapy is to normalize local blood supply and accelerate the process of resorption of hollow capsules. If there is a benign formation in the brain, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- antioxidant Synergin reduces the vulnerability of brain tissue;
- antiplatelet agent Aspirin increases blood clotting and dilates the walls of blood vessels;
- nootropic Cerebramin relieves oxygen deficiency;
- the anticoagulant Longidaz removes adhesions formed in the brain parenchyma;
- The antihypertensive drug Capoten stabilizes blood pressure.
If the provoking factor is an infectious process, the patient is also prescribed antibiotics and immunomodulators.
Operational
Failure of conservative treatment requires surgery. It is also advisable to perform surgical intervention in the case of rapid tumor growth and the development of concomitant symptoms that worsen the patient’s quality of life.
If the diagnostic results indicate the presence of an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the hollow capsule, the patient undergoes cerebral shunting. The operation takes place under general anesthesia: during the procedure, the doctor unites the affected vessels with healthy arteries, thereby stabilizing the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and improving local blood circulation.
The superficial location of the cystic sac is an indication for endoscopy. During the operation, the doctor makes two small punctures in the skull to gain access to the tumor, and then proceeds to resection of the hollow capsule and suctioning out its contents. Removing a brain cyst using the endoscopic method is strictly prohibited if the tumor is localized deep in the gray matter.
In advanced cases, a radical method is used - craniotomy. Despite the fact that the operation has a complex technique, it eliminates the risk of secondary tumor formation, since it involves the removal of not only the cystic sac, but also the tissues surrounding it.
Features of therapy
When diagnosing a retrocerebellar cyst, the patient is registered at a dispensary and the progression and severity of symptoms are monitored. If the tumor parameters do not change, there are no characteristic symptoms, there is no need for surgical intervention - only observations and conservative methods are sufficient.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures will only help at the beginning of the disease if there is no progress. Non-surgical therapy is based on the following areas:
- Treatment of arterial hypertension - drugs Berlipril, Captopril.
- Normalization of blood clotting with anticoagulants - Aspirin, Pentoxifylline.
- Reducing blood cholesterol levels.
- Improved blood circulation.
Homeopathy is effective only as a complement to the main treatment of the cyst. Alternative medicine also does not contribute to cystic resorption, but is used as a symptomatic aid.
In case of infection, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the body's protective functions.
Surgery
If it is not possible to stop the cystic growth with therapeutic methods, surgery is prescribed. Before surgery, specialists assess the extent of the lesion and choose the most appropriate method, taking into account the location and parameters:
- Endoscopy - a special device is used to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate.
An operation to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate from the brain.
- Creation of drainage - selected when there is a constant flow of fluid into the cavity.
- Craniotomy is a radical method that involves removing the cyst and adjacent tissues.
Attention! After surgery, patients need to rehabilitate - to normalize the functioning of the brain.
Why is it dangerous?
Every patient diagnosed with a retrocerebellar cyst needs to know why this pathology is dangerous. A benign brain tumor in a child precedes the manifestation of hypermobility and provokes impairment of both physical and mental development.
In adult patients, a brain cyst is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure, which causes the development of cerebral syndrome. This complication precedes the occurrence of chronic pain and the formation of oxygen deficiency.
Damage to brain cells during surgery provokes the manifestation of focal syndrome. The most common symptoms of the pathological process are hearing loss, motor dysfunction, and slurred speech.
Other possible consequences of the disease are high blood pressure and the presence of seizures. Often, a brain cyst contributes to the development of psychological disorders, as a result of which the patient experiences difficulties communicating with people.
In children
The appearance of cysts in children is especially dangerous, especially at a very young age.
They undergo active growth and development of tissues and systems, and the functions of each organ are determined.
If the disease is advanced, physiological and psychological disorders may occur in the future.
The clinical picture in children is as follows:
- There may be hearing impairment;
- Hands and feet go numb;
- Sometimes paresis and paralysis of the limbs (upper or lower, partially or completely) appear;
- Impaired coordination of movements.
When the formation rapidly increases in size, intracranial pressure rises. Symptoms indicate this:
- Constant severe headaches that do not go away when taking analgesics;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- You may notice swelling and pulsation of the large fontanel;
- Increased drowsiness;
- Fatigue, moodiness, weakness.
Prevention
You can prevent the development of a secondary type retrocerebellar cyst by following simple rules:
- Reducing the risk of injury and concussion.
- Timely elimination of infectious diseases.
- Control of cholesterol levels: increasing its quantitative indicator is an indication for taking medications.
- Regular preventive examination of the brain, which will assess the functioning of local blood flow.
Since children are also vulnerable to the development of brain cysts, during pregnancy a pregnant girl should maintain a healthy lifestyle, not abuse heavy medications and regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations.