Venofer
IV, IV drip and by introducing the drug into the venous section of the dialysis system. Not intended for intramuscular administration. It is unacceptable to administer the full therapeutic dose of the drug at once.
Before opening the ampoule of the drug, it is necessary to inspect for the presence of sediment and damage; only a clear brown solution can be used. The drug, diluted with a 0.9% NaCl solution, should be used within 12 hours when stored at a temperature of 4 to 25 degrees C in daylight.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to administer a test dose in the same way as it is intended to be used during treatment: (1-2.5 ml = 20-50 mg Fe) for adults and children weighing more than 14 kg, and half the daily dose (1.5 mg Fe/kg ) children weighing less than 14 kg. If no adverse events develop within at least 15 minutes of observation, the remainder of the treatment dose can be administered.
Drip administration of the drug: it is preferable to administer by drip infusion in order to reduce the risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and the risk of the solution entering the perivenous space. Immediately before infusion, the drug must be diluted with a 0.9% NaCl solution in a ratio of 1:20 (for example, 1 ml - 20 mg Fe in 20 ml of a 0.9% NaCl solution). The resulting solution is administered at the following speed: 100 ml - no less than 15 minutes; 200 ml - within 30 minutes; 300 ml - within 1.5 hours; 400 ml - within 2.5 hours; 500 ml - within 3.5 hours.
Jet administration: it is also possible to administer it in the form of an undiluted solution slowly intravenously, at a rate of no more than 1 ml/min (20 mg Fe/min). The maximum volume of the drug should not exceed 10 ml. After administration, the patient is recommended to fix his arm in an extended position for a while.
Introduction into the dialysis system: it is possible to administer directly into the venous portion of the dialysis system, strictly following the rules described for intravenous injection.
Calculation of the dose of the drug: the dose is calculated individually in accordance with the general deficiency of Fe in the body according to the formula:
Total Fe deficiency (mg) = body weight (kg) x (normal Hb - patient’s Hb (g/l) x 0.24 + deposited Fe (mg)
For patients with body weight less than 35 kg and normal Hb = 130 g/l, the amount of deposited Fe = 15 mg/kg body weight.
For patients with body weight more than 35 kg and normal Hb = 150 g/l, the amount of deposited Fe = 500 mg
Coefficient 0.24 = 0.0034 x 0.07 x 1000 (Fe concentration in Hb - 0.34%; blood volume - 7% of body weight; coefficient 1000 - conversion of g to mg).
In cases where the total therapeutic dose of the drug exceeds the maximum permissible single dose, split administration of the drug is recommended.
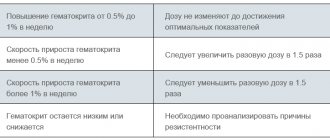
If 1-2 weeks after the start of treatment with the drug there is no improvement in hematological parameters, it is necessary to reconsider the initial diagnosis.
Calculation of the dose to replenish Fe content after blood loss: the dose required to compensate for Fe deficiency is calculated using the following formula:
Amount of Fe needed to be replenished (mg) = units of blood lost x 200
or
Required volume of drug (ml) = number of units of blood lost x 10 (1 unit of blood = 400 ml with an Hb value of 150 g/l; IV administration of 200 mg Fe (10 ml) leads to the same increase in Hb as a transfusion of 1 unit blood).
When Hb decreases: it is necessary to use the previous formula, provided that the Fe depot does not need to be replenished.
The amount of Fe that needs to be replenished (mg) = body weight (kg) x 0.24 x (normal Hb - patient’s Hb (g/l).
Standard dosage of the drug: adults and elderly patients - 5-10 ml (100-200 mg Fe) 1-3 times a week, depending on the Hb level.
Children: There are only limited data on the use of the drug in children. If necessary, it is recommended to administer no more than 0.15 ml/kg body weight (3 mg Fe/kg) 1-3 times a week, depending on the Hb level.
Maximum single dose: adults and elderly patients (for jet administration) - 10 ml (200 mg Fe), duration of administration of at least 10 minutes. For drip administration: depending on the indications, a single dose (administered once a week) can be increased to 0.35 ml/kg body weight (7 mg Fe/kg), but it should not exceed 500 mg Fe.
In general, larger doses of the drug are associated with a higher incidence of adverse events.
special instructions
The drug can only be taken by patients who have been diagnosed in accordance with test results.
You should not use expired ampoules if the medicine has precipitated, become cloudy, or the ampoule is damaged.
Due to the high risk of developing anaphylactoid reactions in patients with polyvalent allergies , folic acid , bronchial asthma and eczema , this group of patients should be treated with Venofer injections with caution.
It is recommended to observe the dosage and rate of administration of the drug in order to avoid a strong decrease in blood pressure in patients or increased side effects.
"Ferinject"
The drug Ferinject is a drug that quickly replenishes the deficiency of this element, rarely causing hypersensitivity reactions characteristic of medications that contain dextran. This product provides a gradual release of iron, which reduces the likelihood of toxic effects.
The dosage form of the iron preparation for intravenous administration “Ferinject” is a solution that is an opaque dark brown liquid. The solutions are poured into transparent glass bottles, which are packed in cardboard boxes. The medication contains the active element - iron carboxymaltose - and auxiliary components: sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, water for injection.
Side effects
Venofer is usually well tolerated by patients. In rare cases, unwanted side effects may occur:
- from the musculoskeletal system - swelling of the joints, arthralgia and myalgia, pain in the back and limbs;
- on the part of the cardiovascular system - increased heartbeat, tachycardia, feeling of heat, flushing of the face, marked decrease in blood pressure, up to a collaptoid state;
- from the nervous system - paresthesia, dizziness and headache, loss of consciousness;
- from the respiratory system - shortness of breath, bronchospasm;
- from the digestive system - abdominal pain, epigastric pain, changes in taste, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- dermatological reactions - itching, rash, erythema, pigmentation disorders, increased sweating;
- allergic reactions – anaphylactoid reactions, swelling of the face/larynx;
- general reactions - pain and heaviness in the chest, asthenia, weakness, pallor of the skin, chills and fever, peripheral edema;
- local reactions - swelling, pain in the area of injection/infusion.
In case of an overdose of the drug due to acute overload, hemosiderosis develops. To eliminate the symptoms of poisoning, symptomatic therapy is carried out. If necessary, iron-binding drugs (deferoxamine intravenously) are prescribed.
Active ingredient
The active component of the iron preparation for intravenous administration for anemia “Ferinject” is ferric iron. The drug is a complex consisting of a carbohydrate ligand and a polynuclear iron-hydroxide core. Due to the stability of the complex, only a small amount of bound iron, also called free or labile, is released. The purpose of creating such a complex is to provide a source of utilized element for proteins that transport and deposit iron.
Based on the results of medical studies, it was determined that the hematological response and filling of the iron depot occurs faster as a result of intravenous administration of the solution than with oral administration of analogue medications.
Ferinject, an intravenous iron preparation, is used to treat iron deficiency anemia, when the use of oral iron medications may be ineffective or for certain reasons impossible. Before using the drug parenterally, it is necessary to confirm anemia by laboratory tests.
Venofer price
You can buy Venofer in Moscow for 2972 rubles for 5 ampoules.
The average price of Venofer is about 1900-2500 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Venofer solution for intravenous administration 20 mg/ml bottle 5 ml 5pcs AI Di Ti Biologica GmbH/BIPSO GmbH
RUR 4,310 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Venofer (IV solution 20 mg/ml 5 ml bottle No. 5) Vifor
RUR 3,944 order
- Venofer (IV solution 20 mg/ml 5 ml bottle No. 5) Vifor/IDT Biology
RUR 3,954 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Venofer 20 mg/ml 5 ml No. 5 Vifor International Inc., Switzerland
1201 UAH order
show more
What is the shortage like?
Deficiency of this element can be absolute and functional. The latter develops when its adequate content in the body is insufficient, but against the background of an increase in the bone marrow's need for it when erythropoiesis is stimulated.
Hepcidin, which is a hormone produced in the liver, plays a special role in metabolism. It comes into contact with ferroportin (a protein that transports iron) and inhibits the absorption of this element in the intestine. An increase in hepcidin levels, which is observed during inflammatory processes, is considered the main cause of anemia. In addition, the concentration of hepcidin increases in chronic kidney disease and affects the development of nephrogenic anemia, as well as susceptibility to erythropoiesis stimulants. Under the influence of erythroepoetin, with increased erythropoiesis, the rate of iron mobilization becomes insufficient to meet the increased need of the bone marrow. Proliferating erythroblasts require increasing amounts of the element, which causes depletion of the labile iron pool and a decrease in ferritin levels. It takes a certain time to dissolve and mobilize it from hemosiderin. As a result, the amount of the element entering the bone marrow decreases, which contributes to the development of its deficiency.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of this medication are: non-iron deficiency anemia, impaired utilization of the element, its excess, age under 14 years, high sensitivity. The medication is used with caution for liver failure, bronchial asthma, infectious diseases (risk of suppression of erythropoiesis), eczema, and atopic dermatitis. To avoid iron overload, careful monitoring of its concentration in the blood is necessary.
What other iron preparation for intravenous administration do doctors prescribe?
Eliminating shortages
Regardless of the underlying causes of iron deficiency anemia, the main way to treat it is to eliminate the deficiency. For these purposes, intravenous iron preparations are most often used. Although oral medications are more convenient, they have a slower effect, may be ineffective if absorption is impaired, and often provoke adverse reactions from the digestive system (in 10-40% of patients). Accordingly, the use of iron preparations for intravenous administration for anemia is advisable in cases where it is necessary to quickly achieve the desired effect (for example, in severe pathology, especially in people suffering from heart disease or undergoing chemotherapy), as well as in cases of poor tolerability of medications for oral use or their ineffectiveness (chronic iron loss, malabsorption syndrome). In addition, intravenous methods of administering iron are considered the methods of choice for therapy with medications that stimulate erythropoiesis in patients with chronic kidney disease, inflammatory bowel pathologies, and malignant tumors.
Some medications based on this element can be used intramuscularly, but such injections are very painful and cause discoloration of the skin.
So, which intravenous iron supplements are most effective?
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacodynamics. Venofer belongs to the group of iron preparations and is used in the treatment of iron deficiency conditions.
Pharmacokinetics. 10 minutes after intravenous administration of Venofer, the maximum plasma concentration of iron is reached. The half-life is 6 hours. During the first four hours, less than 5% of iron is excreted by the kidneys. Within 24 hours, about 75% of sucrose is eliminated, iron is completely eliminated.