A benign growth of the internal mucous membrane of the uterus, accompanied by menstrual irregularities, anovulatory uterine bleeding, and infertility. Signs of endometrial hyperplasia are observed in 5-25% of women. This term refers to a pathological enlargement of the endometrium, the inner mucous layer of the uterine cavity. Normally, it grows every monthly cycle. Thickening under the influence of the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, the mucous membrane prepares to receive the egg. If conception does not occur, then a decrease in hormone levels causes tissue rejection. After menstruation, the process begins again. When there is a hormonal imbalance, the level of estrogen increases, which triggers the process of pathological growth of the epithelium.
How common is endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a fairly common pathology, occurring in 5 percent of gynecological patients. This diagnosis has been heard more and more often in recent years for various reasons. The life expectancy of women has increased, the number of patients with metabolic syndrome and other pathologies has increased, and the environmental situation has worsened. All this affects the reproductive health of the population. Most often, hyperplasia occurs in teenage girls or in women during premenopause, that is, when hormonal changes occur in the body.
Folk remedies
Often, upon learning of their diagnosis, women resort to unconventional methods of therapy. To understand how to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies, you should in any case first consult with your doctor. Although such treatment methods are always gentle, they should not be used recklessly or completely relied on.
How to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies? Doctors recommend combining drug treatment with this gentle type of therapy. This enhances the effect.
If you correctly combine hormonal therapy, herbal medicine and surgery, you can get rid of the disease quite easily. If a woman, having found information on how to treat endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies, relies entirely on them, then there will be no effect.
The main goal of therapy is to block excessive hormone production, since these conditions provoke the division of cancer cells. Alternative medicine methods are aimed at solving precisely this problem.
How is hyperplasia related to the menstrual cycle?
The normal menstrual cycle consists of 3 phases:
- increase in the thickness of the functional layer of the endometrium - proliferation
- endometrial maturation - secretion
- rejection of the functional layer leading to bleeding - desquamation
The first phase begins on the first day of menstruation. Approximately in the middle of the cycle, ovulation occurs - the process of the release of an egg from the ovary; during this period, a woman may notice the appearance of a stretchy, mucous, transparent discharge. If fertilization does not occur at this moment, then under the influence of hormones the functional layer along with the egg is rejected - menstruation occurs and spotting occurs. All processes during the menstrual cycle are controlled by sex hormones:
- estrogens cause proliferation
- progesterone - secretion
In addition, during proliferation, planned cell death occurs - apoptosis, which prevents the endometrium from growing larger than necessary. This only happens if the woman has ovulated, that is, when the ratio of hormones allows it to occur. If there was no ovulation (anovulatory cycle), there is a prolonged effect of estrogen on the endometrium and it thickens - as a result, endometrial hyperplasia is formed.
Diagnostics
A timely and correct diagnosis allows you to choose the right tactics and treatment regimen for the disease. For this, collecting an anamnesis and examining a gynecologist is not enough.
To establish a final diagnosis, the patient is prescribed:
- Undergo a mandatory ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- Echohysterosalpingography (Echo-HSG) , this type of diagnosis, allows you to determine the degree of patency in the fallopian tubes. Determine the structure and morphology of the endometrial layers.
- A histological method for examining the contents of the uterine body, which is performed by curettage.
- Hysteroscopy. The most popular painless technique, which is performed using optical technology. During the procedure, material is taken for subsequent biopsy, and a visual examination of the inner layer of the uterine body is performed.
Sonographic signs
An important point in making a diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia is an ultrasound examination.
Using it, the thickness of the functional layer of the uterus is determined, and the volume of the lesion is established:
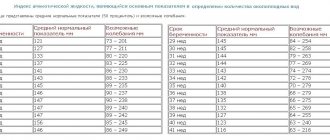
- For the first phase of menstruation, the thickness of the mucous epithelium ranges from 2 to 4 mm.
- During the second phase of the cycle, its thickness can increase to 15 mm.
Echogenicity. The mucous membranes, in a physiological state, are always larger than the muscular layer of the body of the uterus:
- In the case when the process takes on a malignant form, the boundaries of the thickening become heterogeneous and uneven. Echogenicity may either increase or decrease.
- Polypous changes can be noted by an increase in the size of polyps up to 17.5 mm, and a thickened wall of the functional layer up to 20 mm, this can confirm the diagnosis of an oncological neoplasm.
Why does it occur?
The triggering factor for the development of endometrial hyperplasia is an absolute or relative increase in the content of estrogen in the blood - hyperestrogenism, which occurs for various reasons:
- age-related changes in the central regulation of sex hormones - changes in the amount of estrogen before menopause
- hormonal disorders - excess estrogen with progesterone deficiency
- hormone-producing ovarian tumors, polycystic ovary syndrome
- adrenal cortex dysfunction
- improper use of hormonal medications
- frequent abortions (complications), diagnostic curettages
- hereditary predisposition
- inflammatory processes of the female genital organs
- concomitant diseases - hypertension, breast diseases, obesity, diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases.
Causes
As already mentioned, during the menstrual cycle, the hormonal levels in the body change and the endometrium is renewed. Endocrine changes are predominantly manifested by fluctuations in the concentrations of estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen binds to endometrial cell receptors and provokes increased division of epithelial cells in this tissue, due to which the inner lining of the uterus thickens. Destruction of the endometrium due to lack of fertilization occurs due to changes in progesterone levels. When the ratio of these hormones is harmonious, menstrual cycles proceed without complications. Endocrine imbalance can cause improper division of endometrial cells.
Possible reasons:
- Increased estrogen concentration and insufficient progesterone. This is the most common cause of endometrial hyperplasia. Hormonal imbalance can occur due to primary endocrine diseases, improper lifestyle and taking certain medications.
- Medical procedures accompanied by damage to the endometrium. We can talk about diagnostic tissue curettage, abortion or other intervention.
- Expression of genetic mutations. Disruption of DNA structure can contribute to improper development of endometrial cells.
The exact reasons for changes in cellular regulation are unknown.
What types of hyperplasia exist?
According to the type of structure, scale of distribution and the presence of abnormal cells, all hyperplastic processes of the endometrium are divided into groups:
- Glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial polyps (focal form of hyperplasia) Glandular
- Glandular-cystic
- Glandular fibrous
- Adenomatous
Glandular forms of hyperplasia are characterized by a large number of glands, sometimes forming cysts. The structure of cells in such a lesion is not disturbed. The symptoms of glandular endometrial hyperplasia and cystic forms are absolutely the same. With the atypical form of hyperplasia (adenomatosis and adenomatous polyp), changes occur in the structure of cells, which begin to divide at high speed, as a result of which the number of glands grows very quickly.
Modern classification
According to the classification, hyperplasia can be simple or complex, atypical or without atypia.
With simple hyperplasia, the number of glandular and stromal structures increases. There is an increase in the size of the endometrium and changes in its structures. Part of the gland expands in a cystic manner. The vessels are distributed evenly. There is no atypia observed in the nuclei. In 3% of cases, this type of disease develops into a malignant tumor.
The glandular cells acquire an unusual, rounded shape. Polymorphism often appears in the cell nuclei, and vacuoles expand. In such cases, there is a 20% chance that the cells will later become cancerous.
Complex hyperplasia manifests itself in the fact that the glands in the endometrium are located too closely or in separate foci. An abnormal structure of the gland is observed, an imbalance occurs in the growth of stroma and glands. There is no atypia observed in the nuclei. Cancer develops with a 10% chance.
Complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia is recognized as the most dangerous form for patients. In 57% of cases it develops into uterine cancer. With it, the proliferation of the epithelium is significantly pronounced, and atypia is established in cells and tissues. A variety of shapes and sizes appears in the glands.
The epithelium contains large cells whose nuclei are elongated and polymorphic.
A moderate form of hyperplasia is also distinguished separately. This is a transitional phase from a simple to a complex variety. It has few individual characteristics and is not always identified as a separate stage.
Can hyperplasia turn into cancer?
Hyperplastic processes should always cause oncological suspicion, but only in a few cases are they malignant. There are certain conditions under which hyperplasia is considered a precancerous condition:
- atypical hyperplasia at any age. According to statistics, in 40 percent of cases without treatment, such hyperplasia becomes malignant and endometrial cancer occurs.
- frequently recurring glandular hyperplasia in postmenopause
- glandular hyperplasia with dysfunction of the hypothalamus at any age, as well as with metabolic syndrome.
Metabolic syndrome is a special condition of the body in which the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells is sharply reduced, and the tendency to hyperplasia is high. It is characterized by anovulatory infertility, diabetes, and obesity.
Recipes
Since ancient times, nettle decoctions have helped to overcome many ailments. These included endometrial hyperplasia. To carry out therapy using this herb, you will need to prepare a tincture from the plant. To do this, take 200 g of nettle and pour in 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Infuse the mixture for two weeks, and then drink a teaspoon every day in the mornings and evenings. This treatment helps restore the immune system and improve the condition of the uterus.
The next effective folk therapy method is cucumber decoction. To prepare it, cucumber lashes are dried, and then 50 g of the component are boiled in 0.5 liters of water. Boil the product for no more than 5 minutes, then leave for 60 minutes, drink 100 ml three times a day.
To get rid of endometrial hyperplasia, they also drink peony decoctions. To do this, dilute the plant extract with water in a ratio of 1:2. The initial dosage is 2 ml. Take the decoction three times a day. It helps normalize hormonal levels and prevents further development of the disease.
Also, supporters of alternative medicine advise drinking plantain infusion 4 times a day. The herb leaves are finely chopped and then brewed in a glass of boiling water. Infuse the decoction for 2 hours. Before use, strain through cheesecloth.
Traditional healers also recommend using herbal remedies to combat hyperplasia. For example, every day they advise drinking 0.5 cups of a mixture containing serpentine roots, shepherd's purse grass, calamus and cinquefoil roots, knotweed grass and nettle leaves. Mix all ingredients in the following proportion: 1:1:2:2:2:2. The collection is thoroughly crushed, and then take 2 tablespoons of the mixture and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Boil the broth for 5 minutes, then pour it into a thermos and leave for 1.5 hours. Take the product 100 ml at a time. The full course of therapy lasts 1 month, then take a break for 10 days, and then repeat the procedure.
Proven recipes from alternative medicine can quickly get rid of the disease if they are combined with drug treatment and surgery. It should be remembered that it is worth fighting to the last to preserve the uterus, since its removal provokes a number of negative consequences in the body. There are cases when, due to hormonal imbalance, women with a removed uterus began to experience panic attacks and lost their jobs.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat endometrial hyperplasia. Its transformation into a malignant tumor occurs in 55% of cases. The likelihood of developing cancer depends on the patient's age and her history of previous illnesses.
What symptoms occur with endometrial hyperplasia?
Uterine bleeding
The most noticeable and common symptom of endometrial hyperplasia is uterine bleeding.
- More than half of patients note delays in menstruation for 1-3 months, which are replaced by prolonged bleeding of varying intensity.
- In rare cases, bleeding can be cyclical, that is, manifest itself in the form of heavy and prolonged menstruation, painful periods (causes)
- Most often, patients report an unstable menstrual cycle for a long time, which causes bleeding.
- In 5 percent of cases, bleeding occurs against the background of an absolute absence of menstruation.
Metabolic syndrome
An important concomitant of endometrial hyperplasia is metabolic syndrome. In such cases, the symptoms of bleeding include:
- obesity
- hyperinsulinemia
- symptom complex of male traits - the appearance of increased hair growth, changes in voice timbre and other signs of the action of male hormones
Other common symptoms
Women with hyperplasia often name other companions of the disease:
- secondary infertility - absence of pregnancy after a year of regular unprotected sexual activity
- miscarriage - early miscarriages
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs
- mastopathy and fibroids
Other, less common symptoms
- contact bleeding during sexual intercourse or hygiene procedures
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen (more often with polyps)
Scraping
Before treating simple endometrial hyperplasia, you need to understand that traditional methods of therapy can lead to complications. Pregnancy after curettage is possible. Moreover, it may well occur in a month if the patient did not use hormonal drugs. If she followed all the specialist’s instructions while being treated with hormones, then she can become pregnant 2 months after completing the course.
In which cases pregnancy after the procedure is possible and in which it is not is determined only by the attending physician. The thing is that a specialist examines endometrial scrapings under a microscope.
Most often, it is not recommended to get pregnant immediately after the first cycle. There is no guarantee that the internal uterine membranes have already been renewed and can allow the fetus to develop normally before the end of term. Gynecologists advise waiting about 3-6 months before stopping using contraception.
What research is needed to determine it?
- Anamnesis. It is necessary to tell the doctor in detail about the features of the menstrual cycle: at what age menstruation began, how long and how long it lasts, whether there were any irregularities or delays. Anamnesis will allow the specialist to determine all the symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus.
- Transvaginal ultrasound in the first phase of the cycle (on days 5-7). The examination determines the thickness of the endometrium, its homogeneity and structure. Hyperplasia can be suspected if the thickness is more than 7 mm. If the endometrium is thicker than 20 mm, then the doctor may suspect a malignant process. If the bleeding is prolonged, then an ultrasound is performed regardless of the day of the menstrual cycle.
- Hysteroscopy and separate diagnostic curettage (cleaning) simultaneously play the role of research and treatment. Read about the condition after hysteroscopy.
- Study of hormone levels in the blood for suspected metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovary syndrome. Usually the levels of FSH, LH, estradiol, testosterone, and progesterone are determined. And also possibly the level of adrenal and thyroid hormones.
- Mammography - often the doctor prescribes an X-ray examination of the mammary glands to exclude proliferative processes.
For endometrial hyperplasia, the informative value of ultrasound with a vaginal sensor is estimated at 68%, and hysteroscopy at 94%.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and appendages | 2 800 |
| Hysteroscopy (diagnostic, therapeutic) | 47 500 |
| Endometrial ablation | 60 000 — 85 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Therapy for hyperplastic processes depends on the woman’s age, characteristics of the endometrium, and concomitant diseases. For endometrial hyperplasia, treatment can be carried out in several ways.
- Hormonal agents
These include estrogen-progestin drugs, pure gestagens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists, androgen derivatives. These drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, individually and strictly according to indications. The doctor takes into account all possible contraindications to taking hormonal drugs: rheumatism, thrombophlebitis, hypertension, diabetes, diseases of the biliary tract and liver, smoking and alcohol increase the risk of side effects. Before therapy and during treatment, the state of the immune system, vascular, endocrine glands, liver must be examined and monitored, and blood tests must be taken.
- “Minor” or conservative surgery
Removal of the endometrium (functional and basal layers) using a resectoscope. A controversial method, as it results in frequent relapses of the disease and is contraindicated if atypia is suspected.
- Surgery
This is the removal of the uterus with or without the ovaries. Indications for surgical intervention:
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment for precancerous forms of hyperplasia
- recurrent cases of precancerous hyperplasia
- contraindications to hormone treatment
- atypical hyperplasia in peri and postmenopausal women
Stage I of treatment - curettage
The first stage is therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the uterine mucosa under the control of a hysteroscope (cleaning) and examination of the resulting material in cytological laboratories.
Curettage is the removal of the functional layer of the endometrium along with the pathological formations present in it. The examination is carried out under anesthesia, visualization of the contents of the uterine cavity is carried out using a special device - a hysteroscope. This is an optical system equipped with a light source and having a channel for introducing surgical instruments into the uterus. Thanks to the hysteroscope, the curettage procedure is safe and effective.
The cleaning itself is carried out using a curette, and sometimes a mechanism is used to stop bleeding. The functional layer of the endometrium is completely removed, the contents of the uterine cavity are sent for histological examination, which will determine the nature of the process and the tactics for further treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage.
Stage II of treatment
Depending on the results of histological examination, drug therapy is prescribed to prevent relapses. For this purpose, hormonal drugs are used, taken in a certain dosage and according to suitable regimens.
Treatment of glandular cystic hyperplasia
- For girls during puberty and women under 35 years of age, medications containing estrogens and gestagens, for example, combined oral contraceptives (pros and cons of taking them). Preference is given to single-phase drugs with progesterone, which have a continuous effect on the endometrium, preventing its growth. Treatment lasts from three months to six months. Glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia usually does not recur with proper therapy.
- In women from 35 years of age to perimenopause (the process of stopping menstruation). The therapy uses gestagens, without the use of estrogen-containing components. Hormones are prescribed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, from 14 to 26 days after curettage or from the beginning of menstruation. Endometrial hyperplasia is usually treated with duphaston and utrozhestan. Therapy also lasts 3-6 months.
- In postmenopausal women (after menstruation has stopped). Hyperplasia at this age is a rare phenomenon, usually associated with hormone-producing ovarian formations. For endometrial hyperplasia in menopause, treatment should be prescribed only after a thorough examination of the ovaries (ultrasound and, if necessary, laparoscopic examination). If there are no tumors, then 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate is prescribed at a dosage of 125 mg 2 times a week for six to eight months. After completion of therapy, it is necessary to perform an endometrial biopsy and examine the resulting sample in the laboratory.
Treatment of atypical hyperplasia
Women of reproductive age and perimenopause. The treatment of choice is gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists for six months. Some drugs must be taken every day (buserelin acetate), some have a prolonged effect and require taking once every 28 days.
After 6 months from the start of treatment, repeated endometrial curettage with histological examination is usually required. In addition, each month of treatment ends with an ultrasound examination, which monitors the thickness of the endometrium (less than 5 mm).
When atypical hyperplasia is combined with fibroids or metabolic syndrome, surgical treatment with careful examination of the ovaries is necessary. The condition of the mammary glands requires constant monitoring.
Follow-up plan for atypical hyperplasia:
- Endometrial ultrasound once a month
- curettage with histological examination every 3 months
- Ultrasound of the ovaries every 3 months (with Doppler ultrasound)
- Breast ultrasound and mammography every 6 months
- monitoring signs of metabolic syndrome (cholesterol and blood glucose)
For postmenopausal women, surgical treatment with a thorough revision of the ovaries is indicated.
Complications and prevention
| Prevention of hyperplasia | Complications |
|
|
Therapy
The disease is treated using complex therapy methods. How endometrial hyperplasia is treated will be described below. There are several stages of treatment. Each of them contains several different techniques. They are selected depending on the type of hyperplasia. Typically therapy consists of four stages.
Before treating endometrial hyperplasia, stop the bleeding. Then treatment with hormonal agents is carried out. Next, the cycle is normalized. The patient has been observed for 5 years, with follow-up examinations every 6 months.
In extreme cases, the uterus is removed. But such surgical intervention has an extremely negative impact on the woman’s condition, as artificial menopause and hormonal imbalance begin.
Frequently asked questions to a gynecologist
Is it possible to cure endometrial hyperplasia using traditional methods?
Treatment with folk remedies for endometrial hyperplasia has no scientific basis. Usually the use of such methods is simply useless, and sometimes it can be harmful. For example, if a patient is allergic to some herbs used in the traditional treatment of endometrial hyperplasia. In addition, some plants contain so-called phytoestrogens, which can aggravate the process of growth of the inner layer of the uterus.
Is it possible to get pregnant if diagnosed with hyperplasia?
Pregnancy with severe diffuse endometrial hyperplasia usually does not occur or ends in early miscarriage. The whole point is that in order for the fertilized egg to develop into an embryo, it must firmly attach to the inner wall of the uterus, forming the placenta in the future. The hyperplastically altered endometrium does not create the necessary conditions for such implementation. Hormonal treatment and curettage allow you to “renew” the inner layer of the uterus, making pregnancy possible. In some cases (polycystic ovary syndrome), additional treatment may be necessary to achieve pregnancy.
Is it possible to delay treatment for endometrial hyperplasia?
The hyperplastic process is not always accompanied by dangerous bleeding, but often carries a hidden threat. The risk of malignancy, infertility, and chronic anemia requires an immediate visit to the doctor at the first symptoms. In case of endometrial hyperplasia, herbal treatment, many physical procedures and self-administration of medications without prescription from a specialist are unacceptable. Competent and timely treatment will restore reproductive health and well-being.
Is it possible to do curettage for a nulliparous woman with hyperplasia; will there be problems with pregnancy?
If hyperplasia is detected, curettage must be done; the chances of getting pregnant after such treatment will be much greater.
Is it always necessary to clean a polyp?
If the polyp is single, then they are often limited to removing this formation, without curettage.
I was prescribed buserelin for the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia and put me into “artificial menopause.” Is there a risk of not coming out of this menopause in the future?
No, the effect of buserelin is reversible. Only removal of the ovaries and chemotherapy can bring menopause closer.
I am 35 years old, IVF was planned, but during the examination they discovered an endometrial polyp, removal of the formation was prescribed. When can I join the IVF program?
After removal of the polyp, you can immediately enter into the ovulation stimulation protocol.
She underwent treatment for endometrial polyp due to hyperplasia. The doctor said that it was necessary to get tested for sexually transmitted infections. Is this necessary?
There is evidence that mycoplasma and chlamydial infections contribute to the recurrence of endometrial polyps. Infections need to be treated.
I am 50 years old. Curettage revealed atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Is it necessary to remove the uterus or can ablation be performed?
Endometrial ablation is the removal of the entire inner layer while preserving the uterus. The method is non-traumatic, but after it it is very difficult to assess the condition of the uterus, and a tumor can be missed. At this age and with this diagnosis, removal of the uterus is recommended.
On the 2nd day after the “cleansing”, scanty bleeding continues. Is this normal?
This is absolutely normal, you are advised to take physical and sexual rest.
My diagnosis is endometrial hyperplasia, curettage is planned in 2 weeks. Is it possible to have sex now?
Yes, you can, if there is no pain or contact bleeding.
Complications and prevention
Without timely treatment, the disease can cause dangerous complications due to further changes in the epithelium and constant hemorrhages. Doctors diagnose complications after identifying the disease.
Common complications:
- Anemia is a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the patient’s blood. This substance, contained in red blood cells, is necessary for the transfer of oxygen to tissues. Constant uterine bleeding due to the proliferation of the epithelium of the organ leads to the loss of a large number of red blood cells. Women with anemia complain of dizziness, chronic fatigue, insomnia and pale skin.
- Changes in the menstrual cycle and the occurrence of infertility. With a slight proliferation of glandular cells, the doctor can restore reproductive function.
Methods for preventing pathology include the use of hormonal contraception under the supervision of a physician, normalization of body weight, control of diabetes and timely treatment of primary diseases of the reproductive system. It is also important to undergo examination by a gynecologist at least once a year. A consultation with an oncologist will help a woman learn more about the prevention and treatment methods of this disease.
Can it be cured forever?
We examined the concept of endometrial pathology and the causes of its occurrence. After diagnosis, patients are usually interested in further prospects, how to treat and whether it is possible to get rid of the disease forever. Moreover, both surgical and therapeutic methods. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the clinical picture. Additionally, a course is prescribed aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease. A complete cure is possible if the pathology is detected on time.
The prejudice that concerns some treatment methods forces us to look for alternative solutions to the issue. But it is better for patients to use traditional methods of medicine, which allow them to preserve reproductive function and be completely cured.
It should be understood that hyperplasia itself will not disappear; complex treatment is needed, and if the causes of the disease persist, there is a risk of relapse. But with early detection, the chances of a full recovery are high, so after diagnosis it is necessary to begin treatment immediately.
Other folk methods
In addition to herbal tinctures, treatment with leeches is often carried out. The procedures are repeated twice a year for ten sessions. Leeches thin the blood, lower blood pressure, improve metabolism and stimulate the immune system.
The probiotic Narine is often used. If you consume fermented milk products every day, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract improves, the woman gets rid of dysbacteriosis, and the body’s immune system is restored.
Douching is also carried out with infusions of celandine and calendula. The full course of therapy is twelve days.
The use of garlic tampons also gets rid of endometrial polyps, according to proponents of alternative medicine.
Proper nutrition
The diet is aimed at normalizing hormonal levels. Healthy foods are those that will help control estrogen (vegetables and fruits, nuts, grains, legumes). Products containing omega acids (fish) and vitamins are added to the diet.
Meals for hyperplasia should be fractional, 4-5 times a day. Animal proteins, spicy, pickled and salty foods, alcohol, soda coffee, and confectionery are excluded from the diet (or significantly reduced).