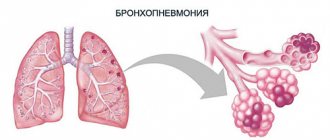
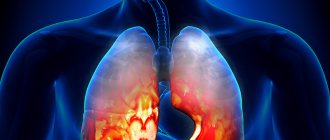
Pneumonia of the right lung is diagnosed more often than of the left. This picture is explained by the anatomical structure of the bronchial tree on the right side. The right main bronchus, located obliquely, from top to bottom, “throws” bacteria into the lower parts of the lung, due to which a large number of colony-forming units accumulate in one place.
Right-sided pneumonia is a common and serious illness that requires immediate and rather complex treatment, often in a hospital setting.
At the Yusupov Hospital’s therapy clinic, highly qualified doctors will perform comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases, including pneumonia of varying severity. Thanks to the impressive experience of our specialists, equipping the hospital with modern medical equipment, high efficiency of treatment and prevention of the development of severe consequences are ensured.
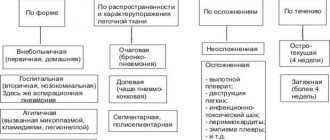
Classification
| By localization |
|
| By symptoms |
|
| According to the location of the source of inflammation |
|
Classification and stages of development of pneumonia
It is the cause of the disease – infectious and non-infectious – that is the main criterion in the classification of pneumonia. Moreover, if pneumonia is caused by an infection, bacterial viral and fungal pneumonia are distinguished:
- Bacterial pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs that develops against the background of damage to the lung tissue by gram-negative and bacterial bacteria. The disease is accompanied by irritation of the pleura (lining the lung from the outside and the chest from the inside) and infiltration of the lung parenchyma (including the alveoral walls). If bacterial pneumonia is not treated in a timely manner, part of the lung tissue may necrosis, and an abscess and gangrene may occur on the lung.
- Viral pneumonia is an acute disease with severe intoxication. The frequency of occurrence is closely related to epidemiological outbreaks (ARVI, coronovirus)
- Fungal pneumonia (pneumomycosis) is an inflammation of the lungs caused by the proliferation of fungal strains in the alveoli and lung parenchyma. One of the most difficult types of pneumonia to diagnose.
Some of the most dangerous are viral pneumonia, complicated by a bacterial or fungal infection. It is with such pneumonia that the risk of death is high.
Pathologies are typical and atypical. There are effective medications and techniques for treating typical pneumonia. Atypical pneumonia is more difficult to treat. The most complex atypical pneumonias are viral. Among bacterial pneumonias, the most problematic are atypical pneumonias caused by intracellular pathogens - chlamydia, legionella.
Their classification depending on the lesion (stage of the lesion) is also essential for the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia.
- Total . The lungs are completely affected.
- Croupous . One lobe is affected. It is extremely rare in children; in adults, especially with bacterial pneumonia, it is a common phenomenon.
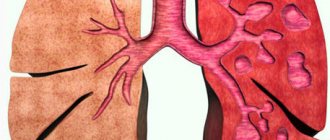
- One-sided and two-sided . Affects only the right or left or both lungs.
- Drain. There are several foci of inflammation, but almost immediately they merge into one.
- Segmental – affects one or more bronchopulmonary segments
Features of symptoms
Right-sided pneumonia is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms, and the course is acute. Symptoms depend on the stage and degree of pneumonia, but they are practically no different from signs of other types of pneumonia:
Heat
- high temperature that lasts for a long time and reaches 39-40 degrees;
- fever with chills, during which a person may even become delirious;
- intoxication;
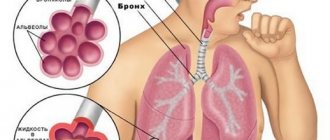
- sputum;
- dyspnea;
- general weakness;
- cyanosis of lips and fingertips;
- wheezing.
The main distinguishing feature of the right-sided type of pneumonia is the localization of chest pain on the right.
In children, pneumonia develops rapidly, especially in newborns. Due to the undeveloped immunity, respiratory tract infections can enter the lung and provoke infection, which can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences and complications. At the slightest suspicion of pneumonia in infants, children should be urgently hospitalized, and treatment should begin as quickly as possible with broad-spectrum antibiotics. If parents observe shortness of breath, high fever, hoarseness, sweating and a wet cough in their child, this is a reason for them to immediately seek medical help.
Right chest pain
In adults, symptoms can be very diverse and manifest themselves as wheezing, coughing with sputum, a sick person complains of pain in the sternum during breathing, severe shortness of breath. The lower lobe form of the disease may develop and is almost asymptomatic for several days: without severe cough or fever. Diagnosis of the disease is complicated, and if treatment is not started for a long time, this can lead to complications. One of them may be pleuropneumonia, in which the upper, middle or lower lobes of the lung and its membrane (pleura) become inflamed. An ill patient develops pleurisy. The course of the disease is severe, most often it is provoked by pneumococcal infection.
Symptoms of coronavirus pneumonia
Covid pneumonia is often found in patients with mild onset of infection. Patients present with symptoms:
- weakness and headaches;
- mild hyperthermia not exceeding 38°C;
- dry cough without sputum;
- sore throat and sore throat;
- loss of taste and smell.
A similar clinical picture is present during the first week of the disease. Then the symptoms begin to increase and become more complicated:
- hyperthermic reactions increase to 39.5-40°C, it is very difficult to bring down the fever, and if it works, it is for a short time;
- the patient sweats profusely and complains of severe weakness;
- coughing and even inhaling/exhaling cause severe chest pain.
The peak manifestations of the complication are reached 6-9 days from the onset of infection. Therefore, doctors strongly advise you to be more vigilant about your health during this period of coronavirus infection and to urgently consult a doctor if severe shortness of breath occurs.
When hypoxia reaches the brain cells, the patient has a strong desire to sleep, his consciousness becomes confused, he is agitated and suffers from frequent bouts of panic attacks.
If cerebral hypoxia intensifies, the patient may fall into unconsciousness.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Most often, right-sided pneumonia can be transmitted by airborne droplets from a sick person or through activation of microorganisms located in the respiratory tract. This occurs when immunity decreases.
Pathogens that can cause right-sided pneumonia:
Chlamydia
- chlamydia;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- streptococci and staphylococci;
- mycoplasma;
- legionella;
- intestinal pathogens;
- viruses;
- mushrooms.
Symptoms of right-sided pneumonia
Right-sided pneumonia of a bacterial nature is manifested by the following symptoms:
- cough;
- secretion of sputum;
- increased temperature;
- leukocytosis;
- blue skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- rapid breathing and heart rate.
Viral right-sided pneumonia manifests itself:
- muscle weakness;
- rapid fatigue;
- fever;
- dry cough with little sputum production.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnostic procedures to determine the disease:
- An x-ray must be taken to determine the size of the affected lesion and its location;
- carry out a sputum analysis for the content of pathogenic microorganisms;
- If necessary, bronchoscopy is performed to examine the bronchi from the inside and histological examination.
Only a pulmonologist or therapist can make a correct diagnosis based on the laboratory tests obtained.
https://youtu.be/hhI3TRVGmFs
What are the differences from bronchitis?
Pneumonia and bronchitis are diseases of the respiratory system that have a similar clinical picture, and it can be very difficult to distinguish them from each other based solely on symptoms. What is the difference between bronchitis and pneumonia:
- in 90% of cases, bronchitis has a viral etiology, and pneumonia has a bacterial etiology;
- with bronchitis there is a slight increase in temperature, and with pneumonia - severe fever (up to 38-39 degrees);
- sputum with bronchitis usually has a light tint, and with pneumonia it is greenish or rusty, streaks of blood may appear;
- When listening to the chest, dry wheezing is heard in patients with bronchitis, and wet wheezing is heard in people with pneumonia.
IMPORTANT! Only a doctor can distinguish one form of the disease from another, as well as prescribe the correct therapy, so if symptoms develop, you should contact a medical facility as soon as possible.
In case of an atypical course of the first or second disease, it is possible to distinguish them from each other only with the help of complex diagnostics.
Treatment of right-sided pneumonia
Medication course
Treatment of any type of pneumonia, including right-sided pneumonia, is carried out with antibiotics, for example, Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin, and cephalosporin antibiotics. If recovery does not occur, sulfur-containing antibiotics are used. If treatment does not work, the doctor increases the dose or prescribes a different antibiotic. Previously, the disease was treated with ordinary Penicillin, but now microorganisms have developed resistance to it, and this drug no longer gives positive results.
Sometimes pneumonia is caused by viruses, then an antibiotic will not help; a medicine against bacteria and viruses is prescribed in combination with immunomodulators. Antifungal drugs are prescribed in case of fungal infection.
Symptomatic therapy is also used:
- antipyretic drugs – for fever;
- general strengthening therapy - with decreased immunity;
- the doctor may prescribe Mucaltin - this remedy is intended for the discharge of sputum;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- for severe anxiety, sedative tablets or syrups are prescribed;
- antibiotics negatively affect the intestinal microflora, so the doctor may prescribe probiotics: Enterozermina, Yogurt capsules, BioGaya, Linex and others to maintain normal intestinal functioning.
The course of treatment is determined only by the attending physician, and he can also correct it. The duration of treatment can last at least two to three weeks, or more in complicated forms.
ethnoscience
Rosehip decoction
It is impossible to cure pneumonia exclusively with folk remedies, but you can combine herbal treatment with drug treatment. For example, plantain and licorice are used to cough up phlegm. To boost immunity, a rosehip decoction is recommended, as it is rich in vitamin C. Drinking plenty of fluids, green tea, herbal infusions, and proper nutrition, enriched with vitamins, primarily vegetables and fruits, are recommended.
Under certain circumstances, a physician may authorize treatment at home, but the patient must be provided with appropriate out-of-hospital care. Patients under 60 years of age without concomitant diseases or people with a mild, uncomplicated form of pneumonia are treated at home.
When treating pneumonia, it is important to constantly get rid of waste sputum to avoid re-infection. If the temperature does not subside, you should drink 3 liters of water per day to prevent intoxication. To avoid pulmonary edema, you should change your body position, move, and do physical exercises in bed. When the patient feels better, you should do breathing exercises, squat, and bend over. If a baby or a child under one year old is sick, he must be constantly turned over, changed body position, or carried in his arms.
Forecast
For a long time, most pneumonias were associated with a risk of death. But with the development of pharmacology, the advent of antibiotics, antiviral and antimycotic agents, if treatment is started in a timely manner, in most cases, especially if a person does not have chronic diseases, the prognosis is favorable.
The main thing is that the cause of the disease (bacteria, viruses, fungus) must be identified in a timely manner and drug therapy initiated in a timely manner.
Timely treatment starts to minimize complications. Most importantly, it is important to take into account the general condition of the patient and concomitant pathologies. The greatest risk of complications is in the elderly, children under 5 years of age, people with chronic diseases of the heart, respiratory tract, kidneys, and weakened immune systems.
The best treatment outcome and favorable prognosis are ensured by comprehensive treatment in a hospital setting.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for suspected pneumonia in adults include:
- External examination of the patient , collecting medical history and complaints, listening to the chest;
- Chest X-ray is the most informative way to identify inflammatory processes in the lungs (characteristic darkening in places of tissue damage and other signs of the disease appear in the pictures);
- Blood, urine and sputum tests are carried out to determine the inflammatory process in the body (increased levels of leukocytes and ESR), as well as the causative agent of pneumonia and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Fiberoptic bronchoscopy, CT and MRI of the chest are necessary when it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis of pneumonia based on the above methods based on the signs.
IMPORTANT! Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on a comprehensive diagnosis, since the clinical course of pneumonia can resemble not only bronchitis, but also other diseases of the respiratory system (inflammation of the pleura of the lungs, bronchopneumonia, COPD, etc.).