Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 36 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
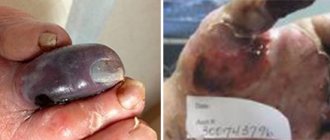
An abscess is an accumulation of purulent contents in various tissues. Purulent inflammation is usually caused by a bacterial infection. In this case, in the process of melting the tissue, a cavity is formed. The occurrence of an abscess is caused by bacteria entering the tissue from the outside - through abrasions and injuries or from other infected tissues and organs. This disease differs from other similar diseases in the formation of a capsule that prevents the spread of inflammation.
Based on the location of the pus, there are superficial accumulations in the subcutaneous fatty area and deep ones inside organs and deep tissues. Depending on the method of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, there are exogenous accumulations (from the external environment) and endogenous (migration within the body of one person).
Symptoms and signs
Regardless of the location of the purulent accumulation, the symptoms of an abscess are the same:
- intoxication – fever, chills, weakness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, muscle and joint pain, headaches;
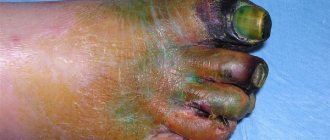
- superficial location - redness and swelling of the skin directly above the site of accumulation, pain on palpation or during movement;
- disruption of the functioning of the damaged organ or related tissues.
A chronic abscess does not have symptoms of an acute inflammatory process. Deeply located accumulations have only general signs of intoxication and are detected by instrumental diagnostics. The most common locations of an abscess are:
- inside the bones - the main symptom is pain from physical activity or when the weather changes;
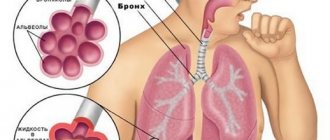
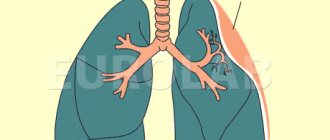
- Lung abscess is manifested by shortness of breath and weak breathing. A lung abscess is often confused with pneumonia;
- in the abdominal cavity and liver is accompanied by signs of any disease of this organ;
- in the brain causes seizures and loss of coordination;
- prostate abscess causes pain when urinating;
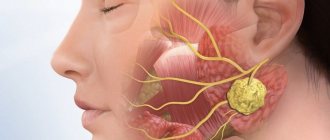
- a throat abscess causes cough spasms and pain;
- Bartholin gland abscess and others.
Cold occurs without signs of intoxication and appears in immunodeficiencies. Natechny eliminates the presence of an inflammatory process in tissues. Acute abscess has more pronounced symptoms compared to other forms.
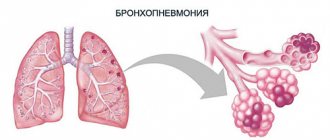
Classification of lung abscesses
When classifying a disease by etiology, attention is paid to the causative agent of the pathology.
According to pathogenesis, they focus on the route of infection:
- Bronchogenic,
- Traumatic,
- Hematogenous.
Based on their location in the lung tissue, they are distinguished:
- Central abscess;
- Peripheral abscess.
In count:
- Unit,
- Multiple abscess.
A lung abscess can be located in one or both lungs (bilateral process).
Causes of occurrence and development
The main cause of an abscess is a bacterial infection that has entered the tissue from the outside world. Bacteria enter the body due to microtraumas that violate the integrity of the skin. Such injuries include cuts and minor abrasions/scratches/damage received during shaving or hair cutting, manicure or pedicure, and others. At the same time, if dirt or small particles in the form of a splinter get in, the likelihood of a purulent accumulation increases.
The occurrence of an accumulation of pus can occur for other reasons for an abscess:
- migration of infection from the primary source of infection;
- festering hematomas and cysts;
- surgical manipulations – violation of sanitary rules in the form of unsterile instruments;
- disturbances during the administration of drugs and preparations, for example, disturbances in concentration during vaccinations.
The abscess develops further under the influence of reduced immunity or poor circulation in the area of the abscess.
Pathogenesis
At the initial stage, the inflammatory process affects only one area, and gradually infiltration of this area occurs. As the purulent process spreads from the center to the periphery, an abscess forms in the form of a cavity. After the breakthrough, pus with sputum is removed through the bronchi from the body. The affected area of the lung tissue is gradually filled with granulation tissue, forming a zone of pneumosclerosis . Pus in the lungs can exist independently for a long time as a result of the formation of a cavity limiting it with fibrous walls.
Forms of the disease and routes of infection
An abscess can be an independent disease, but in the vast majority of cases it appears as a complication of an underlying disease, for example, purulent tonsillitis causes a peritonsillar abscess. Pathogenic microorganisms have a lot of ways to get inside - through damage to the skin as a result of injuries and cuts, from other organs and tissues that were previously infected, through non-sterile equipment during surgical procedures, and others.
Forms of the disease are classified according to the location of purulent accumulation:
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- peripharyngeal;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- subdiaphragmatic;
- soft tissues;
- periodontal;
- appendicular and others.
Questions for the doctor
Causes of pathology
3 months ago I fell ill: my temperature rose and I started coughing. I thought it was a simple cold, I was treated as usual - Paracetamol, took cough drops. Then it got worse, the temperature stayed at 40-41 degrees, it was not going well, and shortness of breath began. They took me to the hospital, did an x-ray, and it turned out there was an abscess in my right lung.
Now I'm on antibiotics and I feel much better. But I have a couple of questions. This is an infectious disease, right? So, did I get it from someone? Can I get it again?
Hello! An acute abscess is more likely a complication of an infectious disease - bronchitis, bronchiolitis or pneumonia. Indeed, some pathogen entered your body (probably through airborne droplets) and caused inflammation of the lower respiratory tract, which you mistook for a cold. Without proper treatment, the immune system could not cope with the infection on its own and “reacted” to it in a similar way - by forming a cavity filled with pus.
Repeated abscess formation of lung tissue is possible. To avoid this, try to follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle and treat lung infections in a timely manner. Be healthy!
Complications
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, complications of abscesses are very dangerous for the life and health of the patient:
- phlegmon;
- neuritis;
- osteomelitis;
- internal bleeding of the walls of blood vessels;
- peritonitis,
- sepsis as a result of purulent abscess of the appendicular region;
- purulent meningitis and others.
Contacting the clinic
A purulent accumulation is fraught with dangerous consequences, therefore, if the slightest sign of the presence of an accumulation of pus in tissues or organs appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. The ideal solution would be to call an ambulance.
At (academician Roitberg’s clinic) you will receive the necessary assistance in treatment. In addition, JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) has the ability to accommodate patients in a 24-hour hospital and has the function of calling a doctor at home around the clock.
Prevention
Prevention consists of preventing microorganisms from entering the lung tissue and strengthening the immune system. What nonspecific preventive measures are carried out:
- Restoring the drainage function of the bronchi in case of pneumonia, bronchitis and other diseases of the respiratory system.
- Compensation for chronic diseases that reduce general and local immunity.
- See a doctor early if symptoms of the disease appear.
- Sanitation of foci of infection (chronic tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis).
Diagnostics
Purulent accumulations located near the surface of the skin are easily diagnosed during an external examination based on characteristic signs. A throat abscess is detected during examination by an otolaryngologist.
Diagnosis of an abscess located deep inside requires special laboratory and instrumental studies:
- a biochemical blood test will show the inflammatory process in the body with an increased content of leukocytes and ESR, as well as shifts in protein fractions;
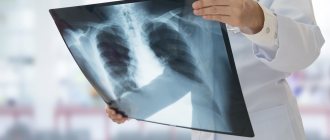
- radiography is used to detect subdiaphragmatic, intraosseous and pulmonary collections;
- Ultrasound is aimed at identifying accumulations in the abdominal cavity and liver;
- computed tomography, as an auxiliary method, detects purulent accumulations in the brain, lungs and liver, subdiaphragmatic region and inside bones and joints;
- encephalography of various forms (echo-, electro-, pneumo-) is aimed at studying the brain;
- laparoscopy and angihepatography are used as an auxiliary method for examining the liver;
- puncture of the abscess and culture of its contents are performed to determine the specific type of pathogen and its sensitivity to certain antibacterial drugs.
Most often, purulent accumulations are caused by streptococci, staphylococci in combination with various kinds of bacilli, but now other aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are also becoming widespread.
1.General information
According to the definition, an abscess is a local acute infectious and inflammatory process with the formation of a sealed infiltration cavity. An obligatory characteristic feature of an abscess, in contrast to, say, a cyst, is that the capsule surrounded by a granulation membrane is filled with pus, i.e. remnants of disintegrated (as they say in medicine, “melted”) tissue and waste products of a pathogenic pathogen. Before opening the abscess, a certain pressure is created in the capsule, mechanically bursting the surrounding healthy tissue, which causes pain, expressed to varying degrees (depending on the location and innervation of the area by nerve endings).
It is obvious that an abscess, for example, on the forearm and an abscess in the lungs are significantly different clinical situations. Suppuration in an open area of skin can also be quite painful and even dangerous - in terms of further spread of the infectious process - however, such an area still has direct access for therapeutic manipulations and, if necessary, for safe antiseptic microsurgical opening. An abscess in the pulmonary parenchyma (the main functional tissue of the respiratory organs) has, of course, its own etiopathogenetic and clinical specificity, representing a much more serious danger.
A must read! Help with hospitalization and treatment!
Treatment
The key to successful treatment of an abscess lies in its timely detection. This is why it is so important to immediately consult a doctor if you have any symptoms.
Treatment principles:
- Only superficial purulent accumulations can be treated at home under the supervision of a doctor. All other cases require hospitalization;
- opening and drainage of the area of purulent accumulation is carried out by a surgeon; it is necessary to remove the abscess;
- drug therapy is based on taking the following drugs: antibacterial agents, antipyretics, painkillers, drugs to reduce intoxication, vitamin complexes, immunomodulators and others;
- balanced nutrition, gentle bed or semi-bed rest, and rest;
- physical therapy, physiotherapy and sanatorium-resort treatment are possible as rehabilitation measures during the recovery stage.
Special ointments are used as adjuncts in the treatment of subcutaneous fatty suppuration.
Purulent accumulations in the lungs are initially treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, and after receiving the results of culture culture studies, adjustments are made to the medications taken. In severe cases, bronchoalveolar lavage may be performed. If there is no positive effect of classical therapy, an abscess operation is forced to remove the affected part of the organ.
Treatment of purulent accumulations in the brain is carried out using surgical methods. Contraindications for removal of accumulations, namely the location in the deep parts of the brain, necessitates washing out the purulent contents by puncture. Treatment of purulent accumulations at home using traditional medicine is unacceptable.
Patient prognosis
A favorable course of the disease is accompanied by complete cleansing of the cavity from purulent exudate and resorption of the infiltrate. Over time, the serous membrane loses its rounded outline, and then completely ceases to be visible on x-rays. On average, complete recovery occurs in 2.5-3 months.
With timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable
Unfortunately, there are no methods for specific prevention of pathology. The likelihood of its development can be reduced by promptly treating bronchitis and pneumonia, fighting foci of chronic infection, and avoiding foreign bodies and liquids entering the respiratory tract. The fight against alcoholism can also be considered an important aspect in reducing the incidence rate.