Liver cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive liver disease in which liver cells degenerate into tissue similar to that from which scars are formed. Liver cirrhosis is not necessarily the fate of alcoholics: this pathology is almost always the final stage of chronic liver disease. Sometimes cirrhosis can become an independent pathology, developed, for example, as a result of an attack of one’s own immunity on the bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis) or have no clear cause at all (cryptogenic cirrhosis).
Pathology greatly complicates a person’s life, imposing restrictions not only on his diet, but also on his physical activity, taking medications, and the warmth of his clothing. It is one of those diseases that cause death, since the function of the liver cannot be replaced by any organ. However, this organ has remarkable regenerative abilities and can grow from a small “piece” to its full size. But this can happen if you pay attention to it in time and do not despair, but find the cause of the disease and begin to eliminate it before decompensation of the condition occurs. In some cases, a liver transplant can help, but it should not be postponed either: when bleeding increases, the operation can no longer be performed.
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Liver cirrhosis is an extensive damage to the organ, in which tissue death occurs and is gradually replaced by fibrous fibers. As a result of replacement, nodes of different sizes are formed, radically changing the structure of the liver. The result is a gradual decrease in the functionality of the organ up to complete loss of performance. This leads to a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life and his further death.
It is the liver that cleanses the body of harmful substances, synthesizes fats, carbohydrates, proteins, participates in digestion, produces albumin, etc. Therefore, damage to the liver lobules, consisting of hepatocytes, and their degeneration is a dangerous disease for the body of both men and women .
This disease is widespread throughout the world. According to the latest data, up to 300 thousand people die from this pathology every year, and the mortality rate is steadily increasing. Despite all the advances in medicine, over the past 10 years the incidence of death from cirrhosis has increased by an impressive 12%. In addition, the same percentage of people with chronic alcohol addiction have a history of the disease, but it is asymptomatic.
The pathology is diagnosed more often in men than in women. There are no strict age limits, but the disease predominantly affects people aged 40 years and older.
How long can you live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The disease has a different prognosis. With adequate treatment, which was started in a timely manner, the progression of the pathological process can be stopped. The presence of concomitant diseases, complications, a person’s lifestyle, and the stage of cirrhosis also play a role.
With preserved functional capabilities of hepatocytes, if a person reconsiders his lifestyle and adheres to the therapeutic regimen prescribed by a doctor, survival rate for seven or more years is 50% of the total number of patients. Such a favorable prognosis is appropriate for the compensated form of the disease.
In the subcompensated form, the average life expectancy is about 5 years. This is due to the fact that hepatocytes are gradually depleted and their number becomes insufficient for the normal functioning of the organ.
Among patients at the stage of decompensation, no more than 40% of people live for three years. This is associated with the development of serious complications that are often incompatible with life.
In addition, there are specially developed systems for calculating the prognosis for survival in cirrhosis according to certain criteria. Among these are the Child-Pugh prognostic system, the Cox proportional hazard model and others. All of them are based on certain indicators of the health of a person with cirrhosis (the etiology of the disease, the effectiveness of treatment, the presence of jaundice, neurological disorders, ascites, dilation of the esophageal veins, etc.) and allow a more or less correct prognosis to be made in each specific case.
Statistics
The highest incidence of cirrhosis is observed in developed countries: 14-30 cases per 100,000 population; Moreover, in the last decade the frequency of occurrence has increased by 12%. This is most often associated with eating habits: the more fried and gourmet foods and alcohol are contained in the diet, the higher the chance of getting sick.
Cirrhosis is one of the six leading causes of death, again, in developed countries: 300 thousand people die from this disease every year. Most often, people aged 35-60 years old suffer from it; men, due to their greater susceptibility to alcoholism, suffer 3 times more often.
The first signs of liver cirrhosis
It is not always possible to suspect the presence of a disease based on early signs, since in 20% of cases it is latent and does not manifest itself in any way. Moreover, in another 20% of patients, pathology is discovered only after death. However, in the remaining 60% the disease still manifests itself.
Therefore, among the early symptoms indicating cirrhosis, the following can be noted:
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.
[Video] Dr. Berg - How to recognize liver cirrhosis in the early stages?
Other symptoms of liver cirrhosis
The main symptoms of the disease increase as it progresses:
- Pain in the right side intensifies due to the expansion of the liver capsule, and may have the nature of colic. With concomitant hypokinetic dyskinesia, they increase, become aching, and are accompanied by a feeling of heaviness;
- The patient experiences attacks of nausea, often accompanied by vomiting. Vomit may contain blood, which indicates bleeding from the veins of the stomach and esophagus;
- Due to the accumulation of excess bile acids in the blood, the patient experiences itchy skin;
- There is a loss of body weight, up to exhaustion;
- Decreased muscle tone, atrophy;
- The skin acquires a jaundiced tint and peels. Severe jaundice is a sign of the final stage of the disease. First, the sclera of the eyes, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, palms and soles, and then the entire body are painted. This is due to the inability of hepatocytes to metabolize bilirubin;
- The appearance of xanthelasmas - spots with a lipid component, localized mainly in the area of the upper eyelids;
- The fingers thicken at the ends, take on the shape of drumsticks, the skin around the nail holes turns red;
- The joints swell and begin to ache;
- The veins in the abdomen dilate;
- Doctors find spider veins on the upper body. A characteristic feature of cirrhosis is that telangiectasias never form below the umbilical zone. During the acute stage of the disease, the number of stars becomes larger and they look very noticeable;
- The edge of the nose and the corners of the eyes are covered with angiomas;
- Redness of the palms, less often of the feet;
- The tongue swells and becomes brightly colored;
- In men, the mammary glands begin to grow, and the functions of the genital organs atrophy. Secondary sexual characteristics decrease: pubic and armpit hair falls out;
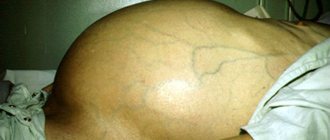
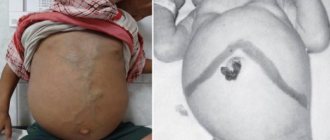
- Ascites is one of the late complications of cirrhosis, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- The face takes on an unhealthy hue, the cheekbones clearly stand out, the salivary glands swell, the capillaries on the face expand, giving it a red color;
- The limbs become thin, the stomach, on the contrary, protrudes forward;
- Bleeding from the nose often occurs;
- The spleen enlarges;
- Obvious disturbances in nervous activity appear: the patient suffers from insomnia and deterioration of memory function. There is a tremor of the limbs, an indifferent attitude to what is happening around.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
Among the main reasons leading to the development of the disease are:
- Viral hepatitis, which, according to various estimates, leads to the formation of liver pathology in 10-24% of cases. The disease results in such types of hepatitis as, , and the recently discovered hepatitis G;
- Drinking large doses of alcohol for 10 years or more. There is no dependence on a specific type of drink; the fundamental factor is the presence of ethyl alcohol in it and its regular intake into the body;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Many autoimmune diseases lead to the development of cirrhosis;
- Various diseases of the biliary tract, including extrahepatic obstruction, cholelithiasis and primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- Portal hypertension;
- Venous congestion in the liver or Budd-Chiari syndrome;
- Diseases transmitted by inheritance, in particular, genetically determined metabolic disorders (anomalies of glycogen accumulation, Wilson-Konovalov disease, deficiency of α1-antitrypsin and galactose-1-phosphate-uridyltransferase);
- Poisoning with chemicals that have a toxic effect on the body. Among such substances, industrial poisons, salts of heavy metals, aflatoxins and mushroom poisons are especially harmful to the liver;
- Long-term use of medications, including Iprazide, anabolic steroids, Isoniazid, androgens, Methyldopa, Inderal, Methotrexate and some others;
- The rare Osler-Rendu disease can also cause cirrhosis.
In addition, it is worth mentioning separately about cryptogenic cirrhosis, the causes of which remain unclear. It occurs in the range from 12 to 40% of cases. Provoking factors for the formation of scar tissue can be systematic malnutrition, infectious diseases, syphilis (which can cause cirrhosis in newborns). The combined influence of etiological factors, for example, a combination of hepatitis and alcoholism, significantly increases the risk of developing the disease.
Pathogenesis [edit | edit code ]
Over many months and years, the genome of hepatocytes changes and clones of pathologically altered cells are created. As a result, an immunoinflammatory process develops.
The following stages of the pathogenesis of cirrhosis are distinguished [7]:
- Action of etiological factors: cytopathogenic effect of viruses, immune mechanisms, influence of hepatotoxic cytokines, chemokines, prooxidants, eicosonoids, acetaldehyde, iron, lipid peroxidation products
- Activation of Ito cell function, which leads to excessive proliferation of connective tissue in the spaces of Disse and pericellular fibrosis of the liver
- Impaired blood supply to the liver parenchyma due to capillarization of sinusoids and a decrease in the vascular bed with the development of ischemic necrosis of hepatocytes
- Activation of immune mechanisms of hepatocyte cytolysis
Stages of liver cirrhosis
The disease goes through several stages of development, each of which has certain clinical symptoms. Not only the person’s condition, but also the therapy he requires will depend on how much the pathology has progressed.
Stage 1 of liver cirrhosis
At this stage of development, the disease practically does not manifest itself at all. If it is detected at this time, then it is still quite possible to compensate for the deficiency of hepatocytes with the help of medications. Therefore, doctors call the initial stage of the disease compensatory.
Despite the fact that the patient does not observe any clinical signs, changes in the organ have already begun. If timely treatment is not started, cirrhosis will progress rapidly and, after a short time, the liver will no longer be able to cope with its functions in full. As for laboratory indicators, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases, and the prothrombic index can drop to 60. But at the same time, the person feels absolutely healthy. He may only occasionally be bothered by pain in the right hypochondrium.
It is precisely because cirrhosis can be suspected based on laboratory parameters that regular preventive examinations by a doctor are necessary.
Stage 2 liver cirrhosis
The next stage is called subcompensated. Based on the name, it can be understood that there is a more pronounced decrease in the functionality of the organ, which is due to an increase in the number of dead hepatocytes.
At this stage, a person is able to notice that something is happening to his body. He begins to suffer from weakness, apathy, decreased performance, nausea, weight loss and other early symptoms of the disease. In men, already at this stage the first signs of gynecomastia appear.
As for laboratory indicators, the albumin level begins to fall, and the prothrombic index can reach 40. However, if treatment is started in a timely manner, it is still possible to transfer this stage to the compensation stage. That is, if medications are taken correctly, the diseased organ will be able to function without complications for human health.
Stage 3 liver cirrhosis
Stage 3 of the disease is dangerous because there are critically few functioning hepatocytes. This causes the progression of liver failure and an increase in symptoms of the disease. The skin takes on a jaundiced tint, and abdominal pain worries the person more and more. Often it is at this stage that ascites develops, which can no longer go away on its own.
Albumin levels and prothrombic index drop to critical values.
Treatment at this stage is no longer effective, although there is still a chance that medications will help cope with the disease. The patient should be in a hospital under the supervision of doctors, since this stage is characterized by severe metabolic disorders.
The danger is posed by complications of the disease, which may well cause death. Among the most dangerous are hepatic coma, liver cancer, internal bleeding, peritonitis and pneumonia. This stage is called terminal.
Stage 4 liver cirrhosis
The final stage of the disease is characterized by the fact that the tissues of the organ are so damaged that they are no longer able to cope with the tasks assigned to them. The pain is very severe, the patient is prescribed constant use of strong painkillers.
It is impossible to stop the progression of the disease at this stage. The prognosis is usually unfavorable, and without a liver transplant the patient dies from severe complications.
Consequences and complications of liver cirrhosis
The disease is dangerous for humans due to the development of serious complications, which most often cause death:
- The development of ascites, that is, the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- The occurrence of peritonitis, that is, inflammation of the peritoneum;
- Varicose veins passing through the esophagus or stomach, and, as a result, the development of internal bleeding. Among the symptoms that characterize the onset of such bleeding are the occurrence of vomiting with blood, staining of stool in black, a drop in blood pressure and a pronounced increase in heart rate;
- Hepatic encephalopathy;
- loss or confusion;
- The development of a malignant tumor (carcinoma), which is difficult to treat and progresses rapidly;
- Hepatorenal syndrome, characterized by renal failure;
- A drop in blood oxygen levels or hepatopulmonary syndrome;
- Hepatic gastropathy – disorders of the stomach;
- Hepatic colopathy – intestinal dysfunction;
- The impossibility of procreation is infertility.
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
A doctor cannot make such a serious diagnosis without conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient. First of all, the patient will need to donate blood for a biochemical analysis. If the results alert the doctor, he will send the patient for further diagnostics.
A coagulogram will show whether there are any disorders of the blood coagulation system. A general blood test will reveal the level of hemoglobin, which is usually low in patients with cirrhosis. Anemia is often diagnosed. In addition, the number of leukocytes and platelets decreases markedly.
To exclude or confirm the viral nature of the disease, the patient must be tested to detect hepatitis - A, B, C, D and G. A stool test for occult blood will help determine the presence of hidden bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Kidney failure is determined by electrolyte and creatine levels. If there is a suspicion of liver cancer, the patient will need to donate blood for alpha-fetoprotein.
In addition, an ultrasound scan of all abdominal organs and portal vessels is necessary. It is important to determine the presence of ascites and enlarged spleen.
Using esophagogastroduodenoscopy, the doctor will make a conclusion about the existing varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach.
A liver biopsy will help clarify the diagnosis and determine the stage of development of the disease. If necessary, the doctor sends the patient for liver scintigraphy or CT.
Biochemical blood parameters in liver cirrhosis
As a rule, an experienced doctor is able to suspect a disease based on only one test - blood biochemistry. Indicators for cirrhosis change according to a certain pattern: there is an increase in the level of bilirubin, liver transaminases (not higher than 40 IU), alkaline phosphatase (should not be higher than 140 IU), globulins, prothrombin time, haptoglobin, and specific liver enzymes. Against this background, there is a fall in albumin (less than 40 g per liter), prothrombin, urea (less than 2.5 µmol), cholesterol (less than 2 µmol).
An increase in the level of bilirubin in cirrhosis is especially indicative, since this substance is a breakdown product of red blood cells and hemoglobin and must be processed by the liver. When the functionality of an organ is impaired, bilirubin begins to circulate in excess in the blood. This leads to a yellow-green coloration of stool, as well as yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes. Therefore, total bilirubin should normally not exceed 20.5 µmol per liter, free - 17.1, and bound - 4.3. As the disease progresses, these numbers can increase several times.
Diet
Boiled or steamed dishes remain in the diet. Meals - fractional - 4-6 times a day. Exclude fried, fatty, smoked, spicy, spicy, chocolate, coffee, strong tea. For a healthy pancreas, no more than 2 medium cloves of garlic per day is desirable. Onions only raw or in prepared dishes.
If there is a feeling of hunger at night - immediately satisfy - gastric bleeding. Replace baked goods with products for diabetics. First courses are served with fillet broth. Gelatin slows down digestion. Lots of liver and vegetables. In most cases, the body will not accept inappropriate dishes or products.
Watch a video about diet for cirrhosis:
Is it possible to cure cirrhosis of the liver?
Most patients, having heard a terrible diagnosis from a doctor, quite reasonably ask the question: is it possible to completely get rid of the disease? Modern medicine does not have such capabilities. The only radical treatment option is to transplant a donor organ. However, liver transplantation is not suitable for every patient and costs a lot of money.
However, do not despair, because if the disease was detected in the early stages, then it is quite possible to stop its progression thanks to adequate therapy. If cirrhosis is detected in the later stages, doctors may be able to somewhat slow down the progression of the disease and delay the onset of complications.
Scientists are still trying to develop a medicine that can cure cirrhosis. But so far, official medicine has not announced a single remedy that can completely cure a person. However, it is quite possible to transfer cirrhosis into the category of controlled chronic diseases.
How to treat liver cirrhosis?
As for treatment, it is selected strictly individually in each specific case. However, there are certain criteria applicable to the treatment of the disease. Thus, the compensated stage of cirrhosis needs to eliminate the main cause that led to the development of the pathology. The patient is prescribed medications for the treatment of hepatitis, attempts are made to relieve his alcohol addiction, etc. In addition, it is necessary to reduce the risk of developing complications that can aggravate the course of the disease.
The patient must adhere to a diet with an optimal content of proteins and carbohydrates. It is important to exclude any type of alcohol and harmful foods. All medications are used only as prescribed by a doctor; their use must be determined by vital necessity.
As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical activity, and heat treatment are not recommended for the patient. No traditional medicine should be used without prior consultation with your doctor.
If a patient seeks help at the stage of decompensation, he is treated in a hospital setting, which is due to the high risk of complications. The main goal pursued by any doctor during this period is to stop the progression of the disease. For this purpose, medications are used that are selected according to an individual regimen and depend on the form of cirrhosis.
It is possible to prescribe hepatoprotectors, ursodeoxycholic acid preparations, nitrates and beta-blockers.
Liver transplant for cirrhosis
The only radical treatment method is transplantation of the damaged organ. The operation is carried out if the liver is not able to cope with the functions assigned to it, and conservative therapy is powerless.
A donor organ is removed from a deceased person who, during his lifetime, did not write a waiver of such removal, although the laws differ in different countries. Since the operation is quite complex and subsequently requires lifelong use of drugs that suppress the immune system, it is not performed in the early stages of cirrhosis.
Indications for transplantation include the following:
- Internal bleeding that cannot be controlled with medication;
- Ascites not responding to treatment;
- Albumin drops below 30 g;
- Increase in prothrombin time above 17 s.
These indicators are a direct threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient, and therefore require organ transplantation. However, the list of contraindications is no shorter, including the presence of an infectious process, severe pathologies of the heart and lungs, any malignant tumors with metastases, brain damage, age over 60 years or under 2 years, obesity, etc.
The operation itself lasts at least 8 hours and consists of removing the damaged organ and transplanting a healthy one. It is possible that only part of the liver will be transplanted from the donor. As for the prognosis after transplantation, it is quite favorable, although certain risks still exist, for example, liver rejection, hepatic artery thrombosis and others. The survival rate for the next five years is 75%, this is a good indicator given the severity of the disease, with about 40% of people living with a foreign organ for more than 20 years.
On the subject: Treatment of liver cirrhosis with folk remedies
Prevention
Preventative measures are very important to maintain health. To do this, you need to follow some rules and lead a healthy lifestyle. Prevention of liver cirrhosis is:
| Complete abstinence from drinking alcoholic beverages | This useful advice should be followed to prevent many diseases. This measure will improve the quality of life. |
| Good protection against viruses | In particular, this rule applies to hepatitis. This disease is transmitted through the blood of an infected person. Therefore, you can become infected through the genital tract, a used syringe, blood transfusion, personal hygiene items, failure to maintain sterility in medical institutions, etc. To protect yourself from this disease, you must be vaccinated against the virus. |
| In protection against parasites | Following the rules of personal hygiene will help here, and preventive maintenance should be done every six months to avoid infection. |
| In protection against toxic substances | They cannot be completely eliminated from life, but it is quite possible to limit their exposure. |
| In protection against heart and vascular diseases | To do this, you need to adhere to a diet, maintain a healthy lifestyle, control blood pressure, etc. |
| In proper nutrition | This principle is fundamental. A good diet helps support not only the liver, but also promotes the proper functioning of other internal organs. |
By adhering to preventive standards, the chance of maintaining your health increases significantly.
Is there any disability for cirrhosis of the liver?
Registration of disability for this disease is possible. The group that will be assigned to a person depends on the severity of cirrhosis and its stage. As a rule, when diagnosing the first stage of the disease, the patient is assigned to the 3rd disability group. If cirrhosis has reached the stage of decompensation, then the person will be assigned disability group 2. When the disease is in terminal stages, the person is assigned to the first group.
To receive help from the state, the patient will need to undergo a special commission, to which he will be referred by the treating doctor.
On the subject: Diet for liver cirrhosis - what can you eat and what can you not?
Treatment of the disease
How to treat cirrhosis of the liver. To do this you need:
- eliminate the cause of the disease;
- stop the progression of liver tissue degeneration into fibrous nodes;
- compensate for any violations that have occurred;
- reduce the load on the veins of the portal system;
- cure complications and prevent the development of further problems.
Eliminating the causes of illness
This treatment depends on the causes of liver cirrhosis:
- In case of alcoholic cirrhosis, eliminate the intake of alcohol into the body.
- For viral hepatitis, special antiviral agents are prescribed: pegylated interferons, ribonuclease, and so on.
- Autoimmune hepatitis is treated with drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Cirrhosis resulting from fatty hepatitis is treated with a low-lipid diet.
- Biliary cirrhosis is treated by eliminating the narrowing of the bile ducts.
Creating conditions for liver restoration
Immediately after diagnosis, while the person is being examined for the cause of the disease, he is prescribed a diet for cirrhosis:
| General rules | Can | It is forbidden |
| Protein: 1-1.5 g/kg body weight. They are canceled at the terminal stage, when consciousness is impaired; Fats – 80-90 g/day (1:1 animal and protein origin); Carbohydrates – 400-500 g/day. Number of meals: 5-6 per day, in small portions |
|
For ascites, exclude juice |
Lifestyle with cirrhosis is also adjusted:
- Do not lift heavy objects, as this can cause gastrointestinal bleeding;
- rest more;
- measure abdominal volume and weight daily: an increase in both indicates fluid retention;
- Be sure to consider the ratio of fluid intake (not just water) and urine excreted. There should be a little less of the latter;
- with the development of ascites, it is necessary to reduce the volume of fluid taken to 1-1.5 l;
- control changes in your handwriting: for example, write a short phrase every day, putting the date in your notebook.
Drug therapy
In case of cirrhosis, each drug is prescribed with reason, because the liver is damaged, and an extra load of drugs is not beneficial for it. But you can’t do without these medications:
- Duphalac, Normaze or Prelaxan. These lactulose preparations bind amino acids that are toxic to the brain and cause encephalopathy.
- Hepatoprotectors are drugs that improve the functioning of liver cells: Heptral, Ornitox, Ursohol.
- Diuretics - to remove excess fluid from tissue. For cirrhosis, the drug Veroshpiron works well in small doses.
- In some cases, with ascites, it makes sense to take antibiotics that cleanse the intestines: Kanamycin, Ampicillin. This is the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
- To reduce pressure in the portal vein, Molsidomine and beta blockers: Propranolol, Atenolol are effective. In this case, blood pressure control is necessary.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative treatment for liver cirrhosis offers the following recipes:
- Mix 10 g, 20 g of wheatgrass rhizomes, 20 g of rose hips. 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of water into the mixture and cook for 10 minutes. Then cool the broth, take 1 tbsp. twice a day.
- Take 3 tbsp. washed oats, birch buds, 2 tbsp. crushed lingonberry leaves, pour 4 liters, leave for 1 day in a cool place. Separately make a rosehip decoction. After a day, mix both decoctions and add 2 tbsp. corn silk and knotweed. Boil the entire infusion for 15 minutes, strain, and store in the refrigerator.
- You need 3 heads of garlic, 4 lemons, 200 g of olive oil, a kilogram of honey. Cut the peel off the lemons, remove the seeds, grind the lemons and garlic in a meat grinder, combine with butter and honey. Mix the mixture, put it in the refrigerator for a day and then store it there. Take a teaspoon 30 minutes before meals three times a day. You need to eat everything, then repeat this manipulation three times a year.