Adenomyosis is a type of endometriosis, a disease in which the glandular tissue of the uterus (endometrium) grows into the underlying layers of the uterine wall. It usually develops in women of reproductive age, but can also be found in very young girls. During menopause it disappears on its own.
- Causes of adenomyosis
- Classification and forms of the disease
- Symptoms of adenomyosis
- How is adenomyosis diagnosed?
- How is adenomyosis treated?
- Postoperative period
- Pregnancy with adenomyosis
- Complications of adenomyosis
- Prevention
- Forecast
The disease is manifested by heavy menstrual bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen, acyclic bleeding and severe premenstrual syndrome. Also, one of the significant manifestations of adenomyosis is infertility, but a direct connection has not yet been established.
What is uterine adenomyosis?
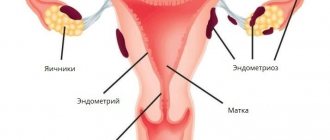
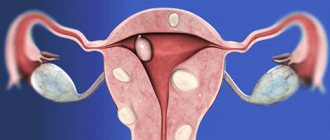
A diagnosis of adenomyosis means that the endometrium, or inner lining of the uterus, has begun to grow into its muscle layer (Fig. 1).
At the same time, endometrial cells that have taken root in an atypical place continue to behave there as usual, causing inflammatory reactions and adhesions in the tissues. As a result, a complex chronic disease develops. The incidence of adenomyosis is from 7 to 60%. Figure 1. Uterine adenomyosis occurs when the endometrium grows into the uterus. Normally, the endometrium lines the uterine cavity and is shed every month during menstruation. Source
Causes of the disease
Currently, scientists do not know exactly why the endometrium begins to grow in places not intended for it. The most popular theories are hormonal and immune.
According to the hormonal theory, the cause of the disease is an imbalance of female sex hormones: excess estrogen with low progesterone levels. Estrogens stimulate the growth of the mucous membrane in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, so when there is an excess of them, the endometrium thickens excessively. Cells of the mucous membrane lose sensitivity to progesterone, which can suppress excessive growth of the endometrium.
The second most popular theory is immune. Due to hormonal imbalance, injuries, infections and other factors, the reactivity of local immunity changes (the ability to adequately respond to emerging threats at the place of their origin). Immune cells cease to control the growth of endometrial cells and do not promptly remove fragments of the mucous membrane that have entered the muscle layer.
How can the endometrium get outside the uterus? One of the earliest assumptions is that endometriosis occurs as a result of the backflow of menstrual blood into the uterus and other organs and tissues (fallopian tubes, abdominal cavity, etc.), but this is a controversial statement. The fact is that not everyone develops the disease, and retrograde blood flow during menstruation is a common occurrence; it occurs periodically in the vast majority of women. Another source of endometrial cells in the most unexpected parts of the body may be mesothelium (a layer of cells lining the surface of the peritoneum, pleura, pericardium) or stem cells.
It is believed that endometrioid tissue is introduced into the uterine body in three ways:
- with blood through the uterine vessels;
- with lymph through the interstitial spaces;
- during surgery: adenomyosis of the operated uterus is a common occurrence.
Recommended Diet
Nutrition for adenomyosis, as for other diseases, is based on the general principles of a healthy diet:
- Elimination of unhealthy foods - sweets, carbonated water, fast foods, etc.
- As for alcohol, it is recommended to use only red wine in limited quantities.
- Greens, fruits, vegetables should be in abundance (apples, citrus fruits, onions, broccoli).
- Some sources recommend excluding dairy products and fatty meats.
- You need to consume enough protein foods and with plenty of hemoglobin.
- Give up coffee in favor of green tea.
- Use B vitamins.
Who is at risk?
Endometriosis, and therefore adenomyosis of the uterus, can develop in any woman if she has menstruation. However, women between 30 and 40 years of age are most susceptible to it.
The risk increases in the presence of predisposing factors, including:
- Hormonal imbalance
- Changes in the reactivity of the immune system,
- Uterine fibroids,
- Chronic inflammation
- Mechanical injury
- Taking corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressants,
- Ionizing radiation
- Heavy physical activity
- Body weight deficiency
- Abortion,
- Difficult birth
- Lack of pregnancy and childbirth,
- Surgery on the uterus,
- High consumption of trans fats (they are found in large quantities in margarine and confectionery products),
- Having relatives suffering from endometriosis
- Menstrual cycles that are too short (less than 27 days),
- Long menstruation (more than 7 days),
- Heavy menstruation
- Early onset of menstruation (at 11-13 years old) or late menopause,
- Health problems that block the flow of blood from the body during menstruation.
There are also factors that reduce the risk of all forms of endometriosis:
- presence of pregnancy and childbirth,
- full breastfeeding,
- the onset of the first menstruation after 14 years,
- taking oral contraceptives,
- consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids (they are found in large quantities in vegetable oils, fish, spinach, seaweed, chia seeds),
- lack of obesity and bad habits.
Preparing for surgery
Preparation is required for all patients, regardless of the method of surgical treatment of adenomyosis. It consists of several stages:
- Donating blood for a general analysis necessary to determine the group and Rh factor, as well as the biochemical composition and other compositional features;
- Repeated examination of smears taken from the vagina;
- Submission of urine for general analysis;
- Examination of the internal thoracic organs using x-rays.
These manipulations are not included in the list of mandatory procedures, but they are needed to eliminate negative consequences. Responsible specialists strongly recommend that you go through all stages of preparation before treatment.
Classification: forms and stages of the disease
Adenomyosis of the uterus is classified according to the shape of the pathological foci, that is, according to their location and the depth of tissue damage.
Depending on the appearance of the pathological focus, three forms of the disease are distinguished - focal, nodular and diffuse (Table 1).
Table 1. Forms of uterine adenomyosis
| Form of adenomyosis | Description |
| Focal | With this form, small, light gray, irregularly shaped lesions without clear boundaries, up to 1.5 cm in size, are found in the uterus. |
| Nodal | Otherwise it is called adenomyoma. The nodes are dense formations of irregular shape, up to 5 cm in size. In the nodular form, the body of the uterus is enlarged. |
| Diffuse | With diffuse damage, the body of the uterus takes on a spherical shape, significantly enlarges and compresses the surrounding tissues. |
| Mixed | At the same time, signs of different forms of the disease are detected - multiple small foci, large nodes and thickening of the entire endometrium. |
Adenomyosis is often attributed to one of the stages, which reflect the degree of endometrial growth inside and outside the uterus (Table 2).
Table 2. Stages of adenomyosis
| Degree/stage | Description |
| I | The pathological process does not extend beyond the submucosal layer |
| II | The lesion extends to the middle of the muscle layer. |
| III | The entire muscle layer is affected, endometrioid tissue grows to the outer membrane - the serous layer. |
| IV | The pathological process spreads to the peritoneum covering the uterus and spreads to neighboring organs - the bladder and rectum. |
Danger of disease
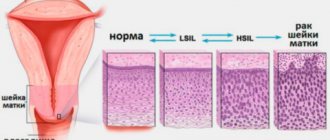
Adenomyosis of the uterus is a benign disease with signs of a tumor-like process. Endometriotic tissue is prone to independent progressive growth, which can accelerate or slow down, depending on hormonal levels and immune regulation. This pathology is unpleasant because it interferes with the ability to work and reproductive function, but it should not be confused with cancer. Endometriosis is not cancer! Some studies suggest a link between endometriosis and ovarian cancer and adenocarcinoma, but so far data is very limited, and these types of cancer are very rare.
Endometriosis is also a risk factor for the development of certain autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Traditional methods
Clay treatment
A very effective and efficient method of treatment from the arsenal of traditional medicine.
- In this case, the clay is diluted with water, left for several hours, then boiled in a water bath for 10 minutes.
- A cake is made from the resulting mass and applied to the lower abdomen, leaving for 2 hours.
- The course of therapy is from 5 to 10 procedures.
Treatment with medicinal leeches
According to doctors, the method is quite effective:
- Leeches are applied to active points on the body, and there is an active effect on them.
- At the same time, leech saliva enters the human blood - the latter has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, blood flow in the affected area increases and hormonal levels stabilize.
Decoctions and infusions
Angelica
- This plant contains plant phytohormones, estrogen and progesterone, due to the action of which the pathological growth of foci of adenomyosis is reduced, pain is relieved and menstrual cycles are normalized.
- For the decoction itself, it is enough to steam 15 grams of rhizome in 400 ml. boiling water and boil for 10 minutes over low heat.
- After cooling, take 1 tbsp. three times a day, before meals.
- It is forbidden to take during pregnancy and lactation, excessive uterine bleeding.
Swamp cinquefoil
- A decoction of it is taken orally and used for douching.
- To prepare a decoction of cinquefoil - 50 g. the raw material is steamed in a liter of water and boiled over low heat for 10 minutes.
- After this, it should be cooled and strained, then take 200 ml. morning and evening after meals.
- Effective therapeutic results show themselves after 2 weeks - the decoction relieves pain and stops foci of pathological tissue growth, and has an antitumor effect on the body.
Hog queen
An effective plant in the treatment of adenomyosis, since it contains plant flavonoids that have a beneficial effect on hormonal levels and the entire woman’s body.
- A decoction of this plant has an anti-inflammatory and antitumor effect, strengthens the body and helps stop heavy bleeding.
- As doctors note, boron uterus in combination with cinquefoil are 2 effective plants in the fight against adenomyosis.
- To prepare the decoction, brew a tablespoon of the original raw material in 400 ml of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes, and then take it an hour before the main meal.
- The positive therapeutic effect will show itself after 2 weeks - the main thing is not to stop taking the herbs throughout the entire course of treatment.
Siberian ginseng
- The plant hormones included in its composition help restore normal hormonal levels , and copper and selenium, cobalt and other microelements restore blood flow and prevent the development of anemia, suppressing the pathological growth of tumors.
- To prepare a medicinal decoction, simply brew a tablespoon of dry plant in 300 ml of boiling water and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. After this, leave for an hour and take 100 ml. three times a day, adding honey for taste.
- You can also prepare an alcohol tincture from this plant - 50 g. The rhizomes of the plant are poured with 5 liters of vodka and left for a month in a dark place. After straining, take 50 ml once a day. The main thing is not to take this tincture if you have hypertension and heart failure.
Yarrow
- A decoction of this plant stops the inflammatory process and has a pronounced hemostatic and bactericidal effect. It is used for heavy uterine bleeding and disruption of the menstrual cycle, inflammation affecting the female reproductive system.
- To prepare a medicinal decoction, steam a tablespoon of the dry plant in a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour. Next, take a third of a glass per day, after the main meal.
- You can also prepare an alcohol tincture - for this, 30 g. The dried plant is poured with 400 ml of medical alcohol or vodka and infused for 2 weeks in a dark, cool place. After straining, take the tincture 30 drops 3 times a day, always after meals.
Wild yam
It helps to successfully relieve inflammation and prevent pathological spread, proliferation of epithelial tissue, relieving muscle spasm.
To prepare the decoction it costs 3 grams. dry raw materials in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour. After straining, take the entire volume at a time for a month.
The main thing is not to take the decoction during pregnancy and while breastfeeding; it is not given to children under 18 years of age.
Symptoms
Uterine adenomyosis, like any type of endometriosis, is very difficult to recognize. Sometimes they do not appear at all, and the main symptom is pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area (such pain can be a consequence of many other diseases).
Women of childbearing age with adenomyosis are usually concerned about the following complaints:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region before and during menstruation,
- Dark brown spotting 3–5 days before menstruation,
- Menstrual irregularities,
- Problems with conception,
- Pain during sexual intercourse or during natural needs.
Important! The pathological process is considered active if severe pain is combined with heavy and prolonged bleeding during menstruation. A gradual increase in menstrual pain from year to year may indicate endometriosis.
If the corners of the uterus are affected, the pain spreads to the groin area, and if the back of the isthmus is affected, to the rectum.
When should I make an appointment with a doctor?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have prolonged, heavy bleeding or severe cramping during your period that interferes with your normal activities.
Complaints during menopause
After the onset of natural or surgical menopause, typical signs of the disease disappear, and health improves significantly. This occurs due to a decrease in estrogen production, as a result of which endometriosis lesions stop enlarging. If a woman undergoes hormone replacement therapy during menopause, the disease may return.
Postoperative period
After surgery using any of these methods, the patient requires inpatient observation. Recovery in hospital lasts several days. After discharge, you should undergo a gynecological examination once every 7-10 days. This is necessary for timely detection of complications that can be caused by adenomyosis and surgery. After completion of therapy, regular visits to the gynecologist are required at least once every six months.
Complete elimination of lesions is characterized by a constant menstrual cycle and the absence of pain, discomfort in the pelvic area, and pathological discharge. Successful therapy eliminates relapses for at least five years after surgery and rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
Endometriosis is very difficult to diagnose clinically, since in the early stages of the disease patients present with nonspecific complaints. On average, making a correct diagnosis takes 7.5 years from the appearance of the first symptoms. Usually the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis after questioning the woman and performing a gynecological examination. With adenomyosis, the uterus is enlarged, hardened and painful to the touch, often tilted back.
To confirm the diagnosis of adenomyosis, the doctor prescribes instrumental studies and a number of laboratory tests. Among other things, a study of hormonal status (determining the level of estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones) can help in making a diagnosis.
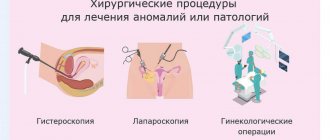
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is currently the “gold standard” for diagnosing endometriosis. This is an invasive procedure performed under general anesthesia (Figure 2). During the operation, through small incisions on the anterior abdominal wall, the woman inserts the necessary instruments and a camera into the abdominal cavity to determine possible pathologies (adhesions, inflammatory processes, neoplasms).
Figure 3. Diagnostic laparoscopy. Source: CC0 Public Domain
Laparoscopy is important for diagnosing grade 3 and 4 adenomyosis. At this time, dotted or nodular structures of blue or purple color are already visible on the surface of the uterus.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound using a vaginal sensor can detect the problem in 80–93% of cases at any stage. Vaginal ultrasound is done before and after menstruation. With a focal form, the doctor detects a heterogeneous focus and an enlargement of one of the walls of the uterus, with a nodular form, zones with an enhanced echo signal of an oval or round shape. The diffuse form is characterized by uneven jagged boundaries between the endometrium and the muscle layer.
CT and MRI
Computed tomography allows visualization of pathological zones and foci in approximately 50% of cases. The method is informative when you need to assess the depth of the lesion and detect foci of endometriosis outside the uterus - in the peritoneum covering its body and the uterosacral ligaments. Magnetic resonance imaging reveals thickening of the transition zone of the mucous membrane, and evaluates the condition of the pelvic organs.
Tumor markers
In healthy women, the level of tumor antigen CA-125 in the blood is 8.3–13.3 U/ml, with adenomyosis – 27.2–35 U/ml.
Important! This marker is not specific. In the early stages of the disease, the indicator may be within normal limits, but with moderate and severe endometriosis it increases significantly.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is an examination of the uterine cavity using video technology. The study makes it possible to identify the disease in 83% of cases, visually assess changes in the mucosa and perform a biopsy - sampling of pathological tissue from the endometrium.
Hysteroscopically, the following degrees of the disease are distinguished:
I – preserved endometrial relief, pathological foci in the form of “eyes” with a shiny surface;
II – “ridges” on the mucosa, compaction of the uterine wall and damage to the isthmus;
III – nodes in the form of bulges with uneven contours, the wall relief resembles a honeycomb.
Important! The diagnosis must be confirmed by histological examination - examination under a microscope of tissue taken from the uterine cavity.
Treatment
Treatment of adenomyosis is indicated for women with symptoms (severe pain, spotting during menstruation) and those who cannot become pregnant. In other cases, the course of the disease is simply monitored. The purpose of therapy for adenomyosis can be: removal of the pathological focus, slowing down its growth, getting rid of pain and restoring reproductive function.
Without surgery
Usually they start with drug treatment. It is prescribed if a woman is not planning a pregnancy. When starting treatment, you should understand that medications will not help to completely and permanently get rid of the disease; they will only reduce the severity of symptoms, slow down the growth of the endometrium and reduce the size of endometriotic lesions.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug treatment for internal endometriosis is hormonal drugs (Table 3).
Additionally, your doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory medications.
They are started one to two days in advance and continued during menstruation to relieve pain and reduce menstrual blood flow. Table 3. Drug therapy for uterine adenomyosis (endometriosis)
| Group of drugs | Description | Can it be used when planning pregnancy? |
| Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) | They contain estrogen and progestin, inhibit the progression of the disease by suppressing ovarian function, cause endometrial atrophy and eliminate pain. Side effects: nausea, breast tenderness, irregular bleeding. Serious complications (thrombosis, stroke) are associated with smoking | No |
| Progestins | They contain synthetic progesterone, suppress the growth of the endometrium, cause its atrophy and reduce pain during menstruation Side effects: weight gain, bloating, acne | No |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH agonists) | Prescribed in the presence of severe symptoms. Drugs in this group emit the onset of menopause by blocking ovarian function and reducing the activity of endometrial tissue. Effectively fight pain Side effects: hot flashes, vaginal dryness, insomnia, lack of libido. Long-term use increases the risk of osteoporosis | No |
| Aromatase inhibitors | Block the enzyme that is responsible for increasing estrogen levels in the blood Side effects: hot flashes, memory loss, depression | No |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Eliminate symptoms, but do not prevent the development of endometriosis. Indicated for women with mild symptoms Side effects: damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines (erosions, ulcers) | Yes |
The duration of drug treatment is usually at least 3 months. After the course, the doctor continues treatment or changes the drug. If there is no effect, surgery is indicated.
Physiotherapy
To relieve symptoms, iodine and zinc electrophoresis with sinusoidal modulated current, acupuncture, therapeutic ultrasound, magnetic therapy and balneotherapy are sometimes used.
Surgery
There are two types of surgical interventions that can combat uterine adenomyosis - with preservation of the organ and radical, when the uterus is completely removed.
Indications for surgery include:
- Severe pain during menstruation,
- Combination of endometriosis with fibroids,
- Prolonged and heavy bleeding leading to anemia,
- Infertility (in which case organ preservation surgery is indicated),
- Ineffectiveness of drug treatment,
- III degree of the disease.
The operation is performed on days 5–12 of the menstrual cycle.
Organ-preserving interventions, minimally invasive
Surgery with preservation of the uterus is indicated for patients with grades I–II of the disease in nodular or focal forms. For diffuse lesions, minimally invasive interventions help alleviate symptoms.
The essence of organ-preserving operations is to excise or destroy pathological lesions or cut off the blood supply to the lesions.
The following minimally invasive or gentle operations are usually performed:
- Mechanical excision of nodes;
- Electroexcision of nodes with partial excision of the myometrium;
- Laser or electrosurgical drilling of the uterus with ligation of the internal iliac arteries;
- Ultrasound or radiofrequency ablation;
- Embolization of the uterine arteries.
The operation is performed openly or laparoscopically through small punctures in the abdominal wall. After removing large lesions, uterine plastic surgery is performed - its structure and shape are restored so that it can ensure reproductive function.
If the operation is not effective, but it is important for the woman to preserve the uterus, a presacral neurectomy is performed - the uterosacral nerve is crossed or cauterized with a laser or electric knife.
Attention! Organ preservation surgery is the only effective treatment for uterine adenomyosis for women who want to become pregnant. Attempts to conceive should begin immediately after the postoperative recovery period is complete.
Radical interventions
These include supravaginal amputation of the uterus and excision of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. Only such an operation allows you to completely get rid of pathological foci; its main disadvantage is the inability to become pregnant and give birth.
Postoperative period
After surgery, hormonal therapy is carried out for 3-6 months to prevent relapses, but if you want to get pregnant, you should immediately begin trying to conceive.
Alternative methods of treatment: are traditional methods effective?
Traditional methods can relieve discomfort, but will not relieve you of endometrial lesions in the uterus. The effectiveness of phytoestrogens has not been proven; moreover, they can cause the disease to progress, because it is the excess of estrogens that underlies endometriosis.
Recommended Diet
Changing your diet cannot be considered a cure for adenomyosis, but to reduce the risk of developing the disease, you can increase your intake of vegetables and fruits rich in antioxidants. Oxidative stress accelerates the growth of endometrioid inclusions. To reduce the level of estrogens and prostaglandins, which stimulate inflammation and spasms of the uterus, it is recommended to avoid trans fats, canned food and red meat.
Forecast
Pathology refers to diseases with a chronic course, so it periodically recurs. It is possible to completely get rid of adenomyosis only by removing the entire uterus, but in this case the girl loses the opportunity to have children.
The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of a favorable outcome. The first and second stages are successfully treated with medications, and for the treatment of the third and fourth stages most often it is necessary to resort to surgery.
Modern medicine allows girls who suffer from adenomyosis to conceive and bear a child. To do this, you need to plan your pregnancy and visit a doctor before it begins.
Risk of infertility
In approximately 50% of cases, the disease reduces the likelihood of pregnancy, since endometrioid tissue prevents the attachment of the embryo and provokes inflammation, resulting in disruption of the functions of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Adenomyosis in later stages leads to deformation of the female reproductive organs.
This is interesting!
Endometriosis occurs in 30-50% of women with infertility and is the most common reason for hysterectomy in women 30-34 years old.
Typically, if a woman who is trying to get pregnant is diagnosed with endometriosis, doctors advise:
- Continue trying to conceive for 6-12 months,
- In some cases, undergo surgery and begin trying to conceive immediately after postoperative rehabilitation,
- Resort to IVF if you cannot conceive for longer than 12 months or extensive tissue damage to the endometrium was discovered during the operation.
Prognosis for cure
Adenomyosis is not life-threatening, but produces unpleasant symptoms. Proper treatment will help alleviate the condition and preserve the organ.
Congruent disorders, risks:
- About 40-50% of patients with adenomyosis probably also have endometriosis.
- In 50% of patients with adenomyosis, fibroids are simultaneously detected.
- Every fifth woman diagnosed with endometriosis develops adenomyosis after age 30 or remains at high risk of developing the disease.
These pathologies have similar causes. This fact once again confirms the need for regular gynecological examinations and the importance of treatment.
Prevention
Endometriosis cannot be prevented. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to promptly eliminate the causes that contribute to the growth of the endometrium into the muscular layer of the uterus or other tissues.
You can reduce your risk of developing endometriosis by lowering the level of the hormone estrogen in your body. Estrogen helps the lining of the uterus thicken during the menstrual cycle.
To reduce estrogen levels in the body, it is recommended:
- Discuss taking COCs with your doctor.
- Exercise regularly (more than 4 hours per week). This will also help keep your body fat percentage low.
- Reduce alcohol consumption. Alcohol increases estrogen levels.
- Reduce consumption of caffeinated drinks - they increase estrogen levels.
If you have already undergone surgery and are not yet planning a pregnancy, you should use hormonal contraceptives. Girls and women with a hereditary predisposition to endometriosis should be regularly examined by a gynecologist.