As sad as it is to say this, women’s problems lie in wait for a girl from the moment of her birth. Vulvitis in girls occupies the top line in the list of gynecological diseases and reaches 70%. The most vulnerable category of girls for this pathology are girls aged 1–9 years. This pathology requires immediate treatment, as it not only causes a lot of inconvenience and anxiety to the child, but also threatens the development of serious complications that may affect sexual and reproductive functions in the future.
Etiology
The main reason for the development of vulvitis as a given disease is tissue damage by microorganisms or fungi. Bacterial flora can be completely different, both specific and non-specific.
Factors contributing to the inflammatory process:
- Foci of chronic infection. These can be either severe systemic diseases or simply a long-term persistent infection. Such pathologies include damage to the urinary system, digestive tract, endocrine pathologies, especially those that disrupt metabolism in the body. The most common cause is infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract and pharynx.
- Helminth infestation of the body, in particular the rectum . These could be roundworms or pinworms, which, affecting the area of the external opening of the direct passage, spread to the vulva area.
- Entry of foreign objects , this can be accidental or intentional. Most often it occurs in young children who play in the sand or in the sea, most often without panties. Particles of dust, dirt, sand, etc. get onto the surface of the vulva or inside the vagina, which provoke an inflammatory reaction.
- Decreased immune system , this can be caused by autoimmune diseases or viral etiology, as well as long-term use of antibacterial agents.
Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of such a common type of inflammation of the vulva of an allergic nature, which occurs against the background of increased sensitivity of the body to environmental factors:
- It can also be the consumption of specific foods such as chocolate, citrus fruits, etc. The use of personal hygiene products containing dyes, fragrances and irritating components.
- Too frequent and incorrect use of diapers, diapers, personal hygiene products . And also in combination with them with powders, ointments or napkins.
- Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene , this can be either too frequent or, conversely, infrequent washing with the wrong technique.
Causes
The high likelihood of developing the disease in girls is due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the vulva. At the moment of birth and several hours after it, the child’s vagina remains sterile and only by the 5th – 7th day of life is it populated by opportunistic microflora. The reaction of a girl’s vaginal contents before the onset of puberty remains alkaline or neutral, since the vaginal microflora does not contain lactobacilli that produce lactic acid.
The absence of lactic acid in the vaginal contents reduces local protection against infectious agents, and a reduced number of sweat and sebaceous glands on the skin of the vulva, incomplete closure of the genital opening, and delicate and vulnerable skin of the external genitalia increase the risk of developing inflammation of the vulva.
Primary nonspecific vulvitis
The cause of primary nonspecific vulvitis is opportunistic microorganisms that live in small quantities in the vagina (protozoa and yeast fungi, anaerobes, proteus and others).
- Recurrence of episodes of nonspecific inflammation of the vulva is typical for girls who suffer from chronic somatic diseases (pathology of the urinary system, hormonal diseases: diabetes, hypothyroidism, blood diseases, etc.).
- It has been noted that the frequency of inflammatory processes of the external genital organs increases in children who often suffer from diseases of the nasopharynx (tonsillitis and chronic tonsillitis, rhinitis, ARVI).
- In addition, nonspecific infectious vulvitis can be caused by helminths (in particular pinworms),
- penetration of foreign bodies into the vagina during play (sand, insects, blades of grass).
- Factors that weaken the body's immune defense also play a role in the development of the disease (antibiotic therapy, lack of vitamins, immunodeficiency states).
Allergic atopic vulvitis
Separately, the causes of allergic vulvitis (or atopic) should be highlighted.
- its development is promoted by some highly allergenic foods (chocolate, citrus fruits, strawberries)
- hygiene products with aromatic additives (soap, sanitary pads)
- synthetic underwear
- In girls of infancy, the occurrence of the disease is provoked by diaper dermatitis
- the mother’s excessive enthusiasm for the baby’s hygiene (frequent and unnecessary washing, the use of ointments, powders and creams), which leads to irritation and disruption of the integrity of the skin and vulvar mucosa
- non-compliance with hygiene rules and the use of general hygiene items (towels, washcloths) contributes to the development of the disease in older girls
- If a teenage girl is sexually active, sexual transmission cannot be ruled out
Specific pathogens of the disease are gonococci and trichomonas, chlamydia and ureaplasma, tuberculosis and diphtheria bacilli, genital herpes virus and human papillomavirus infection, fungi and pathogens of childhood infections (measles, scarlet fever and chicken pox).
In newborn girls, inflammation of the vulva can be caused by infection of the child during childbirth through the infected birth canal of the mother or transplacental infection.
Classification
Depending on the type of development, as well as the duration, vulvitis in girls should be divided into several groups:
- Acute inflammation (usually lasts up to 1 month)
- Subacute inflammation of the vulva (duration can be several months, periodic extinction or exacerbation of symptoms is observed)
- Chronic (symptoms of the disease may worsen over several years)
Depending on the factors that caused vulvitis in girls:
- Bacterial vulvitis
- Fungal vulvitis
- Non-infectious vulvitis (Trauma, chemical damage, allergic nature)
According to the mechanism of infection:
- Primary. In direct contact of the pathogen with the body.
- Secondary. Persistence of the pathogen in the body, chronic infections.
Types of vulvitis according to the age period during which inflammation occurs:
- Vulvitis of newborns.
- When the child is under one year of age.
- Vulvitis of childhood.
- Prepubertal vulvitis. Until the first period appears.
- Vulvitis of puberty.
Folk remedies
Photo: odkrywamyzakryte.com
Treatment of vulvitis at home
Vulvitis can be treated both with medication and using traditional methods. Medicinal plants will quickly and effectively help cope with this disease, which has no age restrictions, as a result of which both young children and the elderly can get sick.
Treatment of this disease is carried out internally and externally.
Alternative treatment for vulvitis internally:
- Stinging nettle. The juice of this plant is consumed 1 tsp. 2-3 times a day. Nettle has long been considered a strong multivitamin and helps replenish vitamins and regulate hormonal imbalances.
- St. John's wort. It is useful in the treatment of many diseases, is a strong antiseptic and helps the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and inflammatory processes in gynecology. An infusion is made from St. John's wort and consumed ¼ tbsp. 2-3 times a day.
- Kalina. Just a storehouse of vitamins. It contains a lot of ascorbic acid, phosphorus, organic acids, carotenes, tannins and is responsible for strengthening the immune system, healing wounds, and replenishing energy. A decoction is made from its flowers: they are poured with boiling water, boiled for about 12 minutes, cooled and infused. Must be consumed in quantities of 1 tbsp. 20 minutes before meals.
- White acacia juice is actively used for gynecological diseases. White acacia can be consumed in different ways: you can simply chew the flowers
- you can prepare an infusion: 1 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water over acacia leaves. Cool, strain. Take a tablespoon before meals for at least four weeks.
Alternative treatment for vulvitis externally:
- Effective folk treatment for vulvitis is carried out by collecting herbs, which include: tansy leaves, plantain leaves, celandine, calendula and chamomile flowers. This composition is poured with hot water (1 liter), infused and filtered. Used for douching.
- Wintergreen roundifolia is used as a lotion and to relieve itching. Two tsp. raw materials are poured with boiling water and infused for 2.5 hours, after which they are decanted through gauze. Wintergreen has antiseptic, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory and cleansing effects.
- White acacia can be taken not only internally. Douching is very effective: the flowers should be boiled, cooled and decanted. The procedure is repeated for one and a half weeks. To make the effect stronger, make not only douches from this plant, but also drink an infusion.
- A very good remedy is a composition containing rosemary, sage, yarrow and oak bark. It is poured with two liters of hot water, left for a couple of hours and douched.
- Tampons with honey should be applied daily for 12 hours for 2 weeks. Honey is a powerful anti-inflammatory and healing agent, but should only be used if it does not cause an allergic reaction.
For vulvitis, especially for children, baths are given. The most popular plant from which they are made is chamomile: 1 tsp. l. per glass of boiling water. Chamomile for vulvitis soothes and disinfects the affected skin.
Potassium permanganate also has a good healing effect. It is prepared in the same way as the previous recipe. Potassium permanganate has excellent disinfecting properties.
These simple methods will quickly get rid of itching and burning. It is enough to devote only 15 minutes a day to this problem so that it begins to bother you less.
But remember: folk remedies only neutralize symptoms, and do not completely cure. Even if the symptoms have passed and the disease does not manifest itself in any way, this does not mean that it has gone away. It is necessary to monitor further changes very strictly, otherwise there is a risk that the disease will develop into a chronic condition. In addition, if you are suffering from symptoms, then it may be time to give up spicy foods and dishes and reduce your salt intake. You should also follow all hygiene rules and regularly carry out preventive procedures. A good purchase in the future will be an intimate hygiene gel that will protect the skin and help prevent this disease.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Symptoms of vulvitis in girls
Most often, the disease occurs acutely; little time passes from the moment of exposure to the pathogen, therefore the incubation period is not prolonged.
After penetration of the pathogen or its contact with the skin, symptoms of vulvitis begin to quickly appear:
- First of all, the main symptoms include redness of the external genitalia , the intensity usually directly depends on the severity of the pathological process. It can be either slightly hyperemic, but sometimes bright burgundy in color. Subsequently, it is accompanied by gradually increasing swelling. In the most severe cases, it can provoke a violation of the outflow of urine.
- Swelling causes severe itching. Up to scratching and the addition of additional infection, maceration and development of cracks.
- Also one of the specific symptoms is discharge from the genital tract. They can look different, their nature depends on the type of pathogen, they are light or have a greenish, yellowish tint, usually with a fairly liquid or creamy consistency. With candidiasis in nature, they have a thick consistency, reminiscent of cottage cheese; it can also be flaky and white.
- The smell is almost always unpleasant , sometimes sour.
- The child begins to behave restlessly, cries often, is constantly bothered by itching, and severe scratching occurs. Sleep and general behavior are disturbed, appetite decreases.
- In some cases, especially with a specific infection, body temperature may increase. Rarely, other systems may be involved, so urination may become more frequent, accompanied by severe pain and cramping. Some children complain of abdominal pain.
- Upon examination, you can also see enlarged lymph nodes , especially the inguinal group.
What happens if the disease is not treated?
The process of inflammation in the vulva area itself does not pose any particular danger and, with timely measures taken, passes absolutely without a trace.
Its main danger is that the inflammatory process goes up, first provoking vulvovaginitis, then cervicitis, and then through the cervical canal it penetrates into the uterine cavity with the development of endometritis and salpingoophoritis.
In addition to damage to the reproductive system, an ascending urinary tract infection (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis) is possible.
One of the specific complications of the chronic course of vulvitis is the occurrence of synechiae, both labia minora and intrauterine.
In a complicated course, synechia can cause atresia of the vaginal opening. The development of inflammation of the Bartholin glands (bartholinitis) or the formation of cysts in them as a result of vulvitis cannot be ruled out.
Diagnosis of vulvitis in girls
Diagnostic stages:
- First of all, the diagnosis of vulvitis is based on communication with a gynecologist , he clarifies the complaints, the time of their appearance, as well as factors that could contribute to the appearance of the pathological reaction.
- The allergy history and cases of specific infections among family members, as well as hygiene methods that are used, are clarified.
- A thorough examination of the child is carried out. Initially gynecological, followed by examination of the anus, as well as all body systems. The lymph nodes are palpated.
- In some cases, vulvitis requires a two-handed digital rectoabdominal examination. This is important if the doctor has doubts about the degree of development of the pathological process. An assessment of the internal genital organs, the degree of their development and involvement in the inflammatory process is carried out.
- Among the laboratory research methods for vulvitis, the study of smears is used , onto which the contents of the discharge are applied. Sensitivity to antibacterial agents is also determined for more accurate selection of treatment.
- This is also a general or, if necessary, urine test according to Nechiporenko.
- Examination of stool for worm eggs is one of the important studies. Especially when the picture of the pathological process is unclear.
- In severe physical conditions, a blood test is also performed to assess the degree of the inflammatory process.
- If necessary or if a specific infection is suspected, the vaginal contents are examined using the PCR method.
- If candidiasis is present, an examination is carried out for the presence of glucose in the blood and urine .
- In addition, one of the instrumental methods to assess the extent of damage is ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Diagnostic measures
In addition to collecting anamnesis, the doctor pays attention to the following aspects:
- obesity;
- exudative diathesis;
- metabolic disorders and hormonal disorders;
- allergic history;
- hygienic features, etc.
A foreign body in the vagina can sometimes be palpated through the rectum.
Performing a vaginoscopy involves examining the vaginal walls without damaging the hymen . During manipulation, if necessary, foreign objects can be removed.
In some cases, the infection spreads to the lower urinary tract - the urethra and bladder.
Catheterization of the bladder at the peak of acute vulvitis can provoke the spread of microbial flora, so it is better to submit urine for analysis after the inflammatory process has stopped. In a general urine test and Nechiporenko's test, the number of leukocytes is higher than normal; bacteria, protein, and red blood cells may be present.
If, after normalization of the condition, bacteria are found in the urine, bacterial culture for flora and sensitivity to drugs is indicated.
Microscopy of vaginal discharge will help diagnose trichomonas and candida, but for a more accurate diagnosis, the biomaterial is examined by the PCR method, this is especially necessary if sexually transmitted infections are suspected.
In addition, they perform a stool test for helminth eggs and dysbacteriosis, check blood sugar and perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If necessary, you may need to consult an allergist, gastroentrologist, infectious disease specialist, or endocrinologist.
Treatment
The regimen will depend primarily on the general condition, as well as the severity of the inflammatory process. If the treatment is mild, then the regimen remains the same, the treatment does not require changing living conditions, only the hygiene correction changes and the selection of medications is carried out.
Moderate condition is usually treated at home with bed rest. In case of severe cases, hospitalization in a hospital may be required.
Diet
As in the case of any inflammatory disease, a nutritious diet is prescribed, with a sufficient content of all necessary substances, including vitamins and minerals. But with vulvitis there are some peculiarities in nutrition.
It is necessary to use those products that cause a change in the body’s environment in the alkaline direction, avoid the use of products that cause acidification of the environment:
- The first group includes such products as dairy products, cereals, boiled meat and vegetable dishes.
- The second group , which is subject to restrictions, includes smoked, salted, fatty and refined products, which contain a large amount of harmful substances, as well as fatty broths or broths and spices of various types.
If vulvitis is of an allergic nature, then the diet is prescribed taking into account the pathogenic component that caused it, as well as other highly allergenic products (these are any citrus fruits, honey, cocoa-containing products).
Local treatment
The main part of local therapy is the use of antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions:
- For this purpose, they can be used as local herbal therapy , such as a decoction of oak bark, chamomile, calendula, and St. John's wort.
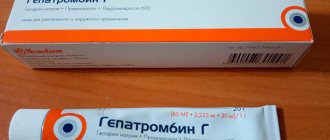
- As well as medicinal antiseptics. Furacilin solution , which is prepared by mixing a tablet or powder with water. Also potassium permanganate , which is dissolved in water and brought to a pale pink color. You can also use a ready-made solution of Chlorhexidine . The advantage of using it is its ease of preparation; all you need to do is buy a bottle of a solution of the required concentration. An analogue of this remedy is Miramistin .
- In advanced cases, antibacterial ointments are prescribed and applied to the vulva area. These most often include Tetracycline and Erythromycin . But tetracycline ointment has age restrictions, so it should not be prescribed to girls under 8 years of age.
Erythromycin ointment
Furacilin
Chlorhexidine
Miramistin
Potassium permanganate
Tetracycline ointment
Etiotropic therapy
Mainly in case of detection of a disease, especially in severe cases, before prescribing therapy, use the determination of sensitivity to antibacterial agents:
- If it is determined that the causative agent is a fungus , then treatment is reduced to the prescription of antifungal agents. This could be Fluconazole, Miconazole, Itraconazole, Levorin, etc. These drugs are prescribed systemically in tablet form.
- And as local therapy, agents such as Clotrimazole and Decamine ointment . With pre-treatment of the vulva with soda solution.
- The bacterial nature of vulvitis is treated by prescribing antibacterial agents such as Metronidazole or Ceftriaxone. A specific infection identified as a pathogen is transferred to a dermatovenerologist for treatment.
Clotrimazole
Fluconazole
Itraconazole
Miconazole
Ceftriaxone
Metronidazole
Hygiene
This is one of the fundamental rules in the treatment of inflammation of the vulva. In case of illness in girls at a young age, hygiene skills are taught to parents or caregivers.
But if these are older girls, then the doctor explains to her the basic recommendations regarding hygiene:
- The main thing everyone needs to remember is the correct movements. They should be carried out only in one direction, from the pubis to the anus. You should not make rubbing movements or rub this area with any hygiene products (rags, washcloths, brushes).
- It is better to perform all manipulations with clean hands. A single movement is required followed by rinsing the hand, thereby washing away the bacteria. The toilet of the genital organs must be carried out after each act of urination or defecation, and it is not always necessary to use specialized means.
- In most cases, it should be clean water, at a comfortable temperature , i.e. slightly warmed up. Under no circumstances should you use excessively hot or cold water.
- Specialized hygiene products are used no more than twice a day . It is better if they are appropriate for their age and purpose, avoiding purchasing scented or substances containing dyes. It is preferable to use products with a hypoallergenic composition, such as the Mustela and Weleda .
- It is recommended to use diapers as little as possible in everyday life , regardless of age. But if this is not possible, then during the day the diaper can be left for a maximum of three hours, after which a mandatory replacement is required, even if it turns out to be unused. And at night it is allowed to increase the time to 5-6 hours.
- At any age, girls need to follow the rules of wearing underwear . Its composition must be natural and not contain any admixtures of artificial components, especially those of synthetic origin. And also true to size, without chafing areas.
Air baths are also mandatory for girls. This does not require special skills or preparation; the girl, naked in the lower parts of the body, is simply placed on a dry and clean diaper in a room with a comfortable temperature. The minimum duration of one procedure should be a quarter of an hour.
Normalization of general condition with vulvitis
First of all, to alleviate general well-being, desensitization agents are prescribed. They help relieve symptoms such as itching, burning, and severe swelling. Can be used in both local and systemic form.
The use of such agents as immunostimulants, vitamins and interferon inducers is also indicated. In case of frequent relapses, hormonal agents based on estrogen begin to be used, since it is through them that the process of formation of a normal microbiocenosis occurs. In addition, subsequently, means are used to restore microbiocenosis based on lactobacilli.
Sanitation of foci of infection
This is one of the mandatory points in the treatment of pathology.
This is due to the fact that vulvitis is almost always provoked by another infection in the body. The most common among them may be the following:
- dental caries,
- inflammatory kidney diseases, often in the chronic stage,
- ORZ.
Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to identify and treat this pathology.
In addition, helminthic infestation can serve as a source of infection; enterobiasis is one of the most common causes. Therefore, the use of anthelmintic therapy is required. In very rare cases, a foreign body can serve as a source of chronic infection. Therefore, its safest removal is required.
Physiotherapy for vulvitis in girls
This method of treating vulvitis in girls is not the main one, but at the same time it can significantly complement medication.
There are several different options for this:
- With the help of UV irradiation it is possible to achieve permanent death of microorganisms.
- Electrophoresis method with drugs, for example, zinc. Used for fungal etiology.
- Ultrahigh-frequency effects are effective in cases of extensive local lesions. Able to reduce swelling, itching, capillary permeability.
- The effect of Darsonval currents on the vulva area has an antipruritic effect and also accelerates the death of fungi.
- Laser irradiation of blood as a method of therapy is used very rarely to treat vaginitis in girls. It is prescribed only in case of frequent relapses and severe course of the process.
Preventive measures
If a girl has had vulvitis once, this does not mean that it will not occur again. There can be no immunity to this disease. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to prevention. And only parents can take care of this. Here are some measures that will help the girl avoid this problem, and at the same time some others:
- Proper hygiene from birth . It is important for a breastfeeding baby to change diapers and diapers on time, to wash them after each bowel movement, and not to use detergent every time. When the girl grows up, you need to teach her how to wash herself correctly (from front to back) and teach her to do this every day, as well as change her underwear.
- The right cleaning products . The first toilet soap you come across can disrupt the microflora of an adult woman, and even more so of a child. Therefore, it is necessary to use special products for intimate hygiene. Overly scented soaps are prohibited, as are toilet paper and sanitary pads.
- Personal bath accessories . Each family member should have their own hygiene products. And we’re not just talking about toothbrushes, but also towels, washcloths, and sponges. Not to mention underwear.
And, of course, a healthy lifestyle should be in everything. This includes proper nutrition, physical activity, healthy sleep, and lack of stress. It is also important to educate a growing girl about sexuality. After all, a thoughtless, illiterate and too early start to sexual activity can lead not only to vulvitis, but also to more serious problems.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Traditional recipes for the treatment of vulvitis in girls
To treat vulvitis in girls at home, baths with decoctions of medicines are used.
The main ones include:
- Chamomile decoction , this remedy has been known for a very long time as an anti-inflammatory drug that can relieve not only swelling and inflammation, but also, to a small extent, itching. It is prepared by steaming several tablespoons of the plant in boiled water; some recommend boiling the mixture in water for a short time or simply leaving it in a container, covered with a towel. After which the mixture is filtered. The resulting solution is used as sitz baths, so the effect is much faster, but it should be noted that the water should be at a comfortable warm temperature; the decoction should not be too cold or hot.
- Calendula decoction. A product that has similar properties, but has certain advantages. More often used for people with a tendency to allergic diseases. It is prepared in the same way as the previous one; you can use either a self-prepared plant or a ready-made one purchased at a pharmacy. Also used as baths or lotions.
- Oak bark extract. Used as a sitz bath and has an anti-inflammatory effect. To do this, pour boiling water over the dry mixture and cook for several minutes, then cool and strain. The duration of the procedure can be up to 30 minutes.
- If a candida cause of inflammation is established, then soda solutions are used to relieve symptoms and reduce the pathogenic properties of the pathogen. More often used as lotions. To do this, you need to prepare a solution of baking soda by mixing a tablespoon with 1 liter of clean boiled warm water.
Medicines
Photo: levinassociates.com
How is vulvitis treated?
In the treatment of the inflammatory process, it is important not only to remove the symptoms, but also to influence the cause that caused it. After all, if you do not exclude the source of the disease, then you will not be able to cure vulvitis. Therefore, if vulvitis is diagnosed, the drug or methods for treating the underlying cause, which was the source of the inflammation of the vulva itself, also need to be selected with a doctor. Often, genital infections become the source of inflammation of the vulva, so treatment should begin with them. Mandatory treatment of such infections is required, otherwise the inflammation of the vulva cannot be stopped.
First of all, a woman is recommended to abstain from sexual activity during treatment; it is also worth reducing the impact of irritating factors.
Drugs used to treat the problem are divided into:
- external,
- oral administration
External products
Ointments, suppositories, creams – means for external use. They lubricate the lesions, and the suppositories are inserted into the vagina. Oral medications for the treatment of vulvitis include antibiotics and antihistamines, as well as anti-infective tablets.
Both home remedies and medications are used. Traditional medicine also offers many remedies, but in any case they should be used after consultation with a gynecologist.
Among the measures taken first, doctors recommend making medicinal baths, douching and washing from decoctions of herbs with disinfectant and antibacterial properties (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, calendula).
In addition to herbs, you can use the drug Miramistin. Vulvitis (an inflammatory process caused by pathogens) can be localized with its help. A solution with the same strong antiseptic properties is chlorhexidine. Areas affected by vulvitis must be disinfected to prevent bacteria from multiplying. Such agents are important in disease therapy and disinfection and have a fungicidal effect, relieving inflammation and accelerating tissue regeneration.
The first drug that is usually prescribed to patients with intense itching (most often observed when severe vulvitis is diagnosed) is hydrocortisone ointment with a reduced content of the active substance. It will help cope with itching and inflammation, relieves swelling. The ointment should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, and with caution in case of diabetes and tuberculosis.
Another remedy for itching is anesthetic ointment, the principle of action of which is obvious from the name.
In general, medications for vulvitis are very numerous, and in addition to ointments, suppositories with antibacterial effects are also used, which are made on the basis of clotrimazole, pimafucin, as well as ovestine and other similar drugs. They are inserted into the vagina, usually at night for 7-10 days. This treatment is sufficient for mild cases of the disease.
To treat vulvitis, levomekol, a drug that has an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, is applied directly to the area of inflammation. Levomikol for vulvitis affects most pathogenic microorganisms.
Among the agents used for local action, it is also worth mentioning syntomycin ointment. It can be used to treat the vulva and suppresses pathogenic microbes. The ointment is used more often in children, as the safest substance.
Creams for the treatment of vulvitis (pimafucin, clotrimazole, McMirror and others) are designed to have an antibacterial effect on the source of inflammation. Clotrimazole has a very wide range of effects on the problem (vulvitis, thrush, trichomoniasis - all these problems can be treated with this vaginal cream, which is applied to the affected areas 2-3 times a day, easily rubbed in).
Bepanthen cream or ointment promotes the healing of ulcers and wounds, epithelization and regeneration of the skin; it contains dexapanthenol. This is perhaps one of the most harmless drugs that can be used in both children and adults.
Stimulates tissue healing and methyluracil. Vulvitis is accompanied by ulcerations and violations of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, so the use of such products is very important for rapid epithelization.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for vulvitis are prescribed extremely rarely, but if the cause is an infectious disease such as gonorrhea or trichomoniasis, then it is impossible to do without them. Oral tablets are also used. Vulvitis caused by sexually transmitted infections is sometimes treated with antibiotics such as ceftriaxone (if gonococci are detected in the smear), metronidazole (if trichomonas are present) and others - this is at the discretion of the doctor.
In addition to the drugs listed above, fluconazole is often used orally for vulvitis caused by fungi of the genus Candida. This drug is usually taken once in an amount of 150 mg. In the chronic form of the disease, it is used longer: on the first, third and seventh day.
An important element in an integrated approach to the treatment of inflammation are vitamins, especially group B (thiamine chloride, riboflavin), aevit, vitamin C.
Antibiotics often provoke vulvitis, but they also often play an important role in the treatment of the disease. However, after oral administration of antibiotics, intestinal dysbiosis may develop, since the beneficial microflora in the body also suffers. Lactocyls and bifidobacteria die during antibiotic therapy. And these microorganisms bring enormous benefits to humans. They destroy pathogenic bacteria and are responsible for immunity. In this case, the microflora should be restored. For this purpose, prebiotics and probiotics containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are widely used.
As you can see, the range of drugs used to treat vulvitis is very extensive. But in order to properly treat the disease in any case, you need to consult a specialist. In no case should you self-medicate or delay the process, then there is a high probability that you will be able to avoid various complications, such as adhesions, the spread of infections to the intestines, uterus and ovaries. Only a comprehensive and competent approach to treatment will bring the desired results.
Complications of vulvitis in girls
They arise against the background of a long-term inflammatory process without adequate and timely treatment.
These include the following conditions:
- Fusion in the area of the labia minora . This occurs due to the gradual development of synechia, against the background of fibrin deposits during vulvitis in girls.
- Adhesions in the vaginal area. They are the result of the transition of the inflammatory process to the overlying sections in severe vulvitis. Subsequently, they lead to problems in sexual life, and can also indirectly complicate the process of labor, leading to the appearance of gaps.
- Involvement of other systems and organs in the inflammatory process. So, due to the close anatomical location, acute cystitis or proctitis, as well as cracks in the anal area, can occur.
- The appearance of scar changes at the site of former vulvitis in girls , which subsequently causes complexes and discomfort.
- Change in skin color . As a result, the external genitalia become bluish and persist for a long time or even for life.
Features of the disease
Vulvitis is an inflammation of the mucous surface of the external female genital organs . It spreads to the labia, vaginal area, and clitoris. Sometimes the redness spreads to the anal area, pubis, and inner thighs of the girl.
In children, this disorder is common and is caused by various reasons. It is important for parents to understand that vulvitis is possible even in newborns. Many people mistake redness and swelling of the mucous membrane for ordinary diaper rash, trying to cope with the problem with creams and powders without consulting a doctor. This can aggravate the situation, and the disease becomes chronic.
Little girls are unable to complain about what is bothering them, expressing dissatisfaction by worrying and crying. Those who are older may be embarrassed to tell their parents about the problem that is tormenting them. Therefore, timely detection of vulvitis in children depends entirely on the vigilance of adult family members .
If this disease is not treated, it easily becomes chronic, periodically making itself felt. During puberty, vulvitis can cause developmental disorders of the genital organs and disruptions in the reproductive system.
Vulvitis can first develop in infancy , up to a year.
However, more often it occurs between one and eight years of age. Later, when a girl begins to mature, the microflora of her vagina changes and becomes less vulnerable to vulvitis. However, other provoking factors appear: improper use of pads, wearing beautiful but uncomfortable synthetic underwear, early onset of sexual activity. Reference! According to ICD-10, vulvitis is numbered 76.3 and 76.4.
Prevention of vulvitis in girls
It comes down to the basic rules that must be included in the lifestyle:
- This is proper and complete nutrition.
- Sanitation of foci of chronic infection. Relieving the manifestations of allergic reactions, eliminating contact with the allergen.
- Regular hygiene procedures , use of correct and clean clothes. Avoiding wearing things that are too tight and that rub, in order to prevent the occurrence of illness.
- Avoid uncontrolled use of medications , mainly antibacterial ones.
- Timely contact a specialist when the first signs of an inflammatory process appear.
Complications and consequences
- Synechia of the labia minora. During the disease, erosions occur, the labia become deformed, stick together and gradually grow together. If the fusion affects the urethra, urination will become difficult. Surgery may be required in the future.
- If infection affects the urethra during illness, cystitis and urethritis .
- Vulvovaginitis . Develops when an infection enters the vagina. A common complication of vulvitis.
Other complications are also possible: erosion, neurogenic and conditional leucorrhoea, and in rare cases, infertility.