Every mother has simple algorithms in stock to combat common diseases: a runny nose - rinse and drip the nose, a cough - give an antitussive or mucolytic, do inhalation, fever - give an antipyretic.
But there are many diseases for which any self-medication or failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner is dangerous and fatal for the child. One of these pathologies is appendicitis; symptoms in children manifest themselves differently, but if several signs are combined, you should immediately call a doctor.
Causes of childhood appendicitis
- The main reason for the development of appendicitis in a child is mechanical blockage of the lumen of the appendix. Obstruction may be caused by a foreign body, fecal calculus, parasites, or lymph node hyperplasia.
- The reason may also be the individual structure of the process. For example, the presence of bends and torsions.
- The problem may appear in a child with reduced immunity due to infection caused by a cold, otitis media, sore throat, sinusitis, measles and other diseases. The infection may also be associated with intestinal diseases (typhoid fever, tuberculosis, amebiasis, and so on).
- Important! Considering these reasons, to prevent the disease it is necessary:
- Provide proper nutrition containing the right amount of fiber
- Avoid overeating
- Don't eat too much sweets
- Regularly carry out preventive measures to combat parasites
- Try to prevent the appearance of dysbacteriosis
How quickly does appendicitis develop in children?
Attack of appendicitis
is developing very rapidly. Therefore, destructive changes in the process appear quite quickly. In this regard, inflammation is often transferred to the peritoneum and a very life-threatening complication appears: appendiceal peritonitis.
From a simple catarrhal form, appendicitis quickly turns into a destructive one (phlegmonous or gangrenous). If you do not resort to treatment in time and ignore the signs of the disease, it can lead to the following serious complications:
- Perforation of the walls of the appendix and peritonitis
- Periappendiceal infiltrate (may develop into chronic)
- Intestinal obstruction
- General blood poisoning
- Appendiceal abscess
Important! The time from the onset of inflammation to peritonitis can take from 24 to 36 hours.
Chronic appendicitis occurs much less frequently in childhood than in adults. Typically, it manifests itself as periodic pain in the lower right side. Moreover, each such attack is accompanied by classic symptoms: nausea and increased body temperature.
Possible complications
Appendicitis (symptoms in children 10-13 years old cannot be ignored) can only in very rare cases go away without treatment. In this case, the intestinal walls, enveloping the inflamed appendix, prevent the development of infection. After the inflammatory process disappears, the position of the intestinal walls may not change, causing spasms to appear from time to time.
But usually without therapy, inflammation begins to progress, which leads to the occurrence of:
- appendicular infiltrate;
- abscess;
- peritonitis.
The infiltrate forms 3-5 days after the onset of inflammation. Neighboring organs are involved in the pathological process. Next, an abscess (purulent inflammation) develops. The most dangerous complication is diffuse peritonitis.
It appears as a result:
- migrating inflammation;
- breakthrough of the wall of the appendix;
- purulent inflammation of the abdominal organs.
If treatment of a 10-13 year old child with appendicitis is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. Surgery completely solves the problem, and complications in children rarely occur after such therapy.
The main thing is not to waste time, spending it on using traditional methods, enemas and gastric lavages if symptoms of illness occur in the baby. Parents must understand that self-medication can result in very dangerous consequences.
The first signs of appendicitis in children
The beginning can proceed in different ways. Where exactly the attack begins depends on the location of the appendix.
The earliest symptom
Pain in the navel area is considered. It then moves and concentrates at the location of the process.
- In the classic location: pain moves to the lower right abdomen
- With a pelvic location: the suprapubic region becomes painful and frequent urination appears, as well as diarrhea with mucus.
- With a subhepatic location: pain is felt in the right hypochondrium
- With a retrocyclical (appendix is located behind the rectum) location: the lower back begins to hurt.
Another early sign is refusal to eat.
Nausea and vomiting
In all cases of the disease, a symptom such as vomiting is present. Unlike ordinary poisoning, vomiting does not bring relief.
- Children vomit repeatedly
- For school-age children, single or double
Temperature
Fever is also one of the most important signs.
- In young children
, the temperature rises high to 40° - At the age of 3–5 years, the temperature rises to 38–39°.
- In older schoolchildren (12 years and older), the attack is accompanied by low-grade fever (up to 38°).
Stool
Changes in stool are another of the main symptoms of appendicitis.
- Babies will have loose stools
- Children aged 3–5 years
experience stool retention (not constipation) - Adolescents, like adults, are more likely to experience constipation.
Condition of the tongue
Regardless of age, the surgeon always pays attention to the condition of the tongue. Based on this sign, you can determine at what stage the disease is currently located.
- At the stage of simple or catarrhal appendicitis, the tongue will be wet and covered with a white coating closer to the root
- At destructive stages, in particular at the phlegmonous stage, the tongue will also be wet, but already completely covered with plaque.
- In the gangrenous stage (the most dangerous), the tongue will be dry and completely white.
This symptom should never be ignored, especially if the child is still small.
Other symptoms by age
Up to three years of age, inflammation occurs suddenly and develops very rapidly, so at the slightest sign you should immediately consult a doctor. If possible, it is best to conduct a doctor's examination while you are asleep.
Among the signs of appendicitis in children that should alert parents are:
- Lack of appetite
- Decreased activity
- Cry
- Anxiety
- Poor sleep (especially on the first night after the attack begins)
- Nausea and vomiting
- The temperature can rise to 40° (if the baby is breastfed, the temperature may not rise above 37.5°)
- Diarrhea or frequent bowel movements
- Painful urination
- Increased heart rate
- The baby does not allow himself to be examined, and also bends and pulls his right leg towards him when squatting.
- The pain intensifies when dressing or bending to the right. It hurts for the baby to lie on his right side.
- Frequent loose stools, discharge may contain mucus. Especially if diarrheal appendicitis is present.
In addition to the fact that appendicitis can quickly turn from a simple stage into a destructive one and lead to complications, the danger of the disease also lies in the fact that frequent diarrhea can lead to dehydration.
You should call an ambulance when your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- have a fever not associated with a cold
- stomach hurts for several hours
- Abdominal pain makes it difficult to walk and worsens when coughing
- if the pain decreases with pressure and intensifies if you release your hand
Between the ages of three and five, a child can point out where it hurts. This greatly simplifies the diagnostic process.
The peculiarity of this age is that the child can endure mild pain for some time and not tell his parents about it.
From the age of seven, symptoms in children are the same as in adults. And yet at this age it is quite difficult to make a diagnosis, since he is scared, often cries and is capricious.
At this age, due to fear of surgery, children may say that nothing bothers them anymore and hide the fact that their stomach continues to hurt.
In adolescents over 12 years of age, the so-called “toxic scissors” symptom is observed. This means that the pulse (100 - 120 beats per minute) and the body temperature, which is quite low for such indicators, do not correspond to each other. Only a qualified doctor can check for this and other symptoms.
The table below provides information on the manifestations of the disease at three main ages when appendicitis is likely to occur. In children under one year of age, appendicitis practically does not occur, and in adolescents (from 11 to 18 years old) the symptoms are similar to those of the disease in adults.
| Symptom | In children under 3 years of age | In children from 3 to 6 years old | In children from 7 to 10 years old |
| Feature of age | Can't tell where it hurts. | Can tell where it hurts, but may ignore mild pain and not tell parents. | A child may be afraid to tell their parents about stomach pain because they are scared. |
| Loss of appetite | Refusal to eat is identified as the earliest sign of appendicitis in children | ||
| General condition of the body (weakness) | The child is lethargic, something is constantly bothering him (poor sleep), sharp monotonous crying. | Weakness. Unreasonable irritation and crying. | Weakness. |
| Pain | I have a stomachache. The pain intensifies when bending to the right. The child cannot lie on his left side. Painful sensations when walking. When you press, the pain subsides, but if you release your hand, it intensifies. | The stomach hurts, the nature of the pain, the child is not able to say | At first the whole abdomen hurts, then after 2-3 hours in the classic case it spreads to the lower right half. The pain intensifies when bending down. |
| Body temperature | Up to 40˚С | 38˚С – 39˚С | Up to 38 ˚С (chills) |
| Language |
| ||
| Nausea and vomiting | Nausea and repeated vomiting occur | Vomiting 1 – 2 times | |
| Dry mouth | Present at the last stage of the disease (the child is thirsty) | ||
| Chair | Liquid (sometimes with mucus), causing dehydration. | Bloating (flatulence or increased gas production), stool retention, but not constipation | Constipation is rarely present |
| Urination | Painful | Normal | Normal in a typical case (or frequent, with a pelvic location) |
| Pulse | Above normal | “Symptom of toxic scissors” Pulse does not correspond to body temperature. It is usually higher than normal. Normally, the pulse should increase by 10 beats/min. with a temperature increase of 1˚C | |
| Child behavior | The small child does not allow himself to be examined and pulls his right leg towards him. | Restless | Weakness |
At the age of 14 to 19 years, inflammation of the appendix occurs most often. The symptoms are absolutely identical to those of appendicitis in adults.
In addition to a general examination, girls are given a referral to be examined by a pediatric gynecologist. This helps to rule out pregnancy or diseases of the female genital organs.
What should you not do before the doctor arrives?
It is important for parents to remember that before the doctor arrives, if signs appear:
- You can't put a heating pad on your stomach
- Do not give painkillers (analgesics).
- You can't do an enema
- You can't give laxatives
Neglecting these tips is fraught with serious consequences.
A case from one's life. According to one patient, during an attack in childhood, she was given painkillers for two days. As a result, the girl lost consciousness and underwent surgery with a diagnosis of gangrenous appendicitis with peritonitis. After the operation, she was in intensive care for 4 days.
There are situations when a child’s appendicitis was diagnosed and excised after twelve hours in the clinic. Perhaps the inflammatory process is sluggish and does not manifest itself immediately. Even if, after the ambulance arrives, appendicitis is ruled out, and the symptoms intensify, it is necessary to organize a second urgent mandatory visit to the clinic. This is confirmed by numerous case histories shared by parents on forums.
Important! If you hesitate to visit a doctor and try to treat the disease at home on your own, it is dangerous for the child. Since appendicitis progresses much faster in children, there is a risk that if there is a delay in making a diagnosis, the little patient may lose his life. Even if doctors are not immediately sure of the diagnosis, it is better to leave the child in the clinic for some time for observation.
Stages and degrees
Appendicitis (symptoms in children 10-13 years old depend on the severity of the inflammatory process) occurs in several stages:
- the initial one lasts about 6 hours and is characterized by slight thickening of the walls of the appendix. I experience aching pain that covers the entire abdomen. They may be unstable and periodically recede;
- in the second stage (phlegmonous), which lasts until the end of the first day, the appendix enlarges, blood thickening occurs, which leads to the formation of blood clots;
- if no help was provided at the previous stage, the disease becomes gangrenous with the death of the walls of the organ;
- at the last stage, which is the most dangerous, the appendix ruptures and peritonitis develops. At this stage, urgent medical intervention is necessary.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children
At home, parents can lightly feel the boy's or girl's belly. Palpation must be done very carefully. If the child has pain on the right side, you should press a little with your fingers in this area, and some kind of compaction may be felt. If you suddenly remove your fingers and the pain intensifies, you may have inflamed appendicitis. If the pain intensifies when coughing, call an ambulance immediately!
To diagnose the problem, a mandatory examination by a doctor is necessary. During the examination, the doctor uses palpation to determine whether there is muscle tension in the right side of the abdomen, and checks the strength and location of the pain. During the examination, it is also clear whether there is irritation of the peritoneum.
If you suspect appendicitis, to clarify the diagnosis and prevent peritonitis, you must do the following:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). This method makes it possible to determine the presence or absence of acute inflammation with 95% accuracy.
- Complete blood count (allows you to determine the level of leukocytes)
- General urine analysis
If the above is not enough and the clinical picture is unclear, you can also resort to:
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Take an x-ray
- Laparoscopy (the method is used not so much to clarify the diagnosis, but to remove appendicitis)
For chronic appendicitis, the following types of diagnostics are also used:
- Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract
- Stool analysis
Developed inflammatory processes
After the end of the phase of uncomplicated appendicitis, usually after 24 hours, the disease enters the 2nd phase, which can occur in 2 ways.
They are:
- phlegmonous. It is characterized by increased pain, rapid breathing and a temperature of 38 degrees. On external examination, tension in the right side of the abdomen is noticeable. The tongue is completely covered with a white coating. At this time, the appendage itself begins to fill with purulent contents, and ulcers appear on the outside of the organ. It is possible that the vessels of the appendix may be blocked by blood clots. Determining the disease at this stage is not difficult;
- gangrenous . There may be either a continuation of the phlegmonous or uncomplicated stage of development of appendicitis. During this phase, necrosis of the tissues and nerve endings of the appendix occurs. As a result, the patient notes a decrease in the pain symptom, but when palpating the appendix, an unbearable pain occurs. The stomach itself is in a bloated state. Temperatures can drop to 36 degrees. Severe intoxication is observed, accompanied by vomiting and increased heart rate. The phase is dangerous due to wall rupture due to cell necrosis.
Treatment of appendicitis in children: surgery
Treatment is surgery to remove the appendix or appendectomy. Although there are extremely rare cases where a child recovers without surgery, most often it is necessary to resort to surgery.
- For children, appendectomy is best done using the laparoscopic method. This is acceptable in cases where there is no peritonitis yet. This operation lasts only 20 minutes. Three small punctures are made to provide access. A small camera and the necessary instruments are inserted through them.
How this operation is performed on a child is shown in the video:
After laparoscopy, the child will have to remain inpatient treatment in the hospital under the supervision of doctors for about seven more days.
- If appendicitis ruptures
, the person is operated on primarily through an open incision. During an appendectomy, in this case, damaged parts of the intestine are removed and the abdominal cavity is cleaned.
After such an operation, recovery will take longer and intensive postoperative antibiotic treatment will be required. Full recovery may take more than one month.
In children, the postoperative period is complicated by the fact that it is difficult for them not to eat or drink anything for the first day after surgery. They cannot lie still and follow other doctor's recommendations.
Complications after surgery to remove appendicitis
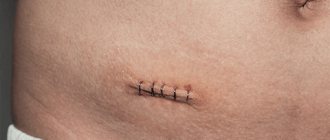
Immediately after an appendectomy, hematoma and swelling in the suture area should be expected. After a few days, the swelling should begin to decrease and the bruising should go away on its own.
During the rehabilitation period, the following undesirable complications are possible:
- Delayed wound healing
- Suppuration of the sutures (often occurs due to the fact that the pus was not completely removed after appendicitis with peritonitis)
If on days 6–9 after surgery the temperature rises sharply, fever is observed and sharp pain appears in the right side, then there is a risk of serious postoperative complications, such as:
- Purulent abscess
- Adhesive disease
- Internal bleeding
- Subphrenic abscess
What will happen in the hospital.
In the emergency room, the child will have an ultrasound and will be examined by a surgeon. If the appendix is inflamed, and tests confirm this, if you have not fed or watered the child for at least 3.5 hours, he will be immediately taken to the operating room. There, using laparoscopy (these are 3 small punctures), the inflamed appendix will be removed through a small hole and a healthy baby will be returned to you, completely free of appendicitis. After 4 hours he will be able to get up and drink water, but all this is only if you have time before the complications begin. If for some reason laparoscopic surgery is not possible, abdominal surgery will be performed and the recovery period will take longer.
Can a child under one year old have appendicitis?
In one-year-old babies
this disease practically never occurs. Most often, this disease appears at the age of 6 years and older. According to statistics from all cases of this disease in childhood:
- Toddlers account for only 5% of cases
- For preschool age – 13%
- For school – 80%
In infants, the problem is extremely rare, since their appendix lumen is wider, and the appendix itself is shorter in size. In addition, newborn babies have not yet fully developed lymphatic follicles. Moreover, the type of nutrition up to 2 years of age is such that the likelihood of obstruction of the appendix is very small.
Important! The symptoms of appendicitis are very similar to those of other diseases. Abdominal pain in a child can also be caused by the presence of an infection in the body, as well as constipation, overeating, poisoning, and so on. To identify the exact cause of the pain, you need to call a doctor.
What diseases can be confused with?
Inflammation of the appendix is often confused with intestinal diseases of a different nature.
Pathologies of other organs can also be transmitted to this area.
The disease is confused with the following organ dysfunctions:
- Meckel's diverculitis. The process of enlargement of the small intestine located near the appendix. In this case, the patient must be operated on as soon as possible.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. The pathology is typical for females since inflammation of appendicitis has common symptoms with the development of inflammation in the fallopian tube or ovaries.
- Inflammation in the upper abdomen. When biological fluid accumulates in the lower abdomen, inflammatory processes develop, which leads to sensations similar to pathologies of the appendix. Similar symptoms also occur with diseases of the appendages.
- Pathologies of the renal system. In the human body, the right kidney is localized near appendicitis, so there are common cases when kidney inflammation was mistaken for the appendix.
Blind but dangerous
The appendix is a short and thin blind vermiform appendix 7-10 cm long, located at the end of the cecum (the initial part of the large intestine). Like any part of the intestine, the appendix produces intestinal juice, but so little that it does not play a special role in digestion. Therefore, for a long time it was considered a “mistake of nature” and was removed by the patient at the first opportunity. But recently, scientists discovered lymphoid cells in the caecum, the same as in human tonsils. And since these cells have the properties to protect the body from infections, the assumption was born that the appendix is part of the immune system.
However, the number of protective cells in it, as it turned out, is very insignificant and cannot have a strong effect on the immune system. So most experts are still confident that there is no benefit from the appendix, but the harm in case of its inflammation can be significant: acute appendicitis not diagnosed in time can cost not only health, but also life.
Forecast
The success of treatment depends on the stage at which the operation was performed. If there was no rupture of the appendix, the child will fully recover within a month after surgery. If the contents of the appendix enter the abdominal cavity, the child can recover and be under the supervision of a pediatrician for more than 3 months, sometimes up to 6.
Symptoms of appendicitis cannot be ignored in both adults and children. Timely detection of inflammation and subsequent treatment help avoid complications. It also guarantees a complete and rapid recovery of the patient.
Author of the article: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky