Chronic dermatosis of the skin caused by yeast-like fungi is called pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor.
The disease is widespread among residents of hot countries , but people living in temperate climates are also susceptible to infection.
Local therapy using effective pharmaceutical preparations in the form of ointment, cream or gel helps to get rid of a fungal infection.
Causes of pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is a superficial mycosis that primarily affects the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
The causative agent belongs to yeast-like fungi and can be found on the skin as a saprophyte in the stratum corneum and hair follicles. The disease is not contagious. The pathogen produces lipoxygenase, which oxidizes unsaturated fatty acids in sebum into dicarboxylic acids that inhibit melanocytes. This leads to a decrease in melanin synthesis and, as a consequence, to the formation of hypopigmented spots. Provoking factors:
- sweating,
- oily seborrhea,
- in young children - lubrication of the skin with fat,
- increased levels of cortisol in the blood,
- long-term treatment with corticosteroids.
With pityriasis versicolor on the skin of the chest, back, neck, shoulders, abdomen, under the armpits, in the groin, rarely on the face, non-inflammatory spots of different sizes with clear outlines appear, prone to merging and forming foci with scalloped boundaries, of different colors (brown, brown, brick and others). Pityriasis-like peeling is observed on the surface of the spots. Often there are lesions on the scalp, but they are invisible and the hair is not affected, so treatment procedures are usually not carried out in this area, which subsequently contributes to relapses.
Subjective sensations due to pityriasis versicolor do not develop. The course is defined as chronic, the disease is prone to relapse.
After tanning in the sun, which is also a therapeutic measure, light spots (the so-called pseudoleukoderma) clearly stand out against the background of tanned skin, which is very disturbing for patients. Leucoderma remains for a long time (up to a year) after the disease is cured. It is especially noticeable in people with dark skin.
The following forms are distinguished:
- hyperpigmented;
- achromatic;
- follicular (light, round, small spots with peeling around the vellus hairs).
Diagnostic features
The signs of the disease are quite specific, so in addition to a standard visual examination, doctors prescribe the following procedures to make an accurate diagnosis:
- microscopic examination of a sample of affected skin;
- use of Wood's lamp;
- iodine test or, as doctors also call it, Balzer's test.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
Each of the above methods is unique and effective in its own way in terms of diagnosis, therefore, if pityriasis versicolor is suspected, they are often prescribed together.
Microscopy
During a microscopic examination, a skin scraping is taken from the affected area of the patient's body, which is then examined under a microscope. This procedure allows you to identify traces of yeast (under a microscope lens, the fungal threads have a rather curved shape, which is clearly visible only with this diagnostic method).
Microscopic examination of the skin
Wood's lamp
A common diagnostic test method prescribed for suspected different types of lichen. With its help, you can identify traces of fungal cells on the patient’s head, or more precisely, on its scalp. To do this, you need a Wood's lamp - a special device that emits ultraviolet rays.
Application of Wood Lamp
Essentially, it is an ultraviolet lamp used in diagnosing skin diseases. During diagnostics using a Wood lamp, the patient's hair is not affected by its radiation. Therefore, this method is considered one of the most popular.
Balzer test
During this procedure, the area of the patient's skin to be examined is treated with an iodine solution and then wiped with alcohol. Under the influence of the liquids used, the upper layer of the epidermis loosens, and the lichen spots become brighter and stand out against the background of healthy skin. The Balzer test is also performed as a confirmatory test to determine whether the disease has been cured.
Balzer iodine test
Important! Differential diagnosis is also necessary to exclude the development of pathologies such as dry streptoderma, syphilitic leukoderma, spotted syphilide or pityriasis rosea (in medicine there is another name - Zhiber's lichen). All these diseases have a similar course to pityriasis versicolor.
How to treat pityriasis versicolor?
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor is determined individually. In cases of limited lesions, it is recommended to rub in antifungal ointments (clotrimazole, clotrisal, nizoral, ketodine, dermazol) twice a day, iodicerrin for 2-4 weeks. In case of significant dissemination of the process, nizoral (ketoconazole) orally 200 mg per day for 10-20 days, orungal (itraconazole) 200 mg per day for 7 days, fluconazole 300-400 mg once a week for 2 days are appropriate. -4 weeks. In order to prevent relapses, they also lubricate the surrounding areas of the skin, where small lesions may go unnoticed, and if there is severe dandruff on the scalp, use Nizoral, Dermazol, Perhotal, Ebersept shampoo.
For 2-3 months after the main course of treatment, also in order to prevent relapses, the site of the former rash and the surrounding skin are wiped twice a week with salicylic, boric, resorcinol alcohol, and tincture of white hellebore.
Physiotherapy is also appropriate - in order to accelerate repigmentation, erythemal doses of UV irradiation are prescribed to areas of pseudoleukoderma after completion of treatment with antifungal drugs.
TOP 10 ointments for lichen on human skin
According to numerous reviews from patients and doctors, the following creams and ointments for lichen are considered effective:
- Terbinafine works successfully against tinea and herpes zoster.
- Zovirax (and other acyclovir derivatives) has a detrimental effect on shingles.
- Miconazole is a drug with a wide spectrum of action. Particularly effective against the pityriasis type of the disease. The substance not only eliminates the causative agent of lichen, but also actively restores the affected areas of the skin.
- Hydrocortisone relieves persistent itching and pain. Used only as directed by a specialist.
- Exoderil is actively used for ringworms of the disease. Its active component, naftifine, kills pathogenic fungi and relieves inflammation.
- Nizoral actively fights the causes of eczema, dermatitis and other skin problems.
- Clotrimazole helps with the presence of color, ringworm and flat varieties of lichen. Kills most viruses and pathogenic fungi.
- Flucinar instantly relieves itching and pain that occurs in the presence of psoriasis, eczema and dermatitis.
- Mycoseptin kills fungi, soothes the skin surface, and disinfects. Shown to be highly effective in treating the ringworm type of the disease.
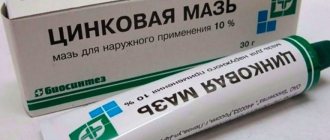
- Ointments created on the basis of zinc, salicylic acid, sulfur and tar: they are practically free of contraindications, which makes their use possible even in children. These drugs have the properties of eliminating inflammation, killing fungi and disinfecting the skin surface.
An effective ointment for lichen on a person’s skin will definitely be needed after diagnosing the disease. Timely identification of the type of lichen allows you to begin a drug fight against it, guaranteeing a speedy recovery.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Individuals with certain medical conditions are more likely to develop pityriasis versicolor. Among them:
- endocrinological diseases - hypothyroidism, thyrotoxic goiter, diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- seborrhea;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Complications of pityriasis versicolor usually include cosmetic defects of the skin, but if you really want to, you can get rid of them without a trace, this can be done with the achievements of modern plastic medicine.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor at home
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor is carried out at home; hospitalization is completely unnecessary. However, this is not a guide to self-medication; consultation with a doctor cannot be avoided. As a result of specialized diagnostics, the causative agent of skin spots will be detected and a drug suitable for a particular case will be prescribed. When treating the disease, you should adhere to a diet containing a minimum amount of sugar and carbohydrates.
Prevention of pityriasis versicolor is defined as secondary - treatment or prevention of excessive sweating, use of soap with sulfur, shampoos with ketoconazole.
Mechanism of action of antimycotics
Antimycotics are a type of medicine that occupies a special place in the complex treatment of pityriasis versicolor.
Antimycotics are antifungal drugs that are characterized by specific activity against fungi that provoke the development of dermatological diseases.
The mechanism of action of antifungal agents is to block the synthesis of nucleic acids, ergosterol and proteins in the cells of harmful microorganisms, as a result of which the cell membrane is damaged and the yeast fungus dies.
Important!
Antimycotics are prescribed depending on the location of the affected area, the type of pathology, the spectrum of action, as well as the pharmacokinetics and toxicity of the drug.
What medications are used to treat pityriasis versicolor?
When treating pityriasis versicolor, it is advisable to use the following medications:
- iodicerrin - generously lubricate the lesion 2-3 times a day for 2-4 weeks;
- nizoral - 200 mg orally per day for 10-20 days;
- itraconazole - 200 mg per day for 7 days;
- fluconazole - 300-400 mg once a week for 2-4 weeks.
Contraindications
Antimycotic ointments have a number of contraindications that should be taken into account before use. Many antifungal drugs are highly toxic.
Medicines for tinea versicolor should not be used in the following cases:
- allergic reaction to the components included in the medicine;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- children under two years old;
- the presence of infectious diseases of the epidermis that arise for various reasons;
- for skin tuberculosis, syphilis;
- open wounds on the skin, the presence of ulcers.
Many products are prohibited from being used for a long time and applied to large areas of the skin. There is a risk of developing negative reactions and worsening the patient's condition.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor with traditional methods
Folk remedies are very popular in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor , but it is better to combine them with the use of pharmaceuticals rather than use them as part of self-medication. Both pharmaceuticals and folk remedies should be agreed upon with the attending physician. The following recipes may be a topic for discussion:
- a glass of crushed celandine herb, add a glass of sugar and wrap in gauze; Place the resulting bag in a 3-liter jar and fill it with yogurt brought to a boil; leave to infuse for 28 days, stirring occasionally; Carefully remove the periodically formed film of mold, and after the allotted time, strain the curdled milk into another jar, close with a nylon lid and store in the refrigerator; take 50 g 3 times a day 15 minutes before meals;
- 1 tbsp. l. peppermint pour 1 cup of boiling water and keep in a water bath for 15 minutes, remove from heat and leave to infuse for half an hour; then use it to wipe and lubricate the affected areas.
To treat spots of pityriasis rosea, you can use one-component herbal products, prepared independently or purchased at a pharmacy. For example, stains are smeared several times a day:
- calendula tincture;
- onion juice;
- cranberry juice;
- burdock juice;
- burdock oil;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- oatmeal;
- apple cider vinegar.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor during pregnancy
The development of pityriasis versicolor in a pregnant woman is usually associated with decreased immunity and a lack of certain beneficial substances in the body of the expectant mother. Lichen itself usually does not pose a threat to either the woman or the intrauterine development of the fetus, unless it is accompanied by serious complications.
Inconveniences may arise during the feeding stage of the baby. After all, close contact between mother and newborn creates ideal conditions for infection.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor during pregnancy should be entrusted to a specialized specialist, who will prescribe the safest one from the variety of medications for the expectant mother.
Predisposing factors
Pityriasis versicolor is observed more often in adults. The incidence of pityriasis versicolor does not differ by gender (i.e., men and women are affected).
This type of dermatological disease is much less commonly diagnosed in older people and children under 14 years of age .
The occurrence and activity of the fungus are provoked by factors predisposing to the disease:
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- changing the formula of the secretion produced by the sweat glands;
- oily seborrhea;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- reduction of natural peeling of the dermis;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- diabetes, tuberculosis, immunodeficiency diseases;
- wet air;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives, antipyretics, antibiotics, glucocorticoids;
- stress;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- genetic (hereditary) predisposition to the disease.
Elimination or correction of the condition that caused the disease speeds up the healing process and prevents relapses in the future. Often, after the elimination of the underlying disease, pityriasis versicolor in a person goes away on its own, without the use of additional therapeutic measures.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - o
| Treatment of obstructive bronchitis |
| Obesity treatment |
| Treatment of burns of the larynx |
| Treatment of herpes zoster |
| Treatment of adrenal tumors |
| Treatment of tracheal tumors |
| Treatment of ARVI |
| Treatment of orchitis |
| Treatment of osteoarthritis |
| Treatment of osteomyelitis |
| Treatment of osteoma |
| Treatment of osteoporosis |
| Treatment of osteochondrosis |
| Treatment of osteochondropathy |
| Treatment of acute abdomen |
| Treatment of acute intestinal failure |
| Treatment of acute mesenteric ischemia |
| Treatment of acute renal failure |
| Treatment of laryngeal edema |
| Treatment of otitis media |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.