Inflammation of the pancreas, symptoms and treatment, is the topic of today’s article. No one thinks that the pancreas is a very important organ in the human body.
It produces enzymes and hormones necessary for digestion that regulate blood sugar levels. If the gland does not work properly, then food is not completely digested, and the sugar that comes with food is not absorbed.
Only a doctor can determine inflammation of the pancreas, all the symptoms and treatment. Treatment on your own is simply unacceptable. Now let’s figure out what the symptoms and causes of this disease are, so that when they appear, immediately run to the doctor.
General information
The gastrointestinal tract is one of the most important functional systems in the human body, which is responsible for well-being, metabolic processes, the production of a number of hormones, as well as appearance. People who have problems with the digestive system have certain external (identifying) signs that allow them to suspect something is wrong in the physiological mechanism of the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, malfunctions in the digestive internal organs are indicated by suspicious yellowness of the skin, hypersensitivity of the third tooth in the upper or lower row, as well as suddenly appearing invisible wrinkles between the eyebrows or around the eyes. Of course, it would be wrong to make a diagnosis for yourself, but it is still logical to take note of the self-diagnosis method.
It is known that pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas tissue, in males is directly caused by alcohol abuse. In women, the appearance of this disease is provoked by cholelithiasis. Both are true, but there are plenty of levers to trigger a dangerous disease. Do not underestimate this important, albeit small, organ.
The weight of the pancreas is extremely small - only 70 g, while the function of this organ is highly active. The pancreas is prone to an immediate reaction to the emotional and nutritional stress that the body experiences. Numerous unfavorable factors: frequent and acute stress, influenza virus, poisoning, aggressive medications and poor-quality food immediately affect her condition. And this is only an incomplete list of reasons that contribute to the initiation of the disease in an acute form and its further transition to the chronic stage. What are the signs of pancreatic disease? Symptoms in women, treatment and prevention will be discussed below.
Laboratory signs
The most characteristic of inflammation or destruction of the pancreas will be changes in clinical and biochemical blood tests, as well as changes in urine.
- Clinical blood test
It will respond by increasing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (more than 10 mm per hour in men and more than 20 in women), relative leukocytosis (an increase in the number of leukocytes over 9 G/l), which indicates inflammation. With pronounced destruction and the addition of a purulent infection, a “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left” will appear, that is, an increase in the number of segmented and band leukocytes.
If you determine the hematocrit (the ratio of the number of red blood cells to the volume of plasma), then it increases due to dehydration (in men >54, in women >47%). The relative increase in red blood cells is also determined. In cases where hemorrhagic pancreatitis occurs in the later stages, anemia may develop (a drop in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin). Blood glucose levels usually rise and exceed 5.5 mmol/l.
- Blood biochemistry
It most often determines the amylase level, rising above 125 U/l in the first 12 hours of the disease. If necrosis of the gland occurs, amylase decreases. Increasing lipase, trypsin and enzyme inhibitor levels are more indicative figures. Today, the most specific is considered to be an increase in blood elastase in the first two days.
However, this enzyme is not determined in all laboratories. ALaT, ASaT and LDH increase, indicating cell breakdown. Due to jaundice, the amount of indirect and total bilirubin increases. Acidosis leads to a drop in calcium, magnesium and chloride levels.
- Changes in urine
relate to an increase in its relative density, the appearance of protein (casts), leukocytes and erythrocytes during dehydration or toxic kidney damage. Urine diastasis begins to exceed 100 units with the upper limit of normal being 64 units. Sugar and ketone bodies also appear in the urine, which indicates disturbances in carbohydrate and protein metabolism.
How to recognize pancreatitis in women?
What are the signs of pancreatic disease in women? Probably, it is hardly possible to compare the general well-being with pancreatitis - the most painful and serious disease of the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the acute phase. The pain has a peculiarity - its girdling nature.
How do you know if you have a diseased pancreas? The first symptoms appear clearly, starting with restlessness in the left hypochondrium. Next, the pain threshold spreads across the upper half of the abdomen and moves to the back area, mainly on the left. Repeated vomiting, which exhausts the patient, is also an indicator of the presence of the disease. The skin is marked by pallor and an earthy tint. Pulse and breathing are rapid.
What should the attending physician pay attention to during the appointment?
In addition to the fact that the doctor carefully studies the listed symptoms and complaints of the patient, he must also examine him. At the appointment, the person is very agitated and irritated, while the skin is pale and covered with sweat. If there is a suspicion of inflammatory processes in the pancreas, palpation of the abdominal area is performed.
The patient should lie on the couch and bend his knees. Sometimes, even with a light touch, the patient may feel severe pain. It’s good when a person can independently show the localization of pain. In order to more accurately determine in which part of the organ inflammation has occurred, the doctor determines three main points on the abdomen where the placement of the organ is planned:
- Desjardins point. This is where the head of the pancreas is located. The point is located on the line that connects the navel and the right armpit. The area 5–7 cm below the ribs on the line corresponds to this point. If there is pain here, it means that this particular part of the gland is inflamed.
- The Mayo–Robson point shows the placement of the tail of the organ. To find it, you need to visually draw a line connecting the navel and the left costal arch. Then the line is divided into three even parts. The point is on the border between the upper and middle parts.
- The Kacha point will determine whether there are changes in the body of the pancreas. This point will be placed at a distance of 5-7 cm from the navel, along the outer edge of the left rectus abdominis muscle. If pain appears during palpation in this area, then the inflammation is most likely located at the border of the tail and body of the gland.
Children are not subject to palpation. In this case, this method is not effective.
Symptoms of pancreatitis in women
What are the signs of the disease? When should you sound the alarm? The first symptoms of pancreatic disease:
- deterioration in health;
- sharp, girdle pain in the upper abdomen, radiating to the back and both hypochondriums;
- nausea;
- frequent vomiting;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- increased body temperature;
- pallor and yellowness of the skin;
- greasy stool, indigestion, diarrhea;
- progression of autonomic symptoms - weakness, dizziness, anxiety, sweating.
During research activities, elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes and leukocytosis are detected in the blood and urine. The diagnosis is confirmed using the ultrasound method.
What else is needed to make a diagnosis?
In addition to the fact that the doctor examines the patient, he must also give directions for a number of other diagnostics that will confirm or refute his assumption. Such diagnostics include:
- A general blood test and, of course, hormones. According to the general analysis, it is clear that the gland is inflamed if the levels of lipases, amylases, trypsin, and sometimes bilirubin have increased. In the case when necrosis has already begun, an insufficient amount of calcium in the serum is added to everything. If the entire gland is affected, the level of insulin in the blood is disrupted.
- Stool and urine analysis. Feces are checked for meat fibers and fatty inclusions, and urine is checked for the presence of amylases.
- It is also necessary to do an ultrasound, MRI or CT scan, angiography of the gland vessels and other examinations.
- If a woman experiences symptoms of inflammation of the gland, the doctor should send her for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Sometimes these symptoms are similar to peritonitis. In women, inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis) can be caused by certain gynecological problems, such as an ectopic pregnancy, a ruptured ovary, or a tumor.
The doctor knows exactly what tests and examinations need to be carried out in order to find out a clear picture of the disease and determine how to treat and what to treat with. Do not neglect the advice of specialists.
The main enemies of the pancreas
What reasons often serve as an obstacle to the normal functioning of the pancreas in women?
- Alcohol. In more than half of the cases, acute and chronic inflammation of gland tissue is directly related to alcohol abuse. Ethanol has a toxic effect on gland cells and leads to disruption of the production and outflow of pancreatic juice. The very first attack is almost always recorded after drinking unreasonable doses of alcohol.
- Gallstone disease and cholecystitis. If a woman has a history of diagnoses indicating complications with the gallbladder or liver: the presence of stones, enlarged liver, sand in the bile ducts, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, enteritis, gastric ulcer, then the pancreas becomes vulnerable. This is due to the fact that the ducts of the pancreas and gallbladder have a common outlet into the duodenum. If there is a stone in this ductal area, then inflammation or blockage of the duct with a stone is inevitable. In this case, bile simply begins to destroy the glandular tissue itself. Acute pancreatitis may well develop due to the transfer of the inflammatory process from neighboring organs.
- Fatty and fried foods. Periodic indulgence in completely unhealthy foods, in particular, overcooked, fatty, spicy, cold foods leads to excessive load on the pancreas, which is an increased risk factor for the development of pancreatitis. In addition, overeating not only aggravates the condition of the pancreas, but also interferes with the stable and coordinated functioning of all body systems.
- Poisoning. Acute inflammation of pancreatic tissue always develops during poisoning of any nature. Poor quality food, taking strong medications, viruses - all this triggers mechanisms of failure in the functioning of the organ, giving way to a serious illness.
- Surgical trauma. Unfortunately, this is possible when the cause of pancreatitis is an operational error.
- Autoimmune disease. With this disease, healthy cells are recognized by the body as foreign, and the immune system destroys them. Violations of this nature lie in hereditary causes that require a special approach.
Complication of the inflammatory process
The inflammatory process during pancreatitis can provoke complications that pose a threat to the patient’s life. The risk of negative consequences increases significantly in the absence of timely therapy and ignoring the symptoms of the pathology. If treatment is carried out in the early stages of the disease, the likelihood of complications is reduced.
Complications of the inflammatory process:
- pancreatic necrosis (progressive death of pancreatic tissue);
- development of peptic ulcer (provoked by a violation of the composition of gastric juice, the result is damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive organs);
- gastrointestinal bleeding (the main provoking factor is rupture of the pancreatic capsule);
- phlegmon (purulent formations);
- peritonitis (a purulent inflammatory process develops in the abdominal cavity);
- abscesses (the appearance of dense formations with purulent contents).
How to help during a seizure
If you notice the first signs of pancreatic disease in women or men, you should immediately consult a doctor. Don't joke with pancreatitis! Hospitalization for acute pancreatitis is strictly required. Before the emergency team arrives, to alleviate the patient’s condition, follow the prescribed recommendations:
- apply a cold object or ice to the solar plexus area;
- do not violate bed rest;
- refrain from eating;
- It is allowed to drink pure non-carbonated water in small sips in small quantities;
- It is forbidden to drink aspirin, analgin, ibuprofen (you can take an antispasmodic);
- hot heating pads and heat are strictly contraindicated.
Where is it located in a person, where is it located?
Considering the anatomical structure of the abdominal cavity of a person standing upright, we can describe how the organs are located in it:
- immediately below the diaphragm are the liver and stomach (the main part of the liver is on the right, the stomach is on the left);
- on the left side, near the stomach, there is another organ, small in size, the spleen;
- the gallbladder is placed in front of the liver, next to the stomach;
- behind the stomach, pressed against the back wall of the abdominal cavity, the pancreas is located;
- below - the large and small intestine begin.
Thus, the organ we are interested in lies not under the stomach, as is mistakenly thought based on the name, but behind it. If a person is in a horizontal position, then the pancreas actually appears exactly under the stomach.
From the back, the location of the pancreas is determined by the vertebrae: the organ rests from the inside in the area between the first and second vertebrae belonging to the lumbar region. From the side of the abdomen, they are guided by the navel: approximately 6–9 cm above it.
If we talk about size, then the norm for an adult is considered to be approximately 20 cm, weighing about 75 grams of the pancreas.
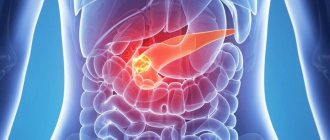
It consists of three departments:
- the main one is the head (starts next to the bile duct);
- body (behind the stomach, along the transverse intestine);
- tail (passes near the spleen).
That is, the main part of the pancreas is located to the right of the midline of the abdomen, and its tail goes to the left hypochondrium.
Treatment of pancreatitis in the acute stage of the disease
In most cases, it is not immediately possible to stop the acute process and alleviate the symptoms of the disease in acute pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis is treated within the walls of a hospital and requires serious medication.
Therapy includes:
- mandatory bed rest,
- cold on the epigastric region,
- creation of functional rest for the gland (absolute hunger),
- taking medications.
Why does it hurt?
Pain syndrome can be caused by pathological processes occurring in the pancreas:
- when internal pressure in an organ increases;
- if the bile duct is compressed;
- perhaps the effect on sensory nerves of fibrotic changes in tissues;
- due to ischemia of blood vessels that enrich the organ with blood;
- the appearance of a cyst or cancer.
The inflamed, swollen pancreas increases in size and puts pressure on neighboring organs. Because of this, the pain can intensify and spread throughout the abdominal area.
There are quite a few reasons why pancreatic pain can occur. The most basic primary factors due to which the pancreas fails to cope with its functions and fails include:
- systematic overeating and passion for fatty foods;
- poisoning of the body with nicotine, alcohol, chemicals, medications;
- cholelithiasis.
Pancreatitis often occurs against the background of long-term mental or physical stress. Almost all causes of pancreatic pain are long-term systematic neglect of health, failure to treat chronic diseases, and weakened immunity.
Effective herbal teas for chronic pancreatitis
Herbal medicine has been used in the treatment of many diseases for a very long time and, it is worth noting, is effective. Herbs act gently, their therapeutic effect is long-lasting and, as part of complex therapy, can bring good results. All herbal infusions are selected individually.
The action has a beneficial effect on the pancreas:
- peppermint,
- coriander fruit,
- immortelle flowers,
- common anise fruit,
- dandelion roots,
- knotweed grass,
- St. John's wort,
- chamomile,
- Salvia officinalis.
What herbs can you drink?
To alleviate the condition, after consulting a doctor, you can drink decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Yelan
“Elan” is a ready-made collection of Altai herbs, sold in pharmacies. Has an anti-inflammatory effect. The decoction should be prepared according to the recommendations on the package.
Parsley
Parsley has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, stimulates gastric secretion. For chronic pancreatitis, an infusion of fresh chopped parsley is taken 2-3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
Herbal mixture No. 213
The collection includes a number of plants useful for inflammation: chamomile, wormwood, horsetail and other herbs. Decoctions based on the collection are prepared according to the recommendations on the packaging.
Diet is an important stage in the treatment of pancreatitis
Now you know what the symptoms of pancreatitis in women are. Treatment and diet are two concepts without which it is impossible to cope with pancreatitis.
Diet is one of the main conditions for recovery. The gland should not be under pressure, and the diet should be gentle. In order not to feel the signs of pancreatic disease in women, you need to listen to the following rules:
- eat often, at least 5 times a day;
- reduce portions, as large amounts of food put too much strain on the pancreas;
- fried foods, smoked foods, fatty foods are excluded, and the processes of creating dishes are defined as steaming, stewing or boiling;
- for pancreatitis, it is undesirable to indulge in foods rich in plant fiber (cabbage, persimmons, celery, tomatoes, bell peppers), since their frequent use can provoke an attack;
- Sour berries and fruits are not allowed in the diet, and it is better to eat apples baked or pureed;
- the amount of carbohydrate foods should be reduced, and in return, increase the consumption of protein foods: lean meat, lean fish, turkey. You can have one egg per day and only soft-boiled. Fermented milk products and cottage cheese are required, but if the body is intolerant, you can replace them with milk;
- the pancreas is harmed to one degree or another by both hot and cold foods, so it is recommended to eat warm foods;
- limit your consumption of salt and canned products.
To no longer worry about signs of pancreatic disease in women, it is necessary to completely eliminate:
- alcohol,
- cocoa, coffee, strong black tea,
- carbonated drinks.
It is important to follow a strict diet for a long time: as a rule, this is at least 9-12 months. Once the patient’s condition has stabilized, there is stable remission and the food is well tolerated, the diet can be expanded somewhat, but only by especially observing the strictest recommendations: a ban on alcohol and fatty foods.
Where does it hurt, on which side?
Very often it is difficult for a person to describe the pain syndrome that engulfs him during a pancreatic attack. The sensations may have the following variations:
- sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the lower back;
- aching pain under the diaphragm with tingling in the left arm;
- severe pain around the navel, which is slightly relieved by bending forward.
An inflamed pancreas, as a rule, begins to hurt from its main part - from the head. Therefore, pain is more likely to occur in the area located just above the navel, to the right of the midline. If a sharp pain resonates in the back, in its lumbar region, we are talking about the spread of inflammation to the tail of the organ and to more serious pathologies.
Prevention of pancreatic diseases
It is very easy to damage the pancreas, and many people mistakenly believe that once they have had pancreatitis, they don’t have to think about it. Having felt an improvement, recent patients forget about the attack and shamelessly exploit the newly recovered organ.
Important! Do not eat monotonously: for each type of product or culinary dish, the stomach reflexively releases its own specific enzyme.
Give up the habit of chewing food poorly, since the digestion of carbohydrate foods begins in the oral cavity. The fact is that the enzyme contained in human saliva and designed by nature to break down carbohydrates, begins to work only if a person makes at least 20 chewing acts or movements. How you swallow food is also important. There is such a thing as a swallowing wave failure. This violation occurs when we smoke, lie, eat and drink in front of the TV screen. The same thing happens if we greedily swallow food, eat dry food or drink in one gulp.
An overgrown round belly puts pressure on a delicate organ, interfering with the normal functioning of the pancreas. It is worthwhile to treat the disease correctly and with special attention and prevent the development of chronic pancreatitis, since if an acute disease is not treated, there is a risk of insufficiency of the insular apparatus and, as a consequence, the development of secondary diabetes. It is important to be prudent during the off-season, when a tendency towards exacerbation of chronic ailments has been identified. In general, paying close attention to yourself after an illness will ensure stable and long-term remission.
Importance of enzymes in digestion
The functioning of the human body is ensured by a complex system of interconnected and interdependent biochemical reactions. Thanks to special protein compounds - enzymes or enzymes - all these reactions are accelerated, ensuring rapid metabolism. The action of enzymes is very selective: each of them is capable of initiating, accelerating or slowing down only one reaction.
The digestive process is based on the work of digestive enzymes. Their main task is to make the process of energy absorption fast and efficient. Enzymes break down food components (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) into substances suitable for absorption. Moreover, the amount of enzymes produced depends on the quantity and quality of what is eaten.
Digestion of food begins in the oral cavity. The food, crushed into small pieces by the teeth, is mixed with saliva, which contains the enzyme alpha-amylase. The better we chew food, the easier it is for the enzyme in the salivary glands to convert starch molecules into soluble sugars and facilitate further processing.
After initial processing, food enters the stomach through the esophagus, where the gastric enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid begin to work. These substances create gastric juice, which:
- provides antibacterial protection for the body;
- stimulates the production of pancreatic hormones;
- regulates gastric motility;
- breaks down fats and performs a number of other functions.
In addition to pepsin, which is responsible for the breakdown of large protein molecules, other enzymes are produced in the stomach, for example:
- gelatinase is a solvent for collagen, gelatin and other connective tissue proteins;
- lipase is an enzyme that breaks down some fat molecules into fatty acids and monoglycerides;
- chymosin - starts the process of digesting milk protein.
Bile plays a significant role in the digestion process. It contains bile acids that stimulate the production of pancreatic secretions.
From the stomach, the food bolus is evacuated into the duodenum, where the main process of food digestion occurs. It is provided by more than 20 pancreatic enzymes. Enzymes are contained in pancreatic juice, which is produced by the gland in a volume of about two liters per day.
Functions of pancreatic enzymes:
- proteases - breakdown of proteins into amino acids;
- nucleases - act on DNA nucleic acids;
- amylase - breaks down starch into simple sugars;
- lipases - break down fats into higher fatty acids and glycerol.
The digestion process is completed under the action of enzymes of the small intestine and beneficial bacteria living in the intestines. The intestines absorb processed food into the body (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Some important digestive enzymes. Source: Jason Northwest
When the function of enzyme production by the organs of the digestive system, especially the pancreas, is disrupted, the entire body becomes unbalanced. Such an imbalance entails nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, followed by anemia and exhaustion.
What to take with meals if you have a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes
With pancreatitis, the process of production of digestive enzymes by the pancreas is disrupted, as a result of which a person suffers from discomfort and pain in the stomach. In this case, after a complete examination, replacement therapy may be prescribed.
The goal of treatment with enzyme preparations is to compensate for their deficiency in the body, while reducing the load on the damaged organ. In some cases, such therapy is prescribed for life.
Important! The effect of all enzyme preparations begins 20-30 minutes after eating, so you need to drink them strictly before meals in the dosage prescribed by your doctor!
Modern pharmacology offers a large number of different enzyme preparations of animal and plant origin. Some of them are aimed only at replenishing the deficiency of a single enzyme, for example, one that breaks down lactose or fats. There are also complex agents prescribed for the deficiency of several enzymes in various organs of the digestive system.
Pancreatic enzymes are obtained from the organs of cows or pigs. The composition of the medicines includes the main pancreatic enzymes - amylase, lipase and trypsin. Polyenzyme preparations, in addition to pure pancreatin, may include bile acids, adsorbents or other enzymes. All drugs are selected strictly individually, taking into account the nature of the disease and the severity of symptoms.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
The diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis should be carried out by a surgeon. Based on characteristic complaints, laboratory and instrumental studies, he differentiates acute pancreatitis from other diseases that cause acute abdominal pain.
- Pancreatitis: diagnosis and treatment
Laboratory diagnostics
- detailed clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- bacteriological examination of abdominal exudate (done during surgery).
Instrumental diagnostics
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs;
- other imaging methods (magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, plain radiography) as indicated.
Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis.
Chronic pancreatitis is more difficult to identify than acute pancreatitis. The doctor asks the patient about the type and dynamics of abdominal pain, learns about bad habits, the nature of food and stool. The specialist pays attention to weight loss and other signs that the body is not getting enough nutrients.
Silent pancreatitis occurs in 10-20% of cases (Warshaw AL et al., 1998)
Laboratory diagnostics:
- Indirect functional tests of the pancreas. Determination of fat content in feces.
- Determination of elastase-1 activity in feces.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- multislice computed tomography (MSCT);
- endoscopic ultrasound (EUS);
- magnetic resonance pancreaticocholangiography (MRCP);
- retrograde endoscopic cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
To diagnose chronic pancreatitis, functional tests have been developed, which, on the one hand, are very sensitive, but on the other, expensive and quite invasive, that is, they involve significant interference in the body’s activities. Therefore, they are used in cases where other data is insufficient. This group includes two methods:
- Collection and analysis of pancreatic juice into a special cannula, which is inserted into the duct during ERCP.
- Collection and analysis of duodenal contents. To do this, the patient is given a special probe capable of separating gastric and intestinal contents. Over the course of about 2 hours, the doctor sucks out the contents of the intestines at certain intervals and forms a sample. In order to stimulate the production of pancreatic juice, the patient is given hormonal drugs or a test is performed after a standard breakfast (Lund test).