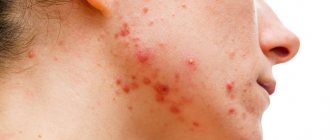
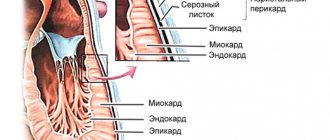
What is balanitis
The skin of the glans penis is very thin and sensitive, so it immediately reacts to any irritant. Accumulating plaque also contributes to inflammation. Tyzon glands in the area of the head and foreskin constantly produce lubricant (smegma), which, with insufficient hygiene, accumulates in the fold at the coronal sulcus. After a certain time, it becomes a breeding ground for bacteria. Predisposing factors for the development of inflammation are a narrowed foreskin, poor hygiene, a tendency to allergic reactions, and indiscriminate unprotected sex.
Isolated balanitis is rare. Usually the inflammation quickly spreads to the foreskin, covering the head (prepuce). This condition is called balanoposthitis. The skin of the prepuce becomes red, painful, and swollen.
Balanitis can be either relatively harmless or very dangerous. It all depends on the form and type of pathogen. In some cases, it comes to deformation of the head or its amputation.
Causes
Inflammation can be either infectious or non-infectious in nature.
Lack of personal hygiene is considered the main factor provoking the disease. The development of pathology can be caused by microtraumas. It can also be caused by a variety of sexually transmitted diseases: syphilis, gonorrhea, etc.
Balanoposthitis is provoked by various bacteria (cocci), unicellular organisms (Trichomonas), fungi (candidiasis) and viruses (herpes). Favorable conditions for the development of infection are created by decreased immunity.
The disease also develops in older people who suffer from diabetes, as well as in those who suffer from psoriasis.
Classification
According to the nature of the course, balanitis can be acute and chronic. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced, in the second - blurred, appearing from time to time under the influence of provoking factors: sex, hypothermia, visiting a bathhouse. Chronic balanitis can be, for example, allergic, fungal, herpetic - that is, it is supported by a pathogen that the immune system cannot cope with.
Based on the degree of skin damage, simple, erosive and gangrenous forms are distinguished. In the absence of adequate treatment, even simple balanitis sometimes turns into gangrenous.
Urologist, dermatovenerologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin talks about the types of balanitis and balanoposthitis
Classification by pathogen type:
- Infectious: fungal, anaerobic, aerobic.
- Non-infectious: allergic.
- Toxic: appears due to prolonged poisoning of the body with harmful substances.
The primary form of balanitis develops due to the entry of pathogens from the outside, the secondary form - against the background of other diseases, when the pathogen is introduced into the bloodstream.
The generally accepted classification of balanitis and balanoposthitis by origin (etiological factor) is presented in the table below. The first group includes infectious lesions, the second - skin and other non-infectious diseases.
Simple or irritative
The term “simple balanitis” combines a whole group of inflammations: bacterial, mechanical, parasitic, chemical. Their peculiarity is the absence of deep ulcerations on the head.
The cause of mechanical stones can be stones coming out of the urethra due to urolithiasis. They get stuck in the area of the preputial sac and provoke inflammation.
Simple balanitis can occur against the background of other diseases (secondary form): scabies, seborrhea, eczema, syphilis. Inflammation of the head often develops due to pus released from the urethra during trichomoniasis or gonorrhea.
Diabetics develop diabetic balanitis. The reason is the constant irritation of the scalp with urine containing a high concentration of sugar. The causative agent in this case is yeast-like fungi (candida). They can also be infected through sexual contact with a partner suffering from genital candidiasis. This type of balanitis is called balanopostomycosis. Characterized by severe itching, burning of the head, its surface is bright red and shiny.
Urologist Oleg Aleksandrovich Junker on the causes and symptoms of candidal balanitis
Below we will show what balanitis looks like in different forms (all photos are 18+):
- Candidal balanitis in the acute phase - https://prntscr.com/s7tmou.
- Candidiasis of the head - https://prntscr.com/s7tng5.
- A variant of the acute phase of candidal balanitis (inflamed edges of the head of the penis) - https://prntscr.com/s7tnoo.
Inflammation of the head of the penis often develops against the background of STDs, for example, trichomonas or chlamydial balanitis:
- Trichomonas balanitis - https://prntscr.com/s7toc5, https://prntscr.com/s7toip.
- Chlamydial balanitis - https://prntscr.com/s7topx.
Bacterial balanitis is the most common and is not always triggered by sex. The pathogen can be picked up in a public shower, bathhouse, pond, or at home. Bacterial balanitis can develop after oral sex. Klebsiella and streptococcus are often present in the pharynx, which, when they come into contact with the skin of the head and in the urethra, provoke inflammation.
Allergic balanitis occurs when the head comes into contact with medications, lubricants, after consuming certain foods, or due to mechanical irritation. Redness occurs in the same places.
Erosive balanitis
Erosive balanitis is characterized by the formation of ulcers at the site of bursting blisters or plaque-covered spots.
Erosive circular
This is a rather rare form, the causative agent of which is gram-negative bacilli and treponema. Pathogens are found in the mouth and genitals. First, the head becomes covered with round light spots (dead skin), then they are rejected, and in their place there remain pink erosive circles with a white rim. Subsequently, they merge with each other, increasing the affected area.
Erosive circinar
Erosive circinar balanitis occurs against the background of Reiter's syndrome (systemic inflammation of the eyes, joints, and genitals). Inflammation of the head most often develops as a reaction to the invasion of chlamydia. Appears as red spots with terry edging.
Folman's balanitis
Folman's syphilitic balanitis is manifested by multiple spots of erosion, peeling, and suppuration. Develops against the background of primary syphilis without a primary focus (chancre).
Folman's balanitis - https://prntscr.com/s7tpvp, https://prntscr.com/s7tqbf.
Pustular-ulcerative
In the area of the coronary sulcus and on the inner lobe of the foreskin, small dark yellow blisters with purulent contents form. Soon they open, leaving ulcers covered with plaque in their place. As healing occurs, the skin becomes scarred.
Shrinkage of the head (kraurosis)
This is a rare type of lesion that occurs mainly in men after 50 years of age. It is a progressive atrophic process, which can be caused by infections, endocrine pathologies, and mechanical irritation. The head is very itchy, the skin on its surface loses its elasticity, becomes rough, peels and wrinkles. Later, areas of compaction and cracks appear.
Xerotic obliterans (lichen sclerosus)
The inflammatory process in this type of lesion is weakly expressed. Light small spots and tracks appear on the head and prepuce, subsequently the skin wrinkles, the foreskin narrows to the point of phimosis. Possible narrowing of the urethra and difficulty urinating. The pathology can occur at any age, but mainly affects men after 50 years of age. The exact reason is unknown. Among the possible ones: viruses, mechanical irritation, heredity, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, hormonal imbalance.
Xerotic balanitis - https://prntscr.com/s7trcw.
Balanitis Zuna (Zoona)
Round plaques with clear boundaries and a shiny brownish surface form on the head of the penis. They are painless, but look scary. Zoon's balanitis is also called plasma cell balanitis.
Gangrenous
Gangrenous balanitis is provoked by the same pathogens as erosive; it begins in the same way, but proceeds more intensely. Quite deep ulcers appear on the head, covered with a gray coating. Subsequently, they can develop into gangrene of the head. The disease is accompanied by an increase in temperature up to 40˚C, enlarged lymph nodes, headaches, bleeding from the head due to the destruction of blood vessels.
Gangrenous balanitis - https://prntscr.com/s7tstd.
Which doctor should I contact?
Regarding pathological changes on the skin of the head of the penis, contact a urologist, venereologist or dermatologist.
A man’s first reaction when redness or blisters are detected is to treat them with chlorhexidine or Miramistin. There is no need to do this! As medical practice shows, in most cases the symptoms worsen, severe itching appears in the urethra and on the head, redness and swelling increase.
Already at the first consultation, the doctor will take the necessary tests. This can be a culture of biomaterial from the head of the penis, a blood test for sugar, an imprint smear from the glans, a scraping from the urethra, a blood test for allergies (indicative of an increase in immunoglobulin E), analysis of the contents of vesicles and ulcers. To make an accurate diagnosis, a piece of tissue is taken for histological analysis (cell structure is examined).
Scheme for taking scrapings from the urethra
Urological smear result (normal)
Urological smear with pathogenic flora
Complications
If you don’t visit the doctor’s office in time and let everything take its course, the following complications will appear:
- spread of fungal infection to the scrotum;
- inflammatory processes of the foreskin;
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes;
- orchiepididymitis;
- cracks on the head of the penis;
- spread of warts on the skin;
- phimosis (impossibility of exposing the penis);
- inflammatory processes in the seminal vesicles;
- oncology.
Candidiasis can worsen with constant nervous stress; it is important to learn to control your emotional sphere.
Doctors classify balanitis as a precancerous condition of body tissue. Therefore, timely treatment is the only way to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Treatment of balanitis in adults
Redness and itching of the head can be a sign of a number of diseases, including those not related to infection, so you cannot treat yourself . The maximum that is allowed is baths with a decoction of chamomile, sage, and oak bark. They will help soothe itching and irritation before visiting a doctor.
If for some reason it is currently impossible to get to a specialist, then you can try treating the head with Tsindol suspension, Bepanten Plus ointment, Dexpanthenol, or furatsilin solution. If the discomfort is caused by a fungus, then the popular chlorhexidine may not help, but only worsen the situation.
Treatment tactics depend on the diagnosis. If the problem arose against the background of systemic diseases, then first of all it is necessary to put them into remission, and then eliminate the consequences in the form of inflammation of the head.
Table 1. Treatment methods for various types of balanitis
| Type of balanitis | Treatment methods |
| Candida | For 2 weeks, apply one of the creams twice a day: “Clotrimazole 1%”, “Miconazole 2%”, “Econazole 1%”. In case of diabetes mellitus or the impossibility of local therapy, Fluconazole is prescribed in a dosage of 150 mg once. |
| Balanitis Zuna | Local therapy with steroid ointments. If there is no effect, use 2% fusidic acid cream, which is used to treat the head daily for 8-16 weeks. CO2 laser radiation is used as an additional therapy. |
| Xerotic obliterans | Local application of testosterone propionate or corticosteroids. Recently, therapy with penicillin antibiotics, as well as laser surgery, has shown good results. |
| Erosive and gangrenous | Irrigation of the head with hydrogen peroxide, taking increased doses of antibiotics: syntomycin, penicillin, biomycin. |
| Infectious balanitis | A course of antibiotics, according to the results of tests and sensitivity cultures. |
For severe itching, Triderm ointment is prescribed, which relieves symptoms and contains antifungal and antibacterial components. However, many men complain about the addictive effect - in the first days there is an improvement, and then it disappears. It is necessary to further examine and identify the pathogen that supports inflammation.
To combat the symptoms of a simple form of balanitis, ointments “Pimafukort” and “Pimafucin” are also prescribed, which have an antifungal effect. For many men, the effect is the same - the remedy works for the first few days, then the symptoms return.
Pimafucin cream is used to treat fungal diseases of the skin and mucous membranes in men and women. Highly active against all types of fungi of the genus Candida. Price from 321 rubles
Forms
Forms
The main urological classification involves dividing the disease into three forms: acute balanitis, subacute and chronic. Acute pathology lasts no more than one month, subacute - about two months. Chronic balanitis is rare and has frequent relapses. Depending on the clinical picture of the disease, acute balanitis has several forms:
- simple exudative;
- ulcerative-erosive;
- gangrenous or necrotic.
The incubation period of the disease depends on the virulence and pathogenicity of the microflora that caused the infectious process. It can last from several days to one month. After the latent period comes the stage of clinical manifestations.
Treatment of balanitis in a child
In boys, balanitis develops mainly from six months to 5 years. Many babies have physiological phimosis (the foreskin is narrowed and interferes with normal hygiene). As the child grows older, the hormonal levels change, the skin of the prepuce becomes more elastic and, in most cases, stretches by itself. Inflammation of the head begins when a large amount of pathogen accumulates. Usually these are Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus. Against the background of the latter, headaches, fever occur, pus is released from the prepuce, and the inguinal lymph nodes become enlarged.
Acute inflammation is relieved using warm baths with manganese (pink solution). When the crisis has passed, the doctor carefully separates the foreskin from the glans by cutting the adhesions.
Symptoms
Symptoms
Balanitis has nonspecific symptoms of an inflammatory reaction, so the manifestations of the disease cannot be reliably attributed only to the signs of this disease. Symptoms of balanitis develop after the incubation period, when the stage of advanced clinical phenomena begins. The main urological complaints of patients are presented as follows:
- manifestation of discomfort of varying severity in the groin area or perineum;
- the appearance of pathological discharge from under the foreskin or from the urethral canal;
- dysuric syndrome, characterized by impaired urination;
- skin and mucous reactions: hyperemia, swelling, peeling or formation of erosions;
- inguinal lymphadenitis – inflammation of the lymph nodes in the area of the inguinal folds;
- dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse.
The severity of the symptom complex depends on the pathogenic agent that caused the disease and on the characteristics of the individual’s immune reactivity.
What to do if balanitis does not go away
If balanitis continues to progress, then there are two options: the treatment was prescribed incorrectly or there is a complex form of pathology against the background of some systemic disease. Doctors in such cases change treatment tactics.
If balanitis constantly recurs, then it is necessary to eliminate the provoking factors: circumcise the foreskin, adjust the diet, give up alcohol and smoking (toxins can also help maintain inflammation), and engage only in protected sex.
How laser circumcision of the foreskin is performed - says a urologist at the MED CITY clinic
Prevention of balanitis
Measures to prevent balanitis:
- Protected sex, including oral.
- Maintain intimate hygiene: you need to wash your penis daily, retracting the foreskin (the best remedy is baby soap), do not allow the head to come into contact with surfaces in common areas, do not touch it with dirty hands, do not wear unwashed underwear (including new ones) .
- Avoid frequent intense masturbation and sex to avoid mechanical damage to the head.
- All intimate lubricants should be pre-tested for allergies (apply to the inner elbow for 15-20 minutes).
If there is persistent redness of the head, the appearance of blisters, ulcers, lumps, a feeling of itching or numbness, you should immediately contact a urologist.
Reviews of successful treatment
Washing with antiseptic solutions (furacilin, Miramistin, chlorhexidine) and ointments (Levomekol, streptocidal) will help only in cases where it is known for sure that balanitis arose due to mechanical irritation or lack of normal hygiene (rapid proliferation of its own microflora). Below is a review from the forum https://hron-prostatit.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=10990:
If diagnosed correctly, severe inflammation can be successfully treated with antibiotics. Review below:
Reviews about ointments "Triderm", "Pimafukort":
Reviews about the treatment of fungal balanitis: https://zdravotvet.ru/kandidoznyj-balanopostit-kak-lechit-molochnicu-u-muzhchin/:
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis is usually not difficult for an experienced doctor. The presence of appropriate symptoms is sufficient to differentiate the disease from other similar pathologies. The only thing that needs to be found out is the reason that caused the inflammatory process. This is necessary in order to identify the pathogen and determine sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. For laboratory testing, a smear from the urethral secretion is used.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
Herpetic balanitis manifests itself as a characteristic rash in the form of blisters filled with fluid