Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine does not appear as often as osteochondrosis in other parts, but it is just as young as other types of this disease. Today, it is diagnosed in 20-year-old young people, which is associated with both lifestyle and diet.
What is thoracic osteochondrosis?
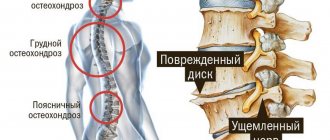
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative process that occurs in the spine between the 8th and 19th vertebrae. These vertebrae form the thoracic spinal column. And it is between them that changes occur in the vertebral discs when this type of osteochondrosis occurs. But due to the fact that this part of a person’s back is not as mobile as the rest, the changes that occur do not manifest themselves until it is too late and the disease progresses into an advanced phase, at which treatment becomes very problematic.
Therefore, it is so important that at the first symptoms of the disease, close attention is paid to them and measures are taken to prevent the development of the disease.
Symptoms
It is worth remembering that the initial stages of thoracic osteochondrosis do not manifest themselves in any way. This is why this type of disease is dangerous. Therefore, it is very important that immediately when the first signs appear, or if there is a hint of them, you should consult a doctor and carry out all the necessary tests and examinations.
Osteochondrosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Feelings of difficulty breathing.
- Feeling of tightness throughout the chest.
- It becomes more and more difficult to bend over. Moreover, this condition is progressing.
- Feeling of freezing of limbs. This occurs due to decreased blood circulation in them.
- Chest pain.
- There may be a burning sensation in the legs and feet.
- Keratin coatings (nails and hair) become brittle.
- Accompanied by thoracic chondrosis, the symptoms of which are similar to those of osteochondrosis.
- The gastrointestinal tract begins to work intermittently.
- Burning in the chest.
- Burning in the stomach area.
- Pectalgia – pain in the front of the chest.
- In men, potency decreases. The genitourinary system begins to malfunction.
- The person is feeling sick. Moreover, this condition also progresses.
- Headaches of varying severity, including migraines.
- Neuralgia of the chest, especially those localized in the ribs.
- On the left side of the body, pain may occur, similar to those that appear with cardiovascular disorders.
- Pain may affect the liver and gallbladder.
- Back and chest often reflexively.
- The appearance of herpes zoster (shingles).
- Signs of thoracic osteochondrosis in women include pain in the mammary glands.
- Discomfort in the throat and difficulty swallowing. A cough may appear, as if the larynx is irritated.
The appearance of several of these symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine requires an immediate and complete examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Dorsago and dorsalgia
Most often, thoracic osteochondrosis manifests symptoms and sensations in which the patient feels pain that varies in duration and strength. All pain symptoms are classified into two groups:
Dorsago - short-term acute pain. They occur when a person performs a monotonous load, that is, the muscles are in one position for a long period of time. The muscles become overstrained, causing sharp pain (neuralgia), which may also be accompanied by difficulty breathing. Dorsago occurs more often in women than in men.
Dorsalgia is prolonged pain. They become more pronounced when a person inhales. At first, the discomfort is mild and gradually intensifies. After 4 weeks, they become more pronounced and acute. The nature of the pain can be pulling, cutting, stabbing or some other type.
Pain due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is localized in the chest, shoulder blades, ribs, collarbones, and sides in the area of the ribs.
What happens at the very beginning of the disease
The initial stage of the disease does not manifest itself or does so in very mild, insignificant ways. You need to pay close attention to symptoms such as:
- I felt stiffness in my movements.
- The range of movements has decreased.
- There are signs of discomfort when bending, turning, bending or bending.
- Pain in the area between the shoulder blades in the chest.
These are sure signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, and to miss them means to transfer the disease to the next, more severe stage.
Chest pain
The main symptom that accompanies all stages of the disease is pain. It can be localized throughout the body to the waist area. So, the pain most often affects:
- The part of the back between the shoulder blades.
- Collarbones and areas below them.
- Ribs and parts of the body below them.
- Heart area.
- Pancreatic region.
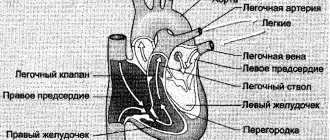
Due to the fact that the pain affects vital organs, such as the heart, thoracic osteochondrosis is confused with other diseases and treatment is prescribed incorrectly.
The thoracic spine consists of 11 vertebrae. And each of them, when damaged and degenerative processes occur, causes a certain type of pain or negative changes in various organs. So, in order to distinguish pain in the sternum with osteochondrosis from cardiac problems, you should understand how pain differs in the two cases. In addition, when chronic diseases appear, a person must be aware that they could be caused by degenerative processes in the spinal column.
| Categories | Cardiac problems | Thoracalgia (pain in the thoracic spine) |
| Nature of pain | The pain has the character of an attack when the thoracic region is affected, but it can be either aching or pressing. | Shooting sensation, burning, aching pain. |
| Place where pain occurs | Soreness is felt on the back, pain is localized behind the sternum. But it can radiate in all directions, both to the shoulder and down under the ribs. | The pain is often either point-like or encircling. But in any case, it is localized precisely at the level where the vertebra in the chest area is affected. The pain radiates to the collarbone, shoulder blade, and back. Women are more likely to experience discomfort in the chest area. |
| Duration | It occurs spontaneously and does not last long, up to 15–20 minutes, but if it is a heart attack, it may occur over a longer period of time. | It can last for several moments or, on the contrary, have a monotonous, long-lasting character, which is very exhausting for a person. |
| Reasons for exacerbation of the condition | Stressful situations, increased stress on the heart during physical activity. Prolonged stay in a horizontal position. | Uncomfortable position, sharp turns, bends, bends, palpation of the ribs or those areas in which pain is felt. |
If your heart hurts, then in order to know how to determine that it is a cardiovascular problem, you should take the appropriate medications and see if the symptoms go away. If not, then these are most likely signs of osteochondrosis.
Feeling of tightness in the chest
This feeling is reminiscent of the feeling when you cannot take in as much air as you want. A so-called incomplete breath appears. A feeling of tightness in the chest may be accompanied by pain in this area. Shortness of breath occurs with osteochondrosis.
This tightness in the chest can also occur with other diseases, such as pneumonia or heart problems. And to understand why the compression occurred, it is worth measuring the number of heart beats per minute. If it is 100 or more, then most likely it is a pulmonary or cardiac disorder. But if there are less than 100 beats, then, with almost complete certainty, we can say that the cause of incomplete breathing is thoracic osteochondrosis.
Other symptoms
As osteochondrosis of the thoracic region develops, additional signs and symptoms of the disease are added to the pain syndromes, such as:
- Tingling in the upper and lower extremities - a sensation of goosebumps running across the skin.
- Then numbness occurs. It can appear in one limb or all at once.
- Excessive sweating appears, and it is situational in nature, regardless of external conditions.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Cold sweat may appear on the forehead and even on the body. This condition resembles panic attacks.
If such symptoms appear for the first time, then you should definitely take a calm and relaxed pose, drink nitroglycerin and call a doctor. Since these may be symptoms of a heart attack, especially if all of the above is supplemented by pain in the chest. It's worth listening to yourself. If after taking nitroglycerin the condition has improved, then this is most likely a heart problem, and if not, then most likely these are symptoms accompanying thoracic osteochondrosis.
In addition, symptoms such as:
- Digestive disorders - this can be irregular bowel movements, accompanied by both constipation and diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain of unknown etiology often occurs.
- Bloating and increased flatulence may also occur.
- Exacerbation of gastritis.
- Nausea appears and vomiting may even occur. All this may be accompanied by loss of appetite.
In addition to all of the above, symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in men include disorders of the genitourinary system, which manifests itself most clearly in a decrease in potency.
But the peculiarities of the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in women include pain due to pathologies of the mammary gland. If pain in the mammary glands torments a woman, then in order to exclude diseases of the mammary glands and confirm thoracic osteochondrosis, you need to visit a mammologist.
The appearance of pain and the occurrence of various diseases with damage to different vertebrae in the thoracic region is expressed as follows.
| Thoracic vertebra number | Accompanying pain |
| 1 thoracic vertebra | When the first thoracic vertebra is damaged or degenerative changes occur in it, numbness appears in the upper limbs of both one and two at the same time. The pain spreads to the shoulders and forearms. May radiate to the hands. The muscles of the back of the head become tense. |
| Second | A state of panic attacks may occur; a person is accompanied by a feeling of fear. The heart rhythm is lost. |
| Third | The pain may spread to different parts of the chest. Cough often occurs with thoracic osteochondrosis, bronchitis, asthmatic condition and other disorders in the respiratory tract appear. |
| Fourth | The functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts is disrupted. Dyskinesia and gallstones may occur. There will also be pain on the right side in the shoulder and head. |
| Fifth | Problems with the liver, insufficiency of hematopoiesis and circulation. Hypotonic states and the associated feeling of chronic fatigue. Arthritis. |
| Sixth | Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. Often problems with the sixth thoracic vertebra are accompanied by heartburn and diabetes. |
| Seventh | Gastrointestinal problems - duodenal ulcer, heartburn, increased acidity, hiccups, nausea. General weakness of the body. |
| Eighth | The spleen suffers in this case. The body's immune system malfunctions, resulting in immunodeficiency. |
| Ninth | Allergic manifestations. |
| Tenth | Violation of water-salt balance and associated malfunctions of the kidneys. The arteries become calcified, which sharply reduces their elasticity. |
| Eleventh | A wide variety of skin problems, from dryness to psoriasis. |
What other pain syndromes exist for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region?
It is important to realize that pain is the companion that always accompanies osteochondrosis. It can manifest itself either very weakly, or it can lead a person to a state in which he will experience constant stress, since the pain is so strong that he will not even be able to take a comfortable position.
Speaking in general about pain, it is worth considering that it must be divided into:
- Local (local).
- Distant.
Local pain occurs precisely around the area of the spine where degenerative changes have occurred. When a person is bothered by thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain will be localized in the back and neck. The amplitude of possible movements decreases, and stiffness appears. All this is accompanied by either short-term pain, or they are permanent.
With distant pain, areas of the abdomen, heart area, arms, even legs are affected. There may be squeezing sensations, burning, and tingling. It is very important that distant pain is accurately diagnosed so as not to confuse its occurrence with any other disease.
Neuralgia of thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by such localization of pain that it is even difficult for the patient to take a breath. Intercostal neuralgia most often occurs precisely because of osteochondrosis in the thoracic vertebrae. But it is worth noting that there is no inverse relationship. That is, neuralgia does not lead to osteochondrosis. But neuralgia can be triggered by a rib fracture or other types of injury. In order to understand whether neuralgia arose precisely because of osteochondrosis, it is worth understanding how different the sensations are with these changes in the body.
| Main signs of neuralgia and osteochondrosis | Neuralgia | Osteochondrosis |
| Type of pain | The pain is sharp, piercing. Looks like an injection. | The pain is rather aching with a burning sensation. |
| Location of pain | On the sides of the body in the places where the ribs are located. | In the area and between the shoulder blades, in the back and in the armpits. |
| Time of onset of discomfort | The pain intensifies during a sigh or during a turn. | Pain with thoracic osteochondrosis occurs after prolonged stress on the body, that is, towards the end of the day. As a rule, it goes away or decreases after rest, either during the day or at night. |
Treatment
Only a holistic approach to treatment will make it possible to put an end to absolutely all signs of osteochondrosis, to suspend or completely stop its spread to healthy discs and vertebrae. For pathology of 1-2 degrees, conservative methods of therapy are used. Osteochondrosis of levels 3-4 is characterized by the formation of large hernias. In order to eliminate their compression of blood vessels and spinal roots, surgical treatment may be necessary .
Medications
In the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, medications are used - substances from different clinical and pharmacological companies. At the initial stage, intravenous agents are used, which quickly have a therapeutic effect. After a few days, injection solutions are replaced with tablets, ointments, and patches.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDs have pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-edematous effects. Intramuscular injection of solutions will allow localization of sharp pain .
To eliminate minor discomfort between the shoulder blades, topical agents are used. And for moderate pain, NSAIDs taken orally will cope well.
Muscle relaxants
To eliminate muscle spasms that form in response to severe pain, muscle relaxants Sirdalud and Baklosan (Baclofen) are used.
Chondroprotectors
In case of level 1 pathology, a course of chondroprotectors promotes the regeneration of damaged discs. In other cases, drugs are prescribed to improve metabolism in the affected sector of the spine and prevent the progression of the disease .
B vitamin preparations
Vitamins are included in the drug regimens of patients with pathology of any severity level. Their use helps to increase blood flow, improve the activity of the peripheral nervous system, and restore trophism and innervation.
The combination of B vitamins has a good effect on degenerative diseases of the nerves and musculoskeletal system.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
In the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF therapy, sinusoidal currents, shock wave therapy, applications with paraffin and ozokerite are used. During exacerbations, electrophoresis and ultraphonophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, anesthetics, B vitamins, and chondroprotectors are performed.
Massage and manual methods
Massage helps eliminate pain between the shoulder blades and relax spastic skeletal muscles.
For osteochondrosis, all types of massage are therapeutically effective - traditional, vacuum, acupuncture, connective tissue .
At home, massage can be comfortably performed using an electric massager with a long handle.
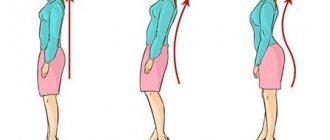
Gymnastics and exercise therapy
With level 1 thoracic osteochondrosis, daily physical therapy exercises make it possible to do without the use of medications. Treatment is carried out by maintaining muscles and improving the blood supply to tissues with nutrients. In other cases, gymnastics and regular exercises can help prevent the inclusion of healthy spinal parts in the destructive process and continue the remission stage.
A set of exercises at home
Exercises while standing:
- bend forward, raising alternately bent legs;
- bending to the side with arms raised alternately;
- bend forward, trying to reach the opposite foot with your hand.
The number of repetitions is 10-12 times in 2-3 approaches.
For exercises in a lying position, you will need a sports carpet or a thick, double-folded blanket:
- lying on your stomach, raise your legs and arms at the same time;
- lying on your back, raise your upper body, reach your hands towards your feet;
- Lying on your back, bend one leg and bring it behind the other, trying to touch the floor with your knee.
Each lesson must be performed 7-10 times.
We invite you to watch a video about a set of exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis:
Folk remedies for chondrosis
Neurologists can use decoctions and infusions of pharmaceutical plants, ointments, alcohol and oil rubs, compresses after performing the main therapy.
Folk remedies are used to eliminate minor ailments between the shoulder blades, sometimes appearing after physical activity. Celery and sunflower roots are used, and you can also make a homemade ointment .
Features of therapy during exacerbation
Treatment involves:
- localization of symptoms with local painkillers and analgesics for internal use;
- bed rest;
- wearing a corset to fix the vertebrae.
If the exacerbation is severe, you must call an ambulance. When admitted to the hospital, the doctor will monitor the patient’s condition and select the necessary medications for him.
How to relieve an attack?
The pain during relapse of thoracic osteochondrosis can be acute and piercing, so first aid should be provided. The patient must be reassured, placed on a hard surface, and covered with a warm blanket. If the recurrence is accompanied by increased heart rate, shortness of breath, or high anxiety, then you need to call a doctor. To relieve pain, you can take any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Causes
Thoracic osteochondrosis appears as a result of a number of the following reasons:
- Hereditary factor.
- Unnecessary and excessive physical activity.
- Lifting a weight from an incorrect position.
- Physical inactivity, which deprives a person of sufficient blood circulation in all tissues.
- Postural defects (curvature of the spinal column, for example, thoracic scoliosis).
- Injuries, damage or bruises to the chest and spinal column.
- Inconvenient shoes, especially those that lead to incorrect position of the spinal column - high heels.
- Bad habits.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Exhausting physical labor.
- Disruptions in the blood supply to the spinal cord.
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the bone structures of the spine.
- Changes in the cartilage tissues of the spine.
- Hypothermia.
- Any changes in the intervertebral discs, including vertebral hernias.
The period of pregnancy in a woman can affect the formation of thoracic osteochondrosis. This is due to the fact that the load on the spinal column increases along with resource costs. As a result, there is a lack of micro- and macroelements, as well as vitamins.
Excess body weight. Moreover, it is enough to have 10% more than normal weight to increase the load on the entire spinal column.
Neuromuscular shock absorption disorders. This occurs when the muscle does not fully compensate for the shock loads that can affect the body. As a result, an intense “blow” falls on the human skeleton, namely the spine. As a result, damage occurs.
Osteochondrosis can occur only under the influence of several factors, as in principle any disease. Therefore, what can be excluded from the list of causes should be eliminated. For example, bad habits, physical inactivity or heavy lifting. Take control of stressful situations.
Classification
The classification of thoracic osteochondrosis is based on the syndromic principle. Depending on which nerve formations the affected structures of the spine affect, the following syndromes are distinguished:
- compression - its development is based on tension, deformation or compression of a nerve root, a section of the spinal cord or a blood vessel, depending on which spinal, vascular or radicular syndromes develop;
- reflex – associated with reflex tension of innervated muscles, dystrophic and vascular disorders;
- myoadaptive.
Signs in the subacute stage
The subacute stage occurs when the acute stage has passed. During this period, the person no longer experiences difficulty breathing. There is no pronounced pain, the symptoms become more subdued. A person falls asleep easier because it is easier for him to take a comfortable position while sleeping.
To prevent the subacute stage from becoming acute again, you should avoid:
- Lifting weights.
- Performing incorrect bends.
- Do not take static poses for a long time, especially if they are unnatural for the spine. These poses also include a sitting position.
- Hypothermia.
Usually the subacute stage lasts about 2 weeks. If the regimen and doctor’s recommendations are not violated, then most often a remission occurs, in which all symptoms disappear. Further, the patient’s task is to prevent the exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine by treatment, for example, with exercise therapy methods, folk remedies, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet.
But if during the subacute stage the following sensations arise, then you need to pay close attention to them:
- Renewed stiffness and inability to raise your arms, even if not accompanied by pain.
- Increasing pain if it has not gone away completely or pain attacks last longer.
- Dizziness and feeling of nausea.
As soon as this happens, it is possible that the subacute stage again turns into acute. You should consult a doctor and fully describe the sensations that arise.
Prevention
In order to never experience what osteochondrosis is (especially if you don’t move much or already have scoliosis), pay attention to the following preventive measures:
- Don't get too cold.
- Do not lift weights suddenly: this should happen after preparation.
- Watch your posture when sitting and walking. You can install an ergonomic chair in the car that will keep your back straight.
- Be sure to take breaks while working: get up, walk, perform self-massage of your back - so that the spine receives enough nutrition.
- Don't let your scoliosis get worse: treat it on time.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Avoid dishes containing smoked meats, marinades, and spicy seasonings. Fried foods will also have to be removed.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and a low (or also orthopedic) pillow.
Author:
Krivega Maria Salavatovna resuscitator
Degrees
After the symptoms have alerted the person and he has consulted a doctor, a comprehensive examination is prescribed. During which, if osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is confirmed, the doctor will determine the extent of the disease.
First degree
Osteochondrosis of the 1st degree of the thoracic spine is characterized by the onset of changes in the intervertebral disc. As a result, already at this stage protrusions may appear and the disc protrudes into the spinal canal. But at this stage there is no rupture of the fibrous ring. In the first degree of the disease, no pain syndromes appear.
Second degree
At the second stage, discomfort appears in the spine. There may be obvious pain, dizziness and a feeling of nausea. In the second stage, the discs protrude into the spinal canal so intensely that they lead to rupture of the fibrous ring, which leads to the formation of intervertebral hernias.
Third degree
The stage of active manifestation of intervertebral hernias with all the ensuing consequences, such as pain and limited mobility.
Fourth degree
The elasticity of the intervertebral discs is completely lost. In addition to pronounced hernias, destruction of the bone structures of the vertebrae also occurs. Bone growths – osteophytes – appear.
Diagnostic measures
The thoracic region should begin to be treated after a comprehensive examination of the patient. It involves performing these procedures:
- The patient is examined and all his observations regarding the course of the disease are recorded. If the disease reaches stage 2-3, the skeleton becomes noticeably deformed. The physician is obliged to take a history of the patient in order to exclude/confirm hereditary factors for the development of osteochondrosis of the chest.
- It is necessary to donate urine and blood for analysis.
- Using radiography, you can establish:
- Presence and size of osteophytes;
- Determine the height/contours of the intervertebral discs.
- Size/localization of hernias;
- Presence of changes in the shape of the disk.
- Discography will provide an opportunity to examine the outlines of the nucleus pulposus. This procedure uses contrast.
- CT scan. This study is used extremely rarely, since during this study the patient is heavily irradiated.
- Electrocardiography. Since the symptoms of thoracic chondrosis are similar to ischemic heart disease, this research method is used to verify this diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Many who first encountered the signs of this disease are concerned with the question - how to determine osteochondrosis in the thoracic region?
The disease is insidious, as it may not manifest itself for a long period of time or disguise itself as other diseases. In this connection, when the patient consults a doctor, he is already diagnosed with a progressive advanced stage of osteochondrosis.
Therefore, it is important, as soon as the first suspicions appear with the first symptoms of the disease, immediately consult a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination in order to accurately diagnose, determine the stage and correctly prescribe comprehensive treatment. Even if the doctor prescribes only drug treatment, it is necessary to ask about exercise therapy, physiotherapy and other therapeutic actions.
When diagnosing, a neurologist can:
- Make a primary diagnosis based on the symptoms the patient describes.
- During the examination, the doctor palpates the areas that the patient points to and examines how severe the pain is.
- Certain functional tests help the doctor assess how intact reflexes and sensitivity are.
- X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs may be prescribed.
- A neurologist may prescribe an ECG in order to exclude interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
After a comprehensive examination has been carried out, the doctor, upon confirmation of osteochondrosis, prescribes treatment that is designed to alleviate symptoms, stop the development of the disease and, if possible, restore functionality to the body.
Remission
In the acute stage of the disease, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Cough with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
- Various symptoms of thoracic neuralgia.
- Pain syndrome that can manifest itself in different places of the upper body.
- Discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the chest area and directly in the middle between the shoulder blades.
- The temperature may rise with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in an advanced form.
If proper treatment is carried out and the symptoms are relieved, then the remission stage begins. During this period, it is important to prevent the recurrence of all of the above symptoms.
As soon as the condition returns to normal, it is necessary to perform feasible physical therapy exercises; if the degree of the disease does not allow this, then at least do intense walking.
Complications
The disease occurs infrequently, but has very serious consequences if it is not treated correctly, is misdiagnosed, or is inattentive to one’s health. Therefore, the doctor must carefully monitor the entire medical history and draw up a call card, especially if thoracic osteochondrosis cannot be stopped and it develops into more severe forms.
Sometimes the disease causes myositis of the chest muscles, when the muscular frame is so weak that it is unable to support the spinal column, and sometimes the patient even finds it difficult to perform the simplest self-care skills.
Radiculitis of the chest often occurs due to damage to the nerve roots.
A chest fracture may occur. The reason for this may be bruises and blows. Or it can arise in a completely “empty” place. In this case, signs of a chest fracture include difficulty and inability to take a breath and move. If the fracture occurred without external influence, then special attention should be paid to this, as this may serve as the first symptoms of cancer and osteoporosis. Chest cancer develops under the influence of many factors, but the main ones include heredity, stressful situations, obesity, unfavorable environmental conditions, etc.
It is necessary to monitor your health very carefully and lead an active and healthy lifestyle without bad habits.
Nutrition
The causes of chest pain can be caused not only by osteochondrosis, as discussed above. But in any case, despite your age, you need to pay attention to your diet.
Treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine must necessarily be accompanied by a balanced diet. It will allow the body to receive all the nutrients that the tissues of the spine and muscle corset need.
Nutrition for thoracic osteochondrosis can be divided into two categories of people who need it:
- Those who are not overweight.
- Those who are overweight.
For anyone who has developed osteochondrosis or has a tendency to do so, we can recommend regularly including the following foods in their diet:
- Nuts, seeds, eggs, high-quality dairy and fermented milk products, cabbage (broccoli, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi), any leafy greens (cilantro, dill, parsley, celery). All of them are rich in calcium. Moreover, it is important to remember that calcium is better absorbed by the body if it has not been subjected to heat treatment.
- Nuts, bananas, dark chocolate, dill, parsley, cilantro, avocado, beans, chickpeas, lentils - they contain a lot of magnesium, and it affects the nervous system, reducing the manifestation of neurology in osteochondrosis.
- Sea fatty fish, different types of cabbage, hard cheeses and cottage cheese. They contain a lot of phosphorus, which is a building material for bones and cartilage.
- Fruits and berries, especially red or orange, especially peaches and apricots, also carrots and green peas. There is a lot of vitamin A, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels.
- Meat, fatty cold-water sea fish, avocados, high-quality unrefined cold-pressed vegetable oils. These products will become a source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are a nutritional element for both blood vessels and cartilage tissue.
- The body will fully receive B vitamins from cereals such as buckwheat, millet, millet, kamut, and quinoa. It is worth considering that quinoa is an intense source of protein that can practically replace meat.
- Sour fruits, such as citrus fruits, rose hips, black and red currants, gooseberries, sea buckthorn, viburnum, sauerkraut will give the body the right amount of vitamin C, which, with its antioxidant properties, can have a rejuvenating and regenerating effect not only on blood vessels, but also on bone and cartilage structures.
These products should be the basis of the diet for both people with normal weight and those who are overweight.
Since excess weight is one of the factors that can provoke the appearance of thoracic osteochondrosis, in this case the diet should be aimed at reducing body weight.
The following foods and dishes should be completely excluded from the menu:
- fast food;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- ready-made breakfasts - due to the fact that they contain excessive amounts of sugar;
- confectionery products, especially industrial ones;
- products containing sugar should be kept to a minimum;
- pickles - since you need to try to remove excess salt from the body;
- overly spicy dishes - as they whip up the appetite.
You should also limit all baked goods. They do not carry any nutritional value other than energy. In addition, you need to be very careful with beef and pork fat, as they are refractory. Therefore, their consumption leads to the deposition of cholesterol plaques and blockage of blood vessels, which further reduces blood circulation and a general deterioration in the nutrition of the affected tissues.
In order to lose weight, you can try different diets. For example, rice or salt-free. But it’s always worth remembering that staying on a diet for too long can have negative consequences.
It is important that the entire daily diet includes more protein and plant foods and less carbohydrates. In addition, it is important that the calorie content is within the following limits:
- for men – 3 thousand kcal;
- for women – 2100 kcal.
The number of meals per day should be at least 4–5. And the volume of clean water drunk is about 2 liters. And do this fractionally and often throughout the day. This will flush out unnecessary salts from the body and give elasticity to the cartilage tissue.
Recommendations
It is very important to prevent the disease from occurring. To do this, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle with a proper diet and nutrition, sufficient but not excessive exercise and the exclusion of stressful situations.
If the disease has already been acquired, then it is important to start treatment as early as possible. Therefore, you should treat your body with due attention so as not to miss the first bells signaling problems in the spine.
If a diagnosis is made of thoracic osteochondrosis, then you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take treatment seriously.
It must be remembered that the process of degenerative changes is considered irreversible by most doctors, therefore, for a quality life, it must be stopped as early as possible.
Consequences
If left untreated, the consequences of osteochondrosis can be catastrophic. Degenerative changes provoke the appearance of a hernia of the spine . Compression of the nerves leads to loss of sensation in the limbs . The most serious complication is paralysis of the arms or legs.
In addition, the functioning of all internal organs and systems is disrupted : cardiovascular, urinary, digestive. The patient develops vegetative-vascular dystonia. The fact is that the spinal vessels are compressed, and the oxygen supply to the brain is disrupted. The patient experiences constant headaches, panic attacks, and sleep disturbances. Intercostal neuralgia is also a consequence of osteochondrosis.