Botkin's disease is an acute viral inflammation of liver tissue caused by the hepatitis A virus. Leads to acute necrosis of hepatocytes. Transmitted by the fecal-oral route, hepatitis A most often affects children 5-6 years old. Hepatitis outbreaks are seasonal. The peak occurs in summer and autumn. Currently, hepatitis A is most common in countries with hot climates and poor hygiene. The source of infection is always a person with hepatitis A. Often the disease is transmitted in a subclinical form.
Why does the skin turn yellow?
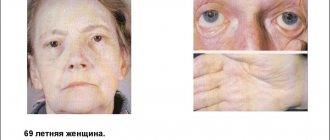
An increase in bilirubin levels, regardless of the reasons that caused it, is accompanied by a change in the color of the skin - they acquire a yellowish tint. The popular name for this is jaundice.
It is believed that different types of jaundice have their own shades, which can be used to suggest what type of jaundice is observed in the patient. The skin color with jaundice of suprahepatic origin has a greenish tint and is similar to the color of a lemon peel.
Botkin's disease, like any other disease that directly affects liver cells, is characterized by a change in skin color from bright to yellow. Unfortunately, it is impossible to understand if jaundice is present - what letter of hepatitis corresponds to it.
Jaundice in adults due to stagnation of bile is characterized by a rich hue. Many people who have encountered this condition note that the color of the skin resembled infused beer.
Preventive measures
As a rule, the disease virus has the ability to be transmitted by entering the body through the oral cavity. For this reason, it is important to follow established rules regarding personal hygiene. These include thorough and regular hand washing (especially before eating), items for eating should be individual, and it is always recommended to eat fresh vegetables and fruits (after washing them well beforehand). In areas with an increased risk of infection, doctors provide preventive vaccinations to patients. Modern medicine actively uses epidemic vaccines when Botkin's disease is detected in the body.
Classification and causes
The classification of jaundice was created specifically to quickly determine the level of damage and select the correct treatment tactics.
Conjugation
Conjugation jaundice most often occurs in newborns - its appearance is associated with the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin and the formation of normal hemoglobin, which circulates in the blood of adults. In adolescence, this pathology can occur as a manifestation
Hemolytic (suprahepatic)
This type is characterized by an increase in total bilirubin due to its unconjugated fraction. More common in the postoperative period. may be associated with injuries and burns. Hemolytic jaundice can also result from bites from poisonous insects and reptiles, or poisoning from toxic substances.
Parenchymal (hepatic)
Patients with parenchymal jaundice will experience an increase in both fractions of bilirubin due to the destruction of liver cells. Most often these are people with hepatitis A and other infectious liver pathologies. To find the source of infection in the case of parenchymal liver disease, it is necessary to undergo many tests and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Mechanical
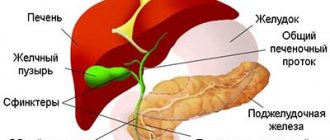
Obstructive jaundice is called so because for its occurrence there must be an obstruction to the outflow of bile. The main cause of this type is a stone at the outlet of the gallbladder or in the common bile duct. It blocks the outflow of bile and leads to an increase in the total level of bilirubin, mainly due to the conjugated fraction.
Species that are found only in young children
There are some types of jaundice that occur only in newborns. An example is a change in skin color in hemorrhagic and hemolytic pathologies of newborns. Conjugative physiological jaundice appears in babies on the second or third day of the neonatal period. This happens due to a large amount of fetal hemoglobin in the blood and immaturity of the liver. Also, only in infants can carotene changes in the skin and lactation jaundice occur.
The causes of jaundice in newborns often do not correspond to those in the adult population. The most common conditions include the following categories:
- Physiological jaundice or conjugation - occurs 24 hours after birth. It is characterized by a mild course and disappears by the second week after birth.
- Hemorrhagic pathology of newborns is characterized by increased bleeding and a gradual increase in changes in the skin. Associated with a lack of blood clotting factors. As a rule, it goes away after administration of vitamin K.
- Hemolytic disease is associated with blood conflict between mother and child. Changes appear already in the first days after birth. From a scientific point of view, this pathology is the most life-threatening and requires blood transfusion.
There is a special table for young children, which indicates the norms of bilirubin according to the age of the baby. Using it. it is possible to understand when the child’s condition remains normal and when immediate medical intervention is required.
Symptoms
The incubation period for hepatitis A lasts from 7 to 50 days. On average it is 30-35 days.
Symptoms of hepatitis A in adults can be varied. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly identify the time of their occurrence and register each manifestation.
- Botkin's disease begins acutely - with a rise in temperature to high numbers, headache, weakness, nausea and vomiting. Sometimes there is pain in the epigastric region. Due to the fact that these symptoms in adults are quite nonspecific, the pathology, in the first days, is often confused with the occurrence of a respiratory or intestinal infection.
- Sometimes an adult may experience a sore throat or pain when swallowing.
- Jaundice syndrome is often the first and only manifestation of the pathology that forces the patient to undergo a medical examination. The color of the skin and mucous membranes changes by 3-5 days, and after 14 days this period completely passes.
- Children may experience sharp, sharp pain in the abdomen. This manifestation often causes hospitalization in a surgical hospital.
- Men over 40 years of age with a high addiction to alcohol constitute a risk group. They are the ones who can get severe hepatitis A. In this case, the appearance of spots before the eyes, dizziness, acute pain in the liver area, fever, hemorrhages on the body and mucous membranes, and tachycardia are observed.
The causative agent of hepatitis A can also lead to acute liver failure. This happens in severe and untreated moderate-severe forms.
Sometimes the pathology occurs without jaundice. At the same time, all other clinical and laboratory symptoms remain, and changes in skin color do not occur.
At-risk groups
In our country, hepatitis A is a disease mainly of children and young people, although anyone who does not have immunity can get sick. The virus leaves behind lasting, lifelong immunity, so people almost never get sick a second time.
Those at risk include:
- travelers, especially those visiting other countries with poor health standards;
- drug addicts;
- homosexuals.
The maximum incidence is observed in the summer and early autumn.
Diagnostics
To understand whether jaundice is a hepatitis, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies.
- Collecting anamnesis - what symptoms were there initially, after which signs appeared (what the patient himself associates with them), what complaints there are at the time of treatment.
- Has the incubation period of hepatitis A been sustained or is the cause not due to an infectious liver lesion?
- General clinical blood test.
- General examination of urine and determination of bile pigments in it.
- Biochemical blood test with determination of liver tests - ALT, AST, prothrombin time, GGTP, total and fractional bilirubin, prothrombin index
- Specific immunological studies to detect the virus in the blood and antibodies to the virus in the liver.
- Additional diagnostic methods are ultrawave examination of the abdominal cavity and liver in particular, computed tomography, chest radiography.
It is also necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with other infectious and non-infectious hepatitis, blood and liver diseases. It must be remembered that there is also a possibility of a latent course of hepatitis C, the symptoms of which at first may not differ from the manifestations of infectious hepatitis A. Only after all tests have been performed, a person can be diagnosed with Botkin’s disease.
Precautionary measures
Nonspecific prevention involves following the rules of personal hygiene and careful handling of food and water. Special methods for preventing hepatitis A infection include vaccination. It is mandatory for military personnel and tourists traveling to hot countries. Children attending children's educational institutions, as well as pregnant women, are required to be vaccinated during epidemic outbreaks. They are injected with gamma globulin, which stimulates the development of strong immunity. If the patient was in a group, then thoroughly disinfect furniture and utensils. Wet cleaning of the premises is carried out.
Treatment
Treatment of jaundice in adults and children always begins with an accurate diagnosis. Without this, it is not possible to cure jaundice! And even if it is possible to eliminate the discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes, after a while the icteric coloration reappears.
Read more about jaundice in children here.
That is why it is necessary to be treated only after all diagnostic tests have been completed and it has been established whether jaundice and hepatitis are the same thing or not. If chronic or acute hepatitis is diagnosed, it is necessary to understand which virus is affecting the liver.
Botkin's disease is treated depending on the severity of the course and the presence or absence of complications. How long therapy lasts can only be determined after treatment has started. Discharge from the hospital is possible after the signs of hepatitis A begin to subside:
- reduction in liver size;
- disappearance of jaundice in an adult;
- a decrease in the activity of hepatic transferases by 3-4 times from the initial level in at least three blood tests.
If at least one of these conditions is not met, treatment for hepatitis A continues.
People who have been treated for a mild form of the disease claim that this is one of the most pleasant treatment options:
- hospitalization with semi-bed rest (you can walk around the ward);
- gentle nutrition;
- drink plenty of fluids - at least three liters per day.
Treatment of hepatitis A in patients with a moderate form is a little more complicated.
- Hospitalization and semi-bed rest.
- Table number 5.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Enterosorbents.
- Detoxification therapy by infusion of drugs.
- Multivitamins.
In severe cases, Botkin's disease is treated similarly to hepatitis B. At the same time, the issue of transferring the patient to intensive care is resolved, powerful infusion therapy is carried out, and treatment is carried out with interferon drugs and specific antiviral agents.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of infection. General measures to prevent infection are:
- high-quality purification of drinking water supply sources;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- epidemiological control at enterprises involved in the production, storage and transportation of food products.
In the event of an outbreak of hepatitis A in organized groups, anti-epidemic quarantine measures are mandatory. Sick people are isolated for a period of 2 weeks. Patients cease to pose a danger to others after the onset of the icteric period.
They are allowed to work and study only after clinical recovery, i.e. when test results return to normal. Persons who have had direct contact with infected people need to be monitored for 35 days. Quarantine is declared in kindergartens and schools for this period. All surfaces in the room are thoroughly sanitized.
It is easier to prevent the development of pathology than to engage in long-term treatment
Folk remedies
Understand what jaundice is and why it occurs. is always extremely important for its successful treatment.
How to get rid of hepatitis, the source of which cannot be detected in the blood? All sick people need to know that in addition to traditional therapeutic measures, there are also traditional medicine recipes that help cope with this condition.
- Drink plenty of fluids - the best herbal remedy against hepatitis, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. It is necessary to brew herbs and drink 200 ml 3-4 times a day.
- Rosehip decoction is one of the best remedies. All you need to do is pour boiling water over the rosehip and let it brew for three hours after that - drink 500 ml per day.
- Rowan and rosehip berries are also poured with boiling water and left for half an hour. You need to drink this product at least twice a day, 200 ml.
When using any traditional treatment methods, you need to remember a few main rules:
- consuming any alcoholic tinctures is strictly prohibited - they can aggravate liver damage;
- even proven recipes cannot be used without consulting your doctor;
- The use of any folk remedies in children can cause allergic reactions.
Caring for a patient with Botkin's disease
The person caring for the patient must follow some recommendations. First of all, the patient must remain in bed. Avoid foods that should not be included in your diet. A large amount of fluid will help remove toxins from the body faster. For this purpose, vitamin teas are made from rowan and cinnamon rose hips. The patient should consume several glasses a day of prepared decoctions.
Drinks are also made in the form of fruit juice from currants and various berries. All fruits can have a diuretic effect. Be sure to have regular bowel movements once a day. If the patient does not go to the toilet, then toxins accumulate and can lead to a worsening of the condition. If you have stool retention, you need to do a cleansing enema. As soon as the patient gets better, he needs to be given freshly squeezed juices.
Jaundice in pregnant women
There are many cases where jaundice syndrome first appears in women during pregnancy. Changes in skin color can occur both due to pregnancy itself and independently of it.
Unfortunately, toxic acute hepatitis quite often occurs as a result of poisoning with alcohol or its surrogates.
Pregnant women are slightly more susceptible to infectious hepatitis than other people due to a functional decrease in the activity of the immune system. A woman can get sick both before and during pregnancy. The incubation period does not change. Treatment of Botkin's disease and any other infectious hepatitis depends on the course of the disease, gestational age, condition of the woman and complications of pregnancy.
In the last trimester of pregnancy, a life-threatening condition for the mother and fetus may occur - HELLP syndrome. In this case, destruction of red blood cells and liver cells occurs with the release of a large number of enzymes from hepatocytes (increased ALT and AST), which is accompanied by thrombocytopenia. One of the main symptoms of this condition is jaundice.
There is also cholestatic hepatosis of pregnant women, which is characterized by damage to hepatocytes and the development of cholestasis under the influence of female sex hormones, which are released in large quantities. This pathology belongs to the group of genetically predisposed ones. Therefore, often during the collection of anamnesis it turns out that symptoms of jaundice occurred in other women in the family during pregnancy. The attending physician determines the treatment tactics. Most often it consists of the use of plasmapheresis and hemosorption.
When wondering how to treat jaundice, you must remember that all therapeutic measures should begin only after a thorough diagnosis. Without finding out the cause of this condition, it is impossible to provide high-quality treatment and save the mother and child from the risk of complications and death.
How do you get infected with the hepatitis A virus?
How is hepatitis A transmitted? From the feces of a sick person, the virus enters the water, and with it into the local reservoir, from where it again reaches the water supply system (as you remember, the microbe is not inactivated by chlorine, but only by boiling). You can also become infected from a sick family member or employee if he did not wash his hands well after using the toilet and touched objects, towels and door handles that you then touched and went to eat without washing his hands. Infection is also possible when eating food from a sick person.
There is also a food route of infection - through food products contaminated with the microbe, which were washed with infected water and were not cooked.
A person who has acquired HAV becomes dangerous to others even before he knows about his illness: 10-14 days before the onset of jaundice (that is, still during the incubation period). The virus is shed for at least 2 weeks after the onset of jaundice.
The virus is found in feces and urine. Microbes are not released with other biological fluids, although you can become infected through a blood transfusion taken from a sick donor in the last days of the incubation period. In a person infected in this way, the incubation period is shortened, and the hepatitis itself is severe.
Transmission of virus A through the placenta has not been proven.
Consequences of jaundice
Most often, Botkin's disease is mild and goes away quickly under the supervision of specialists. However, sometimes patients with hepatitis A develop complications.
- Functional and inflammatory diseases of the biliary system.
- Acute hepatitis of autoimmune origin type 1 (only in people with impaired immune system).
- Hepatic coma is extremely rare, in severe cases of the disease with jaundice.
In most cases, patients with hepatitis A - Botkin's disease, fully recover a few months after discharge from the hospital. Sometimes symptoms and treatment are delayed for up to 6 months, after which full recovery follows.
Broadcast
Distribution of hepatitis A in 2005
The virus is transmitted through the fecal-oral route, usually due to poor sanitation and overcrowding. Hepatitis A virus is extremely rarely transmitted parenterally through blood or blood products[14].
About 40% of all acute viral forms of hepatitis are caused by the hepatitis A virus[7].
The virus is resistant to detergents, in acidic (1) conditions, in the presence of solvents (ether, chloroform), when dried and to temperatures up to 60 ° C. The virus survives for months in fresh and salt water.