Tubal obstruction is a serious disease of the female reproductive system and a common cause of infertility. Pathology develops due to the influence of many factors. Women of fertile age need to be aware of what its signs and symptoms are, how to check whether tubal obstruction can be cured, and whether pregnancy is possible with this diagnosis.
The fallopian tubes are a paired organ of the female reproductive system, which looks like two thin elongated cylinders. They provide communication between two cavities - the abdominal and uterus, and also contribute to the capture and further movement of the egg released from the ovary directly into the abdominal cavity, and the movement of sperm from the uterus to the egg through chemotaxis. The properties of the tubes ensure the normal physiological process of fertilization.
The term “obstruction of the fallopian tubes” characterizes a condition in which there is a violation of the transport function of the fallopian tubes. In this case, obstruction of the internal space of these organs occurs and patency is partially or completely impaired.
What is tubal obstruction
The content of the article
Obstruction (blockage) of the fallopian tubes is one of the main causes of female infertility, in which sperm moving into the tube through the uterus cannot reach the egg to fertilize it. And if conception does occur, the large embryo does not enter the uterine cavity. In this case, a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy occurs, which is life-threatening for the woman.
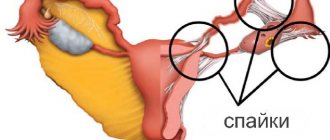
For various reasons, adhesions form in pipes - dense fibers and films that glue tissues located next to each other. The resulting compaction causes obstruction of the fallopian tubes to varying degrees.
Causes: what causes fallopian tube obstruction
The pathology occurs in women of different social classes and with different lifestyles. It is mistakenly believed that its causes are only STIs and abortions. In fact, problems with the fallopian tubes are not always associated with infections and surgeries.
To understand why fallopian tube obstruction occurs, let’s consider the factors leading to the development of the disease. Having identified the problem that has become the trigger, you can understand exactly how the treatment will proceed.
Structural changes in the organ;
- Congenital underdevelopment of the fallopian tubes (often combined with uterine hypoplasia);
- Deformation of the organ (this happens after removal of adhesions);
- Damage to the mucosa (due to hydrosalpinx, inflammation, tumor).
Physiological disorders:
- Hypotonicity of the muscular layer (weak tone of the muscular layer of the appendage);
- Rigidity of the muscle layer (overstrain of the muscle layer, leading to narrowing of the lumen);
- Adynamia of fimbriae (cessation of movement of microvilli lining the inner surface of the pipe);
- Discoordination of fimbriae actions (imbalance of activity).
Functional changes:
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- Endometriosis (proliferation of endometrial cells beyond the inner layer of the uterine wall);
- Mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube (occurs during surgery);
- Hydrosalpinx (a capsule inside the fallopian tube containing serous fluid);
- Congenital anomalies of the tube (subjective reason why there may be obstruction of the fallopian tubes);
- Disorders of embryogenesis (development of the embryo from the 1st day from conception to the 7th week of pregnancy) and postembryogenesis (birth with organs that do not correspond to the required size)
Sexually transmitted infections:
- Gonorrhea (infection caused by gonococci and leading to inflammation of the mucous surfaces);
- Syphilis (caused by a bacterium of the spirochete family, the cause of damage to the mucous membranes);
- Mycoplasmosis (the source of infection is a single-celled microorganism intermediate between a bacterium and a virus, causing infertility);
- Chlamydia (hidden infection, which causes obstruction of the fallopian tubes);
- Genital tuberculosis (causative agent ─ Koch bacterium, which affects the mucous surfaces of the tube).
Postoperative period
After the operation is completed, the patient will still be under anesthesia. She will be taken on a gurney to a ward reserved for patients undergoing surgery. As soon as the anesthesia wears off, the woman will feel dizzy and may experience nausea and vomiting.
At this time, you should not drink water; it is better to blot your lips with a wet cotton swab. For several days, the patient will suffer from the accumulation of gases, so she needs to purchase a drug in advance that can alleviate the condition, for example, Espumisan.
After laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, severe pain will be felt for about three days, to relieve which the medical staff must give injections.
Attention! After surgery, the patient will have to undergo rehabilitation. Due to the low-invasiveness of the method, the healing process will occur quite quickly and with minimal risk of complications.
Prohibitions
Women who have had tubal surgery should not:
- lift heavy objects;
- give the body active physical activity;
- drink alcoholic beverages;
- You should not eat food that can cause constipation, diarrhea, intestinal problems and disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- spend a lot of time in bed (you should walk to avoid adhesions), etc.
Important! If the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations, she will be able to become pregnant a few months after surgery.
Factors leading to obstruction of the appendages
To answer the question of what causes fallopian tube obstruction, the gynecologist has to carefully study the woman’s entire reproductive system. In many cases, pathology is provoked by factors associated with processes occurring in neighboring organs.
Internal factors include diseases of the uterus and ovaries:
- Uterine fibroids (a benign neoplasm in various layers of the uterus; when large, it puts pressure on neighboring organs, deforming and disrupting the blood supply);
- Endometrial polyps (benign formations inside the uterine cavity);
- Ovarian cyst (formation in the structure of the ovary with fluid inside).
Hormonal disorders:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (multiple neoplasms in the ovaries caused by hormonal disorders);
- Adrenal dysfunction (failure of the organ);
- Ovarian dysfunction.
External factors include the following conditions:
- Peritoneal factor (external compression of the fallopian tube);
- Inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- Chronic sluggish appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix);
- Oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries);
- Peritonitis (inflammation of some parts of the peritoneum);
- Enterocolitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large and small intestines);
- Proctitis (inflammation of the rectum);
- Urethritis (inflammation of the ureter).
Inflammation in these organs also spreads to nearby pipes.
Main contraindications
Before performing surgery on the fallopian tubes, the doctor must determine whether the patient has contraindications. Surgical intervention is not performed in the presence of the following pathologies:
- oncological processes in the appendages;
- the presence of infectious diseases occurring in acute form;
- high blood pressure;
- severe failure: renal, cardiac, liver, pulmonary;
- diabetes;
- severe degree of exhaustion of the patient;
- obesity;
- low hemoglobin;
- hemostasis;
- hernias localized in the diaphragm.
Attention! If there is a threat to the patient’s life, then the intervention will be carried out even if there are absolute contraindications.
Surgical procedures that cause tubal obstruction
Medical manipulations, or rather their consequences, which negatively affect the functionality of the appendages:
- Curettage (removal of the fetus by curettage, an undesirable consequence - inflammation or infection)
- Diagnostic uterine curettage (removal of the endometrial layer inside the uterus);
- Failed IVF;
- Incorrectly installed intrauterine device (injures the wall of the organ, provokes infection);
- Difficult childbirth.
Surgery often leads to complications that cause problems with women's health. After surgery, the risk of the following diseases increases:
- Myomectomy (removal of fibroids from the muscular layer of the uterus);
- Tubotomy (laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tubes);
- Cystectomy (removal of a tumor inside the ovary);
- Appendectomy (emergency surgery on the appendix);
- Treatment of ruptured ovarian cyst.
If complex operations on female organs are rare, then every second woman undergoes abortions and curettage. Even if the termination of pregnancy was completed without complications, small fragments of embryonic tissue may remain in the uterus. The decomposition of residues causes inflammation of the organ, which... It spreads to the fallopian tubes. If urgent measures are not taken, the areas of inflammation will heal and become hard and inelastic.
In some cases, hydrosalpinx is formed - a benign neoplasm with serous fluid inside, which blocks the lumen of the tube, preventing pregnancy. After removal of the hydrosalpinx, the lumen of the appendage increases, but the fimbriae can no longer function normally. Infertility occurs, which is not treated conservatively.
Advantages of laparoscopic over abdominal surgery
Laparoscopy differs significantly from traditional abdominal surgery. This surgical technique has many advantages:
- After surgery, only three small scars remain in the lower part of the peritoneum, in the places where the instruments were inserted.
- Patients undergo rehabilitation much faster after laparoscopy. For example, after abdominal surgery, patients get out of bed only on the third day, and after laparoscopic manipulation on the same day.
- Laparoscopy involves both diagnosis and treatment.
- Depending on the severity of the pathology, patients are discharged on the third day after surgery.
- During laparoscopy, specialists can monitor the progress of the operation on a monitor, thereby significantly reducing the risk of injury to neighboring organs and tissues.
- If there is bleeding, doctors use the coagulation method and apply microscopic sutures or clips to the ruptured organ.
- After laparoscopic diagnosis or treatment, the risks of adhesions are reduced.
Types of tubal obstruction, pregnancy prognosis
During fertilization, both the organs of the woman’s reproductive system and the endocrine glands, central nervous system, and immunity are involved. A malfunction in at least one link in the chain leads to the development of a disease leading to tubal obstruction. Based on a number of criteria, tubal obstruction has a complex classification.
According to the degree of lumen blockage:
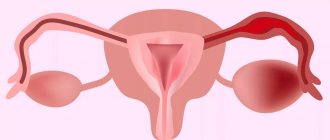
- Unilateral obstruction
. If there are no anatomical abnormalities in the second fallopian tube, then nothing interferes with conception, although the probability of pregnancy is reduced by 2 times. It manifests itself as irregular periods, pain in the lower abdomen, when the egg does not enter the uterus due to blockage of the lumen or due to ectopic pregnancy. - Bilateral obstruction
. 100% leads to infertility. Less common than unilateral. The causes are a consequence of inflammation, hormonal imbalance or other factors. Menstruation sometimes disappears when the fallopian tubes are obstructed on both sides.
According to the degree of lumen blockage:
- Partial obstruction
. The lumen of the epididymis is not blocked, leaving space for the passage of the egg and sperm. But the zygote will no longer be able to penetrate, and the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases. - Complete obstruction
. In this case, there is not the slightest gap left, even serous fluid does not pass through. Fertilization does not occur, the problem means complete infertility.
Due to obstruction:
- Anatomical
. The procedure for obstruction of the fallopian tubes in this case manifests itself in swelling of the mucous membrane, hydrosalpinx, tumors, adhesions, etc. The cause of anatomical changes is inflammation, which is eliminated with antibiotics, and the consequences - with surgery. - Functional
. The tissues of the fallopian tube have no functional changes, there are no adhesions or inflammations, but the organ does not work. The cause is diseases of the central nervous system caused by stress. As a result, the villi (fimbriae) cease to perform the function of capturing the egg, and the appendages lose the ability to peristalsis. - Hormonal
. When there is a hormonal imbalance, the villi stop moving and stick together, blocking the lumen. In some cases, tubal obstruction can be treated with medications and does not require surgery.
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is not a death sentence; treatment, the price of which depends on the complexity and scale of the work, often brings positive results.
Fallopian tube rupture
This pathology can occur with an ectopic pregnancy. There are also cases where damage to the fallopian tube occurred as a result of hydrosalpinx.
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when this organ does not function properly. Most often it leads to this pathology. Before the tube is damaged, a woman may feel bloating and pain in the lower abdomen. Minor bleeding also occurs against the background of positive treatment. Treatment in this case is only surgical. It is worth noting that with timely correction there is a chance to save the organ in which the pathological embryo develops.
A hydrosalpinx is an accumulation of fluid in a pipe. It appears as a result of an inflammatory process or due to the occurrence of a neoplasm, which can be benign or malignant. Treatment can be surgical or conservative. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the situation. If a pipe ruptures, immediate surgical correction is necessary.
Where adhesions form, prognosis for cure, depending on location
The length of the fallopian tube is 10-12 cm, and the width depends on the specific section:
- Distal section (funnel)
. The fallopian tube in this section smoothly passes into the abdominal cavity, and the edges of the opening are bordered by microvilli (fimbriae). They are needed to gently capture the egg expelled from the ovary and direct it into the lumen of the appendage. Blockage in this department is not associated with external factors, because the funnel itself is wide. The narrowing of the lumen is caused by congenital pathologies. With proper surgical treatment, patency can be restored in more than 50% of cases. - Isthmic department (isthmus)
. A short and narrow section that passes into the uterine section. The lumen is blocked due to inflammation of the mucous surface, infection, etc. - Intramural (uterine) section
. A narrow section through which the embryo enters the uterus through an opening in the wall of the organ. Narrowing of the lumen occurs due to endometrial polyps or spasm of the smooth muscles of the uterus. The uterine section of the fallopian tube is a narrow section, so its obstruction means that the opening of the fallopian tube is blocked. If adhesions and neoplasms in other sections are subject to laparoscopic removal and further restoration of the functionality of the organ, then the intramural section is not subject to reconstruction. - Ampullary section.
This is the wide and long part of the fallopian tube where the oocyte meets the sperm and the zygote is born. The lumen narrows due to external compression (pressure from hydrosalpinx, tumor). If the cause of compression is promptly eliminated, patency is restored.
If obstruction of the fallopian tube in the ampullary section is caused by sexually transmitted infections, hypothermia and other unfavorable factors leading to inflammation of the surface of the appendage, then this threatens ectopic pregnancy.
Pathology occurs due to the formation of adhesions - a strip of connective tissue formed at the site of inflammation. Microfibers (fimbriae) lose mobility, stick together and form a bubble where serous fluid accumulates (hydrosalpinx). As a result, the fallopian tube loses its ability to peristalsis due to scarring, its lumen narrows, creating tubal obstruction.
Possible complications
Any surgical intervention is associated with certain risks:
- opening of bleeding;
- penetration of infection into the wound;
- seam divergence;
- thromboembolism, etc.
Preventing possible complications
Women will be able to prevent the development of postoperative complications only if they strictly follow the instructions and recommendations of their attending physicians:
- it is necessary to take prescribed medications;
- Patients should take anticoagulants for several days;
- As soon as the woman recovers from anesthesia, she should try to get up and walk around to prevent the formation of adhesions.
Tubal obstruction: signs, symptoms, sensations
Fallopian tube obstruction does not have characteristic signs or pronounced symptoms, so it is difficult to say what sensations are typical for this disease. Often the problem is discovered only when it is not possible to get pregnant for a long time. But the root causes that caused the pathology can give quite noticeable symptoms.
Any thematic forum eloquently talks about what symptoms of fallopian tube obstruction are most common. Many women note that the main sign of obstruction of the appendages, which forced them to turn to a good gynecologist, is the absence of a long-awaited pregnancy within a year of regular sexual relations.
Most symptoms are associated with a reduction in adhesions - areas of connective tissue formed at sites of inflammation. Frequent signs of obstruction of the fallopian tubes and adhesions:
- Pain in the lower abdomen when cleaning, doing fitness, intensive walking, caused by the inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes;
- Increased temperature, fever are also symptoms of inflammation;
- Discharge mixed with pus and leucorrhoea;
- Pelvic pain syndrome - constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- Algomenorrhea (painful periods);
- Bladder problems (frequent urge, painful urination);
- Disorders in the functioning of the rectum (painful bowel movements, constipation);
- Inability to have sex due to severe pain in the genitals.
The main symptom of obstruction is ectopic pregnancy. It occurs only with pathological narrowing of the lumen of the appendages or with hydrosalpinx.
Another important symptom of tubal obstruction is irregular periods. With complete obstruction of the appendages, menstruation will be absent altogether if the disease of the reproductive organs affects the ovaries. In this case, the egg does not mature, ovulation does not occur, and the endometrium stops growing.
Causes of reproductive disorders
One of the pathologies is the expansion of the fallopian tube. This disease is called hydrosalpinx. In most cases, the reasons why the fallopian tube is dilated are associated with the accumulation of fluid, the development of the inflammatory process and poor circulation.
Why is the fallopian tube dilated?
- simple and follicular hydrosalpinx;
- salpingitis;
- enlarged isthmus of the fallopian tube.
Simple hydrosalpinx. In this case, the increase in the size of the tube in women occurs only in one cavity. Despite the mildness of the disease, the risks of complications become maximum and treatment still becomes mandatory.
Follicular hydrosalpinx. It is assumed that the lumen is divided into several cavities, each of which is filled with liquid.
Salpingitis. The inflammatory process is complicated due to the negative impact of several types of sexually transmitted infections. The acute form of the disease leads to an increase in general temperature and pronounced pain in the intimate organs. Chronic disease leads to the fact that the size of the fallopian tubes decreases and there is a serious risk of ectopic pregnancy or diagnosing infertility.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Why sperm can be transparent
An enlarged isthmus of the fallopian tube also indicates an inflammatory process. Initially, this part of the organ has a very narrow diameter (up to 4 millimeters) and a length of up to 20 millimeters.
Violation of dimensions indicates the need for diagnostics and initiation of a treatment course. Pathological changes can only be detected during examinations by doctors.
How to find out about obstruction of the fallopian tubes: diagnosis
In 25% of cases of infertility in women, the cause is obstruction of the fallopian tubes. How to detect obstruction of the fallopian tubes, since diagnosis is complicated by the fact that a woman, according to subjective feelings, does not know the symptoms of the disease?
You can find out about obstruction of the fallopian tubes only through an examination by a gynecologist. To ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a series of tests, and the pelvic organs are also examined using the latest medical technology. There are methods that simultaneously establish a diagnosis and eliminate problems with the patency of the appendage.
Unfortunately, the examination can be lengthy and difficult, since a biochemical blood test and urine test can only determine the cause of the obstruction - inflammation. If it is not there, the only reliable diagnostic methods are ultrasound of the uterus and invasive methods.
Primary mandatory tests:
- Flora smear
(determines the ratio of pathogenic and lactic acid microflora). - Biocenosis smear - reveals a different number of infections, for example, femoflor gives an answer to 16 indicators;
- Enzyme immunoassay for antigens
to infectious agents (ELISA). - Serodiagnosis (determines the reaction of the patient’s serum to the protein of pathogenic microbes).
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko.
It reveals the ratio of leukocytes, red blood cells and cylinders, determining inflammation of the genitourinary tract. According to Nechiporenko’s analysis, a complete picture of the general condition of the body is visible.
Non-invasive techniques - pelvic ultrasound - are highly informative:
- Comprehensive ultrasound of the pelvic organs
. Includes (through the abdominal wall) examination method. Allows you to see complete or partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes. - Detailed ultrasound of the ovaries, appendages and fallopian tubes. Clearly demonstrates adhesions and other processes in organs.
- Detailed transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus. Determines inflammation and tumors in the organ.
- Hydrosonography
. The uterus fills with colored fluid, which is distributed along the fallopian tubes. Then, using an ultrasound machine, the doctor observes the uniform spread of the saline solution. If there are areas of obstruction, this will be reflected on the screen. The method is not as effective as laparoscopy, but is safe and does not require surgery.
Ultrasound can detect tubal obstruction quickly, safely and without pain, so it is performed first. If the examination is inconclusive, the patient is referred for further examination.
Which method is better?
Here are the most popular methods by which the presence of lumen of the uterine tubes is checked. But which one is actually the best?
An accurate answer to this question can only be obtained from a doctor, based on tests and a general examination of the patient’s body.
It is also necessary to understand that surgical methods for determining the condition of organs pose no less risk than performing an operation.
In addition, they need long-term pre-training, since narcotic painkillers are a fairly large burden on the patient, so it becomes necessary to undergo all the tests that will clarify whether the heart and other internal organs are able to withstand such exposure.
When there is a choice, it is best to prefer non-surgical diagnostic methods of the present time - hysterosalpingography or hydrosonography.
How to determine obstruction of the fallopian tubes using fluoroscopic diagnostic methods
Effective fluoroscopic methods for diagnosing diseases of the appendages are prescribed as necessary, since they are associated with radiation. Radiography and hysterosalpingography (HSG) are usually performed.
The HSG procedure is as follows. Using a rubber tube, a contrast liquid (containing Ultravist, Triombrast iodine) heated to body temperature is injected into the woman’s uterus through the cervical canal. The fluid enters the appendages and, if there is an obstruction, is not distributed further.
Then x-rays are taken, in which, thanks to the contrast agent, the adhesions are visible - in the pictures they are visible as white stripes. If there is hydrosalpinx, the image will show a capsule with translucent contents. If the fluid is distributed in a thin stream and does not fill the lumen, this indicates partial obstruction.
How to determine fallopian tube obstruction using endoscopic methods
The endoscopic method has been used for many years to make an accurate diagnosis in gynecology. The gynecologist may prescribe one of the procedures:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
. This is a minimally invasive diagnostic method in which an optical laparoscope with a microcamera at the end is inserted through a small hole in the abdomen. The image is displayed on the screen and enlarged 6 times. The method is contraindicated if the patient has adhesions between the pelvic organs. - Laparoscopy with chromohydroturbation.
It is carried out under anesthesia. The patient is given three punctures in the abdominal wall, through which the laparoscope is inserted. The blue-tinted saline solution shows areas of obstruction in the fallopian tubes. - Transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy (fertiloscopy)
. The endoscope is inserted through the vagina and a contrast agent is injected through a thin tube. It differs from laparoscopy with chromohydroturbation in the absence of the need for anesthesia, but the results will not be as reliable.
Preparing the patient
The process of preparing a patient for tubal laparoscopy includes several stages:
- examination;
- psychological preparation;
- analyses, hardware diagnostics;
- operating field.
Preoperative examination
Before tubal surgery, the patient must undergo laboratory and hardware examination:
- Blood and urine analysis (general, biochemical).
- Determination of Rh factor and blood group.
- Test for syphilis, HIV.
- Urogenital smear.
- ECG.
Psychological preparation
Before tubal surgery, a woman must undergo psychological preparation. The right attitude will help her endure the postoperative period and rehabilitation more easily.
Pre-medication preparation
Before tubal surgery, patients may be prescribed the following medications:
- Sleeping pills.
- Sedatives.
- Analgesics.
- Antihistamines.
- Anticholinergic drugs.
Preparation of the surgical field
The surgical field before tubal surgery is prepared as follows:
- the patient takes a shower;
- hair in the groin area is shaved;
- the skin is treated with alcohol;
- On the operating table, the peritoneal area is treated with alcohol (70%) and iodonate.
Indications for surgery for infertility
For women diagnosed with infertility, doctors perform laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes in the presence of the following pathologies:
- salpingoophoritis;
- hydrosalpinx;
- adhesive process;
- salpingitis;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Contraindications for infertility
If fallopian tube surgery is performed due to infertility, then pathological conditions may become a contraindication to the operation:
- diabetes;
- obesity stage 3-4;
- malignant neoplasms in the uterus or adjacent organs;
- problems with blood clotting;
- coma;
- exhaustion;
- period;
- hypertension, etc.
Choosing the type of anesthesia
Fallopian tube surgery is performed under general anesthesia. It is performed by a specially invited anesthesiologist. He can administer drugs intravenously or use inhalation anesthesia.
After general anesthesia, a woman may develop complications, the list of which should be supplemented with pathological conditions:
- heart attack;
- swelling of the larynx;
- insufficiency (acute) cardiac, pulmonary;
- thromboembolism;
- recurarization, etc.
Treatment of adhesions in the appendages and other causes of obstruction
Is adnexal obstruction treatable? Yes, it is being treated, this is evidenced by numerous reviews that former patients post on forums. Treatment is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology - STIs, hydrosalpinx, etc.
Medication method
used in the treatment of acute forms of the disease. It consists of constantly taking medications at a certain dosage. The drugs have different effects on the body: some suppress the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms, others relieve inflammation, and others resolve adhesions. Medicines are available in the form of tablets and suppositories.
Use of anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Non-steroidal (analgesics): simultaneously relieve inflammation, relieve pain and relieve fever. They block the production of enzymes - prostaglandins, produced when an infection enters the body. They are not synthetic, so they are taken longer than steroid drugs.
- Steroids (glucocorticosteroids are hormones produced by the adrenal glands). They are divided into natural and artificial. The principle of action is to suppress the production of leukocytes produced during inflammation. Tissue erosion at the site of inflammation disappears, pain and fever go away. But steroid drugs cannot be taken for a long time; they are effective for acute inflammation and severe forms of infection.
- Antibiotics
. A drug that destroys pathogenic bacteria can cure obstruction of the fallopian tubes, or more precisely, eliminate the cause of the dysfunction of the appendages - STIs. Antibiotics are taken under the supervision of a doctor in dosage. There is a threat that with long-term use, normal microflora will be suppressed. Therefore, before prescribing antibiotic treatment, the patient undergoes a test for the sensitivity of the microbe to the active substance. Throughout treatment, the types of antibiotics are changed so that microbes do not adapt to the drug. - Hormone therapy
. Often gynecological problems, including blockage of the lumen of the appendages, are caused by hormonal disorders. Depending on how tubal obstruction is treated, the patient is prescribed natural or synthetic hormones that suppress or restore the normal functioning of the organ. - The surgical method
is used in advanced cases, as well as when medication and physiotherapeutic methods become ineffective. Before surgery, the patient undergoes diagnostics to determine the impassable area. It is usually affected by adhesions, overgrown connective tissue or scars. There are various methods of surgical intervention, each of which is effective in a particular case.
Laparoscopy has proven itself to be excellent. This is a minimally invasive method in which the peritoneum of the patient is punctured in several places, and a laparoscope, a long tube with optics and a camera at the end, is inserted through the punctures. With the help of a camera, the image is visible on the screen, and the optics magnify it 3-4 times. The doctor removes adhesions and scars, instantly cauterizing the operated area.
In some cases, laparotomy relieves obstruction of the appendages. An incision is made along the bottom of the peritoneum through which surgery is performed. After the operation, a scar remains and the woman remains in the hospital for at least 5 days.
Reconstructive surgery works in a similar way. It involves transplanting a healthy section of the donor tube to the site of the damaged one. Or this is an artificial restoration of the lumen.
Drug treatment
If obstruction of the oviduct is caused by an inflammatory process, then treatment should be started immediately. Advanced stages of inflammation are accompanied by changes in the structure of the mucous membrane and then the drug method will be ineffective.
Conservative treatment is carried out using the following groups of drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory: phenylbutazole and cortisone, diclofenac, indomethacin or aspirin. The drugs are used in the form of suppositories or tablets. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, they have antipyretic and analgesic properties.
- Antibacterial: gentamicin or kanamycin, chloramphenicol, metronidazole or tetracycline. The drugs are effective in the fight against microorganisms (if the obstruction was caused by their activity).
- Hormonal drugs are prescribed for vascular and trophic disorders provoked by inflammatory processes.
- Sedatives in the form of vitamins, calcium and immunotherapy stimulate the immune system.
The selection of drugs, their dosage and duration of use is carried out by a surgeon or gynecologist. Throughout the course, the patient visits the attending physician, who determines the effectiveness and makes adjustments to the prescription as needed.
Conservative treatment is recommended to be combined with physiotherapy:
- Balneotherapy;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Electrophoresis using magnesium, calcium and biogenic stimulants;
- Gynecological massages;
- Electrical stimulation of the pelvis.
If drug therapy does not have an effect, a decision is made on surgical intervention.
Surgical methods
Surgical intervention can solve problems with mechanical closure of the lumen in the fallopian tubes. Main directions in surgery:
- The laparoscopic method is most often used. The operation is performed through small openings in the abdomen, through the anus, or through the vagina. If complications or new data about the disease appear during the procedure, the course of the operation may change, and the doctor decides to use the laparotomy method.
- The laparotomy method is performed by dissecting the abdominal wall. More often used to remove tumors. In the absence of postoperative complications, the woman is discharged from the hospital on the 5th day.
- The reconstructive method involves the use of synthetic materials, thanks to which we expand the lumen in the pipes.
Modern medicine offers a fairly large selection of methods to cure tubal patency. With successful treatment, a woman can become pregnant within the first year. But the problem may arise in the future. The pathology of tubal obstruction can recur. There are also cases when the problem is solved and the egg is successfully fertilized, but its transportation to the uterine cavity does not take place. For a woman, this ends in an ectopic pregnancy and emergency surgery.
Additional treatments
Additional methods of treating tubal infertility are different options for physiotherapy:
- Electrophoresis
. It has an immunocorrective effect, which consists in exposing the area of the body where the drug is placed to a direct electric current. Medicines are absorbed through the skin in the form of positively and negatively charged ions. In addition, the electromagnetic field improves blood supply and resolves adhesions. - Balneotherapy
. It consists of treatment with mineral waters (nitrogen-siliceous, sodium chloride, hydrogen sulfide). The beneficial effects of medicinal water normalize hormonal levels, relieve pain and inflammation, and calm the nerves. - Ultrasound therapy
has shown high effectiveness in resolving adhesions. This is an in-office procedure in which local areas are exposed to ultrasonic waves. As a result, adhesions soften, blood circulation improves, and soft tissues become elastic. - Treatment with an electrical stimulator.
This way even old scars are eliminated. Using a special apparatus, the area of the fallopian tubes is exposed to electrical impulses with a frequency of 12 Hz. Muscle contraction occurs, as a result of which the lumen of the tube expands, scars and adhesions soften.
With minor damage to the appendages, gynecological massage will help. It is performed by a gynecologist in an examination chair, then the reproductive organs are manually massaged through the vagina. It is rarely used, but it is also quite effective and safe.
Traditional methods can also complement treatment. The boron uterus, which grows in Altai, has shown itself to be effective. It controls estrogen levels. The herb is brewed as a tea along with wintergreen, a plant in the heather family that has antiseptic and healing properties. St. John's wort, flax seeds, sweet clover, coltsfoot, and knotweed help eliminate tubal obstruction.
Where is tubal obstruction diagnosed and treated in St. Petersburg?
When faced with a problem, women ask the question: where and how to treat obstruction of the appendages, what to do? First of all, you need to go to a good clinic in St. Petersburg and establish the cause, and then eliminate the consequences. At the same time, you cannot self-medicate - this leads to the transition of the disease to an advanced form.
If you suspect tubal obstruction, seek qualified help at the Diana specialized clinic. Here you can inexpensively undergo examination using the latest equipment and be cured of infertility associated with this pathology.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Diagnostic features
The mandatory task of every woman is to carry out diagnostic measures. The main problem during pregnancy is obstruction. In this regard, care must be taken to carry out examinations if violations are suspected.
Lack of patency may be due to natural or purposeful reasons. In the first case, the pathology develops due to factors beyond the control of the woman, in the second case, the patency is disrupted by special intervention to prevent conception.
If the tubes are not passable in the isthmic department, treatment will not be effective and IVF becomes the only chance for motherhood. Moreover, if the intramural section of the fallopian tube is subjected to formed adhesions, the woman is diagnosed with infertility.
Only if the mouths of the fallopian tubes are visualized, the possibility of giving birth to a child remains.
The following disorders can lead to an ectopic pregnancy:
- adhesions;
- kinks;
- narrowing.
If the mouths of the fallopian tubes are free, this means the possibility of conception with further correct development of the fetus. If the fallopian tubes are not visualized, this means that the girl is experiencing pathological processes and additional intervention is required.