Pulse examination has become a routine examination, which is often neglected in medical practice. Most people find it unnecessary and uninformative. This is a big misconception. A correctly performed technique can indicate the presence/absence of heart disease, inflammatory processes in the body, problems with blood pressure and many other pathologies.
Of course, the method is not specific enough to determine a specific diagnosis. But in order to navigate the state of health, it is optimal.
About the human pulse
Oxygen enters human organs and tissues with blood flowing through arteries (blood vessels through which blood is carried from the heart) under a certain pressure - arterial. This causes vibration of the arterial walls. The forward and reverse movement of blood to the heart also (normally) causes emptying and filling of the veins. Under the influence of blood pressure, red blood cells (red blood cells) are forced through capillaries (the thinnest blood vessels), overcoming high resistance; Electrolytes (substances that conduct electric current) pass through their walls.
This creates pulse beats that are felt throughout the body, in all vessels. An amazing phenomenon! Although in reality it is a pulse wave - a wave of movements of the walls of blood vessels under pressure, which is very fast and sounds like a short sound. The number of these waves normally corresponds to the number of heart contractions.
How to calculate?
The most accessible way to measure heart rate is palpation, a manual method based on touch.
Quick and simple, it does not require special training. To obtain the most accurate reading, place your index and middle fingers on the surface of the skin over the artery and count the pulse for 60 seconds.
You can also use a faster method by determining your pulse in 20 seconds and multiplying the resulting value by 3.
Treatment tactics
Depends on the specific reasons for the problem. For heart pathologies, surgical intervention is indicated to eliminate cholesterol plaques, defects, and install an artificial pacemaker.
For older women, this is especially true, since hormonal factors disappear or are reduced to a minimum. It is possible to treat kidney problems in the same ways.
Hormone replacement technique is another available way to eliminate the pathological condition.
Symptomatic therapy comes down to taking stimulating or inhibitory drugs as prescribed by a doctor in a strictly adjusted dosage. It is better to select treatment in a hospital setting.
When provoking tachycardia or bradycardia by physiological factors, they are eliminated by the patient himself. Quitting smoking, alcohol, or excessive exercise will definitely not make things worse.
Why can heart rate change at rest?
The main factors influencing changes in heart rate:
- when the temperature and/or humidity increases, the heart rate increases by 5 – 10 beats per minute;
- when moving from a lying position to a vertical one, heart rate increases in the first 15–20 seconds, then returns to its original value;
- heartbeat increases with tension, anxiety, expressed emotions;
- in people with large weight, the heart rate is usually higher than in people of the same age and gender, but with normal body weight;
- with fever, an increase in temperature of 1 degree is accompanied by an increase in heart rate by 10 beats per minute; There are exceptions to this rule, when the heart rate does not increase so much - these are typhoid fever, sepsis and some variants of viral hepatitis.
Reasons for the slowdown
First of all, you need to make sure that the pulse measurement is carried out technically correctly. A heart rate less than 60 per minute is not always associated with health problems. It can be caused by medications such as beta blockers.
Rare heartbeat (up to 40 per minute) is often observed in physically active people or professional athletes. This is due to the fact that their heart muscle contracts very well and is able to maintain normal blood flow without additional effort. Below we provide tables that allow you to roughly determine a person’s physical fitness by his resting heart rate.
Heart diseases such as ischemic heart disease, endocarditis, myocarditis, as well as some other diseases - hypothyroidism (insufficient hormonal activity of the thyroid gland) or an imbalance of electrolytes in the blood can lead to a slow heartbeat.
Reasons for the increase
The most common cause of accelerated heart rate is inadequate rest before measurement. It is best to measure this indicator in the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed. You should also make sure that your heart rate is counted correctly.
Children and adolescents have a higher heart rate than adults. Other factors that increase heart rate:
- use of caffeine or other stimulants;
- recent smoking or drinking alcohol;
- stress;
- high blood pressure.
Most illnesses increase heart rate, including fever, congenital heart defects, and hyperthyroidism.
Characteristic deviations for women
There are 3 characteristic reasons for the deviation of the pulse from the norm in healthy women, which are not always taken seriously by them:
- Excess weight (obesity is an official disease in medicine, which is classified by stages).
- Uterine fibroids (a benign tumor that can sometimes cause certain symptoms when it appears).
- Menopause (during this age period, women experience a natural increase in heart rate).
Excess weight
Fat deposits in the area of the internal organs interfere with the normal movement of the diaphragm, a breathing muscle located between the chest and abdominal cavities. As a result, the depth of breathing decreases. If you are overweight, hypoventilation of the lungs and shortness of breath occur even with light exertion.
To compensate for the lack of oxygen, the heart is forced to work faster to provide blood supply to the body. The closer your body weight is to normal, the better your heart functions.
Uterine fibroids
Another condition characteristic only of women is uterine fibroids. This benign tumor often does not cause any symptoms, but is accompanied by heavy menstruation and becomes the cause of chronic posthemorrhagic anemia.
The disease develops gradually, and the woman does not feel any sudden changes in her well-being. However, a constantly rapid pulse becomes a sign of tension in the cardiovascular system, which works in an enhanced mode to compensate for the lack of oxygen in the blood.
Climax
During menopause, women often experience rapid heartbeats, significant changes in blood pressure, sweating, and pain in the heart. Many people do not pay attention to this and do not get treatment. However, modern gynecology offers many means to improve well-being during this period. You shouldn't refuse this opportunity.
A deviation of the pulse from normal values in women can be an early or even the only external sign of many diseases. Paying close attention to your health and regularly measuring this indicator will help you recognize dangerous diseases at an early stage, when their course is reversible.
Peculiarities
Pulse - (Pulsus) translated from Latin means blow, push. The frequency and force of heart contraction causes vascular vibrations. If the subject is healthy, then they are rhythmic and have the same period of time. Rhythm disturbances, weakening or increasing pulsation indicate the development of the disease. There are 3 types in total:
Read also: How to properly use a nebulizer at home?
Arterial
It represents jerky movements of the walls of the arteries, which are formed due to periodic changes in blood filling.
Measurement
Heart rate is most often measured at the wrist joint of each hand for 1 minute. Each blow must be of equal force and at equal intervals. If no obvious deviations are found, the procedure lasts 30 seconds. The information received is doubled. If the doctor has doubts, the time is increased to 1 minute. In this case, an additional study may be prescribed using specialized diagnostic equipment. See also: How to choose a blood pressure monitor for home use for elderly people
Daily monitoring
This method allows you to identify disorders during the waking period under the influence of various everyday household factors, as well as during sleep.
Treadmill test
Testing will help determine and evaluate changes that occur due to physical education.
Where can you feel your pulse?
The pulse can be felt in several places on the human body and therefore can be measured:
- On the wrist - the radial artery pulsates
- Ulnar Artery - Look for the ulnar artery, which is located in the crook of the elbow.
- In the armpit
- On the temples
- Temporal artery above the eyebrows
- The neck is the location of the carotid artery
- Corner of the mouth (edge of the jaw) – there you can feel the facial pulse.
- Groin – here you can feel the femoral pulse
- Below the knee (where the leg bends is the popliteal artery).
- Foot or arch
Heart rate tables by age
To find out whether your heart rate is normal for healthy people, it should be measured and compared with the indicators presented in the table by age. In this case, a deviation from the specified standard will in most cases indicate unsatisfactory functioning of the vascular walls or improper functioning of the circulatory system as a whole.
For men
| Physical state | 1 age category | 2nd age category | 3 age category | 4 age category | 5 age category | 6 age category |
| Age table for men | 18 – 25 years old | 26 - 35 years | 36 – 45 years | 46 - 55 years | 56 - 65 years old | 65 and older |
| Athletes | 49-55 beats min. | 49-54 beats min. | 50-56 beats min. | 50-57 beats min. | 51-56 beats min. | 50-55 beats min. |
| Excellent | 56-61 beats min. | 55-61 beats min. | 57-62 beats min. | 58-63 beats min. | 57-61 beats min. | 56-61 beats min. |
| good | 62-65 beats min. | 62-65 beats min. | 63-66 beats min. | 64-67 beats min. | 62-67 beats min. | 62-65 beats min. |
| Better than average | 66-69 beats min. | 66-70 beats min. | 67-70 beats min. | 68-71 beats min. | 68-71 beats min. | 66-69 beats min. |
| Average | 70-73 beats min. | 71-74 beats min. | 71-75 beats min. | 72-76 beats min. | 72-75 beats min. | 70-73 beats min. |
| Worse than average | 74-81 beats min. | 75-81 beats min. | 76-82 beats min. | 77-83 beats min. | 76-81 beats min. | 74-79 beats min. |
| Bad | 82+ beats min. | 82+ beats min. | 83+ beats min. | 84+ beats min. | 82+ beats min. | 80+ beats min. |
What a person's pulse is is affected by his fitness and habit of frequent exercise that requires endurance - for example, medium and long distance running, walking, rowing, cycling, swimming. The heart muscle of such athletes is able to pump the same volume of blood in fewer contractions (athletic heart syndrome).
For women
| Physical state | 1 age category | 2nd age category | 3 age category | 4 age category | 5 age category | 6 age category |
| Age table for women | 18 – 25 years old | 26 - 35 years | 36 – 45 years | 46 - 55 years | 56 - 65 years old | 65 years and older |
| Athletes | 54-60 beats min. | 54-59 beats min. | 54-59 beats min. | 54-60 beats min. | 54-59 beats min. | 54-59 beats min. |
| Excellent | 61-65 beats min. | 60-64 beats min. | 60-64 beats min. | 61-65 beats min. | 60-64 beats min. | 60-64 beats min. |
| good | 66-69 beats min. | 65-68 beats min. | 65-69 beats min. | 66-69 beats min. | 65-68 beats min. | 65-68 beats min. |
| Better than average | 70-73 beats min. | 69-72 beats min. | 70-73 beats min. | 70-73 beats min. | 69-73 beats min. | 69-72 beats min. |
| Average | 74-78 beats min. | 73-76 beats min. | 74-78 beats min. | 74-77 beats min. | 74-77 beats min. | 73-76 beats min. |
| Worse than average | 79-84 beats min. | 77-82 beats min. | 79-84 beats min. | 78-83 beats min. | 78-83 beats min. | 77-84 beats min. |
| Bad | 85+ beats min. | 83+ beats min. | 85+ beats min. | 84+ beats min. | 84+ beats min. | 84+ beats min. |
Movement helps train the blood organs; Cardio exercises (from the Greek kardio, heart) with regularity significantly increase both the length of life and its quality. And they do not require any special means: even an ordinary walk (not even necessarily every day!) with a subjectively fast step instead of immobility fundamentally improves the condition.
Thus, the normal heart rate for a trained and physically healthy person may be lower than the generally accepted normal heart rate.
In childhood, the pulse is a very variable value and changes often. In a newborn, the heart contracts at a rate 2 times higher than in an adult. The older the child, the closer the values are to adults. During adolescence (about 15-18 years), the heart rate gradually decreases and is compared with the heart rate of adults.
Read also: Stress at work: prevention of professional stress
Average heart rate standard for children
The average reference values of cardiac pulsation in children differ quite significantly from the heart rate in adults. is considered normal for newborns .
As the child grows up, the heart rate gradually decreases and by the end of puberty (adolescence) it stops at 60-90 pulsations per minute . What indicators are acceptable for children are shown in the table.
It should be noted that the frequency of pulsation in children is different - one in the morning, completely different in the evening and during night sleep. The most optimal time to measure it is immediately after sleep.
Regularly measuring the child’s pulse will help prevent possible problems in time, or make sure that the child’s heart is functioning normally.
A fairly simple procedure for measuring your pulse will help you quickly diagnose the development of possible diseases.
If children have a rapid heart rate and it is not provoked by physical or emotional stress, this is a good reason to seek medical help.
Assessment of the body's condition
In general, the pulse shows only the state of the cardiovascular system, but since the processes occurring in the body are interconnected, we can talk about determining the entire functional state by heart rate.
Functional state refers to how well the body is prepared to withstand physical activity. To do this, use 3 main methods:
- Ruffier's test (lying position and subsequent squats).
- Martinet test (squats after sitting).
- Orthostatic test (lying and standing position).
The point is to measure the difference in heart rate in different states and whether this indicator corresponds to the norm.
Author of the article: Practicing physician V. O. Chubeiko. Higher medical education (Omsk State Medical University with honors, academic degree: “Candidate of Medical Sciences”).
What heart rate is considered normal for a child at 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 years old?
| Child's age | Minimum (normal) number of beats | Average (normal) number of beats | Maximum (normal) number of strokes |
| 6 years | 90 | 92 | 95 |
| 7 years | 83 | 85 | 90 |
| 8 years | 80 | 83 | 85 |
| 9 years | 80 | 83 | 85 |
| 10 years | 78 | 80 | 85 |
| 11 years | 78 | 82 | 85 |
| 12 years | 75 | 80 | 82 |
What heart rate is considered normal for a teenager at 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 years old?
| Child's age | Minimum (normal) number of beats | Average (normal) number of beats | Maximum (normal) number of strokes |
| 13 years | 72 | 75 | 80 |
| 14 years | 72 | 75 | 78 |
| 15 years | 70 | 73 | 76 |
| 16 years | 68 | 70 | 72 |
| 17 years | 65 | 67 | 70 |
During pregnancy
In pregnant women, starting from 20-22 weeks, an increase in heart rate is recorded. This is due to the increased volume of circulating blood. Often changes do not go beyond the maximum permissible limits. For example, at 3-5 months the number of strokes increases by 10-15, then until the 8th month it reaches maximum levels. By the time pregnancy is completed, it will stabilize.
Dependence on various factors
Contraction rates between 60 and 90 beats per minute are considered normal. However, it tends to change under the influence of certain factors:
- stressful situations;
- fatigue;
- binge eating;
- hypothermia.
You also need to take into account the time of day at which the measurement occurs. For example, in the morning the pulsation is the lowest, and in the evening it reaches its maximum level. In professional athletes, the parameters at rest often drop lower. This is due to the fact that when performing habitual physical exercises, the heart pumps a larger volume of blood and works much more intensely.
The difference by gender is insignificant - 5-7 beats/min. But during the period of hormonal changes, deviations may occur. Tachycardia is often observed during menopause in women (50-60 years old), during pregnancy, and also during cyclical changes. A much larger difference is observed when divided by age:
- significant excess is allowed in infants. This is due to rapid development;
- teenagers and young adults are subject to stress and anxiety. Tachycardia manifests itself most clearly in high school;
- in old people, indicators of 80-100 are recorded even during the rest period. This is due to wear and tear on the body. Even with little activity, the reaction is more pronounced than others.
How to measure the pulse on the hand on the wrist yourself and determine the pulse on the carotid artery?
Measuring your pulse is very simple:
- You will need to have a watch that will measure the time and number of heartbeats over a certain period of time.
- Calm down and sit down, find a quiet and peaceful room.
- Place the index and middle finger of your right hand at the site of the artery pulsation (wrist, neck or other part of the body).
- Record the time (from 30 to 60 seconds) and count the number of beats during this period of time.
- Check the data with the table
What heart rate is considered normal?
Heart rate is affected not only by diseases, but also by temporary external influences. As a rule, a temporary increase in heart rate can be restored after a short rest and elimination of provoking factors. What should be the normal heart rate for a person in various conditions?
At rest
The value that is considered the normal heart rate for an adult is actually the resting heart rate.
That is, when talking about the norm of a healthy heartbeat, we always mean the value measured at rest. For an adult, this norm is 60-80 beats per minute, but under certain conditions the norm can be 50 beats (in trained people) and 90 (in women and young people).
During physical activity
To calculate what a person’s normal heart rate is during moderate physical activity, experts offer the following mathematical operations:
- The maximum heart rate is calculated as the difference between the number 220 and the number of complete years of a person. (For example, for 20-year-olds this value will be: 220-20=200).
- Minimum heart rate value (50% of maximum): 200:100x50 = 100 beats.
- Normal heart rate under moderate loads (70% of maximum): 200:100x70 = 140 beats per minute.
Physical activity can have different intensities - moderate and high, depending on which the heart rate of the person receiving these activities will be different.
Let us remember that for moderate physical activity the heart rate ranges from 50 to 70% of the maximum value, calculated as the difference between the number 220 and the total number of years of a person.
When running
During high physical activity, an example of which is running (as well as speed swimming, aerobics, etc.), the heart rate is calculated according to a similar scheme. To find out what a person’s heart rate is considered normal while running, use the following formulas:
- Find out the difference between the number 220 and a person’s age, that is, maximum heart rate: 220-30 = 190 (for 30-year-olds).
- Determine 70% of the maximum: 190:100x70 = 133.
- Determine 85% of the maximum: 190:100x85 = 162 beats.
The normal heart rate when running ranges from 70 to 85% of the maximum value, which is the difference between 220 and the person’s age.
For burning fat
The formula for calculating maximum heart rate is also useful when calculating the heart rate rate for burning fat.
Most fitness trainers use for calculations the method of the Finnish physiologist and military doctor M. Karvonen, who developed a method for determining heart rate limits for physical training. According to this method, the target zone or FBL (fat burning zone) is a heart rate ranging from 50 to 80% of your maximum heart rate.
Read also How much water does a person need to drink per day to feel great? Simple formula
When calculating the maximum heart rate, the norm by age is not taken into account, but age itself is taken into account. For example, let’s take the age of 40 years and calculate the heart rate rate for life-saving lifestyle:
- 220 – 40 = 180.
- 180x0.5 = 90 (50% of the maximum).
- 180x0.8 = 144 (80% of the maximum).
- The heart rate ranges from 90 to 144 beats per minute.
Why is there such a discrepancy in numbers? The fact is that the normal heart rate for training should be selected individually, taking into account fitness, well-being and other characteristics of the body. Therefore, before starting training (and during it), a medical examination is necessary.
After meal
Gastrocardiac syndrome - a noticeable increase in heart rate after eating - can be observed in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems. A pathological condition is indicated by a heartbeat that is significantly higher than normal. Is there really a norm for heart rate to increase while eating?
Strictly speaking, a slight increase in heart rate during or 10-15 minutes after a meal is a physiological condition. Food entering the stomach puts pressure on the diaphragm, which forces a person to breathe deeper and more often - hence the increase in heart rate. Exceeding the normal heart rate occurs especially often when overeating.
But even if little food is eaten, and the heart still starts beating faster, this is not always a sign of pathology. Simply, digesting food requires an increase in metabolism, and for this a slight increase in heart rate is required.
The heart rate after eating is approximately equal to the normal value during moderate physical activity.
We have already learned how to calculate it, all that remains is to compare your own pulse after eating with the norm calculated using the formula.
Bradycardia
This type of arrhythmia is characterized by a reduced frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. The following types of bradycardia are distinguished:
- physiological, which is observed at complete rest or at night, the pulse does not decrease too much, and such arrhythmia is not considered a pathology and does not require treatment;
- parasympathetic - bradycardia, which is associated with the vagus nerve; Most often, attacks occur at night, in some cases after eating or intense physical activity;
- SA node weakness syndrome – when the sinoatrial node transmits signals to the heart muscle slowly, causing the rhythm to slow down;
- atrioventricular blocks, which appear due to defects in the synchrony of the contractile rhythm if the atria contract more often than the ventricles.
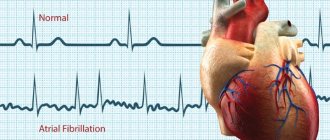
It is worth noting that bradycardia can sometimes occur without any symptoms at all, or can cause significant discomfort. In some cases, it can cause arrhythmic shock and lead to death. Very rarely there is a syndrome in which tachycardia and bradycardia occur simultaneously, and a slow and rapid heartbeat follows each other.
We looked at how to measure heart rate.
Symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances
It happens that a person may not notice an arrhythmia, but finds out about it during routine medical examinations. But more often the disease makes itself felt.
Signs of heart rhythm disturbances include:
- accelerated heartbeat;
- slow heartbeat;
- feeling the heartbeat;
- shortness of breath with minor exertion;
- chest pressure or pain;
- dizziness;
- fainting or lightheadedness.
general information
As a general rule, any primary medical examination begins with checking the basic indicators of the normal functioning of the human body. The doctor examines the skin, palpates the lymph nodes, palpates certain areas of the body in order to assess the condition of the joints or identify superficial changes in the blood vessels, listens to the lungs and heart with a stethoscope, and also measures temperature and pressure .
The listed manipulations allow the specialist to collect the necessary minimum information about the patient’s health status (make an anamnesis) and indicators of arterial or blood pressure play an important role in the diagnosis of many different diseases. What is blood pressure, and what are its norms for people of different ages?
For what reasons does blood pressure increase or, conversely, decrease, and how do such fluctuations affect a person’s health? We will try to answer these and other important questions on the topic in this material. We will start with general, but extremely important aspects.
Possible diseases due to changes in heart rate
In addition to heart disease, pulsation failures can cause the following diseases:
- problems of the thyroid gland (with insufficient function of this organ, the pulse slows down, and with hyperfunction, on the contrary, it accelerates too much, even sometimes causing flickering arrhythmia);
- osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine;
- poisoning (loss of electrolytes: potassium, sodium, chlorine, etc.);
- improper nutrition (fasting, incorrectly selected dietary supplements);
- kidney and liver diseases (if there are disturbances in the functioning of these organs, the blood is not sufficiently purified, therefore, it is more difficult for the heart to pump it).
If the heart rhythm is disturbed, complications may appear, namely:
- myocardial infarction;
- heart failure;
- sudden cardiac death;
- thromboembolism;
- acute circulatory disorder in the brain.
Causes of tachycardia
Tachycardia is manifested by increased heart rate and is divided into physiological and pathological. The first form occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- pain;
- physical and mental overload;
- taking medications;
- stress;
- hot weather;
- bad habits;
- drinking coffee and energy drinks.
Physiological tachycardia goes away on its own and rarely causes complications. The pathological form is a consequence of various diseases and malfunctions in the body:
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- oncological diseases;
- malformations of the heart muscle;
- diseases caused by infections;
- endocrine disruptions;
- anemia (anemia).
In women, the cause of tachycardia may be menorrhagia. It is a disorder in the menstrual cycle, which is characterized by large blood losses during menstruation.
In adolescence, the main cause of palpitations is autonomic failure. It develops under the influence of irritating factors (stress, overwork) and hormonal surges. The problem goes away on its own after puberty.
When to see a doctor if your heart rate is abnormal
Specialists who can help with such problems are a cardiologist and an arrhythmologist.
Symptoms for which a visit to a doctor is required:
- pain in the chest (often radiating to the neck, jaw, arms, back);
- shortness of breath and attacks of suffocation at night;
- increased blood pressure higher than 140/90;
- pressure drop is lower than 90/60;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- cases of loss of consciousness;
- purple lip color;
- swelling of the legs.
List of necessary examinations
Management of patients with arrhythmias is the prerogative of a cardiologist. At the discretion of the doctor, it is possible to involve third-party doctors: an endocrinologist, nephrologist and neurologist. Particularly difficult cases are resolved at a consultation.
An approximate diagnostic scheme looks like this:
- Questioning the patient, assessing health complaints. Essentially, identifying symptoms.
- Collection of anamnestic data. What did you get sick with, how, for how long and why. What treatment did you receive? And other questions of a similar nature. Specialists are also interested in the family history of pathologies.
- Electrocardiography. Study of cardiac activity using a special technique. It is impossible to read the result without appropriate qualifications. Even doctors don't always cope.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound diagnostics.
- Blood tests for hormones, biochemical indicators, formed cells, etc.
- Nephrological and neurological status.
- Assessment of specific reactions during palpation and physical examination.
Only the comprehensive nature of diagnostics makes it possible to quickly identify pathology.