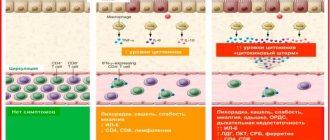
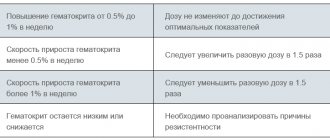
Human immunity is a complex multi-stage system of protecting the body from harmful external influences (viruses, bacteria, allergens, fungi). There is no single organ that is responsible for immune defense. This function is assigned to different systems: starting from the intestines and ending with microscopic protein substances - immunoglobulins.
General characteristics of immunoglobulins
Immunoglobulins (Ig), also known as antibodies, are molecules of glycoproteins (special protein compounds found in blood plasma). They are an important part of the immune system, whose job is to protect the body from infections and other foreign substances. In our body, as in the bodies of vertebrates, immunoglobulins are found in the blood and in some secretory fluids. Antibodies help the body identify and destroy foreign harmful elements. Immunoglobulins are usually produced in response to contact with antigens, such as bacteria or viruses. Sometimes immunoglobulins are produced after contact with the body's own tissues, called autoantigens.
A deficiency or excess of antibodies can be a sign of various pathologies, so determining their amount in the blood is an important part in diagnosing many diseases. In addition, modern advances in biomedicine make it possible to use synthetic antibodies in the treatment of certain diseases.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that the drug is used to enhance immunity and provides benefits to the body, it has its contraindications. It is not recommended to drip, administer the solution intravenously or intramuscularly under the following conditions:
- increased sensitivity of the child to the active component;
- immunoglobulin A deficiency caused by the presence of antibodies in the body;
- exacerbation of chronic allergic reactions;
- renal failure;
- diabetes;
- the likelihood of developing anaphylactic shock due to blood products.
Before using the medication, it is important to take into account not only contraindications for use, but also the patient’s conditions in which the solution should be administered with extreme caution: recurrent migraines, heart failure. If therapy is necessary for a nursing woman, the baby should be temporarily weaned to prevent the medicine from entering his body without indications for this. For diseases caused by immunopathological processes, the solution is used only under the supervision of a physician.
Parents often have questions about the age at which immunoglobulin injections can be given. The manufacturer of the drug does not indicate any age restrictions. Injections, if indicated, are prescribed both to a child in the first days of life and at an older age. It is important to choose the appropriate dosage of the medication.
Expert opinion
Irina Katykova
Pediatrician, pediatric neurologist
Ask a Question
Do you still have questions about your child's health? Ask them right here on the website and we will definitely answer!
Antibody structure
Content:
- General characteristics of immunoglobulins
- Antibody structure
- Types of immunoglobulins
- Characteristics of different classes of immunoglobulins
- The role of immunoglobulins in the body
- Antibodies and immunological memory
- How to determine the amount of antibodies
- Immunoglobulins and vaccination
- Antibodies in medicine
Immunoglobulins are symmetrical Y-shaped molecules consisting of two long heavy chains (H) and two short light chains (L). The chains are connected to each other either by disulfide (SS) or hydrogen bonds. Each immunoglobulin can be divided into two parts: constant (C) and variable (V). While the C portion determines the activity of the antibody, the V region is necessary for binding to specific antigens (that is, specific proteins that signal the presence of a specific bacterium, virus, or other foreign object in the body).
The structure and role of the C-part is identical for all types of antibodies. This area can be figuratively called the brain center of immunoglobulin. It is he who controls how effectively the antibody performs its function. The V region differs among different types of antibodies. Thanks to this variability, antibodies can recognize and bind to different types of foreign bodies in the body. That is, for each type of “stranger” there is its own immunoglobulin with a specific V-region structure.
In other words, each antibody approaches the antigen like a key and lock, and in combination with each other they form so-called immune complexes. But antibodies are also capable of showing flexibility in combination with “strangers”, making it easy to adapt to various antigens. However, this ability of immunoglobulins sometimes provokes cross-allergic reactions in a person - when the immune system of a person with allergies cannot distinguish between allergens. For example, a person with a pollen allergy due to improper functioning of immunoglobulins may also react to raw fruits and vegetables.
special instructions
- Preparations based on Immunoglobulin for children can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. During the first 7 years of life, the child’s immunity is actively developing. Therefore, any interventions, even those suggesting a beneficial effect, are considered inappropriate. Stimulants are used only if there are compelling indications.
- Each administration of medication is documented. The personal card indicates the time of use, volume, number of procedures. Information about the drug is also recorded: date of manufacture, batch, expiration date.
- After the introduction of the stimulant, the child can be vaccinated against measles and mumps no earlier than 90 days later. Other vaccines are prohibited for 2 weeks. When combining immunoglobulin and vaccination, the effect of the latter is reduced.
- The results of serological tests carried out during this period may be distorted under the influence of the immunomodulator.
- It is unacceptable to increase the rate of intravenous administration of the medication. Otherwise, the child may develop severe adverse reactions.
- Patients prone to allergic manifestations require additional use of antihistamines for 8 days after the injection.
- When administering Immunoglobulin drips, it is necessary to use an individual container. The medication is incompatible with immunization drugs, Calcium Gluconate.
Ampoules should be stored at a temperature of 2 to 8 degrees. It is unacceptable to freeze the solution and use cloudy medicine.
Types of immunoglobulins
In the human body, immunoglobulins are presented in two forms:
- soluble (produced by plasma cells);
- associated with the outer membrane of B-lymphocytes, they are also receptor antibodies.
In addition, there are different classes and subclasses (isotopes) of immunoglobulins. They differ in their biological characteristics, structure and targeting. Based on differences in heavy chain structure, several classes of antibodies have been identified. Each of them has different functions and responses.
In placental mammals, including humans, 5 main classes of antibodies have been identified: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM. Human blood contains only three of them - IgA, IgG and IgM. But the rest, according to experts, are no less useful for maintaining the immune system. They all differ in the type of heavy chain. For example, IgG molecules have gamma chains, IgM have mu chains, IgA have alpha chains, IgE have epsilon chains, and IgD have delta chains. These differences allow immunoglobulins to participate in different types and stages of immune responses.
In addition to the main classes of immunoglobulins, there are several subclasses. The difference between them is based on minor differences in the type of heavy chains in each class. There are 4 subclasses of antibodies found in the human body. The numbering corresponds to the order of decreasing their concentration in the serum. Thus, IgG and IgA antibodies are further grouped into subclasses IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, as well as IgA1 and IgA2.
Most antibodies (IgG, IgD, IgE) in the body are presented in the form of a monomer (one molecule). The exceptions are class A antibody, which also occurs in the form of a dimer, and IgM, which forms a snowflake shape (pentamer).
Side effects
Most patients do not have negative reactions to the administration of the stimulant. In rare cases, an allergy, a reaction to immunoglobulin in a child in the form of hypersensitivity and anaphylactic shock may develop. Therefore, after using the medication, children should remain under the supervision of medical personnel for at least half an hour.
Redness and slight swelling may occur at the site of intramuscular injection. These signs do not cause serious discomfort and go away on their own and do not require additional therapy.
After drips, children experienced the following manifestations:
- headache;
- chills;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- backache;
- muscle stiffness;
- deterioration of kidney function.
Cases of overdose with a drug to enhance immunity have not been described. When using an excessive amount of immunoglobulin, an increase in adverse reactions is expected. Treatment in this case is symptomatic.
Characteristics of different classes of immunoglobulins
IgA class
About 15% of the antibodies contained in the body of a healthy person are immunoglobulins of the IgA type. There are two subclasses of IgA present in our bodies – IgA1 and IgA2. They differ in molecular weight of heavy chains and concentration in serum. By the way, in serum IgA is presented mainly as a monomer (consists of one molecule). In secretory fluids, immunoglobulin is present as a dimer associated with a peptide. Most IgA in the body are dimers. They are present in most secretory fluids, including the mucous membranes of the respiratory and genitourinary tracts, gastrointestinal tract, as well as saliva, tears, colostrum and milk in women. Since IgA is present on the mucous membranes of the digestive system, where it can be exposed to enzymes, this antibody contains a special component that protects the molecule from premature destruction.
Class A immunoglobulins, as a rule, are not specific in terms of “adjusting” to a certain type of foreign body. Typically, antibodies from this group are present in vulnerable areas of the body or in areas where germs can easily enter. Class A immunoglobulins provide local humoral immunity. This is due to its properties to prevent the penetration of pathogens through epithelial surfaces. Due to the abundance of IgA in the secretions of the mucous membranes (saliva, tears), it protects the body from some local infections.
The main function of immunoglobulins of this class is not to destroy antigens, but to prevent the penetration of foreign substances into the circulatory system. IgA itself is quite weak and is not capable of destroying bacteria on its own. Therefore, they always work together with lysozymes, enzymes that are also present in secretory fluids and can destroy bacteria.
If the concentration of immunoglobulins of the IgA class in the body is disturbed, a person often suffers from infectious diseases of the respiratory tract and kidney diseases, including nephropathy. People whose bodies lack IgA are more prone to autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, allergies and asthma.
Various diseases can lead to a decrease in the amount of IgA. One of these is gonorrhea. The bacteria that cause gonorrhea produce an enzyme that splits the IgA antibody into two parts: Fc and Fab. Interestingly, Fab can still find bacteria that are dangerous to the body, but without interacting with Fc, it is not able to resist them.
IgD class
Class D immunoglobulins are present in very small quantities in the human body and make up approximately 0.2% of all antibodies. IgD is known to attach to the surface of some B lymphocytes as a B cell receptor. However, its functions in the human body have not yet been fully studied. It is believed that IgD is the cause of allergy to penicillin. Also, sometimes it can be activated after contact with harmless blood proteins, thereby causing autoimmune reactions in the body.
IgE class
Immunoglobulin IgE, like IgD, is found in much smaller quantities in serum than other classes of antibodies. IgE protects against parasites and is also responsible for allergic reactions.
IgE is found in blood plasma. Of all serum antibodies, this accounts for only 0.002%. But this does not prevent it from performing a vital role for humans. Immunoglobulins of this group bind to the surface of basophils and mast cells. Then the antigen attaches to them, which in turn leads to the release of substances that moderate the inflammatory response into the bloodstream. That is, IgE controls allergic reactions.
When antigens such as pollen, toxic substances, fungal spores, dust mites or pet dander bind to IgE, substances such as heparin, histamine, proteolytic enzymes, leukotrienes and cytokines are released in the body. This leads to dilation of blood vessels and increased permeability. As a result, hazardous substances can penetrate the capillaries and then into nearby tissues, resulting in symptoms characteristic of an allergic reaction. By the way, most typical allergic reactions in the form of sneezing, coughing, watery eyes and increased mucus secretion actually help remove remaining allergens from the body.
Studies have shown that disorders such as asthma, rhinitis, eczema, urticaria and dermatitis cause increased IgE levels. E-type antibodies are also actively produced in response to the presence in the body of parasitic worms (helminths), persistent infections (herpes viruses, atypical microorganisms) and some arthropods (for example, lice). In addition, IgE plays an indirect role in the immune response by stimulating other immune components to act. It can also protect the surfaces of mucous membranes, causing inflammatory reactions in case of danger.
Pathologically low levels of IgE antibodies can occur against the background of a rare genetic disease accompanied by impaired muscle coordination (ataxia telangiectasia).
IgG class
Class G immunoglobulins are dominant in the human body. They account for 75% of all antibodies. This is partly due to the long half-life: from 7 to 23 days (depending on the subclass). In addition, they can persist in the blood for several decades after contact with the antigen.
There are 4 subclasses of IgG:
- IgG1 makes up 60 to 65% of the total immunoglobulin of this class. Its deficiency is usually a sign of hypogammaglobulinemia (plasma cell deficiency).
- IgG2 is the second most common isotope, accounting for 20-25% of the total IgG. “Adult” antibody concentrations usually appear by 6-7 years of age. IgG2 deficiency has been associated with recurrent respiratory tract infections.
- IgG3 accounts for 5 to 10% of total IgG. Plays a major role in immune reactions against protein or polypeptide antigens.
- IgG4 accounts for up to 4% of the total share of IgG. Previously, IgG4 was associated only with food allergies, but recent studies have shown that elevated serum IgG4 occurs in patients suffering from sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis and interstitial pneumonia. However, the exact role of IgG4 is still unknown.
IgG plays a key role in the humoral immune response. This is the main immunoglobulin found in the blood, as well as in the lymphatic, cerebrospinal and abdominal fluids. Its ability to remain in the body for a long time makes it the most useful antibody for passive immunization. This is the only antibody that can cross the mother's placenta and enter the fetal circulation, providing postpartum protection to the newborn during the first months of his life.
Main functions of IgG:
- increased phagocytosis in macrophages and neutrophils;
- neutralization of toxins;
- virus inactivation;
- destruction of bacteria.
IgM class
IgM is the most important member of the human immunoglobulin family, although it has a very short half-life of about 5 days.
Immunoglobulins of the IgM class account for approximately 10-13% of the total share of serum antibodies in the human body. They are involved in primary immune reactions and are the most important of the antibodies.
IgM is predominantly found in lymphatic fluid and blood. It is the main neutralizing agent in the early stages of the disease. IgM is, so to speak, the first line of defense of the human body from uninvited guests. During the immune response, they are produced first and then replaced by G antibodies. Interestingly, in children, starting at 9 months of age, the body produces the same amount of IgM antibodies as in adults.
An increase in IgM levels can be regarded as a sign of a recent infection or the presence of an antigen in the body.
Indications for use
Intramuscularly, human immunoglobulin is prescribed to increase the body's nonspecific resistance during immunosuppressive therapy, during the period of convalescence, as well as in weakened patients.
In addition, the IM drug is used for emergency prevention:
- Meningococcal infection;
- Whooping cough;
- Poliomyelitis.
- Corey;
- Hepatitis A;
- Rubella in the first trimester of pregnancy in non-immune patients and in women with unknown immune status.
Intravenous administration of Immunoglobulin is indicated for:
- Blood diseases;
- Kawasaki disease;
- Consequences of immunosuppressive therapy;
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Primary immunodeficiency;
- Hyperimmunoglobulinemia syndrome E;
- Eaton-Lambert syndrome;
- Dermatomyositis;
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV infection);
- Agamma- and hypogammaglobulinemia (primary antibody deficiency syndrome), including the congenital form and physiological deficiency in newborns;
- Secondary antibody deficiency syndrome;
- Infections caused by parvovirus B19;
- Chronic inflammatory demyelination in polyneuropathy;
- Dermatomyositis;
- Severe forms of viral and bacterial-toxic infections, including postoperative complications accompanied by sepsis or bacteremia.
As part of complex treatment, human immunoglobulin is prescribed for long-term diseases that are difficult to respond to antibiotic therapy.
To prevent infections, the drug can be used during bone marrow transplantation, as well as in newborns, children with low birth weight and premature infants.
The role of immunoglobulins in the body
Antibodies are part of the humoral immune response and act very specifically, as they are always directed against a specific antigen.
The task of any antibody in the human body is to participate in immune reactions. Immunoglobulins have the ability to form immune complexes with antigen molecules, activate the complement system (a complex of proteins contained in the blood necessary to protect the body from foreign agents) and cause inflammation. All this should neutralize the antigen and safely remove it from the body.
Due to different biochemical properties, different classes of antibodies may perform specialized functions:
- neutralize parasites (IgE);
- neutralize microorganisms (IgM, IgG);
- protect against recurrent diseases such as mumps (IgG);
- protect mucous membranes (IgA);
- participate in the synthesis of lymphocytes (IgD);
- protect the fetus (IgG) and newborn baby (IgA).
"Wilosen"
The drug is based on the thymus gland of cattle. Contains amino acids, oligopeptides and inorganic salts. The drug perfectly strengthens the body's defenses and also suppresses the development of hypersensitivity. The drug "Vilozen" is used topically. In pharmacies, the drug is presented in the form of drops that can be instilled into the nose or added to a solution for inhalation.
Vilozen drops are prescribed to adults and children over 12 years of age. They cannot be used in their pure form. If the drug is used for instillation into the nose, first add 2 ml of water or isotonic sodium chloride solution to the ampoule. During an exacerbation of the disease, 7 drops are instilled into each nasal passage 5 times a day.
Additionally, intranasal inhalations can be performed. The course of treatment can be no more than 20 days. There are side effects from using the product, but it can only be canceled if there is an individual intolerance to individual components. In the first days of taking Vilozen drops, you may experience slight weakness and dizziness.
The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with bronchial asthma. Severe broncho-obstructive syndrome or the presence of an acute bacterial infection are a contraindication to the use of Vilozen drops.
Antibodies and immunological memory
The immune response is divided into primary and secondary. The primary response occurs during the first contact with the antigen, after which the body produces mostly IgM immunoglobulins, which are then replaced by more specific and stable IgG antibodies.
A secondary immune response occurs upon repeated exposure to the same antigen. It is more intense than the primary one, the concentration of antibodies reaches higher levels than the first time.
This effect is due to immunological memory and the presence of memory in B lymphocytes. These cells live in the body for years, and when they come into contact with an antigen, they begin to divide very intensively and produce specific antibodies.
What tests are there?
There are two types of tests for immunoglobulins M and G - “fast” and “slow”. The first include rapid tests that provide results in 10 minutes, while the second has a turnaround time of 1-2 days or more, depending on the laboratory.
The sensitivity and specificity of rapid tests is close to 90%, so they are considered quite accurate and can detect antibodies specifically to Covid-19. However, in the absence of immunoglobulins, that is, with a negative result, there is no absolute guarantee that the person is healthy. There may be no antibodies if five days have not passed since the infection. To confirm the diagnosis, coronavirus is determined by PCR in nasopharyngeal swabs.
The most reliable information can be obtained by taking the test twice. The first time is when you first see a doctor, the second time is 2 weeks later. If the level of antibodies during the second test is at least doubled, then we can confidently speak about coronavirus infection.
How to determine the amount of antibodies
Antibodies make up 12% to 18% of whey proteins. To estimate the amount of individual protein fractions, a so-called proteinogram is compiled in the laboratory.
An antibody test, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent agglutination (ELISA) method, is usually carried out with venous blood (allows you to determine the amount of immunoglobulins of the IgM, IgG, IgE, IgA classes). In addition, the amount of IgA class antibodies can be determined by biochemical examination of a person’s saliva or feces - the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. In some situations, the test may be performed using other material, such as cerebrospinal fluid.
If a critical increase in certain immunoglobulins is diagnosed in the patient’s blood, they speak of hypergammaglobulinemia. As a rule, in such patients, IgM antibodies are excessively increased, while the rest remain deficient.
Against the background of a pathological increase in certain antibodies, various diseases can develop, including:
- acute and chronic inflammation;
- parasitic, bacterial, viral or fungal diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- sarcoidosis;
- AIDS.
A pathologically low amount of antibodies in the serum may occur against the background of:
- congenital genetic disorders;
- taking certain drugs, including antimalarials, cytostatics, glucocorticoids;
- malnutrition;
- infections, including HIV;
- oncological diseases;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- extensive burns;
- severe diarrhea.
Where to take it
You can be tested for immunoglobulins in commercial clinics, for example Hemotest, Invitro, Medsi, Helix. To do this, you need to call the single telephone number of the selected laboratory and find out the location of the nearest center. Mass production of test systems from the State Scientific Virology Center Vector is also planned. The cost of research ranges from 600 to 1900 rubles.
Taking biomaterial takes only a few seconds, the entire procedure from registration to checking the correctness of personal data on the tube lasts no more than 10 minutes.
Express tests are usually panels with two indentations. A drop of blood is dropped from the patient’s finger into one of them, and the result is displayed in the other.
To answer the question about the presence of antibodies, look at the number of stripes in the window:
- one – there are no immunoglobulins;
- two – the disease is in the acute phase;
- three – the person recovers, the body has overcome the infection.
Rapid tests can be performed outside the laboratory - during doctor's appointments, at the airport and at home. For a more complete examination, venous blood is taken and the sample is examined using the ELISA method: labeled antigens are added to the sample, which, when bound to antibodies, change its shade.
To establish the rate of formation of immunoglobulins, the blood serum is diluted with saline, and drops of the resulting liquid are placed in containers with the reagent. Then the concentration is adjusted by further dilution when the reaction is noticeable.
Immunoglobulins and vaccination
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Antibodies play a key role in the development of immunity after vaccination. As a result of contact with the antigen contained in the vaccine, the immune system produces antibodies. First, less persistent and specific IgM, and then more persistent IgG. For example, during vaccination against the hepatitis B virus, the vaccine is administered three times with a certain interval between vaccinations. This allows you to create lasting immunity to the disease. The effectiveness of such vaccination is determined by changes in the amount of IgG antibodies in the body.
Who are immunomodulators really indicated for?
Strong drugs that stimulate the immune system are prescribed to people with serious health problems. There are a number of diseases in which the body cannot cope with simple infections on its own. This is primarily HIV. In order for a person to feel normal and not be in danger at the slightest hypothermia, he needs to support his body with expensive medications.
Improper functioning of the immune system can also occur in babies who were born prematurely. In order for the child to be able to breathe independently and develop normally, he is prescribed immunomodulators. The list of drugs that can be prescribed to newborns is not too long. All medications in this series are quite expensive.
"Leakadin"
A medication that is used as part of complex therapy for cancer in adults. In pharmacies, the product is presented in the form of a solution for injection. In case of cancer, immunomodulators must be used. Your doctor will tell you the names of drugs that can replace Leakadin. Medicines of this type not only have an immunostimulating effect, but also stop the growth of malignant tumors.
Before use, Leakadin is diluted with isotonic sodium chloride solution. The patient is given an injection once a day for two weeks. If necessary, the course is repeated after a month. Immunomodulators (drugs) have a number of side effects. Reviews show that Leakadin solution can cause a decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, and headache.
"Immunal"
The drug contains echinacea juice, which stimulates bone marrow hematopoiesis. As a result of taking Immunal, the number of leukocytes in the blood almost doubles. In addition, the drug has an antiviral effect. It is prescribed in combination with other medications for the treatment of herpes and respiratory diseases.
immunomodulators are most often used for
and influenza during seasonal temperature changes. Immunal is not prescribed to children under one year of age. During exacerbation of epidemics, the drug is taken once a day. For adults, 20 drops of solution are enough. For children, the dosage is determined by age. For children under 6 years old, 5-10 drops are enough. For colds, the drug "Immunal" can be taken up to three times a day. The course of treatment should not exceed 8 weeks. To preventively strengthen the immune system, it will be enough to take the drug for a week.
The “Immunal” product has virtually no side effects. In rare cases, hypersensitivity to certain elements of the drug occurs. During long-term storage, Immunal drops may become cloudy. There is no point in throwing them away. You just need to shake the bottle a few times and the contents will return to their previous state.
Analogs
As an alternative means to stimulate immune defense in young and middle-aged children, other drugs are used. They are also prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. Analogues of Immunoglobulin are:
- Endobulin;
- Gabriglobin;
- Intratect;
- Pentaglobin;
- Intraglobin;
- Immunovenin;
- Gamunex.
All medications are designed to increase the immune defense of the child’s body. However, priority can be given to a particular drug only after receiving the results of the immunogram and assessing the accompanying indications.
Rating: 4.8, Votes: 11
Immunostimulants of natural origin
It is not always useful to use immunomodulators. The list of drugs is quite large. Moreover, all medications are intended to treat serious diseases. How then to strengthen the immune system during seasonal temperature changes? There are a huge number of products that stimulate the body's protective functions.
If it is not possible to avoid a cold, fermented milk products and honey should be added to drug treatment. Interferon preparations and immunomodulators of natural origin are perfectly combined. Additionally, you can strengthen your immune system with echinacea tincture. You can buy it at the pharmacy.