An excess of vitamins and minerals in the body is often a bigger problem than their deficiency. For example, iron. Mineral deficiency causes weakness, pallor, dry skin, hair loss, problems with the heart and blood vessels, and weakens the immune system. Excess iron is fraught with diabetes, arthritis, diseases of the liver, pancreas, nervous, cardiovascular systems and even the appearance of tumors. We will discuss further how iron overload develops and how it manifests itself.
What is deposited in the liver? The liver does not accumulate waste and toxins, but other substances can be deposited in it. They provoke the development of non-alcoholic fatty disease and increase the risk of cirrhosis.
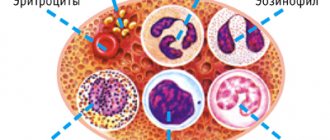
Functions of iron in the human body
Iron is an integral part of many enzymes and proteins, including hemoglobin and the red blood cells that form it. It affects various functions:
- responsible for oxygen transport;
- ensures regeneration and normal cell growth;
- strengthens the body's immunity;
- ensures oxygen transport and carbon dioxide evacuation - regulates cellular respiration;
- regulates metabolism - metabolic processes;
- determines the proper functioning of almost all organs and systems.
Iron not bound to hemoglobin
Free iron accelerates oxidative processes, which are very harmful to health. At age 18, the excess iron that accumulates is about 1 mg per day, about 80% remains in the blood. Women are less susceptible to excess circulating iron in the body because they get rid of iron deposits during menstruation. Many illnesses and diseases are associated with excess iron in the body.
Iron poisoning
This trace element is used to treat anemia and is also included in multivitamin preparations. Severe poisoning occurs in children after taking tablets containing iron salts used for adults. The cause of poisoning is also often self-medication of anemia and exceeding the dose of medication taken.
Preparations containing iron are as follows:
- "Sorbifer Durules";
- "Totem";
- "Ferrum Lek";
- Ferrograd;
- "Actiferrin";
- "Fenuls";
- "Hemofer."
In some cases, people independently take dietary supplements containing iron, which often creates a risk of overdose.
Signs of acute poisoning
The first signs of an iron overdose in the body appear after receiving 10–20 mg per 1 kg of a person’s weight.
stomach bleeding
There are 4 degrees of acute poisoning with iron preparations.
- Taking less than 30 mg/kg of the substance causes gastroenteritis, manifested by nausea and vomiting. After 30–50 mg/kg enters the body in the first stage, gastric bleeding occurs when the walls of the digestive organs are ulcerated.
- The next period of 6–24 hours develops in the case of receiving a trace element of more than 50 mg per 1 kg of human weight. At the same time, blood pressure decreases, tachycardia and drowsiness are noted.
- Manifestations of the shock stage are detected 12–24 hours after receiving 100 mg/kg. This life-threatening period is characterized by damage to the nervous system in the form of seizures. The patient falls into a comatose state.
- Liver failure develops 2–3 days after poisoning.
If such symptoms appear, the person needs urgent measures.
First aid and treatment
Providing first aid for poisoning with iron preparations consists of the following actions.
- At home, do a gastric lavage with plain water.
- Accept any sorbents.
- At the same time, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
- Provide the victim with access to fresh air.
Treatment for iron poisoning is carried out in a hospital and consists of the following therapeutic actions.
- If radiopaque tablets are detected on a plain X-ray of the abdomen, the stomach is washed. If the medicine has already passed through the pylorus of the stomach, the intestines undergo cleansing.
- Fluids are infused to regulate blood circulation and acid-base balance.
- The antidote for iron poisoning is Desferal or its analogue Deferoxamine. Drip administration of a solution of 10–15 mg/kg is indicated.
- If necessary, provide mechanical ventilation of the lungs.
Pregnant women are not contraindicated in administering the antidote because it does not cross the placenta.
Diet to increase hemoglobin
Published: 01/29/2017
Low hemoglobin is a very common problem that many women, mothers of small children, and people who have undergone surgery are familiar with. Why might hemoglobin drop? There are a lot of reasons. Perhaps iron is not absorbed, there was bleeding or lymph is flowing from the wound...
no comments yet
How to increase hemoglobin levels?
Published: 05/23/2015
Our healthy diet recommends these tasty and healthy dietary liver pancakes with carrots. Hemoglobin levels can decrease for many reasons, for example, due to poor nutrition, large blood loss, etc. If you don't care...
no comments yet
Iron is closely related to the aging process, affecting life expectancy.
The main symptoms of iron overload in the body are fatigue, weakness and general malaise.
Back pain after eating: causes and diet
Published: 07/18/2015
We all know very well that food enters the esophagus into the stomach, then is digested and moves on. It seems that the process of eating has nothing to do with the back, where, in fact, there are no digestive organs. But…
no comments yet
It is worth noting that the problem of excess iron mainly affects middle-aged men. And since the symptoms are not typical, they are often confused with fatigue or lack of nutrients. If this situation persists for a long time without a correct diagnosis, extreme exhaustion and lack of energy occurs.
If the problem affects women, then they usually have problems with hormonal levels and irregularities during menstruation.
Decreased libido is observed in both men and women.
Another warning sign may be a change in skin color to a sallow, gray-brown color combined with a metallic sheen. In addition, hair in the pubic area and armpits may disappear.
Blood test results show abnormal liver enzymes, which contribute to liver problems.
Diet for the liver
Published: 08/09/2013
Without realizing it, we constantly put stress on one of the most important organs of the human body - the liver. Frequent consumption of fatty foods, flour, alcoholic beverages, smoked foods and pickles has a detrimental effect on this organ. Infectious…
no comments yet
As iron levels in the blood increase, LDL cholesterol, glucose, and triglyceride levels increase, and blood pressure also increases.
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out on an empty stomach
Usually the study is carried out as planned. The patient comes for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of complete overnight fasting, and if this condition cannot be met, no earlier than 4 hours after the last meal. You can still drink clean water. 2-3 days before the study, it is not recommended to expose yourself to heavy physical activity, including sports training. You should get more rest, go to bed earlier, avoid stress, alcohol consumption and heavy smoking. You should also not smoke in the morning before the test.
For more accurate results, 7-10 days before the analysis, you should avoid taking iron-containing preparations and foods containing large amounts of iron (seaweed, dried and fresh mushrooms, legumes, hazelnuts, buckwheat, oatmeal, almonds, rose hips, prunes, dried apricots, cocoa). When taking medications that do not contain iron, but those that can lead to an increase in iron in the blood (antibiotics, cytostatics, contraceptives, etc.), you should discuss their discontinuation with your doctor.
If discontinuation of these drugs is not possible now, you should complete the course of therapy with these medications, and then conduct an analysis, or find an alternative to them, for example, replace oral contraceptives with barrier contraceptive methods (condoms, spermicides).
If it is necessary to determine the level of iron in the blood when acute intoxication with this metal is suspected, the above rules may not be followed. Such intoxication is an indication for emergency research and treatment.
Excess iron in the blood - consequences
The consequences of overloading the body with iron are very dangerous to health. Problems with joints, heart, liver, and pancreas may occur. There is also a violation of the lipid profile - fat metabolism processes. This chronic condition can lead to the development of diabetes or cirrhosis of the liver.
An excess of this element causes hormonal imbalances and can even lead to the development of tumors.
The musculoskeletal system is subject to chronic inflammation and degeneration, which significantly complicates movement and also causes pain.
Excess iron promotes the growth of bacteria, which can lead to serious complications (for example, sepsis).
Causes of excess iron in the blood
Excessive amounts of iron in the blood may be caused by a diet rich in this element, which is based mainly on red meat because it is rich in heme iron, which is the best absorbable form of the element. The second, very important reason for the appearance of excess iron is a metabolic disorder - hemochromatosis (pigmentary cirrhosis, bronze diabetes), which is associated with excessive absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract obtained from food.
There are two forms of this disease: primary and secondary. The primary form is associated with the inheritance of a gene mutation that is responsible for controlling iron absorption in intestinal epithelial cells. This causes the defective gene to be inherited from both parents. Therefore, this is a rare form of the disease.
The secondary form of hemochromatosis is not common. It may be the result of maintaining an inadequate diet or, in the case of a mixed form, associated with a decrease in iron intake due to disorders of the hematopoietic system, excessive release of iron from red blood cells and liver cells.
Ways to normalize elevated iron levels
Therapy for elevated metal levels in the blood should be aimed at reducing the total amount of the trace element in the body. The first thing the patient is prescribed is normalization of nutrition in accordance with dietary recommendations.
For the most effective and quick relief, various medications can be introduced into the patient’s body to reduce the amount of metal in the blood. In particularly severe cases, phlebotomy, a bloodletting process, may be prescribed.
Medications
There are currently no direct medications for high iron levels. Despite this, your doctor may prescribe certain medications that can reduce the amount of trace elements in the body.
Medications
Commonly used medications:
- heptapeptides of any group;
- zinc-based preparations;
- hepatoprotectors to protect liver function;
- food complexing agents.
The use of any pharmacological medications should be under the strict supervision of the attending physician. Otherwise, various complications are possible. Depending on the patient's condition, any other drugs may be prescribed. Antidepressants, immunomodulators, or fusion inhibitors are often used.
Diet therapy: general principles of nutrition
Based on the tests performed, certain dietary standards are discussed with the attending physician to significantly reduce the iron content in the human body. First of all, it is necessary to completely exclude any vitamin or mineral complexes containing metal.
This also includes almost all dietary supplements. Taking vitamins B and C is also undesirable.
The following foods should be excluded from your daily diet:
- most seafood, especially shellfish;
- seaweed;
- black chocolate;
- bread and legumes;
- strong green tea;
- pomegranate, persimmon, peaches;
- dried apples, prunes, dried apricots;
It is especially important to exclude eggs, fatty red meat and beef liver. It is prohibited to take any alcohol-containing drinks, including even the weakest cocktails. It is not recommended to take sweets, since the sugar they contain promotes faster absorption of various microelements and vitamins, including metal.
In the absence of contraindications, the doctor may introduce dairy products in large quantities.
Patients suffering from high iron levels should drink plenty of water, which can be diluted with lemon juice for variety. In the absence of contraindications, it is possible to take weak black tea, herbal tinctures or compotes. Any carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited.
Approximate daily diet:
- Breakfast. Steamed oatmeal with the addition of pineapple or strawberries. Black tea without sugar with various herbs.
- Lunch. Light salad of broccoli, cucumber and tomato. You can take 25-30 g of dried almonds or pumpkin seeds.
- Dinner. Boiled buckwheat, bread with low-fat cheese.
- Afternoon snack. Fruit salad (without adding apples) and drinking yogurt or kefir.
- Dinner. Boiled chicken meat with a light dietary side dish. Cocoa or weak black tea.
The basis of your daily diet should be raw food of plant origin. It is also advisable to consume large amounts of soy or legume products. It is best to cook and eat food from glass or ceramic dishes. Iron cans, pots or mugs must be excluded.
If the level of Fe in the blood is high, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the established diet. Any dietary requirements must be agreed with your doctor. In most cases, normalizing nutrition is quite enough to lower the level of metal in a person’s blood. Other products can be added to the products described above, which is also discussed with a specialist or nutritionist.
Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy or bloodletting is the most effective method of lowering a person's serum iron levels.
Phlebotomy
The method involves removing a certain amount of blood from a vein using various methods:
- An incision or puncture in the area of the arterial or venous system. The most dangerous use of phlebotomy, which can result in significant blood loss. The intervention is carried out slowly using a wide needle.
- Banking procedure. For this method, small jars are used, which the specialist places on the patient’s body. This allows blood to be quickly sucked out of the outer capillary or vascular surfaces, restoring natural circulation.
- Hirudotherapy. In this case, medicinal leeches are used, which are placed directly on the incision site. The main feature of this method is the collection of already unusable blood.
The main advantage of using phlebotomy is the rapid stabilization of the patient's condition.
In some cases, improvements in the cardiovascular system, as well as the elimination of unwanted joint pain, are possible. Under no circumstances should bloodletting be performed at home. If used incorrectly, complications may be dangerous to health. Contraindications are: low blood pressure, mental disorders or pregnancy.
Diet to reduce iron
Proper nutrition and a healthy diet, recommends poleznaya-dieta.ru, in case of excess iron in the blood, is very important. Food should contain products that will not be a source of an easily digestible form of this element. Thanks to this, the accumulation of iron in the body will stop.
- Foods of plant origin contain difficult-to-digest forms of iron. Therefore, it is better to eat more salads and less meat.
- Drinking green tea after meals can additionally help reduce iron levels, which can be extremely beneficial in the case of elevated hemoglobin in the blood.
- It is advisable to completely abstain from alcohol, since alcohol causes the accumulation of this element in the body.
- Some products contain substances that bind the element. They will reduce its content in the blood. These include: blueberries, coffee, green tea, onions, fruits, whole grains.
Iron deficiency is dangerous and bad for your health. It turns out that too much of it can also be dangerous, causing numerous ailments and, in extreme cases, damaging the organs where it accumulates. A proper healthy diet, combined with medical care and diagnosis, can help eliminate excess iron in the blood.
What products contain
Iron is found in foods of plant and animal origin. For optimal intake, you need to take it in an easily digestible form.
Animal products containing large amounts of iron are the following:
- beef liver;
- pork liver;
- mutton;
- egg;
- beef;
- pork;
- chicken;
- cottage cheese;
- fish.
Although these foods are rich in iron, they are poorly absorbed from the intestines without vitamin C. Therefore, meat foods should be washed down with citrus juice, eat vegetables, or take ascorbic acid tablets.
Plant foods high in iron:
- beans, lentils;
- green vegetables - celery, spinach, broccoli, parsley, carrots, cabbage, pumpkin;
- tomatoes;
- brown rice, buckwheat;
- fruits - apples, pears, peaches;
- berries - raspberries, strawberries, currants;
- sun-dried dried fruits - prunes, dates, dried apricots, raisins;
- pistachios.
Iron from plant foods is also poorly absorbed in the intestines, but absorption increases when combined with meat dishes.
How and where is iron absorbed?
Iron is one of the most difficult macronutrients to deliver, its absorption is very low, and during cooking and cooking, most of the iron is destroyed, that is, lost. And a normal level of iron in our blood is necessary for cellular respiration. So how can you ensure better iron delivery?
Iron is a component of hemoglobin, myoglobin and ferritin, is involved in the transport of oxygen and electrons, is involved in DNA synthesis and tissue respiration, and is an important link in the processes of fatty acid desaturation, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, iodine tyrosine, prostaglandin biosynthesis, tryptophan catabolism, and detoxification in the liver. or in immunomodulation.
Unfortunately, the modern fast diet, based on simple sugars and fatty, processed foods, does not provide enough of this element. Another cause of iron deficiency is malabsorption diseases such as celiac disease (gluten intolerance) or Crohn's disease.
Too low a level of this macroelement manifests itself mainly in decreased immunity and apathy, lack of strength despite prolonged sleep, pale skin, brittle nails and hair. It can also contribute to problems concentrating, memory loss and learning ability.
The relationship between iron and ferritin
Serum iron is increased (the reasons must be identified before starting therapy), and ferritin is decreased - this situation is often explained by a deficiency of the microelement. This prognosis is especially often found in people who abuse alcohol, as well as with infectious diseases or hepatitis.
If ferritin is elevated and total iron levels are within normal limits, this may indicate the presence of various causes, including: arthritis, malignant tumors, colds and much more. To avoid negative consequences, you must immediately consult a doctor.
How much iron does the body need per day?
- Children and adolescent males need 11 mg of iron per day.
- Men over 19 years of age should receive, on average, 8 mg of iron per day.
Iron deficiency is greatest among women because they eat less red meat, the best source of iron, go on weight-loss diets more often than men, and lose blood during menstruation.
- Girls aged 9 to 13 years should receive 8 mg of iron per day.
- From 14 to 18 years old, 15 mg of iron per day is recommended.
- Women aged 19 to 50 years should provide at least 18 mg of iron per day.
- After menopause, women do not need as much iron (from the age of 50), so their daily requirement is 8 mg.
Iron is an essential mineral needed for proper development of the nervous system and brain.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women should get about 25 mg of iron per day
- Children of both sexes from one to 8 years of age need 7-10 mg of iron.
Standard indicators
In medical practice, the normal level of iron is considered to be the level at which the human body functions without any restrictions. This indicator depends on many reasons, including: age, gender, height and many other features.
The total amount of a trace element in the blood can be determined by several biochemical methods. The simplest is a clinical analysis, which is taken from a finger. In addition, there is a test for the ability of serum to bind metal and the total content in the blood, which are determined in µmol/l.
Standard indicators of serum iron
Despite the ease of use, in medical practice they are increasingly resorting to the most accurate and indicative testing - identifying the total iron-binding capacity. In this case, the main analyzes are summarized.
The average reference ranges for this method are measured in micrograms per deciliter:
| Group | Standard indicator |
| Men | from 65 to 176 mcg/dl |
| Women | from 50 to 170 mcg/dl |
| Newborns | from 100 to 250 mcg/dl |
| Children | from 50 to 120 mcg/dl |
Laboratories often use different units of measurement, the normal values of which may vary depending on the techniques used. For example, if the analysis is taken from the fingertips, the reference indicators are completely different than with more accurate methods.
Average normal values when determining a simple biochemical analysis taken from a finger prick:
| Group | Standard indicator |
| Men | from 12 to 31 µmol/l |
| Women | from 9 to 30 µmol/l |
| Newborns | from 18 to 45 µmol/l |
| Children | from 9 to 22 µmol/l |
Serum iron is elevated (the reasons depend on age, gender and other indicators) more often in men than in women. This is due to the effects of the sex hormone testosterone, as well as the inherent physical activity, which leads to higher energy losses.