Mastopathy is a collective term for a large number of breast diseases. Breast adenoma is a type of mastopathy, a benign tumor that develops from glandular epithelial cells. Breast adenoma is a round formation, mobile, of dense consistency. An adenoma can form in one mammary gland or affect both glands; it can form as a single or multiple neoplasm.
Diagnosis of breast adenoma is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital. A preliminary diagnosis is made by a doctor during a visual examination of the patient; the diagnosis is confirmed using MRI, ultrasound, CT and breast biopsy. The Yusupov Hospital sees oncologists, a mammologist, and a gynecologist. Breast treatment can be done at the hospital's oncology department. Treatment of the disease is conservative and surgical.
What is FMC?
FCM of the mammary glands is a benign disease, the cause of which is most often a gap in the proportions between the junction and epithelial materials. Doctors make this diagnosis if they find lumps in a woman’s breast.
The disease is more common after 45 years of age, but can occur during childbearing age. With complications, some forms of FCM can transform into malignant neoplasms.
What forms of this disease exist?
Depending on the nature of cell proliferation in the mammary glands, the following forms of this disease are distinguished:
- epithelial cell proliferation;
- myoepithelial proliferation;
- fibroepithelial proliferation.
All these forms are benign. But when exposed to irritating factors or the disease is ignored for a long time, they can transform into a malignant tumor. The fibroepithelial form of the disease poses the greatest danger to women, since it carries an oncological risk.
It will also be useful to know the following information:
- Read more about fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component.
- About the residual effects of fibrocystic mastopathy.
- Features of severe and moderate forms of the disease.
- All about nodular fibrocystic mastopathy.
Diffuse dyshormonal mastopathy
The difference between diffuse mastopathy and other forms is that it affects the entire mammary gland. Typically, more than half of women suffer from this form. The main patients are female bodybuilders taking various hormones, especially estrogens and progesterones.
Cysts formed during the disease change their size during menstruation. They can be dense or watery, mobile during examination. Various discharge from the nipples, aching, bursting pain are possible. Mandatory monitoring of their growth and other changes is required.
The causes of this disease may be:
- Long-term absence of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Lack of breastfeeding.
- Treatment of infertility with hormonal drugs.
- Chest bruises.
- The onset of an early menstrual cycle.
- A large number of abortions.
- Stressful conditions: lack of adequate sleep.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Chronic female diseases.
- Heredity.
- Lack of libido.
- Functional changes in the thyroid gland.
- Frequent visits to the solarium, prolonged exposure to the sun.
Fibrous disease FCM
Fibrous mastopathy is a condition in which connective tissue grows in the mammary glands. Normally, the structure of the mammary gland contains connective tissue and glandular components.
With fibrous mastopathy, this ratio changes in favor of the fibrous component of the connective tissue of the mammary gland. Small nodules and strands of connective tissue appear that penetrate the gland.
The causes of the disease can be various stresses, abortions, lack of breastfeeding after the birth of a child, diseases of the thyroid gland, ovaries and other organs. That is, this pathology can be caused by conditions accompanied by a failure of the hormonal system.
Fibrous mastopathy is manifested by symptoms such as:
· dull pain and feeling of heaviness in the mammary glands;
· the presence of slightly painful hard lumps in the chest upon palpation;
· asymmetry of the mammary glands, their increase or decrease, change in shape;
· violation of the regularity of the menstrual cycle;
Increased chest pain shortly before the onset of menstruation.
To diagnose the disease, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, examines and palpates the mammary glands. May prescribe an ultrasound examination, mammography or biopsy. Fibrous mastopathy is a benign disease, but it can also transform into a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, prevention, timely detection and treatment are necessary. To prevent the development of pathology, you need to adhere to a healthy and active lifestyle.
Regular sex life, childbirth followed by breastfeeding have a beneficial effect on a woman’s hormonal status. Homeopathic drugs that correct the endocrine background have proven themselves to be positive. Also, you should not worry about trifles and expose yourself to stress. It is important to have time for proper sleep and rest, and to give up bad habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol. It is advisable to walk outdoors more often and exercise regularly. In order not to miss the development of fibrous mastopathy, every woman should conduct a breast self-examination. This simple technique will help to identify the first lumps in the mammary glands and consult a doctor in time.
Nodular mastopathy
The disease is characterized by the existence of transformations in the mammary glands: nodes, soft tissue cysts, hardening of the breasts during menstruation, increased sensitivity, fluid discharge, and growth of gland lobules. Identification of individual atypical cells is a state of increased risk of cancer.
Therapy for nodular mastopathy is successful only at the beginning of the disease. Further treatment requires the intervention of a surgeon. Unlike diagnostics, in the nodular form of the disease, fingering is prohibited.
Classification of pathology
There are several types of adenoma in the mammary gland in women. They have their own characteristics. The main types include:
Nodal . The neoplasm is clearly separated from neighboring tissues.- Leaf-shaped . It consists of many layers and is characterized by fairly active growth. Needs more thorough therapy.
- Tubular . Hardening with a nodular structure.
- Lactating . Education intensively produces the secret. It often appears during lactation.
Types of mastopathy
Mastopathy is divided into 3 main types:
- fibrous;
- cystic;
- mixed.
Fibrous type
If fibrous tissue grows atypically, then the pathology is of the fibrous type. If mastopathy is of a certain nature and not treated, the cells may degenerate into malignant ones.
Cystic type
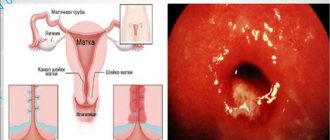
This type of mastopathy is often combined with a woman’s existing gynecological diseases, including menstrual irregularities. A cyst can form not only in the soft tissues of the breast, but also in the ovaries. Multiple cysts and nodules cause pain and discomfort. Cases of detection of cystic mastopathy in men are rare, but they do occur.
FCM of the mammary glands has different forms.
After the menopause ends, the risk of the disease decreases. If there is no therapy, there is a fairly high probability of cells degenerating into malignant ones.
Mixed view
Mixed fibrocystic disease of the mammary glands is usually preceded by diseases of the liver and thyroid gland, chronic female diseases, abortion, lack of breastfeeding, and stressful conditions. There is enlargement of the lobules and enlargement of the ducts.
Palpation reveals a smooth oval or round compaction with unclear contours, as well as small grain size and coarsening of the lobules. The spread of fibrous tissue with cysts is usually present in both breasts, although tenderness may be present in only one.
Diagnosis of mastopathy - forms of diagnosis
— DFCM SF – mixed form of diffuse FCM
— DFCM GC – diffuse FCM with a predominance of the glandular component
— DFCM CC – diffuse FCM with a predominance of the cystic component
— Nodular and diffuse nodular mastopathy
— Fibroadenoma
According to statistics, women with this pathology are almost 5 times more likely to develop breast cancer, so the problem of diagnosing and treating mastopathy is currently very relevant.
Symptoms according to the form of pathology
Signs of mastopathy and its manifestations largely depend on the physical and psychological state of the woman. The pain comes from stagnation of blood. Women usually call this breast engorgement.
Sometimes the pain is unbearable even from touching clothing.
Soreness and swelling decreases after the end of menstruation. The longer the disease continues, the pain becomes incessant. All this leads to a disruption in the woman’s emotional state, creating a state of irritation, aggressiveness or, conversely, tearfulness.
Diagnostics
Some forms of the disease, in which small lumps and cysts form in large numbers, are difficult to detect during self-examination. Typically, women begin to see a specialist only when unpleasant symptoms appear, such as breast pain, changes in the menstrual cycle or discharge from the nipples.
FMC is diagnosed using mammography. If it is present, the image shows pathological changes in the mammary gland, enlarged lymph nodes, and a focus of disease. The mammologist will determine their number, nature, volume, and uniformity. In the photograph, cystic and fibroadenoma formations have the shape of an oval or circle with clear edges.
If there are such complaints, a qualified doctor will prescribe an ultrasound scan. To confirm the diagnosis, a biochemical blood test may be required. If a cyst or tumor is detected, a puncture is prescribed. FCM of the mammary glands on ultrasound images manifests itself in the form of thickening of the walls of the ducts, increased echogenicity of the glandular layer due to the large number of fibrous structures.
Diagnosis of fibrocystic disease
Fibrocystic mastopathy is a mixed form of diffuse mastopathy. It is characterized by approximately the same ratio of fibrous and cystic changes in the structure of the mammary glands. As a rule, the symptoms of this type of disease are in many ways similar to the signs of both cystic and fibrous mastopathy. A universal symptom is breast tenderness. They may swell and a feeling of burning and bloating appears. Upon palpation, you can detect small compacted areas of round or oval shape, which are more noticeable a few days before menstruation and decrease slightly during menstrual bleeding.
Discharge often appears from the breast in the form of colostrum, a clear or bloody fluid. Diagnosis of fibrocystic mastopathy is carried out by examination and palpation of the mammary glands every time a woman visits a gynecologist. Also, all women, starting from 45 years of age, are recommended to regularly see a mammologist and undergo an annual mammogram or ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. Ultrasound examination is safe, it can be prescribed even to pregnant women and patients of almost any age.
The causes of the disease are standard and consist of hormonal changes. Hormonal imbalance can be caused by many pathologies. To choose the right treatment for fibrocystic mastopathy, you need to identify the causes of endocrine disruptions. To do this, your doctor may prescribe laboratory tests for certain hormones. For example, the content of estrogen, progesterone, FSH, lutropin, prolactin, hormones synthesized by the thyroid gland, etc. An ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs (ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes) is also sometimes carried out.
Fibrocystic mastopathy, like other forms of mastopathy, can be a precursor to the cancer process and, to some extent, even provoke it.
Since the disease is accompanied by pathological tissue proliferation and epithelial proliferation, it can lead to the formation of dysplastic cells and the appearance of tumors with malignant growth. Therefore, timely diagnosis of the disease and correct further tactics for the patient are so important - regular observation and preventive courses of therapy. For this, both hormonal and non-hormonal drugs can be used, incl. and homeopathic.
Diagnosis of mammary adenosis
Breast adenosis is one of the most common types of diffuse mastopathy. A distinctive feature of this pathology is the predominance of the glandular component in the structure of the mammary gland. Histologically, the disease is characterized by highly differentiated hyperplasia of the glandular tissue of the gland, namely the cells of the milk lobules, which normally produce milk during lactation. At the same time, the development of fibrous tissue occurs, which compresses the growing glandular tissue and, as a result of compression, damages the lobules.
The causes of mammary adenosis are a disruption in the production of hormones such as somatotropin, prolactin, estrogens, progesterone, insulin and thyroid hormones (thyroxine, T3). It is these biological substances that control the development of the mammary glands, the proliferation of glandular tissue in them and the formation of prolactin receptors in the lobules. Often the disease occurs during excessive synthesis of sex hormones, which is observed during puberty and pregnancy.
Sometimes adenosis is preceded by diseases of the reproductive system such as endometrial hyperplasia, ovarian dysfunction, ovarian cysts, in which the synthesis of estrogen predominates over the synthesis of progesterone. Fatty liver degeneration, hypo- and hyperthyroidism can also be precursors of mammary adenosis, as well as obesity. In adipocytes (adipose tissue cells), the “wrong” fraction of estrogen is synthesized. Symptoms of adenosis include engorgement and an increase in the size of the mammary glands. The glandular tissue grows evenly throughout the entire thickness of the glands and does not have clearly defined boundaries, so upon palpation it is rarely possible to detect any formations of a certain shape.
On the eve of menstruation, subjective signs become more pronounced. Itching in the nipples, a feeling of heaviness appears, and colostrum or serous discharge often occurs, sometimes greenish in color or mixed with blood. By the way, the appearance of blood from the nipples may indicate the development of a malignant tumor, so its exclusion is done first. Like other forms of mastopathy, mammary adenosis is diagnosed using instrumental and laboratory methods, questioning, examination and palpation.
Treatment
Treatment of this disease begins with a high-quality diagnosis using mammography and ultrasound, which is most effectively carried out on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle. If there is swelling, you can take diuretics, or a complex of vitamins to increase metabolism. For pain in the mammary glands, anti-inflammatory therapy is used.
If a nervous disorder occurs during the course of the disease, sedatives and antidepressants are prescribed. Much attention should be paid to vitamins. Their use alleviates the woman’s condition in general. For pain relief, you can additionally use ointments that help reduce inflammation and swelling.
In case of severe advanced form
FCM of the mammary glands in an advanced form is treated with surgery or puncture. If the diagnosis reveals diseases associated with mastopathy in endocrinology or gynecology, treatment is prescribed along with the recommendations of doctors in these areas.
For greater effectiveness, the diseases that cause FCM of the mammary glands are initially treated and hormonal therapy is used.
Non-hormonal treatments
Non-hormonal treatments include diet, taking vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs, and diuretics that improve blood circulation. The prescribed drug Mastodinon, which does not contain hormones, effectively reduces tumors.
It is also necessary to take products containing:
- phospholipids;
- zinc;
- carotene;
- selenium.
The duration of such treatment is approximately 4 months.
For FMC, vitamin therapy is carried out, which includes taking vitamins A, E, B, C, P, PP. The doctor prescribes iodine-containing medications (Iodine-Active, Iodomorin). Due to the psycho-emotional instability of patients, sedatives (valerian, motherwort) are used.
It is mandatory to take medications that stimulate the immune system. They are often replaced with herbal remedies (radiola, eleutherococcus). Medicines from the NSAID group form the basis of therapy (Nise, Indomethacin), which is supplemented with diuretics (Lysix, Fitolysin).
Common Causes
Breast adenoma can form for various reasons. The most important of them include:
- liver dysfunction;
- pathologies of the pancreas and thyroid gland;
- hormonal imbalance.
This disease can be caused by regular stress and nervous tension, for example, when breaking up with a man, problems at work, etc. This is due to the fact that in such situations the synthesis of corticosteroids in the body is significantly increased, which disrupts metabolism.
Factors that contribute to the onset of the disease include breastfeeding, pregnancy, dysmenorrhea (painful periods) and abortion. In addition, adenoma often appears in the presence of chronic forms of pathologies of the genital organs, due to abuse of oral contraception and smoking. Heredity is another common cause of cystic disease.
Hormone therapy
Hormonal drugs can be taken only after a blood test. The drugs are initially prescribed in a minimal dose, as side effects such as sleep disorders are possible. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
Treatment is prescribed by a highly qualified specialist, taking into account all the results of the preliminary examination:
- blood tests;
- Ultrasound;
- mammography;
- palpation.
For complete cure, hormonal drugs must be used for at least 4 months. It is preferable to use preparations that are herbal or for external use. Only in severe cases is it possible to use more serious hormonal medications.
Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a good help for the treatment of mastopathy. The current theory is that this treatment is used by administering small doses of the compounds that caused the disease. Remedies come in plant and animal bases. The components of these drugs are thoroughly diluted.
Homeopathic remedies have no side effects and are widely used as an addition to traditional treatment. They have a gentle effect on the body, are easily tolerated, and allergic reactions do not occur after taking them. You cannot take risks using products from manufacturers from Asian countries, which often have not undergone medical research in Russia.
Preparations:
- relieve swelling;
- pain stops;
- normalize hormonal levels;
- relieve inflammation;
- significantly reduce the risk of cancer.
Traditional methods of treatment
Tinctures, herbal decoctions, and prepared compresses have earned the attention of our grandmothers. The test of time has been carried out, and folk remedies actually confirm their effectiveness in the treatment of mastopathy. They have no contraindications and do not have an allergic effect on the body. Ointments can be combined with most medications.
Here are some plants that help in the treatment of mastopathy:
- Place the peeled burdock on your chest, secure it with a bandage or scarf, and leave it overnight. Apply several nights. Break – 2 days.
- Rub freshly prepared celandine juice and sunflower oil in equal parts daily onto the affected areas of the mammary gland for a month. Break - a week. When preparing this recipe, you must be careful, as celandine juice is highly poisonous.
- A cabbage leaf compress is called the most affordable known traditional medicine. It is applied to the chest for several hours, replacing it periodically with a new one. Hard veins are usually cut off. Honey added in a small amount will enhance the healing effect.
- 2 tbsp. Boil crushed oak bark and a glass of water until half a glass of water evaporates. Apply a compress to the inflamed area of the chest, wrap it in film, insulate it and hold it for 3 hours.
- Make small cakes from melted yellow honey and apply them overnight, securing them with a scarf or dressing.
- Dried rose hips, hawthorn berries in the amount of 2 tbsp. Boil 500 ml of water and let it brew. Take 50 ml half an hour before meals.
Why is mastopathy dangerous?
It is important to find out about the disease at the very beginning of its development. To avoid being at risk, every woman should be examined at least twice a year. The examination must be complete, including ultrasound and mammography. Mastopathy has a negative impact on a woman’s reproductive system and greatly worsens the condition of the thyroid gland.
During illness, the nervous system is severely depleted, headaches that appear aggravate this condition, appetite disappears, which subsequently leads to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If a woman misses the onset of the disease process and refuses treatment, there is a very high probability of developing cancer.
Mastopathy is associated with the genitourinary system. As a result of its development, gynecological diseases appear and libido decreases.
If diagnostic measures are carried out on time, qualified treatment is prescribed on time and the patient strictly complies with it, the possibility of a complete recovery without consequences is very high.
Diagnosis of localized mastopathy (localized fibroadenomatosis)
Localized mastopathy is one of the variants of nodular mastopathy; it is also called localized fibroadenomatosis. Oncologists and mammologists consider this type of mastopathy to be a precancerous process that increases the likelihood of developing breast cancer. Nodules can be multiple or single, located only in one or both mammary glands, so localized adenomatosis can be unilateral or bilateral.
In most cases, localized mastopathy develops against the background of manifestations of the diffuse variant of the disease. The tissues surrounding individual nodes are characterized by dense heaviness and rough lobulation and granularity. All this is accompanied by pain and discharge from the chest. The disease often occurs against the background of liver pathologies (hepatitis, cirrhosis), obesity, gynecological diseases, metabolic disorders (hypothyroidism, diabetes, etc.). It is believed that a predisposition to nodular mastopathy can be inherited.
The symptoms of this form of mastopathy are practically no different from other types of the disease. The only difference from diffuse mastopathy is dense formations of round shape and varying sizes that are visible upon examination or detected upon palpation. They may have a smooth, lobulated or granular surface, and pain may increase with pressure. This symptom is known to be similar to the symptom of breast cancer, so careful diagnosis is required. It includes not only ultrasound examination and mammography, but also puncture or biopsy of nodes and their histological analysis.
On a mammogram, localized mastopathy is characterized by the presence of darkened areas with a uniform structure and clear, even boundaries. Sometimes several forms of nodular mastopathy are combined simultaneously, which gives a motley radiological picture like a “lunar relief”. The levels of various hormones and tumor markers are determined in the blood so as not to miss the development of the early stages of cancer. If intraductal proliferation is suspected, ductography is performed - radiopaque examination of the milk ducts.
Cystic fibroadenomatosis
Cystic fibroadenomatosis has many different synonyms. In fact, this is a type of mastopathy, which is characterized by the formation of large elastic and dense cysts located tightly in relation to each other. More often they are localized in only one mammary gland, but sometimes in two. When pressing on the cysts and nipple, a fairly copious secretion is observed (sometimes in the form of a stream), which can have a different consistency and shade (brownish, greenish, etc.).
Cystic fibroadenomatosis develops on the basis of the milk ducts and small alveoli. First, small cysts form, which gradually merge with each other to form a large multi-chamber cyst. Papillary growths may appear on the walls of these cysts, lined with epithelium, so the disease must be carefully differentiated from breast cancer.
The diagnosis of the disease is based on the patient’s complaints, examination and palpation of the mammary glands, X-ray and ultrasound examination methods, laboratory test results, etc. Women usually complain of chest pain and a feeling of heaviness, which extend to only one or both breasts. Typically, these symptoms worsen before menstruation. In 15% of patients these symptoms are absent at all.
Palpation of the breast is informative mainly in the first half of the cycle. The doctor palpates and examines the glands, determining the presence of pathological formations. Ultrasound examination is a very accessible and informative method, but the technique is quite subjective and does not allow you to see the organ as a whole.
If there is discharge from the nipples, a cytological and biochemical study of the discharge is performed. Often a puncture biopsy of cysts is used, and color Doppler ultrasound is performed, which makes it possible to establish blood supply disturbances in the mammary gland, characteristic of a benign tumor, fibronodular mastopathy and cancer.
To identify the cause of cystic fibroadenomatosis, a specialist examines the patient for the presence of gynecological diseases, pathologies of endocrine organs, such as the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, etc. Very often, these pathologies accompany mastopathy, and their elimination helps improve the condition of the mammary glands.
Diagnosis of breast cyst
A breast cyst is a cavity formation surrounded by a connective tissue capsule and formed from the milk ducts. Often occurs against the background of fibrocystic mastopathy. Cysts can be single or multiple, unilateral or bilateral.
When palpated, cysts resemble small balloons, but sometimes they are hard. Their surface is smooth; when pressed, fluctuation is possible, which indicates the presence of liquid contents in the cavity. The formations usually have a round or oval shape. Women aged 35 to 55 years are more susceptible to the disease, especially those who have never given birth, which is always associated with hyperestrogenemia.
The main cause of the pathology is a disruption in the production of female sex hormones, estrogens and gestagens, and sometimes prolactin. The disease is often accompanied by other gynecological pathologies - ovarian cysts, adnexitis, endometriosis, etc. Symptoms of breast cysts are not always pronounced. They may be erased or absent altogether, for example, if the cyst is small and deep in location. In such cases, a cystic formation is detected incidentally during an ultrasound or mammogram.
Prevention of mastopathy
Regardless of the type and complexity of the disease, there are prevention methods that can prevent mastopathy of the mammary glands.
They are as follows:
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Adjusting your diet.
- Regular sex.
- Periodic examination by a gynecologist.
- Reducing stress load.
Doctors' advice and treatment reviews
Timely treatment helps to completely get rid of the problem. Many who discover breast lumps do not take any further action. All this leads to emergency surgery, without which advanced cases of FCM of the mammary glands cannot be cured.
After the intervention, the breast becomes deformed and requires even more expensive surgery. Doctors recommend being examined by a mammologist twice a year to avoid complications.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky