Fraxiparine is a drug belonging to the group of direct-acting anticoagulants based on low molecular weight heparin. Its effect on the body is to thin the blood and increase the permeability of the walls of cellular structures. Nadroparin calcium, which is the basis of this pharmacological drug, is obtained from standard heparin by depolymerization. This component of the composition exhibits increased binding to the protein structures of blood plasma.
Pharmacological group
Fraxiparine has a pronounced antithrombic and anticoagulant effect on human blood. Low molecular weight heparin, the basis of the pharmacological agent, is a glycosaminoglycan with a molecular weight of about 4.3 thousand daltons. When released into the systemic circulation, fractionated heparin leads to a noticeable decrease in blood viscosity. However, despite the similarity of the effects of this substance with standard (unfractionated) heparin, the effect on platelets, primary hemostasis and aggregation is reduced.
After subcutaneous administration of fractionated heparin, the absorption of the drug is about 88%, and the greatest effect on blood composition is observed after 4-5 hours. The half-life of the drug from the body takes 2 hours, but the effect persists for 18 hours after. Processing and removal of Fraxiparine from the body occurs in the hepatic system due to desulfation and depolymerization.
Drug interactions
Taking Franxiparin concomitantly with certain medications can lead to hyperkalemia.
These include the following drugs: potassium salts, ACE inhibitors, heparins, NSAIDs, potassium-sparing diuretics, Trimethoprim, angiotensin II receptor blockers, Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine.
Drugs that affect hemostasis (indirect anticoagulants, acetylsalicylic acid, NSAIDs, fibrinolytics, dextran), together with the use of this drug, enhance each other’s effect.
The risk of bleeding increases if you also take Abciximab, Beraprost, Iloprost, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban, Ticlopedine. Acetylsalicylic acid can also contribute to this, but only in antiplatelet doses, namely 50-300 mg.
Fraxiparine should be prescribed very carefully when patients receive dextrans, indirect anticoagulants, and systemic corticosteroids. If indirect anticoagulants are taken along with this drug, its use is continued until the INR normalizes.
Fraxiparine and alcohol have negative compatibility. The drug is used to prevent thromboembolic complications, and alcohol, on the contrary, increases the risk of them.
Indications for use
The main use of this drug is due to its effect on the blood - the need to reduce blood clotting. Accordingly, it is used for the risk of thrombosis, which can occur after orthopedic and other surgical interventions. There are also risks of vascular thrombosis in people suffering from acute types of cardiac and respiratory failure.
for adults
Can be used at any age over 18 years. There are no other age restrictions.
for children
The anticoagulant drug is directly contraindicated for use at a young age, as it can affect the development of the child and the state of his hormonal system.
for pregnant women and during lactation
Due to the increased permeability of fractionated heparin, it can pass through the placental barrier and enter breast milk. This leads to a significant limitation in the use of Fraxiparine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The prescription of such a drug is allowed under strict indications and significant health risks in the opposite case.
Fraxiparine can also be prescribed in the process of preparing and performing in vitro fertilization (IVF). Due to its effect, implantation of the egg in the walls of the uterus is facilitated, subject to a significant increase in coagulation when using certain groups of hormones.
Fraxiparine for increased blood clotting in pregnant women
Fraxiparine began to be intensively used in clinical practice about thirty years ago. This was preceded by large-scale research over ten years conducted by the French pharmaceutical company. Dozens of scientists and several thousand patients took part in studying the properties of the drug.
On the Russian pharmaceutical market, Fraxiparine is annually among the top twenty best-selling drugs in the segment of medications for medical institutions. The drug in question is widely used in surgery, cardiology, anesthesiology, and intensive care units. In obstetrics, Fraxiparine is used if a pregnant woman is diagnosed with increased blood clotting, which threatens the health of the woman herself and the development of the fetus.
The human body has a complex system (hemostasis) that regulates blood clotting. The system maintains the liquid state of the latter and restores the walls of blood vessels when damaged by gluing platelets. The result is a blood clot called a thrombus. Increased thrombus formation is the cause of circulatory disorders and various cardiovascular pathologies.
Increased blood clotting leads to increased formation of blood clots, blockage of blood vessels and disrupts normal blood circulation
In expectant mothers, blood clotting increases throughout pregnancy. This mechanism prepares the body for possible bleeding during the gestational period and during childbirth. Thromboembolic complications (complete or partial blockage of a vessel by a blood clot) in pregnant women are also provoked by the following factors:
- heredity;
- age over 35 years;
- oncology;
- prolonged use of oral contraceptives before pregnancy;
- previous unsuccessful pregnancies associated with fetal death;
- multiple pregnancy;
- smoking, overweight, prolonged bed rest.
According to experts, thromboembolism is one of the main causes of maternal mortality. Disturbances in the hemostatic system also lead to the following complications:
- recurrent miscarriage;
- delayed fetal development;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- premature placental abruption;
- inability to get pregnant.
Fortunately, modern medicine has a wide range of tools for managing pregnancy with thromboembolic pathologies. The drugs of choice are the so-called anticoagulant (anti-clotting) agents. Fraxiparine is the most studied of modern anticoagulants.
What is the drug, how does it work, release form
Anticoagulants are a group of chemical compounds that act on various parts of the blood clotting mechanism. Fraxiparine is a direct-acting anticoagulant that suppresses the formation of a special enzyme, thrombin, already at the first stage of hemostasis.
Fraxiparine is the drug of choice for the management of pregnant women with a predisposition to increased thrombosis
The human liver and lungs produce their own anti-clotting substance called heparin. About a hundred years ago, doctors developed a medicine based on it, which is still used today. The active ingredient of Fraxiparin is calcium nadroparin, which is obtained through a special process from regular heparin. Nadroparin belongs to the group of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH).
Numerous studies have shown that LMWHs are preferable in the early stages of thrombosis. For example, Nadroparin quickly reduces the size of a blood clot, acts several times longer than regular heparin, reduces the frequency of relapses and does not provoke bleeding.
Fraxiparine is available in the form of a solution for subcutaneous administration. Nadroparin calcium solution is placed by the manufacturer in safe disposable syringes. The volume of injected solution is from 0.3 to 1.0 ml.
Fraxiparin and Fraxiparin Forte
On the drug market, in addition to the standard Fraxiparine, there is Fraxiparine Forte, in which the concentration of the main component is twice as high. There are no other differences.
Table: concentration of nadroparin calcium in different types of Fraxiparine
| Syringe volume, ml | Fraxiparine, amount of nadroparine, IU | Fraxiparine Forte, amount of nadroparin, IU |
| 0.3 | 2850 | — |
| 0.4 | 3800 | — |
| 0.6 | 5700 | 11400 |
| 0.8 | 7600 | 15200 |
| 1.0 | 9500 | 1900 |
Safety during pregnancy
The instructions for Fraxiparine indicate that there is no reliable information about the effect of the medication on the fetus, since no special studies have been conducted according to the standards of evidence-based medicine. Therefore, the manufacturer does not recommend using the drug during the gestational period, except in special cases, if the therapeutic effect is significantly higher than the possible risk. True, it also reports that in the process of studying the effect of the drug on animals, no negative effect on the fetus was observed.
Despite the manufacturer's precautions, Fraxiparine is recommended for use by the authors of almost all articles in specialized publications. They present the results of clinical practice and small studies on pregnant women, which claim that low molecular weight heparins do not have any teratogenic or toxic effects on the fetus, and therefore are the drugs of choice for thrombosis in pregnant women.
LMWHs are recommended for use in thrombophilic conditions in pregnant women by many international scientific societies and have become the de facto standard for antithrombotic prophylaxis during pregnancy.
E.N. Purebeeva, M.S. Zainulina
“The effectiveness of Fraxiparine in pregnant women with congenital thrombophilia and intrauterine growth retardation syndrome”
Contraindications
Fraxiparine has certain contraindications for use, which can be presented in the following list:
- bleeding;
- thrombocytopenia;
- organ trauma with risks of bleeding;
- severe kidney failure;
- intracranial hemorrhages;
- damage to the brain, spinal cord and eyes (including surgery);
- acute endocarditis of infectious origin.
It is recommended to use with caution in the presence of injuries and diseases associated with an increased risk of bleeding or significant changes in the circulatory system. This rule also applies to patients weighing up to 40 kg, suffering from arterial hypertension, liver/renal failure and using other anticoagulants. In some cases, there is a limitation on the period of use of up to 10 days, depending on the indications and contraindications present.
Side effects
Like most medications, Fraxiparine sometimes causes side effects:
- thrombocytopenia;
- allergic reactions (usually Fraxiparine makes the stomach itch), including Quincke's edema;
- bleeding in various locations;
- skin necrosis;
- prism;
- eosinophilia after drug withdrawal;
- reversible hyperkalemia;
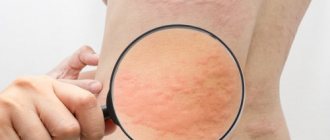
- the formation of a small hematoma at the injection site, sometimes large bruises appear from Fraxiparine (photo below);
- increase in the content of liver enzymes.
Bruises from Fraxiparine
Some patients who used Fraxiparine note a strong burning sensation after the injection.
Applications and dosages
The use of the pharmacological drug Froxiparin involves self-administration of the medicine under the skin with an existing disposable syringe. This procedure can be performed while lying on your side using your stomach as the injection site. It is recommended to alternate sides of the abdomen with each administration of the drug. It is also possible to inject the product into the skin of the thigh. The injection procedure is as follows:
- Form a skin fold using the fingers of your free hand.
- Insert the syringe needle perpendicular to the skin.
- Inject the drug by smoothly lowering the piston and holding the fold.
- The area where the medication is administered should not be rubbed.
It is not recommended to remove air bubbles from the supplied syringe, since loss of the drug at the prescribed dosage is not recommended.
for adults
In this age group, Fraxiparine is used depending on the indications and contraindications present. Dosage varies based on application:
- To prevent thromboembolism during surgical operations, the smallest dosage of the drug is used - 2850 IU, which corresponds to 0.3 ml of the composition. It is administered approximately 4 hours before the expected start of surgery and therapeutic use is continued for 7 days or more (depending on the risks).
- When performing orthopedic operations to prevent thromboembolism, the dosage is calculated based on the patient’s weight - 38 IU per 1 kg. The first administration of the drug is carried out approximately 12 hours before the intended intervention. In the future, to maintain the therapeutic effect, the drug should be used for 10 or more days, 1 time per day with outpatient monitoring of the patient’s condition.
- If there is an increased risk of thrombosis, Fraxiparine is administered subcutaneously once a day. The amount of a single dosage is determined by the patient’s weight - 3800 IU if the weight does not reach 70 kg and 5700 IU if it exceeds the designated limit. The use of the anticoagulant continues throughout the period until the risks are reduced under the supervision of medical personnel.
- For the therapeutic treatment of heart attack or unstable angina, Fraxiparine is administered subcutaneously once every 12 hours. The duration of such treatment is limited to 6 days. The dosage is determined from the ratio - 86 IU per 1 kg of body. The first administration of the drug can be done intravenously.
for children
Being under 18 years of age is a direct contraindication to using Fraxiparine.
for pregnant women and during lactation
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended. Allowed only for special indications with individual dosage calculation and supervision by medical personnel.
Reviews
Maria:
This remedy was prescribed due to the threat of miscarriage. There were a lot of doubts, but everything ended well. I learned how to administer Fraxeparin on my own so as not to bother my husband. I'm very happy that this helped me.
Victoria:
The drug helped me in the treatment of veins and the prevention of thrombosis. Each syringe is packaged separately and has a thin needle. It is a little expensive, but if you look, you can find inexpensive pharmacies without markup. The instructions for Fraxiparin 0.6 helped, telling how to give injections and where to store them. I'm happy with the result.
Analogs
There are many analogues of the drug. However, if it is necessary to replace Fraxiparine, you must consult with your doctor.
Heparin
Heparin is a relative analogue of the drug and its predecessor. The main area of use of this drug is the prevention of thrombolic disorders during surgical interventions and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Video on the topic
How to inject Fraxiparine correctly:
Thus, Fraxiparine is often prescribed for problems with blood clotting, the need for treatment or prevention of thromboembolic complications. The main thing is to follow the recommendations of a specialist who can determine the advisability of its use and the required dosage. Otherwise, in addition to the lack of effect, on the contrary, a negative effect associated with overdose, the development of bleeding, and hyperkalemia is possible.
DIAGEN® - innovation in the treatment of diabetes in humans
- Stabilizes sugar levels for a long time
- Restores insulin production by the pancreas
To learn more…
special instructions
Do not administer the drug intramuscularly!
During treatment with Fraxiparin, its alternation with other drugs belonging to the class of low molecular weight heparin is unacceptable. This is due to the possible violation of the prescribed dosage regimen due to the use of dosage units different from the drug.
Graduated syringes allow you to accurately select an individual dose, taking into account the patient’s body weight.
Signs of the development of necrosis in the area of injection of the solution are usually purpura, a painful erythematous or infiltrated spot (including general symptoms). If they appear, you should stop using Fraxiparine immediately.
Heparins increase the risk of thrombocytopenia, so treatment must be accompanied by careful monitoring of platelet counts. Particular caution should be exercised, and if the following conditions occur, immediately discontinue treatment: thrombocytopenia, a marked decrease (by 30–50% of the initial value) in the platelet count, negative dynamics of thrombosis for which therapy is being carried out, thrombosis that developed during the administration of the drug , disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
If necessary, it is possible to prescribe Fraxiparine to patients with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia that occurred during the use of unfractionated or low molecular weight heparins. In this case, a daily platelet count is indicated. If thrombocytopenia occurs, you should immediately stop using the drug and consider prescribing anticoagulants of other groups.
Fraxiparine should be prescribed only taking into account the results of an assessment of renal function.
When using heparin in patients with elevated blood potassium levels or the risk of increased blood potassium concentrations, the likelihood of hyperkalemia increases. In this regard, during long-term therapy or treatment of patients with chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus, metabolic acidosis, or those on concomitant therapy with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other drugs that contribute to the development of hyperkalemia, it is necessary to carefully control the level of potassium in the blood.
The decision on the possibility of combining anticoagulants with neuraxial blockade is made individually based on an assessment of the benefit-risk ratio of this combination.
When performing spinal and epidural anesthesia or lumbar puncture, an interval is required between the administration of the drug and the insertion or removal of the spinal or epidural needle or catheter. When using Fraxiparine for the purpose of preventing thromboembolism, it is at least 12 hours, for the purpose of treatment - 24 hours. In case of renal failure, the interval may be increased.
Warfarin
Manufacturer: Ozone (Russia)
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: warfarin
Warfarin is an indirect anticoagulant. The activity of the drug is manifested in a decrease in the concentration of blood coagulation factors in plasma, which leads to a slowdown in the formation of blood clots.
This analogue of Fraxiparine in tablets is used as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent for thrombosis, embolism of blood vessels, as well as for heart diseases (myocardial infarction, arrhythmia).
Properly selected analogues, as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent, will prevent the formation of blood clots and avoid serious complications from the cardiovascular system.
Overdose
Symptoms: bleeding, abnormal platelet count and other parameters of the blood coagulation system.
Treatment: for minor bleeding, it is sufficient to reduce the next dose of Fraxiparine or delay its administration. Special therapy is required in severe cases. Protamine sulfate has a pronounced neutralizing effect on the anticoagulant effect of heparin. When calculating the dose of the antidote, it should be taken into account that to neutralize 950 IU of anti-Xa nadroparin, 0.6 ml of protamine sulfate is needed. It is possible to reduce the dose of the antidote if a long period has passed since the overdose.
Chime
Manufacturer: Berlin-Chemie (Germany)
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: dipyridamole
The medicinal properties of Curantil are based on its vasodilating effect. By acting on the vessels of the heart muscle, the speed and volume of blood flow and its oxygen supply improve. The medication reduces platelet aggregation, which leads to the prevention of blood clots.
The drug is effective for placental insufficiency due to complicated pregnancy associated with fetal hypoxia. Curantil shows its activity in the treatment and prevention of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza as a means of enhancing immunity.
Detralex
Manufacturer: Servier (France)
Release form: tablets
Active ingredients: hesperidin, diosmin
Detralex is a venotonic and angioprotector, the activity of which leads to an improvement in venous hemodynamics. The drug reduces venous stagnation and the distensibility of the venous wall, capillary permeability. The action of the active component of Detralex leads to improved microcirculation and lymph drainage.
The medication is effective in the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, hemorrhoids, accompanied by clinical manifestations (pain, swelling, venous trophic ulcers).