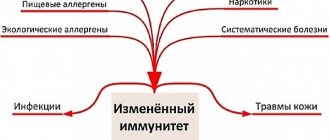
Causes of skin diseases
The main causes that cause or aggravate skin diseases:
- genetic predisposition;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- stress and the presence of obsessive states (touching the face, scratching wounds, constant use of antibacterial soap);
- infection or viral infection;
- hormonal disorders;
- various allergic reactions;
- infection with skin parasites;
- constant exposure to negative factors (poor quality water, heavy dust, high environmental humidity, polluted air, etc.);
- presence of bad habits, violation of hygiene, nutrition and sleep;
- use of inappropriate, low-quality or spoiled cosmetics.
Important! Facial skin diseases that are not associated with infections and viruses can be triggered by chronic diseases, genetic characteristics or external factors.
Conclusion
When contacting a specialist, medications will be prescribed that will help increase the level of immunity, and will also help protect the body from the penetration of additional infections and bacteria. If you lead an unhealthy lifestyle, you may develop basal cell carcinoma of the skin of the nose, which is classified as a malignant neoplasm. Proper nutrition plays a particularly important role. Under no circumstances should you fix problems on your own by squeezing out pimples and other formations. A dangerous infection can enter the body, which can cause great harm to a person, even death. During the treatment, it is prohibited to use cosmetics and perform thermal procedures. You are not allowed to visit the sauna or bathhouse. It is important to avoid alcoholic beverages and not smoke tobacco products, as this will only make the skin more inflamed.
Cuperosis
This disease can be recognized by specific capillary networks or stars. It occurs due to the expansion of the vascular walls and loss of their elasticity, which causes blood stagnation. A skin disease can manifest itself as just one “point” or a whole network that spreads along the wings of the nose, cheeks, and area around the eyes. Often rosacea signals a predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system or liver diseases.
Frequent causes:
- injuries;
- exposure to UV rays;
- heredity;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- prolonged exposure to low temperatures;
- peeling and other cosmetic procedures;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Acne
Symptoms: presence of acne, ulcers, internal pimples. Cause of manifestation: inflammation of the sebaceous glands. There are three degrees of acne severity: high - more than 40 lesions, medium - from 10 to 40, mild - up to 20 formations.
Causes of the disease:
- hormonal changes (age-related, menstrual and others);
- heredity;
- side effect of hormone therapy.
Acne usually occurs in teenagers, but can also occur in adults. People with oily skin or hormonal imbalances are at risk.
Chloasma
Opposites of vitiligo: excessive pigmentation. The area is dark, usually brown, and gradually enlarges. spots may merge into one rounded lesion. May be caused by pregnancy or diseases: disorders of the ovaries, liver or pituitary gland.
Important! Dermatoses are a group of diseases that occur with inflammatory processes. They can be congenital or acquired, including due to neurological abnormalities, dysfunction of the endocrine system, reactions to parasites, and decreased immunity.
Rosacea
As a rule, the lesions affect only the skin of the face; an adult patient with a genetic predisposition is at risk. It has a polyetiological nature and a staged course. Manifestation: facial hyperemia, pustules, edematous papules, telangiectasia. Important: hyperplasia of connective tissue and sebaceous glands is characteristic, and not increased secretion of sebaceous glands (unlike acne). As a rule, the skin disease manifests itself in patients aged 35-40 years, reaching a peak at 40-50 years. The disease is provoked by changes in the tone of the superficial vessels of the skin caused by endogenous and exogenous factors.
Skin structure
The skin consists of three layers:
- The epidermis is the top layer of skin, the thickness of which is 1-3 mm. Consists of keratinized cells containing keratin. It performs a protective function.
- The dermis is the second layer of the skin, consisting of connective tissue fibers. The thickness of this layer is 1-3 mm. Thanks to the dermis, the skin is very elastic. It has a developed vascular system and nerve endings
- Subcutaneous tissue is the third layer, also consisting of connective tissue. It contains many fat cells that form subcutaneous fat, which has a protective function for internal organs.
Small nodular sarcoidosis
Manifestation: nodular elements with a dense consistency with sharp boundaries. They can have a color from pink to brownish-yellow. Telangiectasias form on the surface of some papules. In place of resolved elements, small atrophic scars form. Diascopy reveals the phenomenon of “dustiness” and small yellowish spots. Resolved elements tend to form scars.
Types of spots on a child’s skin and the reasons for their appearance
Important! Fungal and infectious diseases of the facial skin are provoked by pathogenic organisms. Infections on the face can infect deep tissues or enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis.
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases
If you find any pathologies on the skin, you should not start self-medication; first, you should visit a doctor. He will prescribe a series of studies to determine the disease, and, based on this, will prescribe treatment.
Tests that will need to be taken to determine the type of pathology:
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Scraping from the affected area;
- Biopsy (if necessary);
- Allergen test;
- STD test;
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
Note! Most skin diseases cannot be completely cured, but by following basic hygiene rules and other general recommendations, you can maintain them during the sleep stage.
Streptococcal infection
Mainly found in women and children, the lesion affects smooth skin and has no connection with the follicular apparatus. Manifestation: phlectena or impetigo, which quickly opens and forms serous-purulent crusts. It is most often observed in the corners of the mouth and eyes.
Important! Pustular diseases of the facial skin most often occur due to the influence of streptococci, fungal infections, staphylococci and other infections. Factors contributing to the development of the disease: elevated blood sugar, microtrauma, hypovitaminosis. There are superficial and deep forms. Boils with one purulent-necrotic core and carbuncles are a manifestation of the deep form.
FAQ
Does allergies cause fever or not?
A slight increase in temperature when an allergic component enters the body can be considered normal. Thus, a signal is given that a foreign object has penetrated the cells. A change in temperature of more than one degree should be considered a much more alarming symptom. This indicates the addition of inflammation, and therefore in this case a separate recovery course is prescribed.
What is the name of the allergy blood test?
A blood test for allergies is a test of the blood for the content of immunoglobulin E. Depending on the specific food or other allergens, different indices of this component are identified.
What to apply to an allergic rash?
To ensure effective treatment of allergic rashes, the following remedies are used:
- non-hormonal ointments, for example, Fenistil or Bepanten;
- hormonal compounds, namely Advantan or Elokom;
- Fluorocort, Afloderm and others, used for significant allergic and inflammatory reactions.
The most potent components are Galcinonide and Dermovate ointments, the use of which would be best discussed with a specialist. In addition, treatment of skin allergies in adults can be carried out using Levomekoli, Panthenol and other agents that are more likely to be preventive.
Can you be allergic to coffee?
Instant or brewed coffee is a fairly strong allergen. In the vast majority of cases, the reaction manifests itself in vomiting, severe abdominal pain and frustration. Less commonly, skin changes such as rash or itching may occur. The most rare symptoms are an increase in temperature, as well as Quincke's edema.
How to find out what an adult is allergic to?
To determine a specific allergen, specialized tests are used to identify even the rarest species. In the vast majority of cases, skin tests or blood tests for immunoglobulin E are used. It is recommended to use them all together, which will increase the accuracy of the studies, for example, if a reaction to mascara or shellac is formed.
What could you be allergic to in October?
Allergies in mid-autumn, namely in October, can develop due to three factors. When talking about this, people pay attention to pollen, fungal spores and house dust. It should be borne in mind that it is in October that quinoa, wormwood and ragweed bloom, as a result of interaction with which a rash, swelling of the throat and no less serious symptoms can occur. Some of them are directly related to how sweet allergies manifest themselves.
Allergy to milk, is it possible to have fermented milk products?
Fermented milk products can also not be consumed by everyone, because, for example, cow’s milk contains at least 20 components that have different protein natures. Lipoproteins and alpha-lactalbumin deserve special attention in this regard. This is why if an adult begins to sneeze or cough after eating dairy products, it is recommended that they undergo a special check.
Allergy to hair dye, what to do?
Tip: If women are allergic to hair dye, it is recommended to rinse their hair with a herbal decoction, such as chamomile.
If burning and itching occurs in the face or neck, the affected area of skin is lubricated with compounds such as Fenistil-gel or Psilo balm. Antihistamines are used if a person's condition quickly worsens or if they begin to itch excessively. If symptoms and fever do not go away within several hours, it is recommended to seek medical support.
News MirTesen
Acne vulgaris
Purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and the sebaceous gland itself. Often caused by a staph infection. Usually the rashes are observed on the face, chest, and back. The course of the facial disease: the appearance of blackheads - comedones, then the appearance of a painful red nodule, after which - the formation of a purulent pustule.
With infections, necrotic acne is possible, in which necrosis progresses deep in the element. In this case, after healing, a scar forms. The spread of the process increases the risk of abscesses and acne conglobata.
Important! Viral skin diseases occur in 3-4% of adult patients and in up to 10% of children.
Treatment of streptoderma in children
Any form of streptoderma, even local, requires mandatory treatment, as it tends to spread, is contagious and, in addition, streptococcus can provoke such serious autoimmune diseases as rheumatism, glomerulonephritis or endocarditis.
Hygiene rules
Sometimes parents neglect the doctor’s recommendations regarding hygiene and treatment of household items, believing that the main thing is to anoint them three times a day, the rest is unimportant. In some cases, this turns out to be enough, in others, they are very surprised when it turns out that the child cannot recover from a seemingly minor illness for several weeks, new rashes appear, and other family members become infected. Compliance with hygiene recommendations is no less important part of treatment than streptoderma ointment or antibiotic.
Mandatory hygiene aspects when treating streptoderma in children:
- do not wash for at least 3-4 days, do not wet the affected areas with water, as it is an excellent carrier of infection in this case;
- Gently wipe unaffected areas of the skin with a damp towel or a cotton swab dipped in water or a decoction of string/chamomile;
- ensure that the child does not scratch the affected areas; in addition to purely mechanical restrictions, antihistamines, which are prescribed by a doctor, also help to reduce itching of the skin;
- the child must have an individual towel hanging separately from the towels of other family members;
- individual dishes and cutlery, which must be carefully processed after a sick child has used them;
- It is better to remove soft toys during the period of illness, and wash plastic ones regularly;
- constantly change or iron the child’s bed linen, especially pillowcases, with a hot iron;
- If there are minor skin lesions, treat them regularly with an antiseptic.
Local treatment
In some sources on the Internet, recommendations for the treatment of streptoderma in children are still copied from old sources, and there are advice to lubricate with silver nitrate or mercury ointment. The first drug has been discontinued; more precisely, it is produced only for animals or as a chemical reagent; the second has long been banned as highly toxic. Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) is available by prescription.
Modern antiseptics and ointments with antibiotics are much more effective, easier to use and safer. Local treatment includes opening the phlyctena in compliance with the rules of asepsis and subsequent treatment of the affected areas of the skin with liquid antiseptic and ointment.
Antiseptics
- hydrogen peroxide 1%
- brilliant green, 2% aqueous solution (brilliant green)
- fucorcin or boric acid
- salicylic alcohol 2%
They are applied to the affected areas of the skin, covering some area around with a cotton swab or swab 2-4 times a day; at the beginning of treatment, the child will feel a burning sensation and pain for a short time. After the liquid antiseptic has dried, ointment can be applied to the skin.
From folk remedies that have long been adopted by official medicine, the doctor can recommend you decoctions of chamomile, string or oak bark, which are well-known antiseptics. Use them as lotions, for rinsing healthy skin, compresses and bandages on affected areas, but not as the main treatment, because With this pathology, antibiotics cannot be avoided.
Antibiotics in the treatment of streptoderma
Antibiotics for streptoderma in children are used in the form of local forms and orally (systemically) according to strict indications. No one will start systemic antibiotic treatment for a single rash on the face or hands that responds well to topical therapy. At the same time, abandoning this method in common forms, especially with the addition of general symptoms, and especially in severe cases, is at least unreasonable.
A special group of drugs consists of ointments with hormones, which are prescribed in certain cases for a short period of time. With prolonged use, they cause a decrease in the protective properties of the skin and increase its vulnerability to any infection, therefore, for streptoderma, they are prescribed only for a short course, according to strict indications and for certain symptoms.
| Antibiotic ointments (local treatment) | Ointments with antibiotics and hormones (only in extreme cases as prescribed by a doctor) |
|
|
It is possible to carry out such inexpensive local treatment for mild forms of streptodermia. You will need: zinc ointment (30 rubles), chloramphenicol tablets (20 rubles), chloramphenicol alcohol (20 rubles). First, the affected area and surrounding tissue are treated with chloramphenicol, the wound is treated with fucorcin or brilliant green, then allowed to dry. Next, make a mixture of zinc paste/ointment with chloramphenicol tablets crushed into powder, mix thoroughly. And lubricate the wound with this mixture morning and evening.
Systemic treatment of streptoderma with antibiotics
Most often, penicillin antibiotics are used for these purposes. Other groups of antibiotics, macrolides or cephalosporins, are used if the child has recently received penicillins for some other reason, in case of allergic reactions to them, or in the absence of sensitivity to these drugs, revealed by microbiological examination.
Penicillin antibiotics
| Cephalosporins
| Macrolides
|
HPV - Human papillomavirus
Causes the appearance of condylomas and warts on the mucous membranes and skin. More than 200 varieties of the virus are known, of which 50% are the main cause of warts. The cause of the virus is low immunity and skin microtraumas. When infected, the virus may not appear for a long time, but become more active when the body weakens. There is a definite connection between HPV infection and some forms of cancer, including cervical cancer.
Important! Usually, each disease has pronounced symptoms, but often skin changes can be grouped, which complicates the diagnostic process. To find out the reasons for the appearance of deviations, it is necessary to undergo an examination and be extremely frank with the dermatologist, without hiding habits or diseases. Self-medication or use of drugs without an accurate diagnosis can worsen the situation.
We recommend reading the Zen channel “https://zen.yandex.ru/vodakanazer.ru”, where you will find a lot of useful information for summer residents and gardeners.
Signs of ulcers
Such skin disorders can begin along with other disturbances in the normal functioning of the body. The most common symptoms and signs:
- The appearance of hypersensitivity in a certain area of the body after mechanical impact.
- Changes in appearance - skin density, bruising, peeling skin, etc.
- Once the skin has peeled off, new skin appears at a very slow rate. Instead, a non-healing and hypersensitive surface may appear.
With properly selected therapy, the skin will recover much faster: the ulcer is cleared of pus, the recovery rate will be faster than the rate of death of the epidermis.