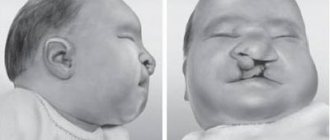
Due to the development of neck deformation, as a result of the development and growth of the child, deformed posture and the skeleton as a whole appear, and impaired symmetrical development of the head is observed.
Torticollis in children is a fairly common pathology, which is more often observed in girls. In some cases, it is considered as one of the developmental defects.
Torticollis in newborns is the third pathology, taking its place after congenital clubfoot and hip dislocation.
In the vast majority of cases, people experience muscular torticollis.
Classification
In medicine, the disease is divided into two main types of torticollis
- congenital torticollis is a form of the disease that appears in a child at birth;
- acquired torticollis is a form of the disease resulting from abnormalities in the development of the skeleton or disorders of muscle tone.
Anatomical landmarks of tissues affected by the disease make it possible to distinguish several more types of torticollis.
Anatomical types of torticollis
- cutaneous form - the skin and subcutaneous tissue are affected;
- desmogenic torticollis - the result of inflammatory processes in the neck, for example, abscesses, phlegmons or lymphadenitis;
- myogenic – a consequence of damage to muscle tissue;
- neurogenic form – a form of the disease in which the receptor muscle-nerve apparatuses are affected, with subsequent disturbance of muscle tone;
- arthrogenic torticollis – develops as a result of damage to the joints of the cervical spine;
- osteogenic – a form in which the osteochondral apparatus is damaged, additional processes of the cervical vertebrae, false cervical ribs, etc. are formed;
- installation torticollis – develops in children as a result of the child being in one position for a long time;
- Spasmodic torticollis is one of the forms of muscular torticollis, also considered a form of development of a disease called dystonia.
Congenital torticollis
When the diagnosis is made after the birth of the baby, this indicates that the pathology arose during pregnancy. The causes of congenital pathology are:
- infection;
- incorrect structure of the pelvis of the expectant mother;
- malposition;
- change in the length of the sternocleidomastoid muscle;
- a number of hereditary diseases;
- gene mutations.
According to statistics, torticollis ranks third among common childhood pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. In first and second place are clubfoot and congenital hip dislocation. Girls are more often affected by the disease.
Types of congenital torticollis
Most often, a change in the shape of the neck occurs due to pathology of the sternocleidomastoid (sternocleidomastoid) muscle. This paired part of the musculoskeletal system is attached at one end to the mastoid process of the skull behind the ear. The other end of the muscle is fixed on the collarbone. The function of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is tilting and turning the head, as well as circular movements of the head. Impaired functioning of this particular department leads to torticollis.
There are several types of congenital torticollis:
- Idiopathic torticollis. The disease is characterized by a slight unfixed tilt of the head. Its causes are currently not fully understood. Research shows that the disease usually appears as a result of pathology during pregnancy and difficult childbirth. If you feel the muscle with your fingers, you can feel its tension. At the same time, the length and shape of the sternocleidomastoid muscle are normal. Idiopathic torticollis is often accompanied by perinatal encephalopathy. This disease is associated with a disorder of the central nervous system in newborns and infants in the first months of life. Develops as a result of damage to the child’s brain during pregnancy or during childbirth. A concomitant disease is a functional disorder of the cervical spine.
- Myogenic torticollis. This type of pathology is the most common. A characteristic sign of the disease is thickening and change in the length of the sternocleidomastoid muscle; it is shorter than a healthy one. The disorder is detected either immediately in the maternity hospital or in the first month of the child’s life. The cause of the pathology is a prolonged intrauterine position of the head tilted towards the shoulder, or a disturbance in the development of muscle fibers and tendons. This usually happens when the fetus is breech, that is, the baby is in the pelvis with his buttocks or buttocks and feet. As a result, fibrosis of the muscle appears, as a result of which it becomes inelastic. Externally, the pathology manifests itself in the tilting of the child’s head to the side and turning it in the opposite direction. Attempts to turn the head cause pain for the newborn. Myogenic torticollis, if not corrected, causes impaired development of bones, muscles of the skull, shoulder girdle and scoliosis. In addition, the symmetry of facial features is disrupted. On the affected side, the eyes, eyebrow and ear are located lower than on the healthy side.
- Osteogenic torticollis. Its cause is pathology of the cervical vertebrae. The disease is also called Klippel-Feil disease. Appears if the size of the vertebrae is smaller than normal or their shape is changed, or the vertebrae are fused into one complex. This leads to impaired neck mobility. In the presence of the disease, the newborn’s head is externally pulled into the shoulders, sometimes turned to the side, hair growth on the back of the head begins lower than usual, and low neck mobility. Osteogenic torticollis does not cause pain, but it leads to radiculitis of the cervical spine. The disease occurs due to inflammation of the nerve fibers, which is accompanied by pain when moving and is difficult to treat.
- Neurogenic torticollis. The pathology develops due to increased muscle tone on one side and decreased muscle tone on the other. This disorder is called dystonic syndrome. The cause of the disease is a number of infections that lead to damage to the nervous system. Externally, the newborn's head is tilted, one arm is clenched and the leg is bent; no abnormalities are observed on the other side. If you lay your baby on his stomach, his spine will be shaped like an arc. At the same time, the child moves his neck freely.
- Arthrogenic torticollis. The disease is caused by malformations in the cervical spine. These include, for example, damage to the intervertebral disc due to trauma, or wedge-shaped deformation of the vertebra, that is, underdevelopment of the lateral or anterior part of the vertebra. Externally, the baby's head tilts towards one shoulder and is turned towards the other. Turns and movements of the neck are very limited and cause pain. This type of pathology can be congenital or acquired.
Infantile torticollis can be unilateral or bilateral. In the second case, the disease develops as a result of disturbances in both sternocleidomastoid muscles. In this case, the newborn's head is tilted towards the chest. Neck movements are limited.
Question answer
Is it possible and necessary to use a special Shants collar to correct torticollis?
Yes, such treatment is welcome, but subject to conditions. Only a doctor should recommend wearing a collar; he will also select the required size and show you how to put it on and take it off correctly. Wearing a collar should be combined with other conservative techniques, and it should be worn to consolidate success after physiotherapy, massage and therapeutic exercises. You can start wearing a collar from 7 months of age.
How to choose the right orthopedic pillow for your baby?
Firstly, you should focus on the filler; it must be breathable, so if the child turns over face down, he will not suffocate. Secondly, you need to inspect the seams of the pillow, they should be well stitched and tucked in, the filling should not protrude through the seams. Thirdly, inspect the pillow cover to see what fabric it is made of. Preferably natural ones (cotton or linen), such pillows are easy to wash. And lastly, choose pillows with hypoallergenic filling (holofiber, padding polyester).
How to prevent the development of torticollis in a newborn?
The risk group for the occurrence of the disease includes mothers with complicated childbirth, various infections during pregnancy, as well as children born in a breech position. Disease prevention should begin immediately after discharge from the hospital. Place the baby on his stomach as often as possible, conduct a daily light body massage, paying special attention to the neck, perform health-improving exercises, alternating bending over with head turns, play with the baby so that he alternately turns his head in one direction or the other.
Author:
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Acquired torticollis
Pathology that appears in the first months after birth is less common than congenital. The causes of congenital torticollis are:
- difficult childbirth (which, for example, took place when the umbilical cord was entwined);
- injury to the neck muscles of a newborn;
- ischemia.
Later, torticollis can develop as a consequence of diseases of the nervous system, injuries, or a number of infections.
Neck curvature, which is caused by subluxation of the C1 cervical vertebra, is easier to treat than others. Its cause is high loads on the cervical spine. It can also be caused by a sharp turn of the head.
Diagnosis of torticollis - examination program for newborns, older children and adults with torticollis
Diagnosing the disease in question is quite easy.
During the examination, the doctor evaluates active and passive movements in the neck area and pays attention to the posture that the patient takes .
The main diagnostic procedure is also palpation , during which changes in muscle cords can be determined.
In order to determine the exact cause of the development of this orthopedic pathology, additional diagnostic procedures may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the spine. Makes it possible to exclude or confirm injury to the spinal column, anomalies in its structure (for example, fusion of the cervical vertebrae).
- Electromyographic study. Allows you to check the quality of conduction of nerve impulses by muscle tissue.
- MRI. Allows a specialist to study questionable areas in more detail.
- Consultation with a neurologist. The specified doctor conducts research to determine the presence of neuralgic disorders that could cause torticollis.
- Biochemical blood testing. Carry out if rickets is suspected. In this case, the level of micro- and macroelements in the taken blood sample is checked.
An accurate determination of the root cause will make it possible to select the most adequate treatment - and avoid complications in the future.
Rate
—
Types of acquired torticollis
For reasons and characteristic signs, several types of acquired torticollis are distinguished:
- Installation. The cause of the pathology is the newborn staying in one position for a long time. For example, the disease can develop if the baby lies in the crib on one side all the time or does not change position during feeding, lying in the arms of adults. The disease does not cause pathological changes in the muscles and spine.
- Desmogenic. The disease occurs as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes, which is caused by a cold or severe hypothermia. These changes cause changes in the position of the neck.
- Dermatogenic. After burns, when the scars heal, they tighten the skin, forcing the neck to change position. Various injuries can cause similar consequences.
- Osteoarticular, or traumatic. The cause of the disease is injury or fracture of the first cervical vertebra, which is called the “atlas”. Touching the injured area causes severe pain, as does moving the neck.
- Infectious. Diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis lead to melting or fracture of the cervical vertebrae.
- Grisel's disease. Usually develops in children 6-10 years old. It occurs as a result of inflammation of the soft tissues of the pharynx or pharynx, which causes subluxation of the first cervical vertebra. A characteristic sign of the disease is a tilt of the head towards the shoulder.
In addition to the listed types of pathology, spinal tumors lead to torticollis. There is also such a thing as “hysterical torticollis.” The cause of dysfunction of the neck muscles is an unnatural turn of the neck. Pathology appears as a consequence of hysterical psychosis.
Consequences
An undiagnosed disease and the absence or late start of treatment leads to the following consequences of torticollis:
- facial asymmetry and deformation;
- spinal curvatures: lordosis/kyphosis, scoliosis;
- pain in the spine – osteochondrosis;
- dysfunction of the spine provokes the development of clumsiness, instability and lameness;
- strabismus due to facial asymmetry and hearing problems;
- constant headaches, vegetative-vascular dystonia, as a result of curvature of the spine and circulatory disorders in the brain;
- delay in physical and psychoneurological development (the child sits up late and does not get up on his feet for a long time, starts walking late;
- flat feet;
- cosmetic defect - the head is constantly tilted to the shoulder.
Symptoms of torticollis
It is not difficult to guess that the most obvious symptom of torticollis is a tilt of the head towards the shoulder. Other signs of the disease are:
- turning the head in the opposite direction from the tilt;
- facial asymmetry;
- restriction of movements and turns of the neck;
- in some cases, the sternocleidomastoid muscle is clearly enlarged;
- forced rotation of the head causes discomfort and pain, the baby actively resists and begins to cry.
During life, if torticollis is not treated, secondary signs of the disease appear. These include gait disturbances, headaches, scoliosis, etc. Sometimes the disease causes strabismus.
Let us add that, as a rule, congenital torticollis is noticeable immediately after the baby is born. Sometimes it is diagnosed a few days after birth. The late form of the disease appears in the second or third week.
It also happens that a mild form of pathology goes unnoticed by parents and pediatricians for 2-4 months.
How to treat an infant at home - stages of recovery
To correct pathological shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and achieve its alignment with a muscle of normal length, a whole range of measures is recommended:
- carrying in your arms and laying the child on his side in a special way - this technique is called “positional treatment” and is necessary for the physiological stretching of muscle fibers;
- performing a massage on the affected area to enhance the tone of the weakened area, activate blood circulation and relieve inflammation;
- the use of orthopedic devices that help temporarily relieve the load on the cervical spine - Shants collar, pillows and bolsters of a certain design;
- performing physical procedures such as heating with lamps and electrophoresis and taking medications prescribed by a doctor to relax smooth muscles;
- physical therapy classes that involve the development of certain muscle groups according to age parameters.
Let's look at each stage of treatment for torticollis in more detail. Start with the simplest steps. For example, rotate your child's bed so that he or she has the best possible view. Approach your baby, communicate and place toys on the side where it is still difficult for him to turn. In order not to overdo it and not transfer the torticollis to the other side, control the situation - let for every 2 approaches on one side, 1 on the opposite side.
It is best to place the child in the correct position during the day, during lunchtime nap. Check the firmness of the mattress - it should be medium. Replace the regular pillow with an orthopedic one or a diaper folded in several layers so that its thickness is equal to the distance from the head of the lying child to the level of the crib.
To maintain the symmetry of the body in relation to the head, place two rolls rolled out of a blanket under the barrels (enough to cover the length from the armpits to the knees). But remember - if the child is prone to regurgitation, this method of correction is excluded, and he must be moved into the correct position manually.
It is important to understand whether you correctly pick up and carry a child with torticollis in your arms. Test yourself how to do it:
- The child must be smoothly transferred to a vertical position facing you, pressing his shoulders to yours. After this, gently turn the baby to the painful side, fixing its position with your own cheek.
- In exactly the same way - supporting the correct position of the head with your cheek - you can carry the baby in a position with his back to you and on his side.
- When communicating with your child, stimulate the rotation of the head and body by showing bright toys and drawings from the left to the right.
Place a baby diagnosed with “acquired torticollis” on his tummy or healthy side, ensuring that he often looks in the direction opposite to the problem area, thereby stretching the muscle. And to speed up the process, in consultation with your doctor, add massage treatments and physical therapy.
Strabismus due to torticollis
A defect such as strabismus occurs quite often in children. Its cause is usually uncoordinated work of the eye muscles or decreased tone in them. With strabismus, the eyes do not focus on one point. The organs of vision receive incorrect alignment, as a result of which they deviate away from the normal angle of vision. Simply put, strabismus causes each eye to focus on a different point. In a healthy state, the brain combines the image received from both eyes into one picture. Strabismus disrupts this balance. As a result, the patient sees a double picture, and subsequently the eye with the pathology is completely excluded from the vision process. Strabismus in a child can be congenital or acquired.
Often, strabismus and torticollis are closely related. This is explained by impaired muscle function. With torticollis, the neck muscles fix it in an unnatural position. In turn, the eye muscles are forced to adapt to this position in order to level the horizon. The patient tries to see objects located on the opposite side. As a result, strabismus develops. Eye problems begin almost immediately after torticollis occurs.
In this case, treatment should first of all be aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. That is, in order to remove strabismus, it is necessary to get rid of torticollis.
Sometimes the process goes in the opposite direction. As a result of strabismus, a newborn develops torticollis.
Treatment of torticollis
Diagnosis of a crooked neck includes an examination by a neurologist and an orthopedist, as well as procedures such as ultrasound of the neck muscles and x-rays of the entire cervical spine.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed. There are two types of therapy - conservative and surgical. In the first case, therapy will consist of massage, physiotherapy, physical therapy and medication. The second method involves surgery. It consists of crossing the heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The operation is classified as simple and gives a good prognosis for recovery. If the cause of the pathology is different muscle lengths, plastic surgery is performed to lengthen the short muscle.
Neurogenic torticollis is eliminated with drugs that reduce muscle tone and excitability of the nervous system. Massage and exercise therapy are also prescribed.
For desmogenic and dermatogenic torticollis, only surgery will help. The method involves removing scar tissue and performing cosmetic plastic surgery.
When the cause of the disease is tumors or infectious bone pathologies, the disease that led to the defect is first treated.
Diagnostics
To diagnose torticollis, you should make an appointment with an orthopedist, neurologist or surgeon. At the appointment, the doctor first palpates and examines the neck, checks muscle tone, head mobility, and assesses the presence of deformation in the bone tissues of the skull.
After the examination, hardware diagnostics of torticollis may be needed for a more detailed assessment of the disorder in the tissue structures.
Hardware diagnostic methods:
- X-ray. One of the simplest and most accessible ways to diagnose torticollis. Allows you to assess the presence of bone deformation in the neck and skull;
- MRI. The most detailed diagnostic method. Allows you to visualize the condition of not only bones, but also muscles, blood vessels and nerve fibers. MRI is painless and can be performed multiple times within a short period of time;
- Dopplerography of the vertebral arteries. Allows you to assess the condition of the walls and patency of arteries and vessels;
- electroneurography. Detailed examination of the condition of the nerve fibers of the head and neck.
The doctor can prescribe one or more hardware diagnostic methods to the patient, after which he can accurately determine the presence and degree of torticollis, as well as prescribe treatment.
Prevention of torticollis in infants
To avoid problems with incorrect neck position, you need to carefully monitor the baby's development. You should not skip visits with your newborn to the therapist. The correct position during sleep is of great importance in the prevention of torticollis in infants. Since after birth the baby spends most of the day in the crib, this particular item should be given special attention. Experts do not recommend using a pillow for up to two years. The mattress should be hard. This way, the baby’s head will lie straight, and posture will be formed correctly from birth.
The baby should be laid in a different direction each time. Experts also recommend placing objects that attract the child’s attention in different parts of the room. So the baby will turn his head in different directions to examine them.
If a child has a cervical spine deformity from birth, treatment should begin immediately. During infancy, the skeleton is still quite flexible, so proper treatment will help completely get rid of the pathology.
Delaying treatment or lack of any treatment subsequently leads to serious health problems. With age, a deformed organ affects the development of the entire organism. In one hundred percent of cases, the child develops scoliosis.