Expecting a baby is perhaps the most joyful period in the life of every woman. However, do not forget that some dangers may arise during pregnancy. Restructuring the body at the hormonal level can lead to the identification of hidden chronic diseases or the emergence of problems. One of the latter is retrochorial hematoma.
Causes of the appearance of pathology in the early stages
Modern medicine does not know the exact etiology of retrochorial bleeding. External and internal causes of the pathological process are secondary and do not guarantee the initiation of detachment with subsequent accumulation of blood. However, there are a number of immunological, hormonal, hemostasiological and other circumstances that significantly increase the risks of formation.
A hematoma during early pregnancy occurs if there is:
- Direct bruises and other injuries to the uterine area;
- Hidden genetic abnormalities of fetal development , not diagnosed by modern methods;
- Intense physical activity;
- Regular stress;
- Background inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- Local genital or systemic generalized infectious lesions;
- External exposure to radiation, vibration, noise on a regular basis;
- Problems with the cardiovascular system;
- Autoimmune spectrum diseases;
- Early toxicosis of a pregnant woman;
- Congenital or acquired anomalies in the development/functioning of the female genital organs;
- Blood clotting disorder.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment of retrochorial hematoma is carried out in a hospital setting. When the accumulation of blood is small and does not pose a threat, the pregnant woman may be allowed to undergo a therapeutic course at home.
Important information: What to anoint a bruise to make it go away faster and what fast-acting remedies (ointments) for resolving hematomas
To relax the muscle tone of the reproductive organ, a woman needs to lie quietly in a horizontal position. Bed rest is necessary so that the body can mobilize its reserves and direct them to fight pathology. Hypertonicity in early pregnancy can be treated with:
- Magne-B6;
- Papaverina;
- No-shpy.
If the hematoma is located on the fundus of the uterus, the woman is recommended to lie on her back with her legs elevated. This position normalizes blood circulation in the pelvic organs and also promotes the release of blood clots.
During the entire period of pregnancy, a woman should not expose herself to nervous strain. Getting enough sleep helps improve your well-being and improve your health.
During the treatment period, the patient is contraindicated in any physical activity and sexual intercourse. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause flatulence and contribute to constipation.
To stop bleeding, the following may be prescribed:
- Vikasol;
- Ascorutin;
- Dicynone.
If the hemorrhage has formed high at the fundus of the uterus, which often makes it impossible to empty the hematoma through the vagina (in the form of brown spotting), with the correct treatment, the bruise will resolve. The healing process can only be seen using ultrasound. For this reason, the patient's condition is constantly monitored. Once a week, the woman undergoes a routine ultrasound scan.
If the therapy gives positive results, then resorption or emptying of the hematoma occurs within a month. For the remainder of the pregnancy, the woman should regularly visit the gynecologist.
Who is at risk?
The main risk group for the potential development of retrochorial pathology in the uterus includes women in the first trimester of pregnancy with a history of the following problems:
- High risk of injury to the abdomen and uterus due to various reasons;
- Predominance of Th-1 response in the general immunological profile;
- Acquired or hereditary thrombophilias, including those caused by anti-hCG sensitization or antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Chronic DIC syndrome;
- Severe arterial hypertension of any nature;
- Compatibility of mother and father according to HLA antigens of the second group;
- Regular bacterial or viral infection;
- Chronic endometritis at any stage.
Methods for diagnosing hematoma
The main method for diagnosing hematoma during pregnancy is ultrasound. It gives the most accurate results. During the examination, the doctor should pay attention to some points:
- location of blood accumulation,
- size of hemorrhage,
- volume of fluid in the cavity,
- general view of the hematoma,
- structure of education,
- uterine tone.
All this information is important. The impact of the hematoma on the membrane surrounding the child depends on the location. The size of the hemorrhage and the volume of fluid indicate a danger to the baby’s development. The general appearance and structure indicate how long ago its existence was. The convulsive state of the uterus is a confirmation of readiness for a miscarriage.
The first ultrasound examination is performed at 12 weeks. But other tests are taken by the woman regularly. Their results may be indirect confirmation of the presence of a hematoma. Blood type tests of the father and mother are of great importance. Problems with pregnancy may occur if the Rh factor of the mother and father does not match. Pregnant women undergo the following tests and tests:
- General blood analysis. It gives a general idea of the health of the expectant mother.
- A clinical urine test allows you to confirm or refute possible kidney problems and late toxicosis.
- Blood test for clotting. The result of this test is very important during childbirth.
- A biochemical blood test gives an idea of the presence of certain diseases that pose a threat to pregnancy.
- Doppler testing of the embryo confirms the correct development of the baby and the correspondence of its size to the gestational age.
- Hormone tests. Only with their help can a conclusion be made about the state of hormonal levels.
- Test for sexually transmitted infections.
We recommend additional reading: How to get rid of edema during pregnancy, treatment, how to deal with it and what to do
Diagnosis and treatment of hematoma are closely related.
Symptoms of hematoma
Early stages of hematoma development are often not accompanied by external clinical symptoms and are detected only as a result of a routine examination using an ultrasound machine.
The woman generally feels fine, as usual, and does not express any objective complaints. At the same time, some patients note a slight pulling sensation in the problem area , but it is in no way associated with the hematoma.
In the middle stages of development of the pathological process, the main external manifestation is uncharacteristic, irregular and minor bleeding from the vagina . They are low-intensity and have a brown or dark red tint.
At the same time, modern gynecologists note that such bleeding, with mandatory monitoring and confirmation of the retrochorial nature of the pathology, is a neutral and even favorable sign, which indicates spontaneous release of the cavity from the hematoma.
The main danger is intense bright red discharge, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. Signs indicate active secondary uterine bleeding and a high risk of miscarriage; the woman needs urgent hospitalization.
Severe degrees of hematomas of a retrochorial nature require the pregnant woman to remain in the hospital constantly. She is treated with complex therapy aimed at preventing the development of complications and miscarriage.
Why does a hematoma occur in pregnant women?
There are many reasons for the formation of blood accumulations in the pregnant uterus. They are conventionally divided into direct and indirect.
Direct causes of violation of the integrity of blood vessels and the formation of hematomas include:
- injuries of the pelvis and abdominal cavity. Often, detachment of the ovum occurs as a result of falls, blows to the abdomen, road traffic accidents, and less often - against the background of violent sexual intercourse.
- The same direct reasons include some medical procedures: amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy and other serious interventions.
There are many more indirect reasons:
- Progesterone deficiency causes rejection of the uterine mucosa, causing the formation of retrochorial hematomas.
- Infectious processes: STIs, streptococci, staphylococci, cytomegalovirus, herpes and others.
- Disorders of the blood coagulation system. Interestingly, there is not always a decrease in blood clotting. As a rule, most often the constant formation of hematomas and chorionic detachments is associated with increased blood clotting - thrombophilia.
- Bad habits: smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction.
- Arterial hypertension or sudden uncontrolled rises in blood pressure.
- Abnormal chorionic attachments: marginal or central location is more often associated with episodes of detachment and bleeding.
Symptoms of hematoma
The hematoma itself may not manifest itself in any way until the coagulated blood begins to leave the cavity. Therefore, the main sign of this condition is brown spotting from the genital tract.
The discharge has a characteristic dark brown color, since the blood in the cavity has already coagulated and the bleeding has stopped. This “daub” can continue for quite a long time - depending on the volume of the hematoma, until the cavity is cleared of blood and clots.
Therefore, we can say that the appearance of brown discharge is a more favorable sign than the appearance of fresh scarlet blood. The last symptom indicates ongoing bleeding.
In some patients, this may be accompanied by dull aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. But more often, women have such complaints not at the moment the “spot” appears, but about 5-10 days before it - just at the moment the hematoma begins to form.
Diagnosis of hematoma
Determining chorionic detachment is quite simple. Obstetricians always assume its presence when a pregnant woman has classic complaints.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is sufficient to use ultrasound. An ultrasound clearly shows the hematoma itself, its location, contours, degree of organization: that is, how long ago it formed. Ultrasound is also used to monitor hematoma and the dynamic condition of the fetus.
Treatment of hematoma
For treatment you need:
- Sexual and physical rest.
- The use of hemostatic drugs: etamsylate, calcium gluconate, ascorutin, tranexam, vitamin K and others.
- Antispasmodics to relax the uterine wall. Excessive tone contributes to the progression of detachment of the embryo from the wall, so papaverine, drotaverine, and magnesium preparations are used to treat this condition.
- In the case of confirmed thrombophilia, on the contrary, special “blood thinners” are used: aspirin and low molecular weight heparins.
- In case of progesterone deficiency, it is important to prescribe replacement therapy in a timely manner (Duphaston, Crinon, Susten and others).
- It is important to understand that if heavy bleeding continues, it is often necessary to perform curettage of the uterine cavity. In such cases, the fetus most often has already died, and the woman risks her health due to bleeding.
Alexandra Pechkovskaya, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Diagnostics and necessary tests
Up to a third of all retrochorial hematomas are detected during routine examination as part of standard stages of regular monitoring of the health status of a pregnant woman. We are talking about pathologies without clinical external signs. Moreover, if there are the primary symptoms of pathology described above and the threat of miscarriage, then the patient is taken for examination immediately.
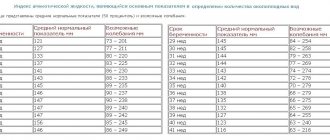
The key sign of retrochorial hematoma on ultrasound is the presence of an anechoic zone in the form of a crescent between the myometrium and the chorionic membrane. Inside, weak echoes from blood clots are observed, the structure is located corporally or supracervically, and may be bipolar. Size and potential hazard assessment:
- Up to 20 percent of the fertilized egg – small, relatively safe;
- From 20 to 50 percent of the ovum is average, requiring therapy and constant monitoring;
- More than 50 percent is massive, a very high risk for the fetus and maternal health.
Secondary signs:
- Thickening of the uterine walls as a consequence of the development of tone;
- Change in the general shape of the fertilized egg;
- Other visually visible pathologies.
In addition to ultrasound, the doctor prescribes:
- General urine and blood tests;
- Blood clotting test;
- Blood biochemistry;
- Tests for STDs;
- Flora smear;
- Hormonal tests;
- Cardiotocography and Dopplerometry of the fetus in the later stages.
Possible consequences of pathology
Sometimes the hemorrhage is so insignificant that its presence is recognized after childbirth, noticing characteristic marks on the separated placenta. In this case, you don’t even have to think about the consequences.
In other cases, when the mother responded promptly and correctly to the presence of this pathology (passed all the examinations and prescribed treatment), the accumulation of blood resolves, causing absolutely no harm to either the woman or the baby.
But it also happens that the pathology was discovered late, the mother decided that “it will go away on its own,” etc. In such situations, the hematoma can grow, tearing away the fertilized egg from the wall of the uterus, and this inevitably leads to the threat of miscarriage. Moreover, the greater the hemorrhage, the higher this threat. And the higher the threat, the more the gap between the chorion and the uterus fills with blood.
If you do not respond to the pathology in a timely manner, various complications are possible, including placental abruption (when the process is delayed up to 2-3 trimesters). Impaired blood circulation between the embryo and the mother’s body leads to its starvation, both oxygen and nutritional. Often this becomes the cause of abnormalities in the born child, in other cases – the reason for the fading of pregnancy or spontaneous abortion. In some cases, it comes to immediate termination of pregnancy, up to cesarean section (in later stages) in order to save the life of the mother.
Don't joke with this pathology , it is not dangerous for either the mother or the baby if you respond to it in time and properly.
Treatment of hematoma during early pregnancy
The procedure for treating internal bleeding is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis exclusively under the supervision of a gynecologist. Self-medication with any medications is contraindicated.
Despite the fact that retrochorial pathology is formed only in the first trimester, basic supportive measures are carried out throughout the entire period before birth. The main treatment is the entire period of threatened miscarriage (on average 1 month). At peaks in the risk of miscarriage and premature birth, therapeutic measures are repeated.
Conservative therapy:
- Stop bleeding and stabilize. Dicynone, vikasol;
- Induction of uteroplacental exchange. Curantil, folic acid, vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Hormonal prevention. Duphaston, utrozhestan;
- Relaxation of uterine tone. Magnesia, drotaverine, papaverine;
- Stabilization of the emotional background. Novopassit, seduxen.
Secondary recommendations:
- Correction of the power system. All foods and drinks that cause gas formation, stool consolidation, and enhance intestinal motility are excluded;
- Prohibitions. Sexual contact, physical activity, heavy lifting, stress;
- Bed rest. The woman spends most of her time horizontally with her legs raised.
Prevention
To avoid problems with pregnancy, a woman should be regularly examined by her doctor and listen to his advice. When visiting a gynecologist for the first time about pregnancy, you should answer all questions truthfully - this will help avoid unnecessary problems. Be sure to take the necessary tests in a timely manner.
Habits and lifestyle play a big role. While carrying a child, you should try to avoid provoking factors, come to your appointment on time, and take care of the well-being of the pregnancy. Walking in the fresh air is beneficial. Physical activity should be feasible. It is necessary to pay attention to proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and microelements. If any alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
How does pathology threaten the fetus, placenta and pregnancy in general?
With timely detection of a hematoma, regular monitoring of its condition, and implementation of the necessary preventive medical actions aimed at preventing the development of complications, retrochorial pathology does not pose a threat to the course of pregnancy. The vast majority of births occur naturally.
If there is a controlled hematoma that exceeds 50 cubic centimeters in volume or occupies more than 40 percent of the total size of the gestational sac, a cesarean section is recommended.
In case of rapid development of bleeding, the appearance of pain, or the uterus becoming unstable, serious complications are possible - miscarriage, frozen pregnancy, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine growth retardation of the unborn child.
Danger for the expectant mother and baby
If a woman during pregnancy adheres to all the recommendations and prescriptions of the gynecologist, there is no threat to the life of the fetus. Even if there is an outflow of blood from the chorionic section, but the pregnant woman adheres to the correct lifestyle and carries out the necessary treatment, the hematoma will resolve within 15-35 days.
During the entire period of pregnancy, the woman’s health condition is carefully monitored. If appropriate measures are not taken in a timely manner, the area increases with exfoliation of the chorionic section, which can be explained by incessant bleeding.
We recommend additional reading: Why do hands and fingers go numb during pregnancy, what to do and the main causes of numbness
The consequences of retrochorial hematoma for a woman during pregnancy and for a child (baby in the womb) are often unpredictable. Among them:
- premature termination of pregnancy (in other words, miscarriage);
- cessation of embryo development in the womb or death;
- hemorrhage in the uterus;
- failure in the development of organs and systems of the embryo;
- the formation of such a neoplasm at a later stage, as a relapse of the pathology.
If pathological exudate begins to be released during pregnancy, pain symptoms occur in the lower abdomen, such clinical manifestations should alert the woman and cause a visit to the doctor. In the first 3 months, the state of discomfort indicates this condition and other problems requiring emergency treatment.
FAQ
Below are the most pressing questions regarding common pregnancy pathologies and qualified answers to them.
How does a hematoma come out during pregnancy?
The process of natural release of retrochorial hematoma is the formation of irregular, scanty, spotting-type discharge with dark red or brown tints.
If the pathology is confirmed by laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, and is regularly monitored, then such discharge is the norm and a positive symptom, indicating the start of the process of emptying the designated localization naturally.
In this case, intense bleeding with bright red discharge and secondary manifestations (tugging feeling and pain in the abdomen) is a symptom indicating the need for immediate hospitalization of the patient.
Can it resolve on its own?
With its small size, stable condition and absence of external symptoms, quite often the hematoma remains unnoticed until childbirth, especially if the woman for some reason did not undergo routine ultrasound examinations.
However, this does not mean that the pathology “dissolves.” In any case, the accumulation of biological fluid comes out - either naturally before/during childbirth, or as a result of a cesarean section.
Is it placed for preservation if there is a hematoma in the uterus?
They are sent for preservation if there is a risk of miscarriage or early labor, which can be caused by a hematoma. If the pathology is stable, small in size, and gradually resolves naturally, then outpatient therapy and regular diagnostics are prescribed, without the need to transfer to a hospital setting.
The main indications for urgent hospitalization are:
- The presence of stable/unstable dynamic tone of the main female sexual organ;
- Pain syndrome in the lower abdomen;
- Vaginal discharge of bright red shades.
Classification
All hematomas are divided into two main types. These are retrochorial and retroplacental. The first occurs during pregnancy before 16 weeks, the second after.
The name retrochorial hematoma is due to the fact that the outer membrane that surrounds the embryo is called the chorion. Subsequently, the placenta appears in its place.
A retroplacental hematoma may appear after the second half of pregnancy, when the chorion has already degenerated into the placenta. It proceeds in the same way as retrochorial.
Also in practice there are:
- subchorionic;
- retroamniotic;
- subamniotic;
- intrauterine.
Subdural hematoma during pregnancy appears after receiving a traumatic brain injury and brain contusions. Its symptoms include speech impairment, bradycardia, convulsions, and headaches.
As soon as signs of a subdural hematoma appear, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. Until this point, you should remain in bed and move as little as possible.
Based on the symptoms that determine the severity of the pathology, three stages of hematomas are identified.
- Easy. Education is small in size. It is often detected during examination. There are practically no symptoms. The expectant mother feels well, and the formation can only be detected by ultrasound.
- Average. During this period, nagging pain in the abdomen occurs. Blood clots may be discharged. In this case, you should contact an obstetrician-gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy. With an average degree of education, while listening to an unborn baby, a disturbance in its heartbeat is observed.
- Heavy. A woman's blood pressure drops sharply. The pain is cramping in nature. There is severe bleeding and the woman may faint.
For moderate to severe pathology, a caesarean section is prescribed. It is carried out earlier than the scheduled date of natural birth.
How to cure the disease - the doctor advises
In case of uterine hemorrhage, the patient must observe a special regime of physical activity. The medical specialist prescribes drugs that stop hemorrhage, help strengthen the vascular walls and resolve the clot.
The expectant mother needs to rest more, avoid any stress or emotional stress. For general weakness, constant pain in the lower abdomen, and bleeding from the vagina, the doctor may prescribe bed rest.
Pay attention to your diet, choosing foods that help normalize intestinal functions. It is unacceptable to consume foods that provoke flatulence and increase peristalsis. You will have to give up smoked, spicy and salty foods, and carbonated drinks. It is necessary to eat boiled cereals and liquid soups, lactic acid products, steamed meat and fish.
Drug therapy involves the use of Actovegin, Curantil, Vikasol, Wobenzym, Dufatson, folic acid, vitamin C and other drugs.
Combinations of drugs are selected by the attending physician depending on the type of pathology, its size, the general condition of the patient and the duration of pregnancy:
- Actovegin. Used to prevent fetal hypoxia, improves tissue oxygenation and energy metabolism.
- Vikasol, dicynon, tranexam. They have an antihemorrhagic effect, improve blood clotting, and help stop bleeding.
- Duphaston or Utrozhestan. Chemical analogues of the pregnancy hormone progesterone. They are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels and prevent miscarriage.
- Papaverine and No-shpa. Used to reduce uterine hypertonicity.
- Magnesia - used to lower blood pressure, eliminate the consequences of placental abruption and delay the development of the child.
The presence of infectious diseases that provoke fragility of the walls of blood vessels requires the use of antiviral or antimicrobial drugs - Cefazolin, Tamiflu, Amoxiclav, Ampicillin. These medications should be used with great caution, carefully choosing the dosage.
If the interthecal hematoma takes a long time to come out, Wobenzym is prescribed. It has a stimulating effect on the immune system, accelerates the resorption and emptying of a blood clot, and prevents the appearance of local edema.
Ascorbic and Folic acid, Magne B6, and complex vitamin preparations are recommended as general strengthening agents.
Any pathology in a woman’s body during pregnancy causes her stress, so to prevent the consequences of anxiety, it is recommended to use mild herbal-based sedatives.
How to prevent hematoma - preventive measures
If we consider each source of the formation of retrograde hematoma during pregnancy, it can be noted that its development can be prevented by carefully analyzing unusual changes in the general condition, identifying and eliminating provoking diseases in a timely manner.
The main preventive rule is to maintain a healthy lifestyle immediately after conception:
- eliminating every bad habit: smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs;
- daily walk in the fresh air;
- rest, avoidance of increased physical activity;
- normalization of work and rest schedule (it is recommended to spend at least 8 hours on sleep);
- exclusion of any stressful situation and emotional experiences;
- exclusion of traumatization;
- maintaining a proper diet.
The health of the expectant mother and baby can be preserved if the pregnant woman promptly treats concomitant infectious or chronic diseases.
Changing lifestyle and diet
If there is no pain or red bloody discharge, and the hematoma is small according to ultrasound, the observing gynecologist may allow the expectant mother to stay at home. But a woman must adhere to the recommended regimen, regularly visit the doctor and strictly follow all his instructions. Relatives need to take care of all household chores.
The expectant mother should observe bed rest, place a cushion under her lower back, creating an elevated position for the pelvis so that there is no stagnation of blood. It is necessary to eliminate worries and emotional stress, give up sexual activity, and normalize nutrition.
It is not recommended to consume foods that thin the blood - legumes, cabbage, coffee, carbonated drinks. It is worth giving preference to dishes rich in proteins and vitamins. It is also important to regulate your bowel movements and drink enough fluids.
Causes
There are many reasons for this pathology. These include:
- hormonal disorders;
- mechanical damage (bruises, abdominal injuries);
- severe stress;
- severe early toxicosis;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- malformations of the reproductive organs;
- diseases of the uterus (fibroids, polyps, endometriosis);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- blood diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- autoimmune conditions;
- endocrine diseases;
- abnormalities of the developing embryo;
- working with hazardous substances;
- physical overload, especially heavy lifting. Read more about how much weight you can lift during pregnancy →
Mode and nutrition
During this period, the expectant mother needs peace. Experts advise spending as much time as possible in bed. There is an opinion that an elevated pelvis improves blood circulation in the genitals. To make it comfortable, you should put a small bolster, pillow or blanket folded in four under your back.
Nutrition during this period should contain fiber, calcium and vitamins. The consumption of various cereals (but not rice), vegetables and fruits, kefir and yoghurt is encouraged. Such nutrition should increase intestinal motility and not contribute to the accumulation of gases.
The less tense the intestines are, the less pressure it puts on the uterine cavity. When choosing a diet, it is important to exclude all foods that promote intestinal consolidation and increased gas formation.