Vero-Amlodipine is a drug (tablets) that corresponds to the group of calcium channel blockers. The instructions for use highlight the following features of the drug:
How to dissolve vascular plaques, normalize blood circulation, blood pressure and forget the way to the pharmacy
- Sold only with a doctor's prescription
- During pregnancy: with caution
- When breastfeeding: contraindicated
- In childhood: contraindicated
- For liver dysfunction: with caution
- If renal function is impaired: with caution
- In old age: possible
Release form and composition
The drug is available in the form of tablets: flat-cylindrical, white or almost white with a light creamy tint, sometimes with slight marbling (10 pieces in blisters, 1 or 3 blisters in a cardboard package; 10 pieces or 30 pieces in polymer jars, in a cardboard package 1 jar and instructions for use of Vero-Amlodipine).
Composition per tablet:
- active ingredient: amlodipine (in the form of amlodipine besylate) – 5 mg or 10 mg;
- auxiliary components: potato starch, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, calcium phosphate dihydrate, colloidal silicon dioxide, Primogel.
Cost and similar means
You can only find out how much Vero-Amlodipine costs at the pharmacy. As a rule, its price depends on the number of tablets in the package and dosage. 10 mg of the drug costs about 57 rubles, and 5 mg costs 30 rubles.
As for analogues, the product in question has quite a lot of them. According to experts, the following medications have antihypertensive properties: “Agen”, “Acridipine”, “Adipin”, “Amlo”, “Amlodipine Sandoz”, “Amlodipine”, “Amlodipine-Teva”, “Amlodak”, “Amlovas”, “Amlodigamma” ", "Amlodipine Alkaloid", "Amlodil", "Amlodipine Zentiva", "Amlodipine-Agio", "Amlodipine Cardio", "Amlodipine besilate", "Amlocard-Sanovel", "Amlodipharm", "Amlong", "Amlorus", “Amlotop”, “Amlonorm”, “Kalchek”, “Karmagip”, “Cardilopin”, “Corvadil”, “Norvadin”, “Cordi Cor”, “Norvask”, “Omelar Cardio”, “Normodipin”, “Stamlo”, "Stamlo M", "Stamlo M", "Tenox".
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
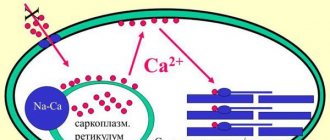
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine derivative and belongs to BMCC (slow calcium channel blockers). It blocks type L calcium channels and reduces the flow of calcium ions through the membrane into the cell (mainly into smooth muscle cells of blood vessels, to a lesser extent into cardiomyocytes).
Vero-Amlodipine has a hypotensive and antianginal effect. Reduces the severity of ischemia of the heart muscle.
The antianginal effect of amlodipine is due to the expansion of peripheral and coronary arterioles and arteries. Due to the expansion of peripheral arterioles, TPVR (total peripheral vascular resistance) decreases and the afterload on the heart decreases, this helps reduce the oxygen demand of the heart muscle. Due to the dilation of coronary arterioles and arteries in ischemic and unchanged areas of the myocardium, the flow of oxygen to the heart muscle increases, especially in patients with Prinzmetal vasospastic angina, and spasm of the coronary arteries (particularly caused by smoking) is prevented. For angina pectoris, a single daily dose of the drug allows you to increase the time of physical exercise, delays the onset of ischemic depression of the ST segment and the development of an angina attack during exercise, and also reduces the frequency of attacks and the number of nitroglycerin doses.
Vero-Amlodipine has a long-term dose-dependent hypotensive effect due to the direct vasodilating effect of the drug on vascular smooth muscle fibers. For high blood pressure, a single dose of the drug provides a decrease in blood pressure (blood pressure) for 24 hours (both with the patient lying down and standing).
Amlodipine lowers blood pressure smoothly; it does not cause a sharp drop in left ventricular ejection fraction and exercise tolerance. The drug has cardioprotective properties against ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease), and also reduces left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy. It does not affect the conductivity and contractility of the heart muscle, does not cause a reflex increase in heart rate (heart rate); slows down platelet aggregation; has a weak natriuretic effect, increases the glomerular filtration rate. In patients with diabetic nephropathy, it does not increase the severity of microalbuminuria.
For cardiovascular diseases (including atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and coronary atherosclerosis with damage to 1–3 or more vessels) in patients who have undergone percutaneous TLP (transluminal plastic surgery) and myocardial infarction, as well as in patients with angina pectoris, the use of Vero-Amlodipine reduces the risk death from stroke, myocardial infarction, CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting) and TLP; prevents thickening of the intima-media complex of the carotid arteries; allows to reduce the number of hospitalizations due to the progression of CHF (chronic heart failure) and unstable angina; reduces the frequency of surgical interventions to restore coronary blood flow.
Amlodipine does not increase the likelihood of complications or deaths in patients with CHF (functional classes III and IV) during treatment with diuretics, ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme) and digoxin. In case of non-ischemic CHF, there is a risk of pulmonary edema while using the drug.
Vero-Amlodipine does not have a negative effect on plasma lipid concentrations and metabolism.
The effect occurs within 2–4 hours of taking the tablets and continues for 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, amlodipine is well absorbed (about 90% of the dose taken is absorbed). The absolute bioavailability of the product is 64–80%. Food intake does not affect the absorption of Vero-Amlodipine. In blood plasma, the maximum concentration of the active substance is reached after 6–9 hours. About 97% of amlodipine binds to plasma proteins. The average volume of distribution is 21 l/kg. The drug passes through the blood-brain barrier. After 7–8 days of treatment, equilibrium concentrations are achieved.
Metabolism occurs in the liver. The resulting metabolites are inactive. The half-life averages 35–50 hours. This allows amlodipine to be taken once a day. Total clearance from plasma is 500 ml/min. The half-life of the drug in patients with arterial hypertension is 48 hours, in patients with liver failure - up to 60 hours, and in elderly people - up to 65 hours. Similar parameters for lengthening the half-life are observed in patients with CHF. In patients with impaired renal function, no significant changes in pharmacokinetics are observed.
Approximately 60% of amlodipine taken is excreted by the kidneys in the form of inactive metabolites, another 10% is excreted unchanged. The drug is excreted through the intestines and bile in the form of metabolites (about 20–25%). During hemodialysis, amlodipine is not removed from the systemic circulation.
Patient reviews
The drug is prescribed for long-term therapy in cases of persistent arterial hypertension, angina pain, and chronic heart failure; antihypertensive and anti-ischemic drugs must be taken for life. Patient reviews of the drug Vero Amlodipine:
- A 65-year-old man suffering from dilated cardiomyopathy and obstructive pulmonary disease takes Vero-Amlodipine 2.5 mg for two weeks. He notes a significant improvement in his condition, the threshold for physical activity has increased, attacks of shortness of breath have decreased, and he is not bothered by dizziness.
- A 50-year-old woman with stage II hypertension and concomitant type 2 diabetes was prescribed Vero-Amlodipine at a dosage of 5 mg. For the first 3 days she felt unwell, then the pathological symptoms disappeared and her blood pressure returned to normal. The blood glucose level measured at home with a glucometer is 5.9 mmol/l.
Tolerability of the drug is strictly individual and requires personal selection of the dose, taking into account the concomitant illness.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- unstable angina (except Prinzmetal's angina);
- pronounced decrease in blood pressure (with systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg);
- children and adolescents under 18 years of age;
- hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary ingredients of the drug, as well as other drugs from the group of dihydropyridine derivatives.
Relative (Vero-Amlodipine is used with caution):
- mitral and aortic stenosis;
- CHF of non-ischemic origin (III–IV functional classes);
- sick sinus syndrome (tachycardia and/or severe bradycardia);
- acute myocardial infarction (as well as a period within one month after it);
- low blood pressure (hypotension);
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
- impaired renal and/or liver function;
- elderly age.
Consumer reviews and messages from doctors
With age, arterial hypertension affects more and more people. This disease is characterized by severe headaches, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, weakness, excessive fatigue, etc. As a rule, all of these symptoms disappear within a few hours after taking the medication in question.
Doctors say that the drug "Vero-Amlodipine" is one of the most effective and fast-acting remedies. In a short period of time, it normalizes blood pressure, significantly improving the patient's condition.
Among the advantages of this medicine, many note its convenient form and method of application. To reduce high blood pressure you only need to take one tablet a day. At the same time, experts warn that exceeding their recommended doses may lead to adverse reactions. Therefore, you should not take more than 10 mg of the drug per day.
It should also be noted that many patients are pleased with the low cost of the mentioned product, its availability and the ability to replace it with analogues from other manufacturers.
Vero-Amlodipine: instructions for use (dosage and method)
Vero-Amlodipine tablets are taken orally with water.
The initial dose of the drug is 5 mg once a day. In the future, the daily dose can be increased to 10 mg once a day.
When used simultaneously with ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers and thiazide diuretics, no dose adjustment of amlodipine is required.
In elderly patients, patients with impaired liver function and/or renal failure, Vero-Amlodipine is used in normal doses.
Kinetic parameters
What kinetic properties are characteristic of Vero-Amlodipine tablets? The instructions for use indicate that when the medicine is taken orally, it is slowly but almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
The peak concentration of this drug in the blood is reached within 8-9 hours. Plasma protein binding is about 97-98%.
The drug in question undergoes minimal metabolism, forming derivatives with insignificant pharmacological activity. This happens during the first passage through the liver.
The average half-life of the drug is 35 hours. In case of arterial hypertension, this period can increase to 48 hours, in elderly people - up to 65 hours, and in case of impaired liver function - up to 60 hours.
This medication is excreted mainly in the form of metabolites through the kidneys (about 58-62%) and through the intestines (about 20-27%).
Side effects
- gastrointestinal tract: often – abdominal pain, nausea; uncommon – dry mouth, anorexia, vomiting, thirst, dyspeptic disorders, diarrhea or constipation, flatulence; rarely – increased appetite, gum hyperplasia; very rarely - hepatitis, pancreatitis, jaundice (usually cholestatic), gastritis, increased activity of liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia;
- cardiovascular system: often – palpitations, swelling of the ankles and feet; uncommon – vasculitis, orthostatic hypotension, marked decrease in blood pressure; rarely – worsening of existing or newly developing heart failure; very rarely - ventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, atrial flutter, chest pain, myocardial infarction, migraine;
- respiratory system: infrequently – rhinitis, dyspnea; very rarely – cough;
- central and peripheral nervous system: often - drowsiness, headache, feeling of heat, dizziness, feeling of flushing, increased fatigue; uncommon – insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, malaise, tremor, asthenia, emotional lability, fainting, unusual dreams, paresthesia, depression, hypoesthesia, peripheral neuropathy; rarely – apathy, anxiety, convulsions; very rarely - amnesia, impaired accuracy and coordination of movements;
- musculoskeletal system: uncommon – muscle cramps, arthrosis, muscle and joint pain, back pain; rarely - myasthenia gravis;
- genitourinary system: infrequently - painful urination, impotence, frequent urination, predominance of nighttime diuresis over daytime; very rarely - polyuria, dysuria;
- hematopoietic system: very rarely - decrease in the number of platelets and leukocytes in the peripheral blood, thrombocytopenic purpura;
- allergic reactions: uncommon – skin rash, itching; very rarely - urticaria, Quincke's edema, erythema multiforme;
- other reactions: infrequently - ringing in the ears, blurred vision (including double vision), distortion of taste perception, conjunctivitis, dry cornea and conjunctiva of the eye, impaired accommodation, eye pain, nosebleeds, baldness, hyperhidrosis, chills, decreased or weight gain, gynecomastia; rarely - impaired skin pigmentation, dry skin, cold sweat, distorted sense of smell, hyperglycemia.
Indications for use: what is the drug used for?
Amlodipine reduces the severity of moderate hypertension in patients by 10%. Because amlodipine dilates the blood vessels that supply oxygen to the heart, the drug also helps with angina.
Pharmacodynamics of Amlodipine
When it comes to preventing heart attacks, other drugs such as beta blockers and ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) are superior to amlodipine. Compared with these two groups of drugs, treatment with amlodipine may increase the risk of heart attack and myocardial failure. Because of this, amlodipine is often prescribed as an adjunct rather than the primary medication if blood pressure cannot be sufficiently lowered by treatment with beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
Overdose
In case of an overdose of Vero-Amlodipine, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is observed, sometimes accompanied by the further development of excessive peripheral vasodilation and reflex tachycardia (with the risk of shock and death).
In the first 2 hours after an overdose of amlodipine, the patient should have his stomach washed and given activated charcoal, and then placed in a horizontal position with his legs raised up.
Therapy is aimed at maintaining the functioning of the cardiovascular system. It is necessary to control the BCC (circulating blood volume) and diuresis, monitor lung and heart parameters. The patient is administered vasoconstrictors, which restore the tone of blood vessels, and calcium gluconate, which eliminates the effects of calcium channel blockade. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Analogs
Analogs of Vero Amlodipine are: Amlodac, Norvasc, Amlotop, Tenox. To identify the advantages and disadvantages, it is worth considering some of the analogues.
Amlodac is a calcium channel blocker whose main substance is amlodipine. Available in 5 mg and 10 mg. Relaxes vascular muscle cells and cardiomyocytes. It has a hypotensive and anti-ischemic effect. Prescribed for:
- essential hypertension;
- symptomatic hypertension;
- angina pectoris stable/unstable;
- Prinzmetal's angina;
- dilated cardiomyopathy with signs of heart failure.
Manufacturer: India.
Norvasc is a calcium channel inhibitor, the active ingredient is amlodipine. Tablet form with a dose of 5 mg and 10 mg. Indicated for:
- primary and secondary hypertension;
- documented angina;
Norvasc is contraindicated in cardiogenic shock. Can be prescribed in combination with beta-blockers and diuretics.
Manufacturer: Germany.
special instructions
Vero-Amlodipine does not affect plasma concentrations of glucose, uric acid, potassium, lipids, creatinine, thyroid hormones and urea nitrogen.
Abrupt withdrawal of the drug is not recommended, as it may worsen the course of angina.
During treatment with Vero-Amlodipine, it is necessary to control body weight, as well as regularly visit the dentist (to prevent hyperplasia, soreness and bleeding of the gums).
There are no data on the safety and effectiveness of the drug in patients with hypertensive crisis.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
During therapy, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other activities that require high concentration and quick psychomotor reactions.
Special recommendations for taking pills
What should a patient know before taking the drug in question? According to the instructions, this drug is prescribed with extreme caution for stenosis of the aorta and impaired functioning of the kidneys and liver.
No adjustment of the above dose is required for elderly people.
The drug "Vero-Amlodipine" can be used to treat patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (non-ischemic) accompanied by heart failure (chronic).
There are no clinical data on the use of this medicine in pediatric practice.
Drug interactions
Inducers of microsomal liver enzymes can reduce the plasma concentration of the drug, and microsomal enzyme inhibitors and antiviral agents can increase the concentration of amlodipine in plasma (the risk of side effects increases).
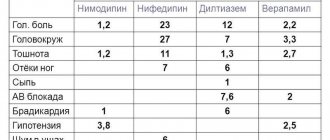
The hypotensive and antianginal effect of Vero-Amlodipine is enhanced by simultaneous use with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, loop and thiazide diuretics, as well as verapamil. Calcium supplements, on the contrary, can reduce the therapeutic effect of amlodipine.
There is no clinically significant interaction with indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Amlodipine does not change the pharmacokinetics of warfarin and digoxin, and cimetidine does not affect the pharmacokinetic parameters of amlodipine.
Lithium preparations enhance the neurotoxicity of BMCC.
Quinidine, amiodarone, antipsychotics, other BMCCs and inhalational anesthetics (for example, isoflurane) may enhance the hypotensive effect of Vero-Amlodipine.
How is Amlodipine Vero different from Amlodipine?
The two drugs contain the same active ingredient. In order to understand how Amlodipine Vero differs from Amlodipine, you need to consider some points:
- The country of origin of Vero-Amlodipine is Russia, the pharmacological representative office of OJSC VEROPHARM. Classic Amlodipine may have different countries of origin, including Russian;
- To highlight their product, pharmaceutical companies add a prefix to the name indicating the manufacturer.
- Manufacturers implement different technological processes, operate different equipment, and use raw materials from different sources - all of which together can affect the final product and the likelihood of side effects.
The choice of medication should be made after consultation with a specialist.