- Read on the topic: Treatment of duodenal ulcers
- Diet for stomach ulcers
A gastric ulcer is a chronic pathology, often recurrent, the main symptom of which is the formation of an ulcerative defect in the wall of the stomach, penetrating into the submucosal layer. This pathology occurs with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
In developed countries, the incidence of the disease is approximately 10-15% of the population, and these are very large numbers. There is also a trend towards an increase in pathology among women, although previously it was believed that stomach ulcers were predominantly a male disease. Mostly people between 30 and 50 years old suffer from this pathology.
Morphology of the ulcer
The gastric mucosa is very durable, it can withstand the action of hydrochloric acid, the causticity of pancreatic enzymes, and hunger strike. Gastric juice kills 99% of pathogens, so a healthy person, even when eating stale food, most often has no consequences.
When a healthy person skips a meal, he or she may experience unpleasant sucking sensations in the epigastrium, but no more. Then he can take food again, and this will not affect his health. It's a completely different matter with an ulcer.
Here the mucous membrane is thinned, and pockets of inflammation may occur in it. These are gastritis, and neglecting the timeliness of meals is already painful. The mucous membrane is easily corroded by gastric juice, acidity increases. Eating any food at any time is no longer an option.
First, erosions form - more superficial damage to the mucosa. When moving into deeper layers (submucosal and muscular), ulcers appear. A healed ulcer is a scar.
Treatment with folk remedies
How to treat stomach ulcers was well known in ancient times, when pharmaceutical drugs were not yet produced. Many recipes are still used today, effectively complementing drug therapy.
One of the popular folk remedies that helps against ulcers is potato juice. It is squeezed through gauze from a grated tuber and drunk 0.5 cups in the morning an hour before meals. Course – 1 week.
The healing properties of herbal mixtures, which include celandine, yarrow, licorice root, and rose hips, are widely known. Decoctions are prepared from them, which you need to drink a tablespoon before meals.
With such a serious problem as peptic ulcer, you cannot self-medicate. Only a set of measures prescribed by a specialist can lead to healing. Before treating a stomach ulcer, an examination is carried out, and based on this, drugs for treatment and an appropriate diet are selected.
Mechanism of ulcer development
There is always mucus on the surface of the mucosa. It is produced by special cells of the stomach, its role is protective. Under stress, predominant vagal tone, or under the influence of hormonal disorders, mucus is produced in a smaller volume, and some area of the mucous membrane appears to be particularly weakened. The further mechanism is as follows: inflammation of the epithelium appears, which is expressed in some discomfort in the stomach area. If measures are not taken, the inflammation process goes deeper, the painful sensations intensify and are replaced by degenerative changes in the mucosa. Next comes erosion, the mucous membrane in some areas is deeply destroyed. This is where an ulcer forms, this is the mechanism of the so-called stress ulcer. With the integrity of the stomach wall, its functionality is also impaired.
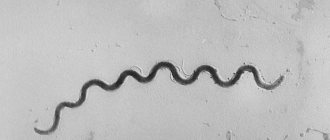
When H. Pylori penetrates the stomach wall, the bacterium uses its flagella. They attach it and remain in place for a number of years. It has the property of producing the enzyme urease, which breaks down urea into ammonia. And it already neutralizes hydrochloric acid, alkalization of the stomach environment occurs.
Nothing prevents bacteria from developing and multiplying, forming an infectious focus. Epithelial cells begin to die, the mucous membrane is destroyed and an ulcer appears.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery from peptic ulcer disease is favorable if the disease is detected in a timely manner. If the diagnosis was made correctly at an early stage and adequate therapy was completed, the patient will recover. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed with the consent of the patient.
An unfavorable prognosis if the disease has caused irreversible complications - 5% are fatal. They speak of complete remission if the disease has not made itself felt for more than 3 years. This should be confirmed by a full examination.
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to fight it later and “bite your elbows.” Therefore, it is worth listening to the signals that the body gives and undergoing appropriate examination so as not to develop a peptic ulcer.
Etiology of the disease
There are many reasons given, as well as theories, but none of them is a direct provocateur. The main factors for the appearance of ulcers are dietary errors, accompanying pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and an unhealthy lifestyle. Particularly harmful are repeated stress, irregular food intake, smoking and alcohol. All this leads to the fact that gastric juice has a destructive effect on the gastric mucosa.
In recent years, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori has been called the culprit of the ulcer. When it multiplies, it alkalizes the stomach, food digestion worsens, and gastritis with low acidity occurs. Currently, the presence of bacteria has been detected in almost all people, but they live in an acidic environment and do not cause harm to everyone.
Helicobacter pylori is a factor in the development of ulcers only in 40% of cases. Otherwise, the culprits are:
- abuse of spicy foods, poor diet, caffeine-containing and energy drinks;
- anomalies of the autonomic system;
- stress;
- infections that reduce immunity - HIV and tuberculosis;
- smoking and alcohol;
- uncontrolled use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
The provocateurs are:
- bad heredity;
- peritoneal injuries;
- anemia and hypovitaminosis;
- disorders in the lungs, heart and kidneys.
conclusions
Peptic ulcer disease in most cases occurs in emotionally labile people due to Helicobacter pylori infection. Features of the localization of defects determine the clinic of the pathological process. If a patient has a stomach ulcer, the symptoms and manifestations are usually undisputed and prompt him to see a doctor. Often, with an asymptomatic course, patients are not aware of the danger and do not consult a gastroenterologist. This hinders timely diagnosis and increases the risk of complications. Therefore, an important task is the prevention of diseases of the digestive tract and timely treatment of stomach pathologies.
Classification of stomach ulcers
So, the ulcer can be:
- with bleeding;
- with perforation;
- combined;
- without bleeding or perforation.
Systematization of YaBZh:
- in size: small – up to 5 mm; average – up to 1 cm; large – up to 3 cm; giant – more than 3 cm;
- by quantity - single and multiple ulcers;
- by stages of scarring;
- with latent, moderate and severe course;
- according to the level of acidity – hyperacid and hypoacid processes, zero acidity;
Depending on the location of a stomach ulcer, it can be:
- cardiac department;
- body of the stomach;
- antrum;
- pyloric;
- combined ulcers (simultaneously in the stomach and duodenum).
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the formation of ulcers. To prevent this you need to:
- prevent bacterial infection (observe hygiene rules);
- support immunity;
- adhere to a healthy diet (reduce the amount of fried and spicy foods, eat often and in small portions);
- treat provoking diseases in a timely manner;
- observe a sleep and rest schedule (at least 8 hours);
- do not be overloaded with physical and mental stress;
- avoid stress;
- comply with the dosage of prescribed medications.
If the diagnosis has already been made, you should not aggravate your condition. To do this you need:
- see a doctor regularly;
- undergo therapeutic courses as necessary (especially during exacerbation seasons);
- follow a diet;
- relax in a sanatorium.
Video on the topic: 5 rules for protecting yourself from stomach ulcers
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomach ulcers in adults at the initial stage do not differ from gastritis:
- Spasmodic drawing gastralgia in the center at the angle of the sternum.
- Sour belching.
- Heartburn.
- Intermittent nausea after eating.
- Decreased appetite and weight loss.
How to understand that a stomach ulcer has occurred:
- Nausea and pain become constant.
- Sour belching with bitterness.
- Heartburn.
- Vomit.
- Constipation.
- Decreased appetite.
What kind of pain occurs with a stomach ulcer? During an attack, the pain is unbearable and manifests itself in the form of contractions and spasms. Accompanied by tachycardia, pallor of the skin. After eating, heaviness and a feeling of fullness in the stomach often appear.
The nature of pain with a stomach ulcer can be supplemented by a fairly common symptom - this is pain at night. After eating or taking antacids it decreases and disappears. A white coating appears on the tongue, a heavy metallic odor from the mouth, and the skin changes. There is an aversion to food or a decrease in appetite, night hunger pains arise, which must be eaten, sweating increases and a tendency to constipation.
Other symptoms of stomach ulcers in adults: a person’s hair becomes dry and brittle, the complexion turns pale, the lips are dry, with puffiness in the corners of the mouth. The ulcer sufferer is constantly tired, anxious and irritable.
Where does it hurt with a stomach ulcer? Localized just below the ribs, the pain often radiates under the shoulder blades, into the sternum. Therefore, it can be confused with a heart attack. The danger of an ulcer lies in its silence: it can occur without symptoms, but the processes of destruction in the wall of the stomach continue. There is a risk of gastric bleeding and peritonitis. People with low acidity are at risk for developing cancer, while high acidity more often provokes perforation of an ulcer.
How does a stomach ulcer hurt? Pain is almost always present, even unexpressed. Already at the initial stage after eating, discomfort occurs. At first, this is felt only with harmful foods - pickles, smoked foods, fats, and then the sensation occurs with any food.
How does a stomach ulcer hurt? In ¾ of all patients, pain is localized in the center of the epigastrium. It is seasonal. In half of the patients the picture is blurred, but the pain always intensifies with physical effort, consumption of prohibited foods, and smoking.
Where does the pain from a stomach ulcer go? It tends to radiate to the heart area, back, and navel, which makes diagnosis difficult. There may also be other manifestations: flatulence, increased appetite, but quick satiety, decreased mood and poor sleep, hyperhidrosis of the palms.
Abdominal pain with a stomach ulcer usually gradually subsides after eating. They manifest themselves differently depending on the location of the ulcer. For example, an ulcer in the cardiac region has the following symptoms: pain occurs after eating 20 minutes, it is not sharp, it is located closer to the heart, in the upper abdomen. Accompanied by vomiting and nausea.
How does a stomach ulcer manifest itself (symptoms) with an ulcer in the lesser curvature? Here the ulcer is prone to perforation. A dangerous complication is peritonitis. The localization of pain is along the midline of the abdomen to the left. Occurs after eating at different times. Intensifies with a long break in use. Characterized by aching pain at night.
How does a stomach ulcer (symptoms) manifest on the greater curvature? This type is more often diagnosed in men over 30 years of age. More than 50% of such ulcers become malignant. The pain is mild and often goes unrecognized.
Characterized by the following features:
- the abdominal area ache slightly;
- nausea, maybe vomiting;
- no appetite, a whitish coating on the tongue;
- constipation.
How does a stomach ulcer (symptoms) manifest in the antrum? This type is diagnosed in 15% of cases, more often in young people. Gives complications in the form of bleeding and cancer. The symptoms are reminiscent of a duodenal ulcer: stomach pain when hungry, pain worse at night, persistent heartburn and vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the stomach and blood in the stool.
How does a stomach ulcer (symptoms) manifest in the pyloric part? Helicobacter pylori likes to settle here more often than other departments, which is why it got its name. The most characteristic signs:
- prolonged (more than half an hour) night pain;
- a lot of saliva in the mouth;
- the stomach is bloated after eating;
- heartburn and belching;
- sometimes vomiting sour;
- nausea.
Other signs
In addition to pain, among the signs of peptic ulcer disease, dyspeptic syndrome is of great importance. The signs are more painful for patients, they “drown out” and intensify the pain. These include:
- heartburn - worries up to 80% of patients, appears one and a half to three hours after eating, is persistent, caused by reflux of acidic contents into the lower part of the esophagus;
- belching - present in half of patients;
- nausea, vomiting - more often they appear at the height of a painful attack, they alleviate the condition, so patients learn to induce vomiting on their own.
Abnormal bowel movements in the form of constipation occur during an exacerbation in half of the patients. Changes in appetite are not very pronounced; a decrease in food eaten is associated with fear of pain. Feeling of fullness or bloating in the stomach.
Possible complications
Complications include the following:
- The most common occurrence is perforation of the ulcer followed by bleeding or peritonitis.
- Pyloric stenosis with the development of even obstruction.
- Malignization - the transition of an ulcer to a tumor - is observed in 2-12% of cases; The causes of degeneration have not been fully explored.
- Gastric perforation can occur suddenly and has a reactive development.
- Stomach bleeding in the form of small blood losses becomes the norm for the pathology. This is usually due to a damaged artery. Profuse bleeding occurs when an ulcer is perforated. Vomiting of “coffee grounds” is characteristic, the skin is pale, cold sweat appears, the pulse increases and decreases, the pressure drops, the stool turns black (melena). An urgent ambulance call and hospitalization are required.
- Penetration - occurs when the stomach wall is destroyed, when the ulcer moves to the surface of a neighboring organ. Most often this is the pancreas.
- Acute destructive pancreatitis - develops when gastric juice enters the pancreas.
Late type
There is also a late type of pain in ulcers, which occurs several hours after eating. They intensify when food passes into the duodenum. As has already become clear, these pains are characteristic of damage to this particular organ.
Please also note that people do not always feel any discomfort. However, many are afraid of the manifestation of a symptom of pathology and begin to eat as often as possible, which also has a bad effect on the patient’s condition.
Medications
Medicines prescribed:
- Groups of antibiotics used for Helicobacter pylori infection: macrolides (“Erythromycin”, “Clarithromycin”); penicillins: Amoxicillin"; nitroimidazoles: Metronidazole and its analogues. To destroy Helicobacter, 1-2 courses of antibiotics are prescribed.
- Antacids reduce the acidity of gastric juice and protect the walls of the stomach - Maalox, Rennie, Almagel, activated carbon and Polysorb.
- Antisecretory agents include: H-2 histamine receptor antagonists. They block the receptors of cells that produce hydrochloric acid - Ranitidine, Nizatidine, Famotidine.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the main drugs used in the treatment of ulcers. They block the final stage of the formation of hydrochloric acid: “Omez”, “Omeprazole”, “Rabeprazole”, “Rabelok”, “Lansoprazole”, “Pariet”, “Nexium”.
- Pain relief from stomach ulcers, which is not blocked by antispasmodics and antacids, is produced by M-cholinergic receptor blockers. There is only 1 drug and its analogues - “Pirenzipine” (“Piregexal”, “Gastrotsepin”, “Gastromen”).
- Protection of the mucous membrane - gastroprotectors: “Venter, De-Nol”, “Solcoseryl”, “Misoprostol”.
- To normalize acidity and increase mucus production, Cytotec and Misoprostol are used.
- Preparations for the repair of the mucous membrane – “Sucralfate”; “Biogastron”, “Kaved-S”, “Entrostil” also accelerate the restoration of the gastric mucosa.
- Bismuth preparations have an antiseptic, enveloping and astringent effect, for example, Vikalin.
- Ganglion blockers are aimed at blocking the passage of impulses from the sympathetic nervous system. This promotes the healing of ulcers and ultimately reduces pain - “Quateron”, “Benzohexonium”, “Dimecoline”.
How to relieve pain with a stomach ulcer? Just the above-mentioned drugs.
How to identify the disease?
The patient's complaints and medical history help the doctor suspect a peptic ulcer. However, in order to accurately diagnose the disease, therapists prescribe a number of special procedures.
Methods for detecting stomach ulcers:
- Complete blood count - Decreased number of red blood cells and hemoglobin (anemia), increased ESR
- Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) - Using a special rubber tube with a camera (fibrogastroscope), the doctor can see with his own eyes the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. This method also allows you to perform a biopsy of the organ wall, that is, pinch off a small piece from it.
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast - The technique is currently somewhat outdated. Its essence is as follows: the patient drinks a barium contrast mixture. The radiologist then takes a series of pictures that show how the contrast moves through the mucosa. The presentation of a peptic ulcer is usually described as a “niche symptom.”
- pH-metry and 24-hour monitoring of gastric juice pH - This is an invasive and painful technique that allows you to assess how aggressive gastric juice is in relation to the mucous membrane.
Methods for identifying Helicobacter:
- Serological - Detection of antibodies in the blood to H. pylori
- Radionuclide urease breath test - Based on the release of urea by a microbe, which comes out with the air. The technique is safe; to detect Helicobacter, you only need to breathe into a special container.
- Stool test - Detection of Helicobacter antigen in stool, used to determine the effectiveness of treatment
- Rapid urease test - Performed after fibrogastroscopy. The resulting piece of mucous membrane is tested with a special indicator that detects H. pylori
Operation
Surgical intervention is indicated in the following cases:
- ulcer perforation, bleeding;
- cicatricial narrowing of the pylorus;
- there has been no effect from conservative treatment for more than six months;
- frequent exacerbations – up to 4 times a year;
- ulcers suspicious for malignancy.
The operation is performed using a classic incision or laparoscopy.
Excision of the ulcer is performed - resection, intersection of the vagus nerve (to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and create conditions for scarring of the ulcer).
In addition, physical therapy, herbs, and diet help. Treatment of concomitant stomach diseases is mandatory.
Physiotherapy is applicable outside of exacerbations: electrophoresis, ultrasound, UHF. Spa treatment is useful.
Nutrition of the sick
There are two main requirements for food: it must be complete and protect the mucous membrane from chemical and physical damage. It is recommended to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions. Dishes should be finely ground or liquid, not hot or cold, boiled or steamed (see the detailed article on nutrition - what you can eat with ulcers and gastritis).
What can you eat? | What should be strictly excluded? |
|
|
Night pain
This type of pain is typical for a duodenal ulcer and belongs to the group of “hungry” hunger. It also appears on an empty stomach. Many ulcer sufferers have noticed more than once that they can wake up in the middle of the night with severe attacks. The pain can be of different types:
- pulling;
- aching;
- cutting.
A light snack or glass of warm milk can help relieve this symptom.