The author of the article is Olga Petrovna Chuklina, general practitioner, therapist. Work experience since 2003.
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an infectious disease in which inflammation of the tonsils occurs.
A person has a lymphoid ring in the pharynx formed by several tonsils, but tonsillitis is predominantly affected by the palatine tonsils.
It is still incorrect to call acute tonsillitis a sore throat, since in world practice the term “angina” refers to angina pectoris (“angina pectoris”).
Acute tonsillitis (J03)
If it is necessary to identify the infectious agent, an additional code (B95-B98) is used.
Excludes: pharyngotonsillitis caused by herpes simplex virus (B00.2)
Tonsillitis (acute):
- NOS
- follicular
- gangrenous
- infectious
- ulcerative
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without further clarification.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
Source
International classification
All diseases in the world are divided into groups and strictly classified.
A doctor can diagnose a patient only on the basis of the international classification. This is done so that doctors all over the world understand each other and equally assess the patient’s condition.
Lacunar tonsillitis also has its own code. According to the latest 10th revision of the classification, it is classified as acute tonsillitis (respiratory diseases) under code J03.
Follicle sore throat code ICD
During the course of follicular tonsillitis, the formation of follicles occurs, which look like formations of a yellow or white-yellow hue, which penetrate through the inflamed mucous membrane of the tonsils. They are no larger than the head of a pin.
If a patient has follicular tonsillitis, then his lymph nodes are enlarged and cause him pain during palpation. There are cases in which the follicular form of tonsillitis affects the increase in the size of the spleen. This illness lasts about five to seven days and is characterized by symptoms such as fever, vomiting and diarrhea, and sore throat. What other type of sore throat is there? The classification of tonsillitis (ICD 10 J03) is ongoing.
Treatment of follicular tonsillitis in adults
On the first day after the development of follicular tonsillitis, swabs from the patient’s throat and nose should be taken for Lefler’s bacillus (the causative agent of diphtheria), with which it is necessary to differentiate the sore throat. After this, treatment of the disease begins.
Effective treatment with medications is impossible without strict adherence to the following instructions:
Bed rest, refusal to stay outside for 5-6 days to avoid a sharp deterioration.
Drink plenty of warm drinks, especially still mineral water, milk with soda, herbal teas with rose hips, chamomile and sage. In order not to injure the inflamed mucosa, the temperature of the liquid should not be too high.
The diet should be uniform, since when swallowing solid food significantly increases pain, the diet should be formed from liquid broths, soups, cereals
It is also important to ventilate the room frequently and clean the room regularly (daily). Since the disease is quite contagious, it is necessary to isolate the patient and provide individual utensils and care items. The room where the patient is located must be cleaned and ventilated daily.
Gargle constantly. To do this, you can prepare anti-inflammatory and antiseptic solutions at home, or purchase them ready-made at the pharmacy.
Antibiotics
Drug treatment of follicular tonsillitis necessarily includes broad-spectrum antibiotics. Their main task is to destroy the causative agent of the disease.
The following antibiotics are widely used for follicular sore throat:
- benzylpenicillin;
- amoxicillin;
- summed;
- erythromycin.
The prescription of a particular drug for follicular tonsillitis should be etiologically justified and pathogenetically targeted.
A mandatory rule for all infectious disease specialists is to exclude the use of antibacterial drugs when the bacterial nature of follicular tonsillitis is not established, which is quite common in pediatric practice.
Medications
Follicular tonsillitis is characterized by increased body temperature and pain of varying intensity. If necessary, the doctor prescribes medications to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
- After taking antibiotics, it is advisable to prescribe probiotics to restore the intestinal flora - these can be the drugs “Linex”, “Bifiform”, or “Bifidumbacterin”.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin); rinsing should be frequent (2-3 times per hour), since the purpose of this procedure is not only to suppress microorganisms, but also to cleanse the surface of the tonsils from purulent deposits, and therefore prevent further spread of infection;
- Antihistamines such as Fenistil, Suprastin, Zyrtek or Zodaka relieve swelling in the throat and reduce the severity of the body's allergic response to antibiotics.
- The disease is often accompanied by rhinitis, which requires the use of nasal drops. For example, the drug Derinat, in addition to affecting the source of inflammation, also has an immunomodulatory effect, so it is often used in pediatric practice.
Surgery
The main indications for this procedure are:
- ineffectiveness of antibacterial treatment;
- enlarged tonsils, making swallowing and breathing difficult;
- spread of the purulent process to nearby tissues.
The doctor recommends various methods of tonsillectomy:
- wire loop and scissors method;
- electrocoagulation or ultrasonic scalpel;
- radiofrequency ablation;
- removal of tonsils with a cablator;
- carbon dioxide or infrared laser.
In the absence of dangerous complications from the heart, kidneys, or musculoskeletal system, the prognosis for follicular tonsillitis is favorable.
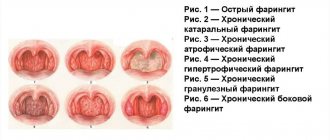
Kinds
Sore throat can occur in various types, including the nature of the pathology, the volume of the affected mucosal surface and the severity of the inflammatory process. The following types of sore throats are distinguished.
Catarrhal tonsillitis
In the catarrhal form, the damage to the tonsils is superficial. Intoxication in patients is moderate. The increase in temperature is observed slightly and sporadically. A visual examination of the pharynx confirms swelling of the soft and hard palate. The spread of the inflammatory process occurs in the superficial area of the pharynx. The duration of the disease in children does not exceed 2 days, after which the symptoms subside. In this case, the transition of the catarrhal form to the follicular or lacunar form is not excluded.
Herpangina
More often, herpetic tonsillitis occurs in young children. The main causative agent of the pathology is the Coxsackie virus group A. The disease is particularly contagious, so it is important to isolate the sick child from other children. Infectious microflora is transmitted by airborne droplets. In children, the pathology always manifests itself acutely and progresses quickly. The main symptoms are:
- high body temperature;
- soreness of the larynx of varying intensity;
- pain in muscle structures, dyspeptic disorders.
At the first stage, reddish-whitish bubbles form on the tonsils, palatine arches and soft palate. After about 4-5 days, the vesicles resolve, and the mucous epithelium takes on its previous appearance.
Lacunar tonsillitis
With the intensive development of this form, the tonsils are damaged in the lacunar space. The mucous epithelium is lined with purulent plaque, which tends to spread to the tonsils. Among the main symptoms are:
- increased body temperature;
- joint pain;
- pain in the projection of the heart;
- constant headaches.
On physical examination, the tonsils are infiltrated, swollen, and have traces of redness. The lacunae are expanded, and the cavities are filled with purulent contents.
Follicular tonsillitis
Damage to the follicular apparatus of the tonsils leads to characteristic symptoms: fever, intoxication, swelling of the tonsils, and the formation of a purulent infiltrate. On physical examination of the pharynx, suppurating follicular fragments are noted, which are visible through the thin epithelial layer of the mucosa. Clinicians call the syndrome “starry sky.” As the pathology develops, the affected follicles open, forming a purulent plaque that does not extend beyond the tonsils.
Fibrinous form of sore throat
This clinical form is characterized by the appearance of fibrinous plaques of a yellowish white color in the tonsil area, as well as the development of regional lymphadenitis. Pathology can occur as an independent pathological process or develop due to the course of lacunar tonsillitis. Among the main symptoms are the appearance of severe intoxication, pain when swallowing, the formation of a continuous fibrinous film lining the surface of the tonsils, as well as chills, fever and, in rare cases, serious brain damage.
Phlegmonous form of sore throat
In clinical practice, the pathology is also called intratonsillar abscess. The disease is characterized by a one-sided course; progression of phlegmonous tonsillitis occurs quite rarely. The main symptoms are:
- sore throat when swallowing or talking;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- increase in body temperature.
At the same time, joint pain, nausea, and loss of appetite appear. The affected tonsil increases in size, its surface is very tense, swollen, and there are signs of hyperemia. On palpation, patients experience severe pain.
Necrotic form
The clinical form of angina has the most striking symptomatic course, regardless of the patient’s age. Necrotizing tonsillitis has serious complications in the absence of adequate therapy or self-medication. The main features are:
- swelling and redness of the larynx;
- nausea, vomiting;
- disturbance of consciousness.
The surface of the tonsil is lined with a gray or yellowish coating. The affected areas are abundantly saturated with fibrin and change to a more dense structure. When they are removed, a permanently bleeding wound remains. When necrotic areas are rejected, a defect of 1.5-2 cm remains.
Ulcerative-membranous
The main difference between the form is the absence of hyperthermia; a rare cause of occurrence is damage by a spindle-shaped rod or symbiosis of a spirochete. Visually, there is a necrotic lesion of the pharyngeal surface of the tonsil and the subsequent formation of an ulcerative lesion. Symptoms include:
- foreign body sensation;
- bad breath;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The disease can last from 1 week to a month, so it is important to start timely treatment to avoid serious complications.
Each type of angina, as it develops, is a complication of the previous one and requires serious therapeutic intervention. Children's forms of sore throat are much more difficult to tolerate, so the first symptoms literally immediately after inflammation.
Treatment
If you have a severe sore throat, it is very important to seek medical help promptly. The doctor will be able to correctly determine the type of sore throat and prescribe effective treatment. Possible development of tonsillopharyngitis, respiratory failure, convulsions, disruptions in the cardiovascular system, pulmonary inflammation, folliculitis (infection of hair follicles)
Possible development of tonsillopharyngitis, respiratory failure, convulsions, disruptions in the cardiovascular system, pulmonary inflammation, folliculitis (an infection of the hair follicles).
For a correct diagnosis, a visual examination is sufficient for an experienced doctor. A blood test and the result of a smear of throat mucus will help confirm it.
Treatment is aimed at:
- Elimination of the pathogen.
- Alleviation of the patient's condition and elimination of symptoms.
- Boosting immunity.
Prevention
Sore throat can be avoided by following simple preventive recommendations. They provide:
- General strengthening of the body. Taking vitamins, regular exercise, hardening.
- Disinfection of all things in the house after one of the family members had a sore throat. This measure will allow you to avoid re-infection.
- Timely and complete treatment of various respiratory diseases, as well as dental caries. These ailments can also trigger the development of sore throat.
- Compliance with quarantine in the office, schools and circles where a person with a sore throat was found. Quarantine in such cases must be established immediately.
This measure will allow you to make sure that you have completely coped with the disease, and it will not bother you in the future.
Folk recipes
It should be remembered that folk recipes do not replace drug treatment, and before using them you should consult a doctor.
- Gargling with soda, salt and iodine. In a glass of boiled water, put half a teaspoon of salt, the same amount of soda and 3 drops of iodine. Stir thoroughly. You can use sea salt instead of table salt.
- Grate raw beets (1 cup of prepared mass), add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of apple cider vinegar, mix and leave for 4 hours in a cool, dark place. After this, the composition is filtered and used to gargle.
- You can fight the infectious pathogen with the help of propolis. Chew a small piece of the product until soft and place it behind the cheek for 30-40 minutes.
- Using aloe: take the lower leaves, rinse them with running water, then rinse with boiled water, dry a little, chop and squeeze out the juice. The resulting juice should be diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio and gargled every time after eating for several days.
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis
The main thing during therapy in a child and an adult is to suppress the infectious environment and prevent background infections. This is achieved by taking antibiotics, without which all other medical procedures will be a waste of time.
Yes, attention should be paid to symptomatic treatment for lacunar angina, but this is pointless without suppressing the bacterial environment
Successful treatment requires a set of therapeutic measures, including three stages:
- Elimination of infectious causes by taking systemic antibacterial agents and antibiotics.
- Direct treatment of the source of the inflammatory reaction using antiseptics for rinsing and surface application.
- Taking medications aimed at suppressing the most pronounced and dangerous symptoms, for example, antipyretics at elevated temperatures in adults above 38.5, and in children above 38 degrees.
How to be treated with antibiotics
Only a doctor is competent to prescribe such drugs; lacunar tonsillitis is usually treated with Cephalexin, Sumamed, Gramox, Ampicillin and other drugs. The treatment lasts for about a week, otherwise a relapse is possible.
Proper antibiotic treatment provides:
- Complete suppression of infection;
- Elimination of background ailments that aggravate the consequences;
When selecting an antibiotic, it is important to maintain a balance between its effectiveness and harm, which is especially important for young children and adults in a state of immunodeficiency. A side effect of any antibiotics is intestinal dysbiosis, so at the same time you should always use probiotics and drugs that help restore normal intestinal microflora. A side effect of any antibiotics is intestinal dysbiosis, so at the same time you should always use probiotics and drugs that help restore normal intestinal microflora
A side effect of any antibiotics is intestinal dysbiosis, so at the same time you should always use probiotics and drugs that help restore normal intestinal microflora.
Other medicines
Additionally, therapy against lacunar tonsillitis is carried out:
- Antihistamines that reduce swelling, making a person breathe easier and reduce sore throat.
- Periodic irrigation of the throat, for example, with Hexoral, which has an antimicrobial effect. Other sprays are also used, which must be applied twice a day throughout the entire treatment process.
- Another type of local effect is preparations in the form of sucking lozenges such as Strepsils. They are well received by young children as they are perceived as sweets.
- Lubricating with Lugol is prescribed up to 5 times a day, based on the phase of the sore throat.
- Antipyretics are used for elevated temperatures, which are unnecessary and only cause more severe symptoms. This mark is taken to be 38 degrees.
- Immunomodulators are prescribed for severe internal weakness of the body in adults and children; treatment is carried out with Lykopid, Polyoxidonium.
How to gargle
The purpose of rinsing for lacunar tonsillitis is to remove purulent plaque from the tonsils and have a local effect on pathogenic microflora. Procedures are carried out for children and adults at home 3-5 times a day. Typically, a solution of 2% soda or salt is used for this.
In addition, you can gargle with a sore throat:
- Kalanchoe juice, obtained by squeezing the leaves or purchased at the pharmacy. To prepare the solution, one part of the juice is diluted with one part of warm water. It is recommended to repeat the procedure after 3-4 hours.
- Rinse with beet juice. A very affordable method of treatment, beets are crushed using a grater, vinegar is added to it in the amount of one tablespoon. After infusion and straining, the medicine is diluted with warm water.
Question answer
Is it possible to remove pus from lacunar tonsillitis?
It is dangerous to remove purulent deposits on your own with a cotton swab or spatula; you can injure the inflamed tonsils. Doctors recommend gargling with antiseptic solutions.
Lacunar tonsillitis: can it be cured without antibiotics?
Acute tonsillitis cannot be treated without antibiotics. This will lead to the spread of infection to adjacent tissues and the formation of a retropharyngeal abscess. If streptococci penetrate through the blood into the myocardium, kidneys or joints, severe damage to these organs will occur.
Lacunar tonsillitis: can you be cured by the sun?
Ultraviolet light will not affect bacteria in the mouth. Their activity can only be suppressed with antibiotics.
Can lacunar tonsillitis occur without fever?
In rare cases, the body may not respond with an increase in temperature. But this does not mean the course of the disease is mild; the risk of complications remains.
Lacunar tonsillitis: is it possible to go to work?
The disease is accompanied by intoxication and fever and can lead to serious complications. This condition cannot be tolerated on your feet. The sick person becomes a source of infection and can infect others. Therefore, you need to stay home while you are sick.
Diagnosis of the disease
The development of follicular tonsillitis directly depends on the physiological significance of lymphoid follicles and lacunae of the tonsils.
The structure of the tonsils is determined by their protective functions:
- capture, absorption and neutralization of all foreign agents (pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, fungi or their associations);
- the formation of specific immune defense cells (T - and B - lymphocytes), providing local cellular immunity in the nasopharynx.
The palatine and pharyngeal tonsils are located superficially, and constant contact with infectious agents that settle on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and upper respiratory tract, combined with decreased immunity, causes the occurrence of various forms of acute inflammatory process - tonsillitis or sore throat
Factors predisposing and provoking follicular tonsillitis:
Reduced immunological reactivity of the body:
- general and local hypothermia;
- prolonged stress;
- hypovitaminosis, anemia;
- eating disorders;
- frequent physical activity.
- Foci of chronic infection (sinusitis, caries, adenoids, otitis media, tonsillitis).
- Family predisposition - structural features of the tonsils and/or immunity disorders.
- Bad habits (smoking), constant irritation by mucous dust, chemical and physical factors.
There are two methods of infection:
- Exogenous - a pathogenic agent enters with infected air, droplets of mucus when coughing, sneezing, with food and water, transmission is also possible through dirty hands and toys.
- Endogenous - the pathogen circulates in the body and is activated against the background of a decrease in immunological reactivity.
Most often, follicular tonsillitis is caused by streptococci (90% of all cases).
The causative agents of the infectious process in follicular angina include:
- pathogenic streptococcus;
- staphylococci;
- pneumococci;
- fungi of the genus Candida;
- viruses.
Establishing a diagnosis requires the following activities:
Finding out the patient's medical history and complaints
The doctor pays special attention to the duration and intensity of pathological symptoms. Visual examination of the throat. A preliminary diagnosis is determined by enlargement of the tonsils, redness of the mucous membrane and the presence of white purulent spots in the throat
In some cases, specialists resort to laboratory blood tests. Acute purulent-inflammatory lesion is accompanied by an increase in ESR and leukocyte count. The price of such a diagnostic method depends on the urgency of the analysis. Throat swab. Such a bacteriological examination makes it possible to determine the reliable cause of the development of the disease. The only drawback of this method is the duration of the study. The patient receives the results of the analysis in 7-10 days, and treatment must begin from the first day of the purulent disease
A preliminary diagnosis is determined by enlargement of the tonsils, redness of the mucous membrane and the presence of white purulent spots in the throat. In some cases, specialists resort to laboratory blood tests. Acute purulent-inflammatory lesion is accompanied by an increase in ESR and leukocyte count. The price of such a diagnostic method depends on the urgency of the analysis. Throat swab. Such a bacteriological examination makes it possible to determine the reliable cause of the development of the disease. The only drawback of this method is the duration of the study. The patient receives the results of the analysis in 7-10 days, and treatment must begin from the first day of the purulent disease.
Visual examination of the throat.
Viral and bacterial sore throats have fundamental differences in their treatment methods. A disease caused by pathological microorganisms requires mandatory use of antibiotics.
Purulent tonsillitis is usually distinguished depending on the location of the pathological process. Suppuration of lymphoid tissue can begin in the lacunae or follicles of the palatine tonsils.
So, what is the difference between lacunar angina and follicular angina? In fact, such diseases have an identical onset and a similar clinical picture.
The only differences are:
- lacunar tonsillitis predominantly occurs with a very high temperature;
- upon visual examination of the throat, the doctor detects the accumulation of purulent masses in the recesses of the tonsils.
Incubation period and routes of transmission
The incubation period in adults lasts up to 2 days, in children - 12 hours.
This explains the rapid onset of the disease in children and the severe symptomatic course. The main causes of pathological inflammation of the larynx are the penetration of streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, enteroviruses and diplococci. Outbreaks of tonsillitis among various social groups occur in the fall or spring. Reduced immunity plays an important role in tonsillitis. The main routes of transmission of infectious media are:
- airborne;
- enteral route (entry of pathogenic microflora through the mouth, intestines);
- hematogenous (through blood);
- endogenous (internal causes of infection: prolonged rhinitis, chronic tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, inflammatory processes);
- artificial (for traumatizing the mucous membranes of the nose and nasopharynx during surgical procedures).
Sore throat often affects people with reduced sensitization of the body, autoimmune diseases of complex origin, and chronic pathologies of the ENT organs. In an acute inflammatory process, swelling of the mucous membrane, impaired outflow of lymphatic fluid, thrombosis of vascular lumens, the formation of microabscesses and the formation of ulcerative lesions are noted.
Folk remedies
- For gargling:
- Lemon acid.
- Elderberry decoction.
- Beetroot juice with the addition of vinegar (no more than 15 ml of vinegar per glass of juice).
- Salt.
- Carrot juice.
- Pharmaceutical camomile.
- Eucalyptus herb infused for 20 minutes in hot water.
- Add beaten egg white and a teaspoon of salt to a glass of warm water. The components are mixed until the mixture is homogeneous.
- Teas:
- Linden with honey.
- Cranberry.
- With thyme.
- With rose hips.
- Raspberry, sage, and St. John's wort leaves also have an anti-inflammatory effect.4. For sore throat, people often inhale pine buds or chew a piece of dried pine resin in the mouth without swallowing.
Features of treatment during pregnancy
Pregnant women with follicular tonsillitis are required to undergo a course of antibiotics. This poses less risk to the development of the fetus than no appropriate treatment. Basically, preference is given to aerosol topical antibiotics and modern drugs approved for pregnant women.
The high temperature of the expectant mother can cause congenital defects in the baby, so before the doctor arrives, you must try to reduce it. Wiping your feet with a vinegar-alcohol solution and a paracetamol tablet will help in most cases.
- You should not take aspirin, it reduces blood clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Thermal procedures are also extremely undesirable. They can cause uterine contractions and premature birth.
- It is better to eat food in small portions in crushed form, but you cannot refuse food.
- Regular gargling will help you cope with the infection faster, but you should be careful when choosing medicinal herbs for this purpose. During pregnancy, the likelihood of allergies to certain natural components increases.
- Stressful situations, especially against the background of illness, are unacceptable.
Physiotherapy
After the acute symptoms of the disease disappear, the doctor may refer the patient for further physiotherapeutic treatment
This is especially important for chronic tonsillitis and in childhood. The following procedures are most commonly practiced:
- Warming up.
- Laser treatment.
- Electrophoresis.
- Phototherapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Ultraviolet irradiation of the tonsils.
Resort and sanatorium prevention of relapses is desirable, but during the period of remission it is enough to change the environmental situation to a more favorable one.
ICD-10 code
The international classification classifies sore throat as a group of throat diseases. The ICD-10 code for sore throat is J03 (acute sore throat or tonsillitis). The most common types of tonsillitis that affect both children and adults are:
Streptococcal tonsillitis (code J03.0). Sore throat caused by group A streptococcus. It is acute, accompanied by high temperature with signs of intoxication of the body. The lymph nodes enlarge significantly, the structure of the tonsils loosens, the mucous membranes are partially or completely lined with a whitish coating.
Acute tonsillitis caused by other specified pathogens (code J03.8). The classification also includes viral herpes. The disease begins as an acute sore throat, but as the pathology develops, the symptoms inherent in a particular type of pathogen increase.
Complications
Complications of acute tonsillitis are divided into local and general.
Local complications include:
- peritonsillar abscess;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- laryngitis;
- bronchitis;
- otitis.
Common complications include:
- rheumatic damage to the heart, joints;
- glomerulonephritis (kidney inflammation);
- meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain);
- infectious-toxic shock (intoxication with waste products of microorganisms);
- sepsis (bacteria entering the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body).
To prevent the development of complications, timely treatment of acute tonsillitis is necessary.
Antibiotics for catarrhal tonsillitis and their treatment
Treatment of catarrhal sore throat is carried out with antibiotics active against streptococcal or staphylococcal infections:
- Penicillin family drugs - amoxicillin, ampicillin, phenoxymethylpenicillin, benzathine penicillin, inhibitor-protected penicillins - augmentin, sultamicillin. The optimal drug of choice here is amoxicillin, the safest, fastest and most effective. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe bicillin injections for treatment, but this is rare;
- Cephalosporins prescribed when the pathogen is resistant to penicillins - cefadroxil, cephalexin, cefaclor;
- Macrolides - erythromycin, azithromycin, josamycin, spiramycin, prescribed if the angina pathogen is resistant to β-lactam antibiotics in general, or if the patient is allergic to drugs of the previous groups;
- Lincosamides are rarely prescribed, mainly when patients are intolerant to either β-lactams or macrolides.
Lincomycin is a natural antibiotic of the lincosamide group.
The doctor must choose a specific antibiotic. He does this taking into account the following factors:
- Suspected or detected antibiotic resistance of the pathogen (for example, staphylococcus is often resistant to penicillins, streptococcus is often resistant to macrolides);
- The presence of sensitivity in the patient to antibiotics of different groups, signs of the presence of such sensitivity when analyzing the anamnesis;
- Side effects of the drugs (many macrolides cause gastrointestinal dysbiosis and digestive disorders);
- The patient's performance, as well as his ability or inability to self-administer antibiotics in certain forms. When treating catarrhal tonsillitis in adults, such situations may arise when the patient is unconscious or hostile to the doctor. In some cases, children cannot swallow the tablet themselves, or intoxication due to a sore throat causes them to vomit severely, preventing them from taking the medicine orally.
For these reasons, you cannot treat catarrhal tonsillitis and choose a remedy yourself, without understanding the specifics of each specific antibiotic.
Typically, treatment for catarrhal tonsillitis is prescribed for a period of 10-12 days, the minimum possible course lasts 7 days - during this period, if the antibiotic is taken correctly, it can completely destroy the infection in the body.
Staphylococcus causes a sore throat much less frequently than streptococcus, but it is more difficult to treat the disease in such cases
As a rule, in most cases, catarrhal tonsillitis can be treated at home. After the doctor prescribes an antibiotic, the medicine itself is taken at home in accordance with the instructions for the entire specified period.
It is strictly forbidden to stop taking antibiotics if the patient’s condition has significantly improved. As a rule, if the remedy is effective, the patient begins to feel relief within 1-2 days. But at the same time, the pathogen itself continues to persist in the body and is capable of causing relapse and complications.
Practice shows that the risk of developing complications of sore throat increases sharply if antibiotics are taken for less than 7 days.
Antibiotics are usually prescribed in tablet form. Modern drugs in this form are not inferior in speed of action to classical drugs in the form of injections. Treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis in children is usually carried out with means in the form of powder for the preparation of suspensions.
Antibiotic injections for sore throats are prescribed less and less today. This is due to the complexity of this procedure, the need for hospital treatment, and the fear of injections in children. Only in some cases may injections be the optimal treatment.
Depending on the severity of the disease, in addition to the main course of treatment, the doctor may prescribe bicillins for long-term prevention of complications of angina. Today, bicillin prophylaxis is increasingly prescribed due to the high incidence of complications and the constant increase in the resistance of angina pathogens to antibiotics.
Bicillin is a medicine in the form of a white powder for injection. Effective against streptococci and staphylococci
In many cases, treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis in adults is limited to taking antibiotics only. Children more often require the use of painkillers and antipyretics.
Causes
To develop the correct treatment, lacunar tonsillitis is divided into acute and chronic. Based on the existing symptoms, an appropriate diagnosis is made. The acute form is formed during primary infection of the tissue structure of the tonsils, the chronic form appears during exacerbations of tonsillitis of the same name.
Adults and children become infected with lacunar tonsillitis, the main reasons for this are:
- Introducing a large volume of infectious microenvironment;
- A state of decreased immune system strength;
- Weak protection at the local mucosal level;
You can get sick after one contact with an infected person, so in children's groups the disease spreads instantly. If one of the children has the slightest symptoms, he must be isolated and treated separately.
The causative agents of the primary form in adults and children are:
- Streptococcal, pneumococcal and staphylococcal infections;
- Fungal microorganisms
- Sticks;
- Different types of viruses;
Lacunar tonsillitis penetrates into the throat tissue more easily if:
- Inflamed oropharynx or nasopharynx;
- The teeth are unhealthy, there are pockets of caries and periodontal disease;
- The person was exposed to hypothermia;
- There is constant fatigue, which often happens to adults;
- You have to live in an environment with unfavorable ecology;
When treating lacunar tonsillitis, it is important to adhere to all recommendations and observe bed rest, otherwise the disease will drag on longer than the usual 1-1.5 weeks required for complete cure and recovery.
Symptoms
Tonsillitis most often begins with a catarrhal form, the mildest being redness and pain in the throat. However, if conditions are favorable and treatment is not undertaken, it quickly turns into a purulent form - lacunar or follicular.
Types of sore throat
Purulent forms are characterized by very severe symptoms:
- Redness of the tonsils;
- A sharp jump in temperature, often up to 39-40°C;
- Severe pain when swallowing;
- Enlarged lymph nodes near the jaw nodes;
- Aches and pain in muscles and joints;
- Headache;
- General intoxication of the body (nausea, vomiting, chills, weakness, lack of appetite).
After a few hours, purulent rashes appear on the tonsils in the form of dots at the site of the follicles, which are the main sign of the follicular form.
This form of the disease can occur as a result of reduced immunity, heart failure, after taking systemic antibiotics, metabolic disorders, poisoning of the body with alcohol and smoking. Follicular tonsillitis without fever is fraught with particularly serious complications that arise from incorrect and, most importantly, untimely treatment of the disease.