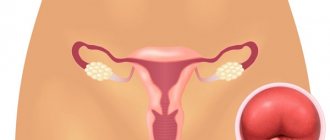
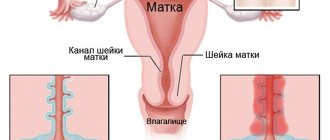
Unilateral or bilateral removal of the ovary (oophorectomy) is not a common operation, as it is performed according to a limited number of indications. Sometimes the ovary has to be removed together with the fallopian tube, less often - with the uterus.
The importance of the ovaries for the female body cannot be overestimated. They are responsible for three main functions:
— Vegetative, thanks to which girls undergo puberty and a “feminine” appearance is formed. The ovaries “turn on” during puberty and function until menopause.
- Hormonal. The ovaries secrete two determining hormones in a cyclic manner: estrogen (in the first phase) and progesterone (in the second phase). The rhythmic production of ovarian hormones is regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland located in the brain.
- Generative (childbearing). The ovaries produce fertilizable eggs throughout the reproductive period.
The full and adequate performance of all these functions by the ovaries ensures a woman’s health and the possibility of motherhood.
The ovaries are a paired hormonal gland. The completely identical structure and functioning of the right and left ovaries testifies to the wisdom of nature, which prudently decided “just in case” to make this organ a pair. It is thanks to this decision that the removal of the right ovary allows a woman to realize the function of childbearing at the expense of the remaining left ovary, and the removal of the left ovary is compensated by the remaining right one.
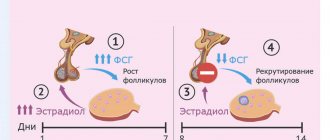
The ovary (each) has a dense connective tissue outer shell; under it in the cortical layer there are many small underdeveloped follicles containing the same undeveloped eggs. One of these follicles (they are called primordial) becomes fully mature over a period equal to one menstrual cycle, and the egg inside it reaches the development necessary for fertilization. The full development of the follicle and egg, respectively, is ensured by estrogens. A mature follicle (Graafian vesicle) bursts by the middle of the cycle, and the egg leaves it (ovulation), moving through the abdominal cavity to the fallopian tube - the site of potential fertilization. If fertilization does not occur, the egg dies within two days, and in the ovary, from the remnants of the burst Graafian vesicle, a corpus luteum is formed, capable of synthesizing progesterone. When the corpus luteum is destroyed (shortly before menstruation), under the influence of a sharp decline in hormones, the endometrium is rejected, and menstrual bleeding begins.
Thus, the menstrual cycle is conventionally divided by the period of ovulation into two phases of equal duration - follicular (first) and luteal (second). All changes that occur in the follicular phase occur with the participation of FSH of the pituitary gland (follicle-stimulating hormone), and in the luteal phase the pituitary gland secretes LH (luteinizing hormone).
Similar cyclical structural and hormonal processes continue throughout the reproductive period.
The most common diagnosed ovarian pathology is hormonal dysfunction, when, due to improper hormonal secretion, the cycle is disrupted and/or infertility develops. As a rule, such disorders are corrected with the help of hormone therapy. The ovary is removed only in situations where its presence is associated with life-threatening consequences, for example, bleeding, septic complications, large tumors, and the like.
As a rule, unilateral removal of the ovaries leaves a woman the chance of motherhood. Pregnancy after removal of the ovary is possible, but its likelihood, for obvious reasons, is reduced.
Serious consequences are provoked by bilateral oophorectomy, since the body is deprived of proper hormonal influence and enters a period of artificial premature menopause.
Therapy after removal of the ovaries is intended to correct hormonal imbalances in order to eliminate menopausal disorders.
Indications for surgery
The method of treating appendage pathology is determined after extensive diagnostics. Laparoscopic or endoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is prescribed for both young and older people. Main indications:
- formation more than 5-7 cm in diameter;
- risk of cancer;
- hormone-producing formations;
- bilateral damage to the appendages;
- risk of pathology rupture;
- the presence of a leg in the formation.
There are two types of adnexal cysts - functional and epithelial. The first type occurs when the menstrual cycle is disrupted and does not pose a serious health hazard and can resolve on its own within a few months. Epithelial formations are a consequence of diseases of the genital area or failures of body systems; surgery is necessary to eliminate them. They rarely respond to drug treatment.
The appointment of laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst on the left or right side is necessary for large functional formations or when there are a large number of them on one or both appendages.
Surgeries for polycystic disease
Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome is aimed at removing large cysts and activating ovulatory function. Most often, the reason for its implementation is infertility and lack of effect from drug treatment. The main goal of treatment is not only to remove the altered parenchyma, but also to provide conditions for egg maturation, ovulation and fertilization.
For polycystic disease, several types of operations are possible:
- Decortication - when during the intervention the dense sclerotic tunica albuginea is excised, which facilitates the maturation of follicles in the future and the release of the egg from them;
- Cauterization - 6-8 circular incisions are made on the outer part of the ovary up to 1 cm deep into the organ, which enable the growth of the follicle and the maturation of the egg without the formation of a cyst;
- Wedge resection - removal of a wedge-shaped section of tissue in one of the poles of the ovary;
- Endothermocoagulation - insertion of an electrode deep into the organ and formation of up to 15 holes with the electrode;
- Electrodrilling is the excision of many cystic cavities of the cortical layer using an electric current.
Prohibitions on surgery
The operation may be contraindicated even if the life and health of the patient is threatened. Laparoscopy of the ovaries is prohibited in the following cases:
- severe course of infectious and viral diseases;
- late stages of cancer;
- decreased blood clotting;
- high degree of obesity;
- adhesions in the peritoneum;
- skin dermatitis, ulcers and other lesions;
- intolerance to anesthetic drugs;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- pregnancy;
- state of shock.
To prescribe laparoscopy, the size of the ovarian cyst should not exceed 14 cm.
Some contraindications do not exclude the possibility of performing another type of surgery.
Is it possible to get pregnant with one ovary?
Performing a unilateral oophorectomy reduces the chances of motherhood, as it leads to premature depletion of the ovarian reserve. However, if initially its level was high, and the woman had no other pathologies in the reproductive system, except for the disease that became an indication for surgical intervention, then she can become pregnant. This can be determined almost immediately after the operation. Ultrasound and X-ray examinations allow us to assess the patency and shape of the remaining appendage, and the chances of pregnancy. If ovulation occurs, the tube is patent, and the partner’s spermogram is good, then the probability of conception is quite high. In some cases, IVF may be required, the main indications for which are:
- obstruction of the remaining fallopian tube;
- presence of associated risks of infertility;
- poor quality of the partner’s ejaculate;
- no pregnancy after six cycles of taking gonadotropins.
If the supply of oocytes in the remaining ovary is completely depleted, it will be possible to achieve conception only through the implantation of donor eggs. In our IVF center you can undergo all types of examinations and, if necessary, perform in vitro fertilization after an oophorectomy.
Preparation process
To reduce the risk of negative consequences, a woman must go through several stages of preparation for laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. Some additional rules make the operation easier and speed up recovery. Based on research results, the treatment regimen may be changed.
Diagnosis before laparoscopy of a cyst
It is a mandatory component of the preparatory process. During the examination, a method of treating the pathology is selected, and the risks of its implementation are determined.
List of tests before laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst:
- Ultrasound - determination of the size of the formation, the degree of damage to the genital organs;
- general and biochemical blood tests - a general picture of the state of the body;
- general urinalysis and bacterial culture - assessment of kidney function, detection of infections;
- screening to exclude the course of hepatitis, syphilis, HIV;
- biopsy of the ovaries and their formations;
- gynecological smear - determination of the state of microflora;
- colonoscopy - examination of the intestines, mandatory before laparoscopy of ovarian cysts;
- determination of Rh factor and blood group;
- assessment of blood coagulation function;
- fluorography – exclusion of tuberculosis;
- determination of hormonal levels;
- checking the tolerability of anesthetics.
When to plan a pregnancy
The question of the possibility of conceiving a child with one ovary very often interests women. Of course, any operation on the pelvic organs can lead to infertility, especially if it is performed incorrectly or complications are observed. Modern surgery makes it possible to make the removal of one appendage and ovary very safe for a woman’s health. If no negative consequences from oophorectomy are observed, and hormonal therapy has allowed the second ovary to completely take over the functions of two organs, no noticeable changes will occur in the patient’s life. In this case, menstrual cycles will be restored, and ovulation, as before, will occur every month. The only difference is that the remaining organ will exhaust its resource faster, because it will have to release eggs not every month, but every cycle.
Based on this, doctors recommend not delaying the conception of a child, especially if there are no concomitant diseases and postoperative complications. If you delay pregnancy for a long time, you can wait until the ovary gets tired and stops ovulating.
Please note: According to statistics, menopause occurs earlier in patients with an organ removed than in healthy women. Menstrual function is disrupted and it becomes impossible to conceive a child.
If a woman is healthy and an ultrasound confirms the presence of ovulation, doctors recommend not postponing pregnancy. Of course, this does not mean that you need to conceive a child in the next year, however, you should not wait too long. If pregnancy has occurred, it is very important to make sure that it is progressing normally. It has been statistically found that after unilateral oophorectomy, the risk of ectopic attachment of the fetus increases significantly.
To summarize, it must be said that not all women with an ovary removed experience changes in their quality of life. In most cases, such an operation has little effect on the patient’s health, provided that it is performed correctly and the postoperative treatment brings positive results. The menstrual cycle is restored quite quickly, because a healthy organ begins to be responsible for the production of the required amount of hormones. This allows a woman to conceive and bear a healthy baby.
Types of laparoscopy
There are several techniques for removing pathologies. They are determined by the type of formation, the presence of a malignant process and damage to neighboring organs. Surgical techniques of laparoscopy:
- Ovarian cystectomy. Enucleation, i.e. enucleation of an ovarian cyst while fully maintaining the integrity of the latter. Prescribed for small formations that do not damage the epididymal capsule.
- Laparoscopic resection of ovarian cyst. Necessary when a formation grows into an organ cavity, characterized by partial removal of the appendage.
- Ovariectomy. Complete removal of pathology and the affected organ. It is used for suppuration, ruptures, and malignant processes.
In all of these cases, the woman’s reproductive ability is preserved, because Conception is possible even with only one appendage.
With a full abdominal operation of another type, it is possible to perform a hysterectomy - the complete removal of the woman’s genital organs. This is required if there is an oncological process or if there is a high risk of its occurrence.
When is prophylactic oophorectomy indicated?
Ovariectomy of hormonally dependent breast cancer is used for adjuvant - preventive therapy and widespread metastatic process. Naturally, a woman should be menstruating or without menstruation, but with a certain level of sex hormones in the blood. During chemotherapy, suppression of the ovaries occurs, which is manifested by the absence of menstruation - amenorrhea, but this is temporary, some time after the completion of chemotherapy the ovaries restore their function.
In the preventive treatment of breast cancer, oophorectomy should not complement systemic treatment, which means any use of anticancer drugs: chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Today, oophorectomy is recommended as a completely independent preventive treatment when there are contraindications to chemotherapy or tamoxifen. But there are exceptions when oophorectomy in the adjuvant mode is mandatory, this is the use of aromatase inhibitors; otherwise, these tablets are prohibited for use in menstruating women.
Another exception is preventive treatment for breast cancer in women under 40 years of age. As a rule, the course of the disease at this age is more aggressive, so maximum blockade of estrogen production is used. Until recently, the combined use of oophorectomy and tamoxifen in the adjuvant mode was standard for all patients of reproductive age; sometimes prednisone was also added, but at present such a regimen of hormonal influence “from all sides” is not considered justified.
How is laparoscopy of a cyst performed?
Treatment is prescribed on a specific day, before which the patient must go through all stages of preparation. Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst requires general anesthesia. Order of conduct:
- Administration of sedatives and sleeping pills, then anesthesia.
- Installation of the operating table in a position convenient for performing all manipulations.
- A puncture of the navel to fill the peritoneum with gas is necessary to create a space that facilitates the intervention.
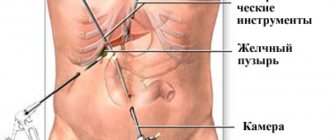
- Inserting a laparoscope into the hole is a special device with a camera and a light source.
- Performing two punctures to insert medical instruments.
- Thorough examination of the genitals.
- Removal of pathology and/or part of an appendage and/or the entire organ.
- Check for bleeding.
- Gas suction.
- Removing tools.
- Applying sutures and sterile dressings.
- Checking the patient's condition - breathing, heart rate, blood pressure.
- Transferring the woman to the ward.
After examination with a laparoscope, it is possible to change the course of the operation - for this, all instruments are removed and an incision is made in the peritoneum.
On average, removal of an ovarian cyst by laparoscopy lasts from 20 minutes to an hour and a half; at the discretion of the doctor during the intervention, the time can be extended. The duration of the operation is determined by its complexity, the size of the formations and their number. Depending on how long the laparoscopy of the ovarian cyst lasts, the amount of anesthesia is determined. The required volume of the latter is also significantly influenced by the patient’s weight and her age.
General information and benefits of the intervention
During laparoscopic surgery, surgeons have the opportunity to carefully examine the structure of the ovary, see as much as possible the problem and carefully eliminate it. It is used to remove cysts, remove part or the entire organ, and eliminate foci of endometriosis.
The dimensions of the incision through which the instrument is inserted do not exceed 0.5-1 cm. A total of three holes are made. An endoscope is inserted through one, and operating instruments are inserted through the others. This operation is minimally traumatic, so the recovery period is relatively short.
As for the advantages of laparoscopic intervention in the area of the appendages, they are as follows:
- since the size of the holes is very small, the tissues are not greatly traumatized;
- minimizing the adhesive process, because internal organs are not affected to such a significant extent as during laparotomy;
- recovery in the postoperative period is faster and better;
- reducing the risk of developing infection or blood poisoning;
- there is no danger of sutures coming apart and bleeding, since the tissues are amenable to slight coagulation;
- preserving a woman’s ability to have children, because complete removal of the ovary or uterus is not always required;
- the ability to perform even the most complex operations in a relatively short time.
All necessary manipulations are carried out under supervision via a video camera and monitor. Specialists have the opportunity to see the smallest details of the operation without cutting into the abdomen.
Rehabilitation period
In the first few days after the intervention, it is necessary to observe bed rest, partially limiting physical activity. In this case, the woman is allowed to get out of bed after 2-3 hours. She can walk around the room and go to the toilet. At first, pain is felt in the area of the stitches and in the lower abdomen - this is considered normal. Symptoms will disappear after complete healing of the skin damaged during laparoscopy and the incisions on the ovaries. From the first days after treatment, a woman is prescribed the following types of drugs:
- anticoagulants – prevent the development of thrombosis;
- painkillers - make you feel better;
- antibacterial - prevent suppuration of sutures.
In a hospital setting, the patient follows a diet. Her diet consists of liquid soups and cereals, crackers, boiled vegetables and lean meat, and omelettes. During this period, it is forbidden to consume any heavy foods, as this can worsen intestinal function. You should return to your usual menu gradually as you feel better.
After several days spent in the hospital after laparoscopy of the cyst, and when your own condition normalizes, you are allowed to do light exercises. It will restore blood circulation, increase body tone, and improve mood. In the first 1-2 weeks, it is forbidden to engage in active gymnastics; abdominal exercises are allowed only after the stitches have healed.
Other recommendations for patients:
- refusal of excessive physical activity;
- prohibition on lifting weights;
- carrying out hygiene procedures only in the shower, baths cannot be taken;
- wearing compression stockings to reduce the risk of thrombosis;
- use of a postoperative bandage;
- refusal of sexual activity for 1-2 months;
- excluding visits to baths, saunas, and open reservoirs.
The length of stay in the hospital depends on the woman’s well-being. Typically, patients are discharged on the third day after the intervention.
Impact of surgery on health
After surgery, many women experience such an unpleasant consequence as post-castration syndrome. It is worth remembering that it is not observed in everyone and can have a fairly mild course. For approximately 25 percent of patients, the quality of life with one remaining organ does not change at all. However, for some, post-castration syndrome can be quite intense. All this depends on the individual characteristics of the body. There are three groups of disorders that may accompany the postoperative period. Typically, the first signs of this process are observed 2-3 weeks after surgery, and they become more pronounced after a few months.
The group of disorders includes the following symptoms:
- hot flashes, especially at night;
- increased sweating and feeling of chills;
- headaches and dizziness;
- hypertension and constant pressure surges even at rest;
- feeling of general weakness and fatigue;
- mood swings and irritability;
- worsening sleep and insomnia;
- decreased or complete loss of libido;
- violation of memory processes.
All these reactions begin to disappear a year after removal. Due to hormone deficiency, some patients experience sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system. Women often suffer from vaginal dryness, discomfort in the pelvic organs, frequent urination and discomfort during sexual intercourse. Rarely, but still there are cases of disruption of other mucous membranes. Thus, conjunctivitis, intestinal dysfunction and dry mouth occur.
If a woman has undergone bilateral surgery, the manifestations of post-castration syndrome become more obvious. Such patients face more significant hormonal imbalances. The body stops producing sex hormones in the required quantities, which leads to atherosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, circulatory disorders, osteoporosis, deterioration of the skin and hair, and other undesirable consequences.
We recommend you find out: Delayed menstruation and left ovary pain
Other types of cyst removal surgeries
Surgical treatment of pathology is also possible during other types of operations. The type of intervention depends on the characteristics of the disease:
- Laparotomy. Making one large incision in the abdominal wall. This type of operation is used for large formations, the need to remove the appendage itself and/or the uterus. Laparotomy of an ovarian cyst can be used when it is impossible to fully assess the condition of the organs with a laparoscope or in emergency cases.
- Laser. Minimally invasive surgery. It consists of using a laser for surgical treatment, removing the ovarian cyst and cauterizing the tissue, eliminating bleeding. Suitable for small types of formations, not used in the presence of malignant cells. Does not require making incisions on the ovaries.
Most often, laparotomy or laparoscopy is used to eliminate pathology. Laser surgery is highly effective, but is only suitable for certain types of formations.
Anesthesia during surgery
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, and each patient undergoes training before it is performed. The anesthesiologist selects the drug and its dose individually for each patient. There are several methods of administering anesthesia before laparoscopic surgery:
- Local epidural anesthesia.
- Regional epidural anesthesia.
- General anesthesia.
During general anesthesia, tracheal intubation is performed to ensure the patient can breathe freely and prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
At the Yusupov Hospital, they carefully select substances for anesthesia, using minimally morphine derivatives. The anesthetic drug should have minimal side effects and not affect muscle relaxation - this can complicate the operation. Anesthesia has a large number of side effects and can cause an allergic reaction in the patient, so every patient undergoes preparation before the operation. The quality of anesthesia depends on the experience and qualifications of the doctor. Reviews of anesthesia vary, depending on how well the patient was prepared and the anesthesia was selected. Epidural local and regional anesthesia is used for short-term surgical interventions.
Advantages of laparoscopy
Removing the ovaries laparoscopically has many advantages. This is explained by the small volume of injured tissue. Main advantages:
- low risk of adhesions;
- small number of seams;
- fast rehabilitation period;
- no scars;
- gentle effect on neighboring internal organs;
- low likelihood of developing a hernia after surgery.
The patient's speed of recovery is achieved due to small sutures that do not interfere with her free movement. Their small size reduces the likelihood of suppuration.
It is important to understand! Although laparoscopy is considered a gentle operation to remove an ovarian cyst, it is impossible to neglect the advice of doctors before and after surgery. In addition to the benefits, there is a risk of relapse and re-formation of the cyst.
Consequences after removal of ovaries
Negative consequences after removal of the ovaries can be conditionally classified into functional and organic.
Organic are associated with the removal of the organ as such, when its absence provokes the appearance of postoperative consequences. One of them is pain syndrome. Pain after removal of the ovary in the early period is associated with minor changes in the topography of the pelvic organs: they shift slightly and the apparatus that fixes them “stretches,” causing pain. As a rule, after two weeks (or earlier) these pains stop.
Unfortunately, sometimes pain after removal of the ovary is provoked by an adhesive process that cannot be completely eliminated. More often, adhesions form against the background of inflammatory phenomena, when inflammatory exudate appears in the pelvic cavity; over time, it becomes viscous and thick, so it literally “glues” adjacent tissues, disrupting their proper mobility. Early rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries involves the prevention of inflammatory and, accordingly, adhesive processes.
The most serious consequence of oophorectomy, especially in young patients, is a complex of functional disorders. Their severity is determined by the number of removed ovaries. Unilateral oophorectomy leaves the patient the opportunity to have her own sex hormones and also realize reproductive function. More often, after the removal of one ovary, dishormonal disturbances occur, which can be compensated for.
If both ovaries are removed, the woman is artificially deprived of the necessary estrogenic influence, and a condition similar to menopause occurs, called post-castration syndrome. Unlike natural menopause, when the body has the ability to gradually adapt to the attenuation of the hormonal function of the ovaries, menopausal syndrome of artificial origin is quite difficult.
Pregnancy after surgery
After laparoscopy of the cyst, ovarian function is gradually restored. Their full functionality returns after 3-6 months. At this time, you can begin planning for pregnancy, the likelihood of which increases significantly due to the increased work of the appendages.
The onset of conception is also determined by other characteristics of the woman. The success of fertilization depends on her hormonal levels and the presence of other gynecological diseases. In the complete absence of pathologies, pregnancy can occur within a year after the intervention.
In approximately 15% of cases, women fail to conceive a child after laparoscopy of a cyst. In such cases, IVF is used. Doctors do not recommend delaying pregnancy planning after surgery.
Therapeutic oophorectomy
In case of advanced cancer or metastatic stage in menstruating women with hormonal receptors in the tumor, oophorectomy may be recommended in parallel with hormonal therapy with the antiestrogen tamoxifen. Why is this option not considered useful for prevention, but for metastasis it is included in the standard? Preventive therapy is aimed at the tumor cells remaining after radical treatment; there are few or none of them; metastasis requires the mobilization of all therapeutic resources.
Secondly, double hormonal exposure is justified when there is a high level of hormonal receptors in tumor cells, especially with metastases to bones and soft tissues; it is less advisable for tumor damage to internal organs. Ovariectomy is absolutely necessary when taking aromatase inhibitors, which stimulate the ovaries. Again, this category does not include women who went through menopause more than 5 years ago.
Possible complications
Laparoscopy has a low number of complications. Their likelihood increases under the influence of the following factors:
- improper operation;
- incomplete diagnosis by the patient;
- lack of preparation for treatment;
- neglect of contraindications;
- the presence of an oncological process;
- old age woman.
Possible complications after laparoscopy of cysts:
- injury to neighboring organs;
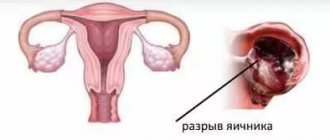
- internal and uterine bleeding;
- slow recovery process;
- suppuration of sutures;
- development of the adhesive process;
- the appearance of cancer cells in the body or the acceleration of their reproduction;
- thrombophlebitis;
- peritonitis;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
If you have an increase in body temperature, severe weakness, nausea, dizziness, clouding of consciousness, or acute pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Complications can appear both in the first few days after surgical removal of an ovarian cyst, and several weeks or months later. To prevent their development, regular monitoring by a gynecologist is necessary.
After 40 years
At the age of 40, surgery leads to forced menopause and massive changes in the body. After surgery, doctors tend to carry out hormonal therapy. If the treatment is inadequate, the woman begins to experience:
- heart problems;
- Bad mood;
- tides;
- blood pressure fluctuations;
- forgetfulness.
Due to hormonal imbalance, sudden weight gain often occurs. Therefore, it is important to monitor your diet. Other symptoms include rapid aging: the skin ceases to be elastic, the development of periodontal disease, which can lead to tooth loss, and metabolic problems.
Symptoms can appear either selectively or complexly. After the operation, you must be under the supervision of a doctor.
Is it necessary to remove an ovarian cyst and what will happen if laparoscopy is not performed in a timely manner?
Only epithelial formations are subject to mandatory removal. This is necessary if it is impossible to eliminate them by taking medications. Functional pathologies in the vast majority of cases do not require surgical intervention and go away on their own.
The operation is necessary if the doctor insists on it. If you refuse, the following diseases and conditions of the body may develop:
- increased pain in the lower abdomen;
- absence of menstruation or irregularity;
- increase in cyst size;
- damage to the second appendage;
- rupture of the formation or the ovary itself;
- infertility;
- the occurrence of a malignant process;
- damage to neighboring pelvic organs.
The likelihood of developing consequences depends on the type of pathology, the presence of other gynecological diseases, the age of the patient and her hormonal levels.
Laparoscopy is a gentle method of surgery to remove an ovarian cyst. It is carried out strictly according to indications, after a complete medical examination. The effectiveness of the intervention depends on the qualifications of the surgeon, compliance with the rules of preparation and subsequent rehabilitation by the patient, and the type of remote education.
Features of the event
Reduced hospital stay, short recovery time.
The laparoscopic method of removing a cyst is a cavity intervention, but access is through incisions that are minimal in length.
The main advantages of the operation over traditional techniques are the minimal invasiveness of the method, a more pronounced cosmetic effect, a reduction in hospital stay, and an acceleration of the recovery period. Complications such as the formation of adhesions, hernias, and intestinal paresis are recorded with significantly lower frequency than with open approaches.
Ovarian laparoscopy requires special equipment and trained personnel. It is carried out for urgent and planned reasons. Tactics depend on the patient’s age, location of the cystic formation, and desire to become pregnant in the future.
Depression
Most women who have had their ovaries removed confirm the consequences in the form of depression. This condition can be explained by extreme stress. The whole meaning of a woman’s life lies in childbearing, as nature intended. When a representative of the fairer sex loses these organs, she understands that she can no longer be a mother. Perhaps the woman never intended to give birth again, but the very realization of reality is very depressing. What can be said about young ladies who were still planning a pregnancy?
Laparotomy of the ovary - abdominal surgery
The doctor treats the pubis and the site of the intended incision with an antiseptic. It can run horizontally or vertically. In the first case, the scar is less noticeable, in the second, the surgeon has a better view.
Using a scalpel, the doctor cuts the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The abdominal muscles move apart. The ovaries and appendages (plexus of blood vessels that supply the organ) are removed from the cavity. The ligaments on which they are attached are clamped with terminals. Above them, incisions are made. After this, the terminals are replaced with ligatures (threads). The ligament stumps return to the abdominal cavity. The fabrics are sutured in layers. A bandage is applied over it. The removed organs are sent to a laboratory for examination.
Hormonal imbalance
The consequences of ovarian removal in women are hormonal disorders. When a woman loses both organs, cyclical changes cease to occur in her body. In a word, a woman experiences menopause.
If this condition comes naturally, then the body experiences much less stress, since the fading of the ovaries occurs gradually. In the case of surgery, the change in hormones is carried out abruptly. Just yesterday, the body fully felt cyclical changes that no longer exist today.
General state
After both ovaries are removed, a woman withdraws into herself. She becomes more distracted and slow. What a lady could previously do in five minutes, she now does in half an hour.
In addition, a woman’s sexual desire disappears and many complexes develop. Very often, such representatives of the fairer sex suffer from insomnia.
Due to metabolic disorders, a woman's bones become very fragile. This can lead to the development of atherosclerosis or frequent fractures. Nails and hair are also negatively affected. The hair becomes more brittle, dull and lifeless. Nails begin to break and peel.
Spaying also affects the condition of the teeth. Women often experience periodontal disease and other gum diseases. Teeth become brittle and may fall out or crumble.
"Pleasures" of menopause
So, the woman had her ovaries removed. The consequences of this manipulation are expressed in the fact that the lady has to face all the signs of menopause.
In addition to the fact that a woman falls into a prolonged depression, the functioning of her body is completely restructured. The lady constantly feels hot flashes, increased sweating, she feels either hot or cold. In addition, the woman experiences frequent headaches, fatigue and weakness.
Also, the lack of hormones greatly affects the general condition of the body. The body begins to age, the skin becomes covered with fine wrinkles and slowly sags.
Patient reviews
Oophorectomy, especially when accompanied by the removal of other organs of the reproductive system (uterus, fallopian tubes), turns out to be a serious test for the patient. Many write that they no longer feel like women, sex life has become difficult, and husbands have a negative attitude towards such changes in the body of their life partner.
The support of loved ones, the presence of children, or the rejection of the idea of having offspring contribute to a calm attitude towards the operation. Some patients in their reviews say that the improvement in their condition after surgery, on the contrary, had a beneficial effect on their personal life, and note that psychological comfort largely depends on their inner mood.
The hardest thing for a woman is the realization of the futility of all the procedures she has undergone. This can happen, in particular, with a cancerous tumor. In this case, the operation is accompanied by courses of chemotherapy. Sometimes even this doesn't stop the cancer. Women talk about stress, depression, nervous breakdowns. Such problems should be solved by a specialist (neurologist or psychotherapist). A positive outlook on things, the desire to live and faith in the best greatly contribute to recovery and overcoming difficulties.
A big shock for the patient can be the indifferent attitude of the doctors, their reluctance to pay attention to complaints and provide advice after the operation. Therefore, you should immediately choose a specialist who inspires trust, enlist the support of loved ones and friends, and set yourself up for a good outcome of the operation.
Oophorectomy, despite the fact that it is a great stress for a woman’s body and her psycho-emotional state, gives the patient a chance to survive and cope with the main illness. Even at a young age, you should not postpone it and waste time. Modern medicine makes it possible to successfully cope with almost all the undesirable consequences of ovarian removal.