Atrophic colpitis is a non-specific inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. In most cases, it is observed as a result of a decrease in estrogen levels in a woman’s body, which leads to structural changes in the mucosa (thinning of the epithelial layer of the vagina). That is why this form of the disease more often affects patients whose bodies undergo natural age-related or menopausal changes. Those who undergo artificial menopause (for example, as a result of removal of the ovaries, etc.) also suffer from this type of colpitis. Other causes of the disease include:
- irradiation of the pelvic organs;
- injury to mucous membranes as a result of careless medical manipulations or sexual intercourse;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- medication to suppress ovarian function.
Additional factors predisposing to the formation of such colpitis are wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics, violation of hygiene rules, frequent use of alkaline hygiene products, and a general weakening of the immune system. The latter may be associated with age-related changes, which result in exacerbation of chronic diseases and decreased resistance to infections (ARVI, influenza, herpes virus infection, etc.).
Features of atrophic colpitis
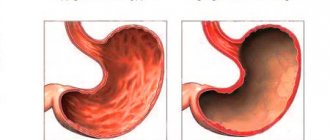
Atrophic colpitis is changes in the vaginal epithelium provoked by structural and functional changes. The consequence of this pathological condition is the thinning of the vaginal epithelium and the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
The development of this pathology is caused by a significant decrease in the content of estrogen in a woman’s body, which can be triggered by physiological reasons. In addition, artificial menopause may occur, during which the production of female sex hormones stops. In medical practice, the disease is often called senile or senile colpitis.
Reviews
Atrophic vaginitis causes a lot of discomfort for many women. Normal functioning is disrupted, as the patient constantly feels pain and swelling of the vaginal mucosa.
Atrophic colpitis reviews from women: symptoms
Constant itching prevents many from even sleeping, and it becomes especially bad after an evening shower. To relieve itching and burning, many people use douching with antiseptics.
Many note that sexual life is also disrupted during the development of this disease. It becomes painful with every sexual intercourse and treatment of intimate areas.
But some patients also note that they learned about the current disease only at an appointment with a gynecologist; they did not feel any pronounced symptoms. Therefore, you need to undergo a routine examination by a specialist every six months to a year.
Causes of atrophic colpitis
The development of atrophic colpitis is based on hypoestrogenism, which can be physiological or artificial. Pathology can occur after the last menstruation or after various manipulations on the ovaries.
In patients of childbearing age, hypoestrogenism can develop for the following reasons:
- After childbirth and especially in women who are breastfeeding. The fact is that after childbirth, the normalization of hormone levels in a woman’s body occurs gradually, and especially for those mothers who are breastfeeding. Against this background, hypoestrogenism persists for a long time and the consequence of this is often atrophic colpitis.
- Hormonal dysfunction of the ovaries. Hormonal imbalance that persists for a long time becomes the cause of persistent hypoestrogenism and the development of pathology.
Atrophic colpitis can be caused by frequent stress and emotional experiences, which are accompanied by disturbances in the level of hormones in a woman’s body. In patients with thyroid diseases and diabetes mellitus, changes in the vaginal epithelium can also be diagnosed.
The following reasons can also cause pathology:
- removal of ovaries;
- radiation treatment of the pelvic organs;
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- HIV infection or AIDS.
In addition, experts identify provoking factors, the impact of which on the female body can lead to atrophy:
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene;
- general chronic pathologies;
- trichomonas, chlamydia and mycoplasma;
- promiscuous and unprotected sexual intercourse;
- wearing tight underwear made of synthetic materials;
- improper and irrational nutrition;
- chronic inflammation of the genitals.
The risk group for the development of atrophic colpitis consists of patients with early menopause and hypothyroidism. Trichomonas or trichomoniasis are common pathogens. A disease such as trichomonas colpitis is accompanied by the development of specific symptoms and requires effective treatment.
Local therapy
This form is characterized by a wave-like increase in the inflammatory reaction. Atrophic colpitis is accompanied by vaginal dryness and itching. These symptoms of the disease often force women to refuse intimacy, since sexual intercourse does not bring pleasure, but pain and discomfort. Disease of the genital organs also affects the functioning of the urinary tract.
Systemic therapy
Systemic therapy involves the use of drugs such as Cliogest, Ovestin, Ortho-ginest, Gynoflor E, Estriol, Climodien, Davina. All of them are sold over-the-counter. Available in various forms, they can be used orally, vaginally or externally (ointments).
Colpitis in women can be caused by opportunistic microorganisms: staphylococci, streptococci, Proteus, E. coli, Trichomonas, chlamydia, Candida fungi and others that enter the body through sexual contact or through the rectum.
Clinical picture of atrophic colpitis
With atrophic colpitis, symptoms can be noticed 5 days after the last menstruation. This pathology is characterized by a sluggish course and the development of a mild clinical picture. Symptoms become more pronounced if a secondary infection occurs and opportunistic microorganisms are activated. This often happens after a gynecological examination, washing or douching, which causes microtrauma to the mucous membrane.
Atrophic colpitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Discomfortable sensations in the vagina. The woman begins to complain of a feeling of vaginal tightness and dryness, as well as the development of pain. If pathogenic microflora is added to the pathology, then additional manifestations such as burning and itching are noted.
- Dyspareunia. With atrophic colpitis, the stratified squamous epithelium becomes very thin and this leads to pain during sexual intercourse. In addition, nerve endings are exposed and the production of special lubricant by the vaginal glands is reduced.
- Vaginal discharge. With atrophic colpitis, moderate discharge is observed, which has a watery consistency. When an infection occurs, the leucorrhoea becomes cheesy or greenish in color, and is accompanied by the appearance of a specific odor. In acute atrophic colpitis, bleeding may appear caused by injuries to the mucous membrane. If discharge mixed with blood appears in a woman during menopause, she should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Frequent urination. With senile vaginitis, thinning of the bladder wall and weakening of the tone of the pelvic muscles are always observed. Such pathological processes are accompanied by frequent urination, but the amount of urine released during the day remains the same. The pelvic muscles are severely weakened, and urinary incontinence occurs when sneezing or coughing.
When examined on a gynecological chair, a pale pink vaginal mucosa is noted, which has many pinpoint hemorrhages. When you touch the mucous membrane with a medical instrument, drops of blood are released. If a secondary infection occurs, swelling of the vagina and its redness, as well as the appearance of purulent discharge, are noted.
Symptoms
Age-related atrophic colpitis (treatment is prescribed only after a diagnostic examination) is quite difficult to detect at the initial stage, since it hardly manifests itself. As the disease progresses, symptoms appear.
The first sign will be an increase in the amount of discharge and a change in its smell. It becomes unpleasant, sometimes a small amount of blood is present in the discharge, which indicates damage to the mucous membrane and the formation of microcracks.
When urinating or performing hygiene procedures, the patient feels a burning sensation of varying degrees of intensity. In advanced stages it is quite strong and long-lasting.
In most women, colpitis is accompanied by a feeling of dryness in the vagina, discomfort and itching in the external genital area. This indicates the progression of the disease, a decrease in the amount of lubrication and disruption of the microflora.
During sexual intercourse, the patient feels discomfort or even severe pain, which also indicates thinning of the epithelium and the formation of multiple areas of damage.
In this case, the sensations persist for quite a long time, even after the end of intimacy. Upon visual examination of the external mucous membranes, swelling and redness are noted. In advanced stages, the color turns from red to burgundy or bluish, which indicates the severity of the condition.
Swelling is observed not only during visual examination of the external genitalia. When examining the vagina using gynecological speculum, such manifestations are almost always present.
At an advanced stage, other symptoms appear. The patient reports increased urination and pain in the lower abdomen. Her general condition is deteriorating, there may be an increase in body temperature and weakness.
With a prolonged course of the disease, a woman’s appetite worsens and her body weight decreases. The patient becomes irritable, performance decreases, and signs of depression appear. General immunity also deteriorates, which can lead to complications.
Methods for diagnosing atrophic colpitis
When the first signs of the disease appear, a woman needs to visit her gynecologist, who will conduct a thorough examination and collect the necessary tests.
The following diagnostic methods are usually used to make a diagnosis:
- A visual examination of the cervix and vulva in a mirror allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and identify purulent deposits on its walls, as well as microcracks and other damage.
- Colposcopy is an examination of the vagina with an optical instrument. If there is an inflammatory process, the cervix becomes red and vulnerable. In addition to assessing the condition of the vagina, the acidity of the vagina is determined.
- Examination of smears under a microscope helps reveal the presence of bacteria, leukocytes and dead epithelial cells.
- An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed to identify the pathological process in the uterine appendages.
In addition to the listed diagnostic procedures, a specialist may prescribe a vaginal scraping test using the PCR method. This study allows us to exclude specific vaginitis. If a sexually transmitted infection is detected in a patient, a consultation with a venereologist will be required.
Diagnostic measures
To make a final diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out. Atrophic colpitis of the menopausal period has symptoms characteristic of other diseases of the reproductive and urinary systems. All manipulations carried out are aimed at eliminating them.
First of all, the patient is subjected to:
- Instrumental examination of the condition of the vaginal wall and mucous membrane of the cervix
- Taking vaginal smears
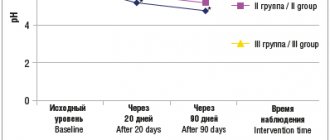
If the smear reveals a high content of leukocytes, then we are talking about inflammation and possible secondary infection. In case of severe inflammation, the patient is referred for tests to determine hidden genital tract infections. In addition to smears, blood and urine are examined. It is also necessary to determine the acidity of the vagina. For this purpose, use a pH test strip.
To determine the spread of the inflammatory process, an ultrasound examination of the reproductive and urinary systems is performed. In advanced cases, the disease can affect the functioning of the muscle tissue of the bladder, which leads to incontinence. During atrophic colpitis, the likelihood of contracting diseases transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse increases.
Features of the treatment of atrophic colpitis
In case of atrophic colpitis, the damaged epithelium is treated first of all and measures are taken to prevent recurrent vaginitis. In most cases, to eliminate age-related disease, patients are selected for hormone replacement therapy, which can be either local or systemic.
The disease can be treated using the following types of suppositories:
- Estriol. The main active ingredient is estriol, and you can purchase the drug at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. With the help of suppositories, it is possible to reduce vaginal itching, eliminate dryness and dyspareunia.
- Ovestin. This medicine is available in the form of tablets, vaginal cream and suppositories. At the beginning of treatment, suppositories are inserted into the vagina every day for 4 weeks, and after the condition improves, the dosage can be reduced to 2 suppositories every 7 days.
- Elvagin. The drug is produced in the form of cream and vaginal suppositories. The main active ingredient is estriol, and treatment involves daily insertion of suppositories into the vagina for 2-3 weeks. After the disappearance of unpleasant symptoms, the dose is reduced to 2 suppositories per week.
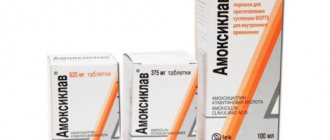
For atrophic colpitis, treatment can be carried out using medications in the form of suppositories, tablets and powders. You can quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms with the help of vaginal suppositories such as Flagyl, Metrovagin, Nystatin and Pimafucin.
When using vaginal tablets, moisten them with a small amount of water before inserting into the vagina. A good effect in the fight against atrophic colpitis is given by drugs such as Trichopolum, Clotrimazole and Ornisid, which are prescribed by the doctor.
For atrophic colpitis, treatment in women is also carried out using vaginal capsules, but they take a long time to dissolve. It is for this reason that they will not be able to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Most often, women are prescribed drugs such as Polygynax and Gyno-dactanol.
When treating pathology, local procedures can be carried out in the form of baths with the addition of various herbal solutions. Plants such as chamomile, sage and pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory preparations have a good effect in combating the disease.
At home, baths help relieve pain and get rid of swelling. In addition, this procedure accelerates the healing of affected epithelial cells of the vaginal mucosa. For a bath, fill a basin with water at a temperature of up to 40 degrees, then pour a decoction of herbs into it. You should sit in the bath until the water has cooled completely.
After such a procedure, suppositories with an antimicrobial effect are introduced into the vagina if a pathogen is identified. At the end of the course of antimicrobial treatment, ointments and suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect, which contain estrogens, are used.
When treating age-related atrophic colpitis, experts recommend douching with the following solutions:
- Furacilin;
- Citeal;
- soda solution.
The medicine must be administered warmly into the vagina, after which you need to lie down for 20 minutes. After half an hour, you are allowed to use other medications and forms. The use of folk remedies is allowed, but only after consultation with a specialist.
Mkb
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it for a long time. The same rule applies to atrophic vaginitis. Women begin to detect it in themselves after the end of the reproductive period.
In the latest revision of diseases, atrophic colpitis is designated according to ICD-10. But since this pathology is divided into 2 types, they are indicated in the document under different codes.
Atrophic colpitis ICD 10
- Postmenopausal colpitis with tissue atrophy. The exact formulation of the diagnosis can be found using code No. 95.2.
- Atrophic colpitis caused by artificially induced menopause. A description of this pathology and recommendations for treating the disease are hidden under code No. 95.3.
Atrophic colpitis ICD code 10
The disease has a code of 95.2, which provides information about the nature of the spread of the disease. The causes, symptoms, basic principles of treatment and prevention of the disease are described here.
The disease is difficult to diagnose and treat, since the cause is a hormonal imbalance in the body. Atrophic colpitis (ICD 10 code No. 95.2 and No. 95.3) must be carried out through differential diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis is necessary to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. It is carried out by a specialist who determines which pathological organism led to the pathology. Comparisons are made with candidomycosis and various infections that are sexually transmitted. If the latter are detected, even in small quantities, consultation with a venereologist is required.
Atrophic colpitis according to ICD-10
The international document defines the goals of treatment as measures aimed at rehabilitation, restoration of stratified epithelium, and reducing the number of relapses. Since this type of disease very often becomes chronic, it is important to identify the pathology in time and treat it correctly.
The document states that any therapy takes place on an outpatient basis; there are no indications for hospitalization. This disease cannot be treated using traditional medicine recipes; there are no herbs or solutions that could replace estrogens for a woman. Hormonal agents must be used. Chamomile infusions can be used to relieve inflammation. But they will not in any way affect the structure of the cell or the causes of pathology.
Lifestyle during treatment of atrophic colpitis
It is necessary to remember that it is necessary to complete the course of treatment to the end, which will avoid a recurrence of the chronic course of the disease.
During treatment, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse and check your partner for the presence of an inflammatory process. In addition, you should avoid hypothermia, monitor your diet and minimize bad habits. During the treatment period, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes and lactobacilli for the intestines, as well as sedatives.
The duration of therapy is determined by the form of colpitis, its neglect and the age of the patient. The prognosis for atrophic colpitis is quite favorable. At the same time, frequent relapses are possible, which negatively affect a woman’s usual lifestyle.
Video: About colpitis, cervicitis - Dr. Elena Berezovskaya
About colpitis, cervicitis, etc. —Dr. Elena Berezovskaya
Video: colpitis.
Colpitis. Gynecologist Kyiv. Cervical Pathology Center
Video: what does colpitis lead to?
What does colpitis lead to?
Video: treatment of colpitis, cervicitis and erosions with natural suppositories
Treatment of colpitis, cervicitis and erosions with natural suppositories
Forms of the disease
Atrophic colpitis can occur in two forms - acute and chronic. The age-related type of the disease is most often chronic, so treatment is long and complex.
Acute colpitis occurs with severe symptoms, is often complicated and greatly worsens the woman’s general condition. All signs worsen over several days, and complications appear within a week. At the same time, all the classic manifestations of the disease are present in the clinical picture.
The chronic type of the disease develops much more often . The symptoms are mild, which is dangerous, since the woman does not notice the worsening of the condition.
Itching and dryness of the vagina are present, the burning sensation when urinating is slight. Often the patient considers the symptoms to be a sign of diseases of the bladder or urethra. For any form of the disease, a full diagnostic examination is required to identify the cause and degree of neglect of the condition.