Hemoptysis is a manifestation of respiratory tract pathology, which is the release of blood during coughing. Spit may consist of blood alone, but more often it is contained in sputum in the form of streaks and clots. Hemoptysis often precedes bleeding from the lungs. This potentially dangerous disorder can be fatal and requires a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation. Hemoptysis and pulmonary hemorrhage have similar etiopathogenetic mechanisms. They differ quantitatively: in the first case, less than 50 ml of blood is released per day, and in the second - more than 100 ml. When the patient loses 600-800 ml of blood, life is threatened.
The causes of this symptom are very diverse. These are infectious diseases, heart and blood diseases, parasitosis, breast injuries, oncological pathologies, immunological, vascular and systemic diseases, congenital anomalies. Most often, hemoptysis occurs when the pulmonary and bronchial vessels are damaged. Provoking factors for the disorder are: physical overexertion, insolation, hypo- or hyperthermia. The appearance of this symptom is usually preceded by a persistent cough, a sharp rise in blood pressure, sore throat, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
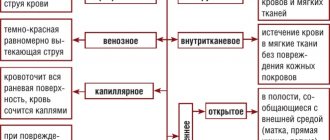
During a coughing attack, the patient discovers bloody traces in the sputum. At the same time, he feels a peculiar smell and salty taste of blood, which colors the bronchopulmonary discharge in various shades of red and gives it a foamy or jelly-like consistency. Scarlet blood, secreted systematically and in large quantities, is a sign of pulmonary hemorrhage. Patients turn pale, panic, feel weak and dizzy. Frequent bouts of hemoptysis lead to anemia.
Hemoptysis can be true or false. In the first case, light and foamy blood is released from damaged vessels of the respiratory tract, and in the second - from the nose, esophagus, stomach, and gums. To determine the specific cause of the disorder, it is necessary to undergo laboratory and instrumental studies - radiographic, tomographic, endoscopic, paraclinical, microbiological. Treatment of hemoptysis is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that led to its occurrence. If a large amount of blood is released, it is necessary to call an ambulance, and until it arrives, remain calm - lie silently on a bed with a high headboard.
Hemoptysis has a code according to ICD 10 - R04.2 “Bloody sputum”.
Causes
Hemoptysis occurs under the influence of many causes - various diseases and exogenous factors. In 20% of cases, the etiology of this disorder is not determined.
Pathological processes manifested by the release of blood when coughing:
- Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system - inflammation of the bronchi, lungs, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, abscess formation of lung tissue, aspergilloma, mycetoma.
- Parasitoses – trichinosis, strongyloidiasis, paragonimiasis, ascariasis, echinococcosis.
- Neoplasms of the respiratory system - benign tumors of the bronchi, lung cancer.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system - congestive cardiovascular failure, narrowing of the left atrioventricular orifice, pulmonary embolism, hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, cardiac asthma.
- Traumatic injuries to the chest and foreign bodies - contusion of the lung and its damage due to wounds, fractured ribs.
- Systemic and autoimmune diseases - Rendu-Osler syndrome, Wegener's granulomatosis, Goodpasture's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa, sarcoidosis.
- Congenital anomalies - cystic fibrosis, hemorrhagic disease, bronchial cyst, hypoplasia of the pulmonary arteries.
- Metabolic disorders - pulmonary amyloidosis, vitamin deficiency C, uremia, cholemia.
- Hematological diseases - thrombocytopenia, leukemia, hemophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis.
- Infectious diseases - whooping cough, measles, hemorrhagic fever, syphilis.
Exogenous factors contributing to the appearance of hemoptysis:
- Occupational hazards - constant inhalation of toxic substances, smoke, gases;
- Excessive insolation;
- Psycho-emotional stress;
- Long-term treatment with anticoagulants that disrupt the blood clotting process;
- Medical procedures – pulmonary artery catheterization, bronchoscopy, percutaneous lung puncture, transbronchial biopsy.
Persons with hemoptysis who are at risk and have an unfavorable prognosis for recovery:
- Elderly and old people,
- Having chronic heart disease in the stage of decompensation,
- Suffering from severe respiratory diseases,
- Having suffered pulmonary hemorrhage,
- In a state of shock.
Respiratory pathologies accompanied by destruction of lung tissue are manifested by bleeding. The walls of the blood vessels located in the lesion are destroyed. Blood from the arteries, veins and capillaries of the bronchopulmonary system flows into the bronchioles and alveoli. The amount of blood loss depends on the caliber of the damaged vessel.
General characteristics of hemoptysis
The causes and mechanisms of development of hemoptysis (hemoptysis) are generally similar to the etiology and pathogenesis of pulmonary hemorrhage (hemoptoea).
The difference between these conditions is mainly quantitative: when coughing up a small amount of blood (less than 50 ml per day), it is customary to talk about hemoptysis, when coughing up a larger volume - about bleeding. The occurrence of hemoptisis may be preceded by a persistent cough, hypertensive crisis, or intercurrent diseases. This symptom can be provoked by active physical activity, thermal and water procedures, for example, steaming in a bathhouse, paraffin therapy, general baths and therapeutic showers. Also, the onset of hemoptysis is often facilitated by meteorological factors: increased atmospheric pressure, cold or hot weather.
Hemoptysis usually begins suddenly. During the next coughing up of sputum, the patient notices traces of blood in it. Some patients note precursors of hemoptysis: tickling (tickling) and gurgling (gurgling) in the throat, chest pain, and sometimes an unpleasant warmth spreading throughout the chest. Due to difficulty breathing, a cough with blood discharge occurs. At the same time, a salty taste of blood in the mouth and its specific smell are felt.
During hemoptysis, blood is released periodically, not with every coughing attack. In some cases, hemoptysis appears as streaks in saliva or sputum, in others as separate spits of scarlet (fresh) or dark (old) blood. If the discharge of scarlet blood is repeated systematically when coughing, it is considered that the patient has begun to have pulmonary hemorrhage. During an episode of hemoptysis, the patient turns pale, looks frightened, feels weak throughout the body, and dizzy. Chronic and recurrent attacks of hemoptysis lead to anemia.
Symptoms
Cough is the main provocateur of hemoptysis. It is a clinical sign of lung, heart, blood, metabolic disorders and autoimmune disorders. But most often, hemoptysis is a manifestation of infectious and oncological diseases of the bronchopulmonary system. Its precursors are: local soreness and unpleasant warmth in the chest, salty taste of sputum in the mouth, anxiety and pallor of patients, and the appearance of blistering rales over the site of the lesion in the lungs. Hemoptysis never occurs during sleep, since coughing wakes the patient. Bloody sputum has various shades of red - pinkish, bright, rusty, brownish. The dark shade of the discharge indicates the breakdown of hemoglobin in the lung tissue. Sputum that looks like raspberry or currant jelly indicates the breakdown of lung tissue due to malignant processes. Pulmonary edema is accompanied by the release of light pink secretion with foam.
- Hemoptysis is not obligatory, but a common sign of tumor processes in the respiratory organs. Bronchopulmonary neoplasia is characterized by compression and destruction of large vascular trunks. Most patients with oncological pathology consult a doctor with a complaint of repeated hemoptysis. It is accompanied by the following symptoms: painful, debilitating, frequent cough, chest discomfort, weight loss, wheezing, nocturnal hyperhidrosis, rapid heartbeat, peripheral cyanosis, tachypnea, fever, hoarseness, dysphagia, muscle weakness, dizziness, arrhythmia.
With tuberculosis of the lungs, hemoptysis occurs in 80% of patients. This is a sign of the fibrocavernous form of infection, in which large cavities form in the lungs. The sputum consists of bloody spittle. The cough is accompanied by burning and soreness in the chest, increased body temperature, hyperhidrosis at night, weight loss, unmotivated dizziness, apathy and lethargy, sleep disturbance, pale skin, flushed cheeks, lack of appetite, shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air, wheezing on auscultation, symptoms of vegetative symptoms -vascular dystonia.- At pneumonia first, intoxication and catarrhal symptoms appear - fever, chills, myalgia and arthralgia, lethargy, loss of strength, hoarseness and sore throat, rhinorrhea. Then a cough appears with copious mucopurulent discharge containing blood inclusions. Sputum in different forms of inflammation has its own characteristics: with pleuropneumonia it is rusty, with influenza infection it is foamy and red. As the underlying pathology progresses, patients develop signs of respiratory failure: shortness of breath, suffocation, cyanosis, hemorrhagic manifestations, confusion.
pneumonia
- With a lung abscess, the blood vessels are damaged, and pus breaks into the lumen of the bronchus. When the patient coughs, purulent sputum is released, which has a foul odor and contains an admixture of blood. Patients complain of chest pain, fever, intoxication and shortness of breath, loss of appetite, headache, exhaustion, excessive sweating, and rapid deterioration in general condition.
manifests itself as a severe hacking cough, which damages the blood vessels. Blood mixes with bronchial secretions and gives sputum its characteristic appearance. Other distinctive signs of bronchial lesions are: difficulty breathing, characteristic wheezing, pain and spasms in the throat, intoxication, and attacks of suffocation.
Bronchitis- Bronchiectasis is a complication of chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract. When the blood vessels supplying the bronchi and lungs are destroyed, streaks of blood appear in the sputum. In the morning it is released in large quantities - “a mouthful”. Patients experience anemia, weight loss, general weakness, pale skin, children are retarded in physical and sexual development. Over time, signs of respiratory failure appear - cyanosis, shortness of breath, fingers like “drumsticks”, nails in the shape of “hour glasses”, chest deformation . In autumn and spring, the pathology worsens. Congenital bronchiectasis is the cause of hemoptysis in children. Often this symptom is the only sign of pathology.
- Foreign bodies and respiratory tract injuries are the cause of hemoptysis in children and adults. Foreign objects affect the bronchial mucosa and contribute to the development of bronchial inflammation. Victims experience paroxysmal whooping cough with hemoptysis, stridor and shortness of breath. When the respiratory organs are damaged, the integrity of the blood vessels is disrupted, and the pulmonary parenchyma becomes saturated with blood.
- Various mycoses and helminthiases that affect lung tissue are accompanied by the formation of cysts and foci of destruction. Patients develop a paroxysmal cough, accompanied by shortness of breath and bronchospasm. Microscopic examination of mucopurulent sputum reveals large spherical fungal cells or helminth larvae. Fungal diseases of the respiratory system are accompanied by the germination of mycelium and the production of pathogenicity factors by microbes, which melt the lung tissue. This leads to the formation of copious sputum with blood inclusions. In addition to coughing, patients experience fever and shortness of breath.
- Heart diseases with congestion are manifested by hemoptysis, stabbing pain behind the sternum, fatigue, muscle weakness, shortness of breath, palpitations, sleep apnea, cyanosis, swelling of the extremities, impaired urine flow, swelling of the neck veins, hemorrhages on the skin, severe suffocation, puffiness of the face, fear death, a bubbling breath that can be heard from a distance.
Therapy methods
Upon completion of a comprehensive diagnosis, patients are prescribed a treatment regimen. Due to the fact that the symptom of hemoptysis is often severe and alarming, pulmonologists can admit the patient to the hospital. Advanced pneumonia with blood threatens such pathologies as pulmonary gangrene, the development of respiratory failure, endocarditis and others, so constant monitoring by doctors in the hospital helps prevent the development of complications.
Treatment of pneumonia in pregnant women and children is carried out only within the walls of the hospital. It happens that the pathology in these categories of patients is mild, then treatment at home is allowed, but with daily observation of the woman and child by the attending doctor and in compliance with all medical recommendations.
The treatment regimen for patients is always individual, as it depends on the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, and drug tolerance. The task of the attending physicians is to calm a severe cough, relieve spasms, disperse thick mucus and stabilize the patient’s general condition. For this purpose, antipyretics, mucolytics, and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. To stop blood from entering the sputum, an oxygenation procedure and the use of drugs such as Tranexam and Cyclocaprone are prescribed.
With intense bleeding, the doctors’ task is to stop the situation, so the therapy will be different. If it also does not bring the desired result, then doctors solve the problem with the help of surgery. In such cases, cauterization of damaged tissues or laser exposure is often prescribed.
Diagnostic procedures
To get rid of hemoptysis, you need to find out its cause. It is quite difficult to make a final diagnosis of a pathology manifested by the release of blood during coughing. Difficulties in diagnosis are due to the variety of causes of this disorder. To save the patient, specialists must solve the most important diagnostic problems as soon as possible.
Methods to determine the etiological factors of hemoptysis:
- Study of clinical signs,
- Collection of anamnestic data,
- General inspection,
- Physical examination.
Based on the results of the initial diagnosis, therapists make a preliminary diagnosis and refer the patient for consultation to more specialized specialists in the field of pulmonology, phthisiology, rheumatology, oncology, cardiology, and hematology.
Additional laboratory and hardware tests allow you to obtain objective data.
- X-ray of the chest organs of a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis
X-ray of the lungs - detection of tuberculous infiltrates and cavities, foci of inflammation in pneumonia, neoplastic signs in oncopathology, cysts, parasitic infestations. An X-ray contrast study will help you get a more detailed picture of the process.
- A tomogram of the chest can detect an affected vessel, small tumors, collapse of the lung lobe, and expansion of individual sections of the bronchi. Computed tomography with intravenous administration of a contrast agent allows one to assess the condition of the bronchopulmonary vessels.
- Bronchoscopy - methods for identifying endobronchial pathology, taking material for analysis, removing foreign bodies, removing tumors and cauterizing damaged vessels.
- Pulmonary angiography and radioisotope scanning of the lungs can detect recurrent infarction and increasing pulmonary thrombosis.
- Hemogram - signs of inflammation and anemia.
- Coagulogram – blood clotting disorder, change in platelet count.
- Blood test for indicators of acid-base status and gas composition.
- Sputum microscopy - detection of red blood cells, atypical cells, tubercle bacilli, fungi or parasites.
- Microbiological examination of bronchial secretions - bacteriological seeding of biomaterial on nutrient media in order to isolate the causative agent of infection and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- ECG and EchoCG - detection of heart defects, consequences of pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary embolism.
When the listed methods do not allow identifying the source of hemoptysis, diagnostic operations are performed. Thoracoscopy and thoracotomy are especially relevant in case of traumatic injury to the lung and with increased hemoptysis.
Types of pulmonary hemorrhage
Since 1990, domestic specialists have used the classification of pulmonary hemorrhage into three degrees:
- First, A, B and C - successively from 50 to 500 ml of daily blood loss;
- Second, A and B - from 30 ml to 500 ml in an hour;
- Third degree, A and B - simultaneous outpouring of up to 100 ml of blood or more.
Tactics for different intensities of blood loss differ, and if the patient’s hemoptysis does not frighten the oncologist, although he makes adjustments to therapy, then bleeding from the lung requires urgent medical and resuscitation care.
Book a consultation around the clock +7+7+78
Treatment and prevention
The goal of treatment is to stop hemoptysis and prevent it from turning into bleeding. Minor bleeding during coughing goes away on its own and does not require treatment. Frequently repeated and profuse hemoptysis is dangerous for human life. Such patients require emergency medical care.
If a person starts hemoptysis at home, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. The patient should be placed on a bed with a high headboard and reassured. It is important to ensure that he breathes calmly, does not talk and, if possible, does not cough. It is advisable to ensure an influx of fresh air by unbuttoning the collar of your clothes and opening the window. The patient should put ice on the chest and give ice cubes inside every half hour.
First aid also includes the use of:
- Anxiolytics,
- Blood pressure lowering drugs
- Drugs that suppress the cough reflex
- Medicines that dilate blood vessels.
Doctors and paramedics, arriving on call, provide emergency medical care to the patient with the help of medications. He is given intravenous and intramuscular hemostatic agents. Until the complete cessation of hemoptysis, patients are prohibited from physical activity, hot drinks and any food, alcohol, smoking, thermal procedures, and taking various medications.
All persons with hemoptysis are subject to mandatory hospitalization. In the hospital, after diagnosis and determination of the cause of the process, patients are prescribed specialized treatment. It is aimed not only at eliminating hemoptysis, but also at normalizing the functioning of the lungs and heart and preventing asphyxia.
Drug treatment of hemoptysis:
- To suppress coughing attacks - Codeine, Promedol intravenously.
- Hemostatic therapy - intravenous aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid, transfusion of fresh frozen plasma.
- To replenish the volume of circulating blood - intravenous colloid and crystalloid solutions.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Sedatives, tranquilizers.
Surgical treatment is performed for persons who have been diagnosed with lung abscess, cavernous tuberculosis or cancer.
Measures to prevent the development of diseases manifested by hemoptysis:
- Timely and correct detection and treatment of diseases of the respiratory tract, heart and blood vessels, autoimmune disorders,
- Quitting smoking and alcohol,
- Balanced diet,
- Daily walks in the fresh air
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The prognosis of the disorder depends on the causative pathology. Persistent hemoptysis often ends in profuse bleeding, which can cause death in patients.
Hemoptysis is a rather alarming symptom, the treatment of which must be taken very seriously. Even a single episode requires immediate attention to a doctor and a thorough comprehensive examination.
Video: hemoptysis
Urgent Care
First aid is necessary for massive hemoptysis (pulmonary hemorrhage). First of all, you should call an ambulance. What to do, how to provide first aid for hemoptysis before hospitalization:
Calm the patient, give him a sitting position or lay him down so that the diseased lung is below. A person should not be laid down if the affected area is in doubt. You must remain in a sitting position until the doctors arrive. To reduce bleeding in the lungs, you can give the patient a piece of ice to swallow, drink cold water - this helps to constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding
You can repeat taking ice every 15 minutes until the doctors arrive. In order to reduce pain and the force of bleeding, it is very important to persuade the patient to breathe deeply, try to restrain the cough, if possible, not to speak.
Emergency medical care for hemoptysis consists of reducing the intensity of the cough, eliminating chest pain, and stopping the release of blood. As a pain reliever, you can give a solution of analgin with pipolfen. If the pain cannot be reduced and its intensity increases, narcotic drugs are administered against the pain syndrome. It is imperative to administer a drug to suppress cough (codeine, dionine), but not to completely stop it, otherwise blood will not be removed from the lungs. To reduce a strong cough reflex, promedol is usually used, but in very rare cases.
Calcium chloride is used to stop bleeding. In the absence of thromboembolism, a gelatin solution is injected into the thigh. In patients with low blood pressure, therapy with vasoconstrictor drugs is contraindicated. If this algorithm for stopping pulmonary bleeding does not help, a blood transfusion is performed after checking compatibility. Other procedures that are used to treat massive hemoptysis:
- Embolization of bronchial vessels. The procedure is otherwise called catheterization. To perform embolization using angiography, it is necessary to determine which artery is causing the bleeding. After this, a special material is injected through the catheter to block it.
- Ventilation of the lungs. Bleeding can lead to asphyxia (suffocation), so patients often require a special apparatus to support breathing. It is important to insert a special tube into the canal of the unaffected bronchus.
- Packing the site of massive hemoptysis. This reduces blood aspiration to a minimum.
The treatment of large amounts of blood pouring into the lungs due to myocardial infarction has some features. Fibrinolysin, sodium chloride, and heparin are administered. In case of circulatory failure, strophanthin, korglykon, and glucose solution are used. Painkillers and antibiotics are used. Oxygen therapy and diuretics are administered in case of left ventricular failure.
In cases where embolization is not possible and massive hemoptysis threatens shock and respiratory failure, it can be stopped through surgery. Resection of the respiratory organ is performed. In this way, it is impossible to stop hemoptysis in lung cancer and serious diffuse pathology, since removal of even a small part of the lung is contraindicated. The shock state of the pulmonary organ is difficult for resuscitation - ventilation, blood transfusion, and administration of heparin and contrical are necessary. After the critical condition has been alleviated, the patient remains in the hospital, the doctor determines the category of nursing intervention, prescribes medications for recovery, and monitors the patient.
How is the analysis carried out?
The blood discharge, depending on the disease, has a different composition, appearance, and consistency. It is left to settle for some time, then the two or three layers that have formed are carefully examined, testing under a microscope for protein levels, chemical reactions, the presence of parasites, rotting products, foreign bodies, and purulent plugs.
In addition to the microscope, glass slides are also used for research. In this way, bacteria, cancer cells, fibers, epithelia, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and eosinophils are isolated.
To prescribe antibiotics to a patient, the sputum culture method is used: the secretions are placed in a nutrient medium, then they are tested for sensitivity to the components of the drug.
Ability to use a pocket inhaler, teaching the patient how to use a pocket inhaler.
Indications: Bronchial asthma (to improve bronchial patency).
Contraindications: Identified during the examination of the patient.
Inhaler with medicinal substance.
Inhaler without medicinal substance.
Possible patient problems:
Fear of using an inhaler or medication.
Decreased intellectual capabilities, etc.
Difficulty breathing when administering a drug through the mouth.
Sequence of m/s actions to ensure environmental safety:
Inform the patient about the use of the inhaler.
Inform the patient about the drug.
Check the name and expiration date of the medicinal substance.
Perform hand hygiene.
Demonstrate the procedure to the patient using a drug-free inhalation canister.
Remove the protective cap from the mouthpiece of the can.
Turn the aerosol can upside down.
Take the mouthpiece of the can into your mouth, wrapping your lips tightly around it.
Take a deep breath through your mouth and simultaneously press down on the bottom of the can.
Hold your breath for 5-10 seconds.
Remove the mouthpiece from your mouth.
Invite the patient to perform the procedure independently with an inhaler filled with medicinal substance.
Close the inhaler with the protective cap.
Evaluation of achieved results: The patient correctly demonstrated the inhalation technique using an inhalation cartridge.
Note: The number of inhalations is determined by the doctor. If the patient’s condition allows, then it is better to do this procedure while standing, since the breathing excursion is more effective.
source
Symptoms of pulmonary hemorrhage
Bleeding can happen at any time and even completely for no reason against the background of complete rest or moderate exercise. Everything else depends on the rate of blood loss. If hemoptysis has already been noted before, then the patient is less afraid, but when blood comes out of the throat, everyone is scared.
As a rule, with serious bleeding, a strong and uncontrollable cough begins, which is accompanied by progressive shortness of breath, as blood flows into the alveoli and turns off gas exchange in them. Blood may foam when mixed with air. Vomiting of swallowed blood often occurs; in the rejected masses the blood is red. The heartbeat increases, the patient becomes covered in sticky cold sweat, the hands and feet become cold due to a decrease in peripheral pressure. Blood drains, strength is lost.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Which doctor should I contact?
If bright red blood is discharged from the respiratory tract, a tickling sensation in the throat, pallor, the appearance of cold sticky sweat, tachycardia, dizziness and a deterioration in the general condition, you should call an ambulance. Before her arrival, it is necessary to provide the patient with maximum rest and follow all recommendations for emergency care for pulmonary hemorrhage. Treatment of the patient should be carried out in the department of pulmonology or thoracic surgery.
Pulmonary hemorrhage is accompanied by the release of large volumes of blood from the respiratory tract along with sputum or in pure form. It develops as a result of a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels of the bronchi or lungs and can be provoked by various diseases or injuries.
source
Submitting sputum for analysis: rules, recommendations
Coughing up blood is a serious sign that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. For diagnosis, you need to submit sputum for examination. How to do this correctly?
- During the day, drink expectorants, mineral and regular warm water;
- Immediately before the examination, thoroughly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with an antibacterial agent;
- Sputum is collected in the morning in a special disposable container. The discharge should be collected in five to six coughs. To confirm/refute some diagnoses (tuberculous cavity, bronchiectamia, pulmonary abscess) several liters of sputum per day are required!
- To avoid infecting loved ones and family members, it is better to carry out the procedures in a closed room, and after it is completed, ventilate it.
Can't collect the required amount of sputum?
You need to relax, relieve nervous and muscle tension: stand up, walk around, do some light exercise, light chest massage. Do you need to give sputum to your child? Children, especially young children, are unable to cough it up on their own. Therefore, the parent/health care worker needs to take a sterile cotton swab and press it on the root of the tongue, causing a cough reflex. Next, the swab with sputum is placed in a container and sent for examination. This method can be used to collect contents from an elderly, physically weakened person.